Market Overview:
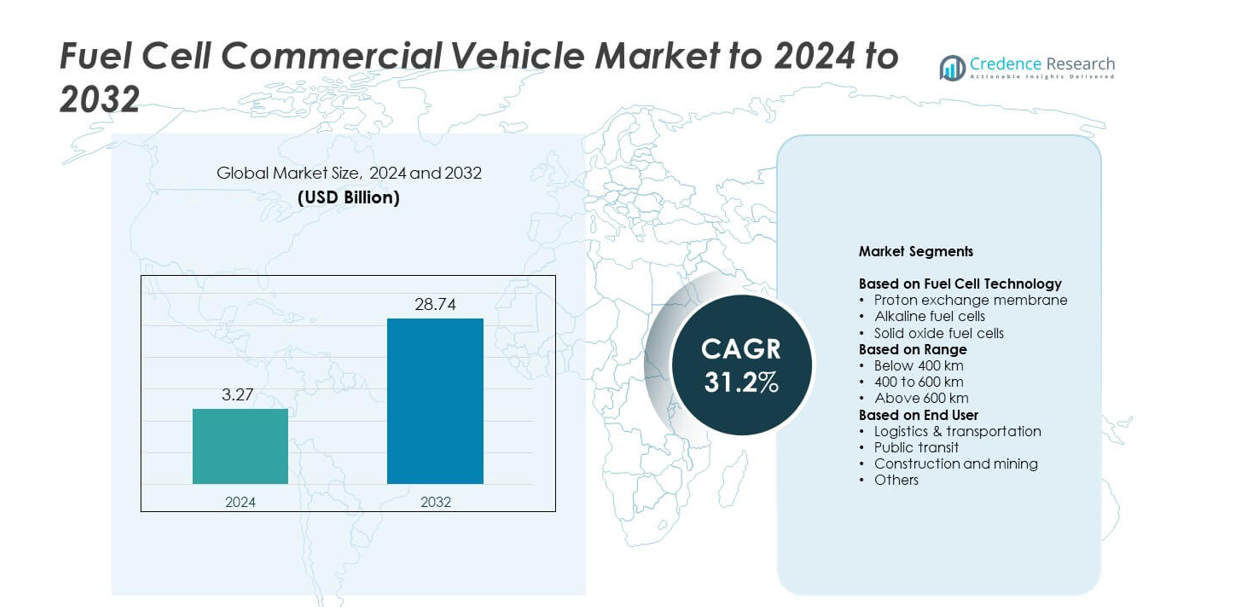
Fuel Cell Commercial Vehicle Market size was valued at USD 3.27 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 28.74 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 31.2% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Fuel Cell Commercial Vehicle Market Size 2024 |
USD 3.27 billion |
| Fuel Cell Commercial Vehicle Market, CAGR |
31.2% |
| Fuel Cell Commercial Vehicle Market Size 2032 |
USD 28.74 billion |
The Fuel Cell Commercial Vehicle Market features strong participation from global manufacturers that focus on advanced fuel cell platforms, long-range capability, and integration with expanding hydrogen corridors. Competition centers on improving stack durability, reducing operating cost, and scaling production for heavy-duty trucks, buses, and logistics fleets. Companies accelerate adoption through partnerships with energy providers and pilot programs across freight and municipal transport. Asia Pacific leads the market with a 24% share, supported by national hydrogen roadmaps and large deployment programs, while North America follows with a 38% share driven by corridor development and fleet electrification. Europe maintains a 32% share due to strict emission rules and coordinated hydrogen infrastructure expansion.
Market Insights
- The Fuel Cell Commercial Vehicle Market was valued at 3.27 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach 28.74 billion by 2032 at a 31.2% CAGR.
- Growth strengthens as logistics and transit operators adopt zero-emission fleets, with the proton exchange membrane segment leading at 64% due to high power density and fast refueling.
- Major trends include expansion of hydrogen refueling corridors, wider use of long-haul fuel cell trucks, and rising investment in green hydrogen to support sustainable commercial mobility.
- Competition increases as manufacturers enhance stack efficiency, reduce operating cost, and partner with hydrogen producers and fleet operators to accelerate large-scale deployment.
- Regionally, North America leads with 38% share, Europe holds 32%, and Asia Pacific accounts for 24%, while the below-400 km range segment dominates with 52% due to strong adoption in urban logistics and short-distance freight.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Fuel Cell Technology
The proton exchange membrane segment leads the Fuel Cell Commercial Vehicle Market with a 64% share due to its fast start-up ability, high power density, and strong suitability for heavy commercial fleets. Transport operators choose this technology because it supports quick refueling and stable performance in varied climates. Growing investment in hydrogen hubs also accelerates adoption across long-haul trucks and buses. Alkaline and solid oxide systems expand more slowly because they require higher temperatures or complex integration, which limits large-scale commercial deployment.
- For instance, the Toyota second-generation Mirai features a fuel cell stack (model code FCB130) with a maximum output of 128 kW (172 bhp).
By Range
The below 400 km segment dominates the market with a 52% share, supported by strong use in urban delivery, municipal fleets, and short-haul transport. Operators prefer this range because it offers efficient routing, lower operational cost, and easy access to existing hydrogen stations in city networks. Rising e-commerce growth further boosts demand for short-range fuel cell vans and trucks. The 400 to 600 km and above 600 km segments grow steadily but serve mainly regional freight and long-distance haulage needs.
- For instance, Van Hool’s A330 fuel cell electric bus offers a range of 350–400 km between refuelings, matching typical urban and regional transit duty cycles.
By End User
Logistics and transportation hold the largest share at 57% in the Fuel Cell Commercial Vehicle Market due to rising demand for zero-emission freight movement. Fleet owners value fuel cell vehicles for their long driving ability, high payload support, and rapid refueling time. Expansion of hydrogen corridors near warehouses and industrial hubs also drives wider adoption. Public transit, construction, and mining applications grow at a moderate pace but remain smaller contributors compared to freight-focused operations.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Demand for Zero-Emission Commercial Fleets
The Fuel Cell Commercial Vehicle Market grows strongly as governments and fleet operators push for cleaner transport options to meet strict emission rules. Hydrogen vehicles attract interest because they support long driving distances, fast refueling, and high payload capacity, which suits logistics and transit fleets. Many countries expand hydrogen corridors, which helps operators shift from diesel to fuel cell trucks and buses. This transition strengthens long-term fleet decarbonization goals and supports wider adoption across freight, municipal, and regional transport applications.
- For instance, Volvo Trucks’ hydrogen fuel cell electric prototypes are designed for ranges of up to 1,000 km, giving performance comparable to long-haul diesel trucks used in heavy commercial operations.
Expansion of Hydrogen Refueling Infrastructure
Growth accelerates as public and private organizations invest in new hydrogen refueling stations across highways, industrial hubs, and metro regions. This expansion reduces operational barriers and supports daily fleet use for trucking, last-mile delivery, and public transit. Large-scale infrastructure programs across Asia, Europe, and North America also improve fuel availability, enabling commercial operators to adopt hydrogen vehicles with lower risk. Better fueling access enhances route planning and increases confidence among logistics and transit companies.
- For instance, Air Liquide’s modular hydrogen stations are designed with capacities from 300 to 1,200 kilograms of hydrogen per day, enabling continuous refueling of commercial fleets at logistics and highway hubs.
Advancements in Fuel Cell Efficiency and Durability
Rapid improvements in stack durability, power density, and cold-start performance strengthen adoption across heavy-duty use cases. Newer systems support longer operating hours and lower maintenance needs, which benefit long-haul trucking and continuous industrial operations. Better hydrogen storage designs also extend driving range while keeping vehicle weight manageable. These advancements reduce lifetime operating cost and help fleets transition toward fuel cell platforms as a reliable alternative to diesel for intense commercial workloads.
Key Trends and Opportunities
Growth of Heavy-Duty Hydrogen Trucks and Buses
A major trend is the rising deployment of heavy-duty hydrogen trucks and buses for regional haulage and urban transit. Operators value the longer range and faster refueling compared to battery-electric alternatives. Governments support pilot projects for cross-border trucking corridors and high-capacity bus networks, creating long-term opportunity for fleet-scale adoption. This expansion opens demand for components such as stacks, storage tanks, and high-pressure systems, encouraging broader investment across the supply chain.
- For instance, Hyundai’s XCIENT Fuel Cell truck provides a driving range of around 400 km per refueling and can be refueled in about 8–20 minutes, making it suitable for heavy-duty commercial routes.
Integration of Fuel Cell Systems with Renewable Hydrogen
A key opportunity emerges as many regions scale green hydrogen production using renewable energy. This alignment supports true zero-carbon mobility and makes hydrogen fleets more sustainable. Partnerships between energy producers, truck makers, and fleet operators help establish cohesive hydrogen ecosystems. As fuel cost decreases and production expands, more commercial fleets view hydrogen vehicles as a long-term alternative to diesel, boosting adoption across logistics, transit, and industrial transport sectors.
- For instance, Siemens Energy’s Silyzer 300 technology is used in an electrolysis plant that produces up to 1,200 cubic meters of green hydrogen per hour, supplying low-carbon hydrogen for industrial and mobility applications.
Rising Focus on Modular and Scalable Vehicle Platforms
Manufacturers increasingly develop modular platforms that support multiple vehicle types, such as vans, mid-duty trucks, and heavy-duty tractors. This trend cuts production cost and accelerates development cycles. Fleet operators benefit because they can scale hydrogen adoption across different duty profiles with unified maintenance and fueling patterns. This modular shift strengthens market flexibility and encourages wider uptake across both short-range and long-haul applications.
Key Challenges
High Upfront Cost of Fuel Cell Vehicles and Components
One major challenge is the high acquisition cost of fuel cell trucks, buses, and power systems. Prices remain above diesel equivalents due to costly materials, complex manufacturing, and limited production scale. Many smaller operators hesitate to shift fleets without financial support or long-term incentives. These high capital costs slow adoption in cost-sensitive markets and delay large fleet conversions, even though operational benefits improve over time.
Limited Hydrogen Production and Supply Chain Maturity
Another challenge is the limited availability of hydrogen, especially green hydrogen, which restricts widespread commercial use. Production capacity remains uneven across regions, and supply chains often lack the reliability needed for daily fleet operations. Transporting and storing hydrogen also creates logistical complexity. These gaps slow infrastructure deployment and influence fleet operators’ confidence in long-term availability, which affects adoption momentum across logistics, transit, and industrial sectors.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds a 38% share in the Fuel Cell Commercial Vehicle Market, supported by strong adoption across freight transport, public transit, and municipal services. The United States leads with expanding hydrogen corridors for long-haul trucking and dedicated funding for clean fleet transitions. Canada strengthens uptake through zero-emission vehicle mandates and investments in hydrogen hubs near industrial zones. Wider availability of refueling stations and large-scale pilot programs encourage commercial operators to shift from diesel toward hydrogen-powered fleets, driving sustained growth across regional and long-distance transport routes.
Europe
Europe accounts for a 32% share, driven by strict emission requirements and coordinated hydrogen mobility programs across major economies. Germany, France, the Netherlands, and Nordic countries advance adoption through subsidies, large fleet trials, and integrated hydrogen ecosystems. Public transit agencies deploy fuel cell buses at scale, while logistics operators test hydrogen trucks along cross-border freight corridors. Rapid expansion of green hydrogen production improves supply stability and supports broader adoption across freight, municipal transport, and long-haul applications, keeping Europe at the forefront of zero-emission commercial mobility.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific holds a 24% share, led by strong government-backed hydrogen strategies in China, Japan, and South Korea. China deploys fuel cell trucks and buses across port zones and industrial regions supported by provincial incentives. Japan expands its hydrogen refueling network under its national roadmap, and South Korea accelerates commercial fleet adoption through large-scale clean transport programs. Increasing manufacturing capacity for fuel cell components and integrated hydrogen value chains strengthens adoption across logistics, public transit, and heavy industry, positioning the region for long-term leadership.
Middle East and Africa
Middle East and Africa account for a 4% share, driven by early commercial adoption in energy-focused economies. The United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia develop hydrogen hubs that support fuel cell trucks for port logistics, industrial transport, and planned smart city projects. South Africa explores hydrogen mobility to support mining and freight operations. Although deployment is limited, rising investment in hydrogen production and clean transport frameworks positions the region as an emerging growth zone for future fleet electrification.
Latin America
Latin America holds a 2% share, with uptake centered on pilot programs across Chile, Brazil, and Argentina. Chile leads hydrogen initiatives through large renewable-energy-based production projects and early trials of fuel cell trucks in mining corridors. Brazil expands interest in hydrogen mobility for heavy-duty transport in urban and industrial regions. Limited refueling infrastructure slows adoption, but strong renewable resources and national hydrogen roadmaps create long-term potential for commercial fleet transition. Growing focus on clean transport policies supports gradual market development across the region.
Market Segmentations:
By Fuel Cell Technology
- Proton exchange membrane
- Alkaline fuel cells
- Solid oxide fuel cells
By Range
- Below 400 km
- 400 to 600 km
- Above 600 km
By End User
- Logistics & transportation
- Public transit
- Construction and mining
- Others
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
Toyota, Volvo, Foton Motor, Hyundai Motor, PACCAR, Scania, and Nikola shape the competitive landscape of the Fuel Cell Commercial Vehicle Market through expanding fuel cell portfolios and strategic partnerships. Companies focus on developing advanced powertrains, higher-density hydrogen storage, and durable fuel cell stacks suited for long-haul and regional freight operations. Many manufacturers strengthen supply chains by collaborating with hydrogen producers, infrastructure developers, and component suppliers to ensure stable fuel availability. Competitive activity also increases through pilot deployments with logistics fleets, public transit agencies, and industrial operators across key regions. Firms invest in modular platforms that support multiple commercial vehicle classes, enabling faster scaling and lower production cost. Continuous innovation in thermal management, stack efficiency, and integration with digital fleet systems further intensifies competition as manufacturers target larger fleet contracts and long-term decarbonization programs.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
Recent Developments
- In 2025, Toyota announced its all-new 3rd Generation Fuel Cell (FC) System designed specifically for commercial vehicles, improving fuel efficiency by 20% and doubling system durability.
- In 2025, Hyundai unveiled a new XCIENT Class-8 fuel-cell truck with 180 kW power and a 450-mile range, alongside plans for launching the HTWO Energy Savannah hydrogen refueling station in late 2025
- In 2025, Scania delivered a prototype hydrogen fuel cell electric vehicle (6×2 tractor unit) to Explore Transport in the UK for real-world testing as part of the HyHAUL consortium and the UK’s Zero Emission HGV Infrastructure Demonstrator Programme.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Fuel Cell Technology, Range, End-User and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market will expand as more fleet operators shift to zero-emission trucks and buses.
- Hydrogen refueling corridors will grow across major freight routes, supporting wider adoption.
- Advancements in fuel cell durability and efficiency will reduce long-term operating cost.
- Governments will introduce stronger incentives to accelerate commercial fleet transition.
- Heavy-duty fuel cell trucks will gain traction in long-haul logistics and regional transport.
- Green hydrogen production will increase, strengthening the sustainability of fuel cell fleets.
- More OEMs will launch modular fuel cell platforms for trucks, vans, and buses.
- Integration with digital fleet management systems will improve operational uptime.
- Strategic partnerships will rise among energy firms, vehicle manufacturers, and logistics companies.
- Emerging economies will adopt fuel cell vehicles through pilot programs and hydrogen development plans.




