Market Overview
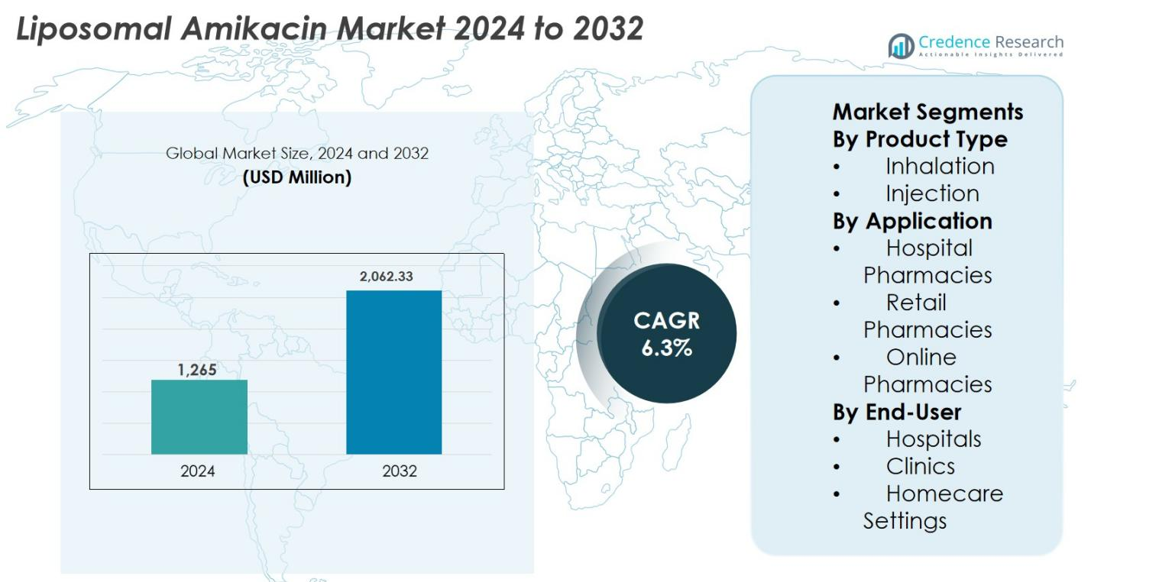
The Liposomal Amikacin market size was valued at USD 1,265 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 2,062.33 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 6.3% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Liposomal Amikacin Market Size 2024 |
USD 1,265 million |
| Liposomal Amikacin Market, CAGR |
6.3% |
| Liposomal Amikacin Market Size 2032 |
USD 2,062.33 million |
Liposomal Amikacin market is characterized by the presence of established global pharmaceutical companies focusing on advanced anti-infective and respiratory therapies. Key players such as Gilead Sciences, Inc., Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Cipla Limited, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Mylan N.V., Pfizer Inc., Novartis AG, Sanofi S.A., Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, and AstraZeneca plc strengthen the market through formulation innovation, regulatory expertise, and global distribution capabilities. These companies emphasize inhalation-based drug delivery, clinical differentiation, and expansion across developed and emerging markets. Regionally, North America leads the Liposomal Amikacin market with an exact market share of 42.6%, supported by strong healthcare infrastructure, early adoption of advanced inhaled therapies, and high diagnosis rates of drug-resistant respiratory infections, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific.
Market Insights
- Liposomal Amikacin market was valued at USD 1,265 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 2,062.33 million by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 6.3% during the forecast period.
- Market growth is driven by the rising prevalence of drug-resistant respiratory infections, increasing adoption of targeted inhalation therapies, and growing demand for safer antibiotics with reduced systemic toxicity.
- Ongoing trends include advancements in liposomal drug delivery systems, increased use of portable nebulizers, and a shift toward outpatient and home-based inhalation therapy models supporting long-term treatment adherence.
- The market shows moderate concentration, with leading pharmaceutical companies focusing on formulation innovation, global commercialization strategies, and expansion into emerging markets to strengthen their positioning.
- North America leads with 42.6% share, followed by Europe at 28.4% and Asia-Pacific at 20.8%, while inhalation formulations dominate the product segment with approximately 64.2% share due to superior pulmonary targeting.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Product Type
The Liposomal Amikacin market by product type is led by the inhalation segment, accounting for approximately 64.2% market share in 2024. Inhalation dominates due to its targeted drug delivery to the lungs, improved bioavailability, and reduced systemic toxicity, making it highly effective for treating chronic and drug-resistant pulmonary infections such as nontuberculous mycobacterial lung disease. The growing preference for patient-friendly, non-invasive administration and strong clinical outcomes supports adoption. Meanwhile, injectable formulations maintain relevance in acute care settings but face slower growth due to higher toxicity risks and inpatient dependency.
- For instance, ARIKAYCE (amikacin liposome inhalation suspension) is administered once daily via the Lamira® Nebulizer System at a 590 mg/8.4 mL dose and was approved by the U.S. FDA specifically for refractory Mycobacterium avium complex lung disease, reflecting strong clinical utility in difficult-to-treat pulmonary infections.
By Application
Based on application, hospital pharmacies held the dominant share of around 58.7% in 2024 within the Liposomal Amikacin market. This leadership is driven by the hospital-centric nature of severe respiratory infections requiring specialist oversight, controlled administration, and reimbursement support. Hospital pharmacies benefit from established procurement contracts, availability of trained healthcare professionals, and higher diagnosis rates of complex infections. Retail pharmacies account for a moderate share, supported by discharge prescriptions, while online pharmacies remain nascent but are gradually expanding due to rising digital health adoption and chronic disease management models.
- For instance, reimbursement for specialty anti-infective therapies is frequently processed through hospital billing and pharmacy systems, particularly during inpatient care or structured outpatient hospital programs, limiting early access through retail and online pharmacies.
By End-User
Among end users, hospitals emerged as the leading sub-segment with nearly 61.9% market share in 2024 in the Liposomal Amikacin market. Hospitals dominate due to their role in diagnosing and managing severe, drug-resistant infections that require advanced inhalation therapies and close monitoring. High patient inflow, access to specialized pulmonology care, and integration with hospital pharmacy services drive utilization. Clinics represent a growing segment as outpatient respiratory care expands, while homecare settings gain traction with increased emphasis on long-term therapy, portable inhalation devices, and patient convenience.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Burden of Drug-Resistant Respiratory Infections
The Liposomal Amikacin market is significantly driven by the rising prevalence of drug-resistant respiratory infections, particularly nontuberculous mycobacterial lung disease and multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. Conventional aminoglycosides often show limited pulmonary penetration and are associated with systemic toxicities such as nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity. Liposomal Amikacin overcomes these limitations by delivering high drug concentrations directly to the lungs while minimizing systemic exposure. Increasing awareness among pulmonologists and infectious disease specialists regarding improved clinical outcomes supports adoption. Additionally, aging populations, higher survival rates among immunocompromised patients, and growing chronic lung disease incidence increase susceptibility to persistent infections, creating sustained demand for targeted inhaled antibiotic therapies.
- For instance, clinical studies have shown that inhaled liposomal amikacin achieves sustained amikacin concentrations in lung tissue while maintaining low plasma levels, supporting reduced nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity compared with systemic aminoglycoside therapy.
Advancements in Liposomal Drug Delivery Technologies
Continuous advancements in liposomal drug delivery technologies strongly support the growth of the Liposomal Amikacin market. Innovations in liposome stability, particle size optimization, and sustained-release formulations enhance lung deposition and therapeutic consistency. Improved nebulization systems ensure accurate dosing, better patient compliance, and reduced treatment variability. Manufacturers are investing in formulation scalability, shelf-life extension, and manufacturing efficiency to support broader commercialization. These technological improvements strengthen regulatory acceptance by demonstrating superior pharmacokinetic and safety profiles compared to conventional formulations. As respiratory drug delivery science evolves, liposomal platforms increasingly integrate into precision medicine approaches, reinforcing Liposomal Amikacin’s role in managing complex and resistant pulmonary infections.
- For instance, vibrating mesh nebulizer systems are specifically designed and validated for liposomal formulations, delivering consistent aerosol output and minimizing shear stress that could destabilize liposomes, thereby improving dosing accuracy and patient adherence.
Expansion of Healthcare Infrastructure and Specialty Care Access
Expanding healthcare infrastructure and improved access to specialty respiratory care are key growth drivers for the Liposomal Amikacin market. Increased availability of advanced diagnostic tools enables earlier and more accurate detection of resistant pulmonary infections. Hospitals and specialty clinics are expanding inhalation therapy capabilities, supported by trained healthcare professionals and standardized treatment protocols. Favorable reimbursement structures in developed regions and gradual insurance penetration in emerging economies enhance treatment affordability. Global initiatives targeting antimicrobial resistance further encourage adoption of advanced therapies. These improvements collectively increase patient access, support appropriate utilization, and strengthen long-term demand for Liposomal Amikacin across diverse healthcare settings.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Shift Toward Outpatient and Home-Based Inhalation Therapy
A major trend shaping the Liposomal Amikacin market is the shift toward outpatient and home-based inhalation therapy. Advances in portable nebulizers, simplified administration protocols, and patient education enable long-term treatment outside hospital environments. This transition reduces hospitalization costs, alleviates inpatient capacity constraints, and improves patient quality of life. Home-based therapy is particularly beneficial for chronic infections requiring prolonged treatment durations. Healthcare systems increasingly favor decentralized care models to improve efficiency. Manufacturers can capitalize on this trend by developing user-friendly delivery devices, patient support services, and digital adherence tools, expanding market penetration beyond traditional hospital-centric treatment models.
- For instance, home-based inhalation programs are increasingly supported by follow-up monitoring and adherence education, reducing hospitalization burden while sustaining long-term therapy for patients with persistent and recurrent pulmonary infections.
Pipeline Expansion and Label-Expansion Opportunities
Pipeline development and potential label expansions present significant opportunities in the Liposomal Amikacin market. Ongoing clinical studies exploring broader respiratory indications, combination regimens, and earlier-line therapy use may substantially expand the addressable patient population. Research into optimized dosing strategies and long-term safety profiles further supports wider clinical acceptance. Strategic collaborations between pharmaceutical companies, research institutions, and healthcare providers accelerate innovation and evidence generation. As real-world data accumulates, physician confidence in expanded use increases. Successful label expansions could unlock new therapeutic segments, driving sustained revenue growth and reinforcing the long-term commercial potential of Liposomal Amikacin.
- For instance, ongoing real-world evidence programs are collecting long-term safety and adherence data in outpatient and home-based settings, helping clinicians better understand tolerability and sustained use beyond controlled trial environments.
Key Challenges
High Treatment Costs and Limited Market Accessibility
High treatment costs remain a major challenge for the Liposomal Amikacin market. Complex manufacturing processes, stringent quality controls, and specialized inhalation delivery systems contribute to premium pricing. In cost-sensitive regions, limited reimbursement coverage and high out-of-pocket expenses restrict patient access. Healthcare providers often reserve Liposomal Amikacin for severe or refractory cases, limiting treatment volumes. Budget constraints within public healthcare systems further slow adoption. Addressing affordability through pricing strategies, reimbursement expansion, and long-term potential for generic or biosimilar alternatives will be critical to improving accessibility and supporting broader global market penetration.
Regulatory Complexity and Clinical Adoption Barriers
Regulatory complexity and cautious clinical adoption present additional challenges for the Liposomal Amikacin market. Liposomal formulations require extensive clinical validation to demonstrate long-term safety, efficacy, and compatibility with delivery devices. Regulatory approval timelines can be lengthy, increasing development costs and delaying market entry. Additionally, some clinicians remain conservative in prescribing due to limited real-world evidence and familiarity with inhaled liposomal antibiotics. Overcoming these barriers requires robust clinical trials, post-marketing surveillance, and targeted education initiatives. Strengthening physician confidence and streamlining regulatory pathways are essential for sustained adoption and market growth.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America dominates the Liposomal Amikacin market with an 42.6% market share in 2024, supported by high diagnosis rates of nontuberculous mycobacterial lung disease and strong adoption of advanced inhalation therapies. The region benefits from well-established healthcare infrastructure, early access to innovative drug delivery technologies, and favorable reimbursement frameworks. The United States leads regional demand due to higher awareness among pulmonologists, robust clinical research activity, and strong presence of key pharmaceutical players. Continued focus on antimicrobial resistance management and outpatient inhalation therapy models further sustains North America’s leading position.
Europe
Europe accounted for 28.4% of the Liposomal Amikacin market share in 2024, driven by rising prevalence of chronic respiratory infections and supportive regulatory frameworks for advanced drug delivery systems. Countries such as Germany, France, and the UK lead regional adoption due to strong healthcare systems and growing use of inhaled antibiotics in specialty care. Increasing government focus on antimicrobial stewardship and hospital-based respiratory care supports demand. Additionally, expanding access to specialty pulmonology services and gradual uptake of home-based inhalation therapy contribute to steady market growth across Western and Northern Europe.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific represented 20.8% market share in 2024 and is the fastest-growing region in the Liposomal Amikacin market. Growth is driven by large patient populations, increasing incidence of respiratory infections, and improving diagnostic capabilities. Countries such as China, Japan, and India are witnessing rising adoption of advanced inhaled therapies as healthcare infrastructure expands. Government initiatives to combat antimicrobial resistance, growing healthcare spending, and increased awareness among clinicians support market expansion. While access and affordability challenges remain in some markets, improving reimbursement and hospital capacity are strengthening regional demand.
Latin America
Latin America held an 5.1% share of the Liposomal Amikacin market in 2024, supported by gradual improvements in healthcare infrastructure and increasing recognition of drug-resistant respiratory infections. Brazil and Mexico lead regional demand due to higher urbanization, expanding hospital networks, and improved access to specialty care. Adoption remains concentrated in tertiary hospitals where advanced inhalation therapies are available. However, limited reimbursement coverage and budget constraints restrict widespread uptake. Ongoing healthcare modernization efforts and rising investment in respiratory disease management are expected to support moderate growth across the region.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa accounted for 3.1% of the Liposomal Amikacin market share in 2024. Growth is primarily driven by increasing investments in healthcare infrastructure in the Gulf Cooperation Council countries and rising awareness of complex respiratory infections. Advanced therapies are mainly utilized in large hospitals and specialty centers, particularly in Saudi Arabia and the UAE. In Africa, limited access, high treatment costs, and diagnostic gaps constrain adoption. However, gradual expansion of specialty care facilities and international health initiatives targeting infectious diseases support long-term growth potential.
Market Segmentations:
By Product Type
By Application
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
By End-User
- Hospitals
- Clinics
- Homecare Settings
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The Liposomal Amikacin market features a moderately concentrated competitive landscape characterized by the presence of established pharmaceutical companies and select specialty drug developers focused on advanced respiratory therapies. Key players such as Gilead Sciences, Inc., Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Cipla Limited, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Mylan N.V., Pfizer Inc., Novartis AG, Sanofi S.A., Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, and AstraZeneca plc compete through product differentiation, regulatory approvals, and strategic commercialization initiatives. Companies emphasize investment in liposomal drug delivery technologies, inhalation platforms, and clinical evidence generation to strengthen market positioning. Strategic collaborations, licensing agreements, and regional expansion remain common approaches to enhance global reach. Market participants also focus on improving manufacturing capabilities and ensuring regulatory compliance to support consistent supply. As demand for targeted pulmonary therapies grows, competition increasingly centers on innovation, pricing strategies, and expansion into emerging healthcare markets.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- AstraZeneca plc
- Cipla Limited
- Sanofi S.A.
- Gilead Sciences, Inc.
- Pfizer Inc.
- Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
- Mylan N.V.
- Novartis AG
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
- Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
Recent Developments
- In October 2025, Insmed raised its full-year 2025 global ARIKAYCE® revenue guidance to a range of USD 420 million-430 million, signaling robust market performance and broader adoption of liposomal amikacin therapy globally.
- In January 2025, Insmed Incorporated provided a business update at the 43rd Annual J.P. Morgan Healthcare Conference, highlighting ongoing global commercialization and regulatory positioning of ARIKAYCE® (amikacin liposome inhalation suspension) across the U.S., Europe, and Japan, delivered via the Lamira® Nebulizer System developed with PARI Pharma GmbH
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Product Type, Application, End-User and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The Liposomal Amikacin market is expected to benefit from continued growth in the diagnosis and treatment of drug-resistant respiratory infections.
- Advancements in liposomal formulation and inhalation device technologies will improve therapeutic efficiency and patient adherence.
- Expansion of outpatient and home-based inhalation therapy will support wider adoption beyond hospital settings.
- Increasing clinical awareness and specialist training will strengthen prescribing confidence across regions.
- Ongoing clinical trials may enable label expansions into additional respiratory indications.
- Growing focus on antimicrobial resistance management will support long-term demand for targeted antibiotics.
- Emerging markets will contribute incremental growth as healthcare infrastructure and access to specialty care improve.
- Strategic collaborations and licensing agreements will accelerate global market penetration.
- Enhanced real-world evidence generation will support broader clinical acceptance and guideline inclusion.
- Manufacturing optimization and supply chain resilience will improve availability and support sustained market expansion.




