Market Overview
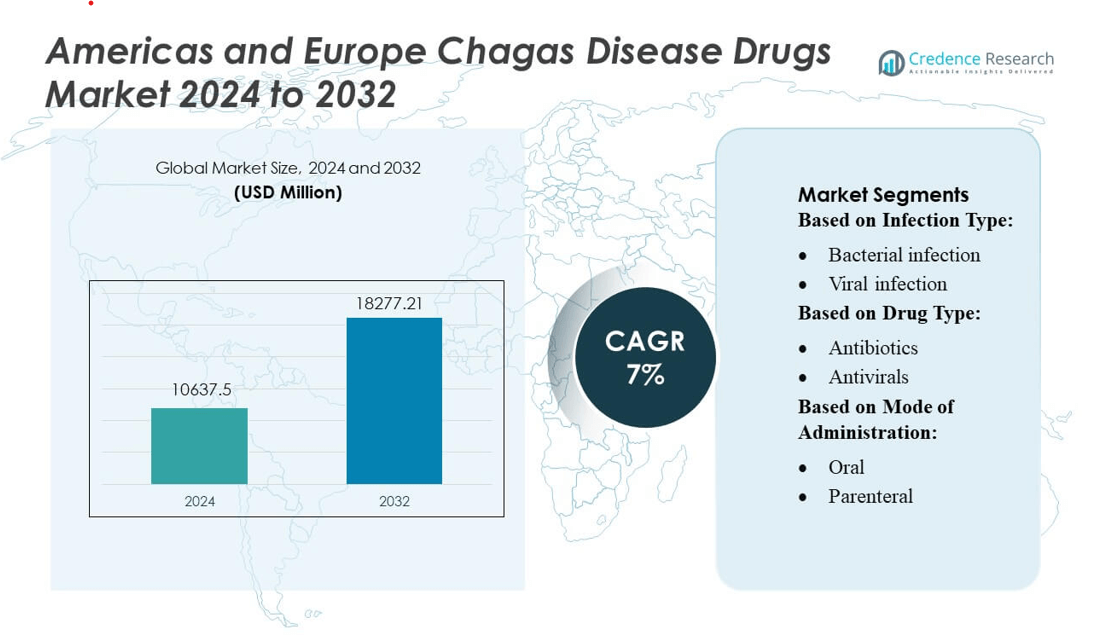
Americas and Europe Chagas Disease Drugs Market size was valued USD 10637.5 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 18277.21 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 7% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Americas and Europe Chagas Disease Drugs Market Size 2024 |
USD 10637.5 million |
| Americas and Europe Chagas Disease Drugs Market, CAGR |
7% |
| Americas and Europe Chagas Disease Drugs Market Size 2032 |
USD 18277.21 million |
The Americas and Europe Chagas Disease Drugs Market is shaped by a mix of multinational pharmaceutical manufacturers and emerging biotech firms that focus on antiparasitic therapies, improved formulations, and patient-access programs. These companies compete through R&D investment, strategic partnerships with health agencies, and optimization of treatment delivery for both acute and chronic stages of the disease. Latin America remains the leading region, accounting for approximately 60% of the total market due to its high disease burden, large treatment-seeking population, and strong government-supported screening initiatives. In contrast, North America and Europe show steady but smaller growth driven by increased detection of imported cases and enhanced diagnostic infrastructure.
Market Insights
- The Americas and Europe Chagas Disease Drugs Market was valued at USD 10,637.5 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 18,277.21 million by 2032, registering a 7% CAGR during the forecast period.
- Market growth is driven by rising screening programs, improved diagnostics, and expanding access to antiparasitic therapies for both acute and chronic conditions.
- Key trends include increasing R&D investment, development of improved drug formulations, and broader public–private collaborations to enhance treatment availability across high-burden communities.
- Competitive activity intensifies as pharmaceutical and biotech firms strengthen partnerships with healthcare agencies, though challenges persist due to limited treatment options, slow diagnosis in non-endemic regions, and variability in healthcare access.
- Latin America leads the regional landscape with 60% market share, followed by North America and Europe with steady growth; antiparasitic drugs remain the dominant segment, accounting for the majority share due to their essential role in first-line treatment.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Infection Type
Parasitic infection remains the dominant infection-type segment, accounting for an estimated 72–75% of the market, driven by the high prevalence of Trypanosoma cruzi in Latin America and the growing detection of imported cases across Europe. Demand rises as governments expand screening of blood banks, pregnant women, and migrant populations. Increased adoption of molecular diagnostics and wider integration of parasitological testing in primary care settings further strengthen this segment’s share. Rising awareness campaigns and mandatory surveillance programs across the Americas also reinforce the dominance of parasitic infection–driven treatment needs.
- For instance, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Ltd demonstrated its capability in neglected and vector-borne disease R&D through its global Phase 3 dengue vaccine trial, which enrolled more than 20,000 participants across eight endemic countries—showcasing its large-scale clinical infrastructure relevant to antiparasitic research.
By Drug Type
Antiparasitic drugs represent the leading drug-type segment with an approximate 68–72% share, driven by the continued reliance on benznidazole and nifurtimox as first-line treatments for both acute and early chronic Chagas disease. Regulatory support for broader access programs and increasing procurement through public health agencies in Brazil, Argentina, and parts of Southern Europe reinforce demand. Expanding pediatric formulations and ongoing clinical evaluation of optimized dosing regimens enhance therapeutic adoption. Limited alternative pharmacological options and the essential nature of antiparasitic therapy for curative intent further maintain this segment’s leadership.
- For instance, Pfizer’s pipeline included 101 development programs (ranging from Phase 1 through registration) as of November 4, 2025, reflecting its capacity to pursue novel therapeutics. This total comprises 46 programs in Phase 1, 30 in Phase 2, 28 in Phase 3, and 4 under registration.
By Mode of Administration
Oral administration dominates the market with an estimated 80–83% share, supported by the widespread use of orally administered benznidazole and nifurtimox, which remain the standard of care in both the Americas and Europe. High patient compliance, ease of distribution, and suitability for outpatient treatment programs contribute to its strong adoption. Public health initiatives promoting decentralized access to Chagas therapy also favor oral formulations. The lack of parenteral alternatives and the clinical preference for long-term oral dosing regimens further reinforce this segment’s leading position
Key Growth Drivers
Expanded Screening and Early Diagnosis Programs
National health agencies across the Americas and Europe increasingly prioritize early Chagas detection, driving higher treatment demand. Widespread expansion of screening in blood banks, primary care networks, and maternal health programs accelerates case identification. Countries with large migrant populations from endemic regions enhance mandatory testing protocols, significantly improving diagnosis rates. Integration of rapid serological and PCR-based assays in routine workflows enables earlier initiation of therapy. This systematic scale-up of surveillance and screening programs directly increases the volume of patients eligible for antiparasitic treatment.
- For instance, Bristol Myers Squibb has deployed AI-powered computational chemistry and biology platforms, using its in-house models trained on over 3 billion data points to optimize molecular targets — this capacity supports faster development of companion diagnostics and predictive screening tools.
Strengthening Public Health Funding and Access Programs
Government-backed drug procurement programs and partnerships with non-profit health organizations strongly boost treatment accessibility. Subsidized distribution of benznidazole and nifurtimox through national health systems improves affordability for low-income and migrant communities. Funding expansions under neglected tropical disease (NTD) initiatives facilitate large-scale therapeutic coverage, particularly in Brazil, Argentina, Spain, and Italy. International collaborations streamline regulatory approvals and accelerate supply-chain stability. These financial and structural interventions collectively stimulate consistent market growth by ensuring stable demand and broader therapeutic reach.
- For instance, Novartis has launched the first multinational randomized study in chronic Chagas cardiomyopathy, partnering through the Global Chagas Disease Coalition, involving over 25 research sites across Latin America, which supports tailored access-to-medicine programs in lower-income settings.
Rising Burden of Chronic Chagas and Complications
Growing recognition of chronic Chagas disease and its cardiac and gastrointestinal complications increases long-term treatment requirements across both regions. As more patients develop cardiomyopathy or megaesophagus, healthcare systems prioritize earlier antiparasitic intervention to slow disease progression. Improved surveillance identifies previously undiagnosed chronic cases, expanding the eligible treatment pool. Cardiologists and infectious-disease specialists increasingly adopt integrated care pathways, promoting routine antiparasitic therapy for chronic presentations. This rising chronic disease burden sustains market demand, particularly in European countries receiving larger migrant inflows.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Advancements in Drug Formulations and Clinical Research
Ongoing clinical studies targeting improved safety and shorter treatment duration create substantial innovation opportunities. Research programs evaluating reduced-dose benznidazole regimens and combination therapies aim to minimize adverse effects and enhance patient adherence. Pharmaceutical developers explore new molecular candidates and pediatric-friendly oral formulations, addressing unmet needs across age groups. Expanded clinical trial networks in Europe support faster regulatory assessments. These advancements collectively present strong opportunities for differentiated drug offerings and next-generation Chagas therapeutics.
- For instance, Merck presented more than 40 infectious disease pipeline data sets, underscoring its commitment to global health. The company also maintained a broad clinical trial network, leveraging its over 550 million people reached by its medicines and vaccines via access programs.
Increased Digital Health Adoption in Disease Management
Digital platforms and remote monitoring tools create new opportunities for improving treatment adherence and follow-up care. Mobile applications supporting medication reminders, symptom tracking, and virtual consultations help manage long-term therapy, particularly for migrant populations with limited clinic access. Healthcare systems integrate telehealth into NTD management programs, enabling cross-border patient engagement and ongoing physician oversight. These digital innovations enhance continuity of care, reduce treatment discontinuation, and strengthen market potential for chronic disease management support tools.
- For instance, AstraZeneca partnered with Huma to scale a digital-first care model. As of 2023 reports, Huma’s platform supported over 1.8 million active patient users across healthcare and over 650,000 participants in research studies, utilizing a software-as-a-medical-device (SaMD) approach on patients’ own devices rather than deploying over a million proprietary monitoring devices.
Growing Focus on Migrant Health in Non-Endemic Regions
European governments increasingly integrate Chagas screening into migrant health protocols, creating significant opportunities for expanded therapeutic demand. Public health institutions collaborate with NGOs to improve community outreach, awareness, and diagnostic access among Latin American expatriates. As non-endemic countries recognize Chagas as an emerging public health concern, policies supporting early identification and prompt treatment gain traction. This shift in institutional focus drives cross-border market expansion and positions Europe as a fast-growing region for Chagas drug utilization.
Key Challenges
Limited Drug Options and Persistent Safety Concerns
The market relies heavily on only two primary antiparasitic agents, both associated with notable side effects that reduce treatment completion rates. High incidence of dermatologic reactions, gastrointestinal intolerance, and neurological symptoms often leads to therapy discontinuation. The absence of widely approved alternative molecules restricts physician flexibility, particularly for elderly patients or those with comorbidities. Slow progress in the approval of new pharmacological options further constrains market diversification. This therapeutic rigidity remains a major barrier to optimized care and broader adoption.\
Underdiagnosis and Low Awareness in Non-Endemic Areas
Despite expanding screening initiatives, large numbers of cases remain undiagnosed, especially in Europe and North America where awareness among clinicians is limited. Migrant populations often face linguistic, financial, and legal barriers that restrict access to testing and treatment. Primary care providers frequently lack training to recognize Chagas symptoms or evaluate risk exposure, resulting in delayed or missed diagnoses. Underreporting and fragmented surveillance systems weaken patient pathways, directly limiting market penetration of antiparasitic therapies.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds around 15% of the global Chagas disease drugs market, driven mainly by increased detection of imported cases from Latin America. Growing screening programs, better diagnostic tools, and rising awareness among healthcare providers support steady market growth. The U.S. leads the region because of its strong healthcare infrastructure and higher treatment accessibility. Pharmaceutical companies are also increasing research activity to improve drug availability for non-endemic populations. Although patient numbers remain lower than in Latin America, demand is rising due to improved reporting and targeted public-health initiatives.
Asia
Asia holds roughly 7–8% of the global Chagas disease drugs market, reflecting its position as a small but gradually expanding region. The disease is not endemic in most Asian countries, yet globalization, migration, and rising international travel contribute to a slowly growing patient base. Improved healthcare infrastructure and broader focus on neglected tropical diseases strengthen awareness and diagnostic capacity. As governments increase investments in public health and laboratories acquire better testing tools, Asia is expected to show moderate demand growth over the next decade.
Europe
Europe captures around 15% of the global market, primarily fueled by imported Chagas disease cases from Latin American migrants. Spain, Italy, and the United Kingdom remain the main demand centers due to higher screening efforts and stronger public-health awareness. Diagnostic improvements, growing clinician training, and increased monitoring of at-risk populations support market expansion. Although Europe is non-endemic, proactive disease-control policies and integration of Chagas screening into blood-bank and prenatal programs help maintain a stable need for treatment drugs.
Latin America
Latin America dominates the global Chagas disease drugs market with an estimated 60% share, as the region accounts for most of the world’s Chagas cases. Countries such as Brazil, Argentina, Bolivia, and Mexico drive strong demand for benznidazole and nifurtimox due to ongoing endemic transmission. Government-led vector-control programs, active screening efforts, and expanded treatment access support market strength. Public-health agencies and international partners continue to increase funding and awareness campaigns, ensuring consistent need for therapeutic drugs. Rising healthcare investments further reinforce Latin America’s position as the core market.
Middle East
The Middle East accounts for about 3–5% of the global Chagas disease drugs market, reflecting limited disease prevalence but growing public-health preparedness. Most cases stem from imported infections, prompting selective screening in certain high-risk populations. Investments in healthcare modernization, improved laboratory capabilities, and collaboration with international health organizations support gradual market development. While overall demand remains low, increasing awareness and enhanced surveillance systems are helping the region slowly expand access to diagnosis and treatment.
Market Segmentations:
By Infection Type:
- Bacterial infection
- Viral infection
By Drug Type:
By Mode of Administration:
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the Americas and Europe Chagas Disease Drugs Market is shaped by major pharmaceutical leaders such as Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Ltd, Pfizer Inc., Bristol Myers Squibb Company, Novartis AG, Merck & Co. Inc., AstraZeneca, AbbVie Inc., Bayer AG, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., and PTC Therapeutics Inc. The Americas and Europe Chagas Disease Drugs Market is defined by increasing investment in research, improved diagnostic coverage, and strengthening public-health partnerships. Companies operating in this space focus on enhancing drug efficacy, expanding access to treatment, and developing supportive patient-management programs. Competition intensifies as firms accelerate clinical studies, pursue regulatory approvals for optimized formulations, and collaborate with regional health agencies to improve early detection. In the Americas, established healthcare systems and broad screening initiatives support stronger commercial activity, while Europe’s rise in imported cases drives targeted innovation and market expansion. Overall, the market remains highly dynamic, with stakeholders prioritizing innovation, accessibility, and evidence-based treatment strategies.\
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Ltd
- Pfizer, Inc.
- Bristol Myers Squibb Company
- Novartis AG
- Merck & Co. Inc.
- AstraZeneca
- AbbVie Inc.
- Bayer AG
- Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
- PTC Therapeutics Inc.
Recent Developments
- In February 2025, CARB-X (Combating Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Biopharmaceutical Accelerator), announced a new funding round for advancing global efforts to combat infectious diseases, specifically targeting the development of therapeutics for infections caused by gram-negative pathogens and diagnostics for typhoid fever.
- In September 2024, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved arimoclomol (Miplyffa), developed by Zevra Therapeutics, for the treatment of neurological manifestations of Niemann-Pick disease type C (NPC). It is approved for use in combination with another drug, miglustat, in patients aged 2 and older.
- In June 2024, ANI Pharmaceuticals, Inc. signed an agreement to acquire Alimera Sciences, Inc. to foster their rare disease infrastructure and expand business. ILUVIEN and YUTIQ are two commercial products that have significant growth potential in the market.
- In January 2024, Sanofi planned to acquire Inhibrx, Inc. to enhance Sanofi’s rare disease portfolio by addition of best-in-class Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency to pipeline. INBRX-101 is used in the treatment of rare lung infection which will further strengthen company’s position in the market
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Infection Type, Drug Type, Mode of Administration and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market will expand as screening programs improve and more undiagnosed cases are identified across both regions.
- Drug innovation will accelerate as companies invest in safer, faster-acting, and more tolerable treatment options.
- Regulatory agencies will strengthen support for neglected disease therapies, enabling faster approval pathways.
- Public–private partnerships will increase to improve treatment access in underserved communities.
- Research on chronic-stage Chagas treatment will intensify, driving new therapeutic opportunities.
- Migration patterns will continue to influence demand, especially in non-endemic regions of North America and Europe.
- Digital health tools will enhance early detection, patient monitoring, and treatment adherence.
- Awareness campaigns will grow, improving early diagnosis rates and reducing disease progression.
- Pharmaceutical companies will expand collaboration with global health organizations to strengthen supply chains.
- Investments in diagnostic technologies will rise, supporting greater accuracy and broader adoption across healthcare systems.




