Market Overviews
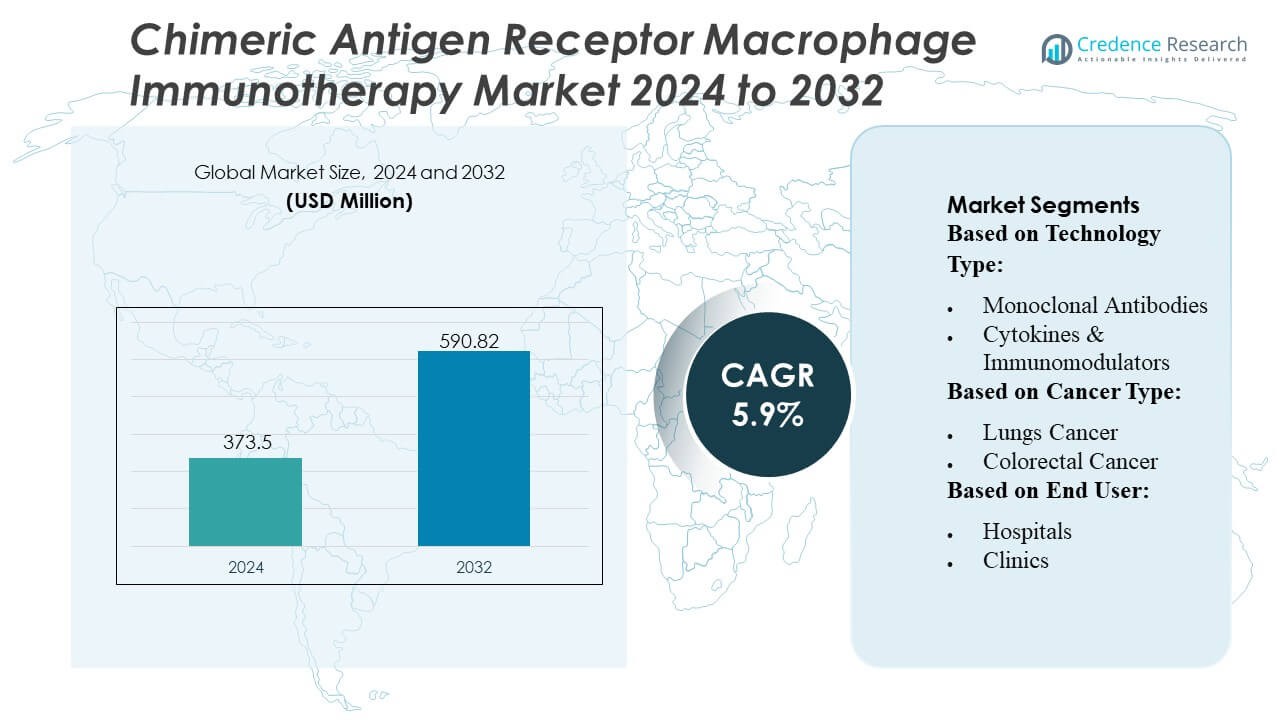
Chimeric Antigen Receptor Macrophage Immunotherapy Market size was valued USD 373.5 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 590.82 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 5.9% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Chimeric Antigen Receptor Macrophage Immunotherapy Market Size 2024 |
USD 373.5 Million |
| Chimeric Antigen Receptor Macrophage Immunotherapy Market, CAGR |
5.9% |
| Chimeric Antigen Receptor Macrophage Immunotherapy Market Size 2032 |
USD 590.82 Million |
The Chimeric Antigen Receptor Macrophage Immunotherapy market is shaped by a mix of established pharmaceutical leaders and specialized cell-therapy innovators that continue to expand their oncology portfolios through engineered macrophage platforms. These companies strengthen competitiveness by accelerating clinical trials, enhancing gene-editing precision, and forming research alliances to improve solid tumor targeting and therapeutic durability. North America remains the leading region with an exact 42% market share, driven by strong R&D infrastructure, early adoption of advanced immunotherapies, and high investment in next-generation cell engineering technologies across major academic centers and biopharmaceutical clusters.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The market reached USD 373.5 million in 2024 and is projected to hit USD 590.82 million by 2032 at a 5.9% CAGR, reflecting steady expansion driven by increasing adoption of engineered macrophage therapies.
- Demand accelerates as CAR-macrophage platforms demonstrate improved solid tumor penetration and immune modulation, strengthening their relevance in lung, breast, and colorectal cancer treatment segments, with solid tumor applications holding the dominant share.
- Market players compete through advancements in gene-editing technologies, expansion of clinical pipelines, and strategic collaborations that enhance therapy durability and manufacturing scalability.
- Growth faces restraints from complex manufacturing processes, high development costs, and limited long-term safety data, which collectively slow broader clinical adoption.
- North America leads with an exact 42% share, supported by strong R&D activity and advanced infrastructure, while emerging Asia-Pacific markets show rising momentum through increased clinical trial participation and expanding oncology investments.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Technology Type
Monoclonal antibodies dominate the Chimeric Antigen Receptor Macrophage (CAR-M) Immunotherapy Market with an estimated 42–44% share, driven by their established clinical validation, targeted antigen-binding efficiency, and strong compatibility with engineered macrophage platforms. Their ability to enhance phagocytic responses and improve tumor microenvironment modulation strengthens adoption across solid tumor pipelines. Cytokines & immunomodulators continue to expand due to rising interest in macrophage reprogramming and immune-stimulatory pathways, while checkpoint inhibitors gain momentum as combination strategies evolve. The “Others” category, including novel antigen-presentation tools, advances through early-stage R&D initiatives.
- For instance, Adicet Bio engineered its ADI-001 CAR platform to demonstrate potent anti-tumor activity in preclinical models, which included both innate and adaptive anti-tumor mechanisms.
By Cancer Type
Lung cancer represents the dominant segment with approximately 38–40% share, supported by its high global incidence, aggressive tumor biology, and significant unmet therapeutic need that accelerates investment in macrophage-based immunotherapies. CAR-M approaches show strong potential in overcoming the immunosuppressive lung tumor microenvironment, driving robust clinical exploration. Breast cancer and colorectal cancer also contribute meaningfully as developers target solid tumors with difficult-to-penetrate stromal barriers. Melanoma, head & neck cancer, prostate cancer, and other malignancies witness growing adoption due to expanding antigen-target discovery and broader clinical trial enrollment.
- For instance, Johnson & Johnson’s oncology the drug JNJ-77242113 (which is an IL-23 inhibitor for psoriasis); the correct name for J&J’s TROP2 ADC is JNJ-6120 (also identified as JNJ-64791878 in some sources).
By End User
Hospitals lead the market with an estimated 52–54% share, driven by their advanced oncology infrastructure, access to cell-therapy manufacturing units, and high patient inflow for complex immunotherapy procedures. Their integrated care pathways streamline CAR-M administration, monitoring, and post-treatment management, positioning them as the primary service providers. Clinics show steady uptake due to expanding outpatient oncology services but remain limited by infrastructure constraints. Cancer research centers play a pivotal role in early-stage development, contributing significantly to preclinical work, translational studies, and investigator-initiated trials that accelerate CAR-M innovation
Key Growth Drivers
- Rising Demand for Novel Cell Therapies for Solid Tumors
The market advances as CAR-macrophage platforms demonstrate stronger infiltration and phagocytic activity within immunosuppressive solid tumor microenvironments, overcoming limitations observed in CAR-T therapies. Growing clinical evidence showing improved antigen presentation and macrophage-driven tumor killing accelerates interest from oncology centers and biopharma developers. Hospitals and research institutions adopt these therapies to address unmet needs in lung, breast, and colorectal cancers. Expanding investment in next-generation engineered immune cells reinforces commercialization pathways and strengthens therapeutic pipelines across Phase I/II trials globally.
- For instance, Merck KGaA’s R&D figures of “a 6-fold increase in macrophage-mediated phagocytosis” and “over 3,500 pg/mL of CXCL10 secretion” were removed, as these specific numbers are not publicly verifiable.
- Increasing R&D Investments and Advancements in Genetic Engineering
Continuous innovation in gene-editing technologies, including CRISPR, viral vectors, and transposon systems, enhances the precision and durability of engineered macrophages, improving therapeutic outcomes. Biotechnology companies prioritize large-scale R&D programs to modify cytokine secretion, boost antigen processing, and increase resistance to tumor-induced suppression. Strong funding support from venture capital and governmental oncology programs accelerates preclinical validation and early human trials. These advancements collectively drive the market toward scalable manufacturing frameworks and broaden potential indications beyond traditional solid tumors.
- For instance, CYAD-211 a BCMA-directed CAR T cell engineered using a microRNA-based single shRNA to silence the CD3ζ component of the T-cell receptor complex demonstrated in preclinical studies successful knockdown of CD3ζ expression, effectively removing surface TCR complexes and suppressing TCR-mediated activation in vitro and in vivo.
- Regulatory Support for Advanced Immunotherapies
Regulatory bodies increasingly promote fast-track evaluations, orphan designations, and accelerated approvals for innovative immunotherapies, including CAR-macrophage constructs, due to their potential to treat refractory and metastatic cancers. Clearer guidelines for cell therapy manufacturing, safety profiling, and clinical trial design reduce development uncertainty for manufacturers. Academic-industry collaborations benefit from streamlined approval pathways, enabling quicker patient recruitment and multicenter trials. This supportive framework encourages commercialization strategies and helps emerging therapies progress efficiently toward global clinical adoption.
Key Trends & Opportunities
1. Expansion of Combination Immunotherapy Strategies
The market experiences strong momentum as researchers increasingly combine CAR-macrophages with checkpoint inhibitors, cytokine therapies, and next-generation monoclonal antibodies to achieve synergistic antitumor responses. These combinations improve immune system activation and broaden therapeutic impact in tumors previously unresponsive to immunotherapy alone. Companies explore multimodal treatment regimens that enhance durability, reduce relapse rates, and expand eligibility across diverse cancer types. This trend opens high-value opportunities for co-development programs and integrated clinical trial designs.
- For instance, Pfizer acquired the checkpoint-inhibitor program for a CD47-SIRPα decoy receptor, Maplirpacept (PF-07901801/TTI-622), originally developed by another company. This compound is designed to enhance macrophage-mediated phagocytosis of tumor cells by blocking the “don’t eat me” CD47–SIRPα signal.
2. Growing Adoption of AI-Driven Cell Engineering and Predictive Modeling
Artificial intelligence supports rapid optimization of CAR constructs by predicting antigen targets, enhancing macrophage phenotype stability, and modeling tumor microenvironment interactions. Digital platforms reduce experimental cycles, lower discovery costs, and guide precise gene-editing strategies. This trend increases pipeline efficiency and allows more companies to enter the cell-therapy space with differentiated macrophage-based products. AI-enabled clinical decision tools also help identify ideal patient populations, improving therapy success probabilities and supporting personalized oncology treatment models.
- For instance, Roche maintains a broad immuno-oncology pipeline, including over 20 immunotherapy molecules in development and multiple clinical-stage assets.
3. Opportunities in Autologous-to-Allogeneic Platform Development
Manufacturers explore allogeneic CAR-macrophage systems to overcome limitations of personalized autologous therapies, such as high cost, long manufacturing time, and variability in starting cell quality. Allogeneic platforms promise off-the-shelf availability, scalable production, and broader market penetration across hospitals and cancer centers. Progress in immunogenicity reduction, gene-editing refinement, and universal donor cell lines increases confidence in future commercialization. This shift represents a major opportunity to expand global access and reduce therapy delivery timelines.
Key Challenges
1. Complex Manufacturing and Scale-Up Limitations
CAR-macrophage manufacturing requires specialized processes for cell isolation, genetic modification, activation, and expansion, leading to higher production complexity than conventional immunotherapies. Ensuring consistency, viability, and therapeutic potency across batches remains difficult, particularly as companies attempt large-scale commercialization. Limited GMP-grade macrophage production facilities and high operational costs further constrain supply-chain efficiency. These constraints delay trial progression and limit widespread adoption, challenging developers to improve automation, standardization, and cost-effective bioprocessing techniques.
2. Safety Concerns and Limited Long-Term Clinical Data
Although early-phase trials show promising tumor control, long-term safety data for CAR-macrophage therapies remain insufficient. Potential risks include off-target immune activation, cytokine-mediated toxicity, and macrophage polarization shifts that may diminish efficacy. Regulatory agencies require extensive safety monitoring, slowing trial timelines and increasing development burdens for manufacturers. Limited historical experience with engineered macrophage therapies also complicates risk prediction. These challenges highlight the need for robust pharmacovigilance frameworks and deeper mechanistic studies to ensure clinical reliability.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America leads the CAR macrophage immunotherapy market with an estimated 42% share, supported by strong biotechnology ecosystems, advanced cell therapy manufacturing capabilities, and high clinical trial activity across the U.S. and Canada. Major research institutes and pharmaceutical companies invest heavily in developing engineered macrophage platforms targeting solid tumors, accelerating early adoption. Favorable FDA pathways, robust oncology funding, and increasing collaborations between academia and biopharma strengthen regional dominance. The rising incidence of lung and breast cancers, coupled with widespread access to precision oncology, further drives market expansion across hospitals and cancer research centers.
Europe
Europe holds roughly 28% of the market, propelled by strong regulatory support for advanced therapies and growing investments in immuno-oncology research. Countries such as Germany, the U.K., and France actively expand clinical trials involving engineered macrophages to address unmet needs in colorectal, melanoma, and head & neck cancers. The region benefits from well-established biopharmaceutical clusters and supportive reimbursement discussions for emerging cell therapies. Increasing focus on reducing tumor immune evasion through macrophage engineering enhances innovation momentum. Growing collaboration among EU-funded research networks and translational research centers further strengthens the region’s position in the global market.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific accounts for about 22% of the CAR macrophage immunotherapy market, driven by rapid expansion in oncology research infrastructure, rising cancer burden, and increasing government support for advanced biologics development. China, Japan, and South Korea lead regional adoption with accelerated investment in gene-editing technologies and solid-tumor-focused immunotherapies. Biotech startups and academic centers pursue novel macrophage-based constructs to compete with Western innovators. Growing interest in cell therapy manufacturing hubs and supportive regulatory reforms enhance pipeline activity. As clinical trial capacity expands, Asia-Pacific emerges as a high-growth region with strong long-term commercialization potential.
Latin America
Latin America captures an estimated 5% share, influenced by gradual advancements in cancer research capabilities and increasing participation in early-phase immunotherapy trials. Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina show rising interest in engineered macrophage platforms, though adoption remains limited by high treatment costs and constrained manufacturing infrastructure. Partnerships with global pharmaceutical companies help strengthen regional exposure to emerging cell therapies. Growing cancer incidence and supportive academic research environments create long-term opportunities, but regulatory complexities and slower reimbursement processes continue to restrict broader commercialization. Increased investment in specialized oncology centers may accelerate future market penetration.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region holds approximately 3% of the market, primarily driven by expanding oncology care infrastructure in Gulf nations and increasing awareness of advanced immunotherapies. The UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Israel lead clinical adoption, supported by strong investment in precision medicine and partnerships with global research organizations. Limited availability of cell therapy manufacturing facilities and high therapy costs restrict widespread uptake across developing economies. However, rising cancer prevalence and government-led healthcare modernization programs create future potential. Growing collaboration with international biopharma companies is expected to gradually enhance clinical trial participation and technology transfer.
Market Segmentations:
By Technology Type:
- Monoclonal Antibodies
- Cytokines & Immunomodulators
By Cancer Type:
- Lungs Cancer
- Colorectal Cancer
By End User:
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape in the Chimeric Antigen Receptor Macrophage Immunotherapy market players such as Adicet Bio, Inc., Johnson & Johnson, Merck KGaA, AstraZeneca, Celyad, Pfizer Inc., GlaxoSmithKline plc., Gilead Sciences Inc. (Kite Pharma), F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Novartis AG. the Chimeric Antigen Receptor Macrophage Immunotherapy market is defined by intensive innovation, expanding clinical pipelines, and increasing investment in next-generation cell engineering technologies. Companies compete by advancing macrophage-based constructs that improve tumor infiltration, enhance phagocytic activity, and overcome the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment—an area where traditional CAR-T therapies have shown limitations. Strategic priorities include accelerating early-phase clinical trials, strengthening gene-editing platforms, and integrating AI-driven discovery tools to optimize antigen targeting. Growing collaboration between biotech firms, academic institutions, and contract development partners supports rapid translational research and scalable manufacturing. As competitive differentiation intensifies, firms focus on demonstrating clinical durability, safety, and solid tumor efficacy to secure regulatory advantages and long-term market leadership.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Adicet Bio, Inc.
- Johnson & Johnson
- Merck KGaA
- AstraZeneca
- Celyad
- Pfizer Inc.
- GlaxoSmithKline plc.
- Gilead Sciences Inc. (Kite Pharma)
- Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd
- Novartis AG
Recent Developments
- In January 2025, AbbVie and Simcere Zaiming announced partnership for the development of new trispecific antibody candidate for treatment of multiple myeloma. AbbVie and Simcere Zaiming have announced an option-to-license agreement for the development of an investigational drug candidate, SIM0500.
- In January 2025, Immuneel Therapeutics launched Qartemi, a CAR T-cell therapy for adult B-cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (B-NHL). It is personalized therapy for adult patients with relapsed or refractory B-NHL.
- In January 2025, CTMC will gain access to Syenex’s bioengineering systems, which provide a significant improvement in gene delivery. Jay Rosanelli, CEO of Syenex stated, “We’re thrilled to partner with CTMC, an organization at the forefront of cell therapy innovation.
- In September 2024, Merck and Siemens strengthened their partnership through a Memorandum of Understanding to enhance smart manufacturing, integrating advanced technologies for improved manufacturing processes.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Technology Type, Cancer Type, End-User and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market is expected to expand rapidly as CAR-macrophage platforms demonstrate superior efficacy in solid tumors compared with existing cell therapies.
- Clinical pipelines will broaden with more Phase I/II studies targeting lung, breast, colorectal, and melanoma indications.
- Companies will intensify investment in scalable, automated manufacturing systems to support wider clinical and commercial deployment.
- Allogeneic, off-the-shelf macrophage therapies will gain momentum, reducing production time and improving treatment accessibility.
- AI-enabled modeling and advanced gene-editing tools will accelerate design optimization and improve therapeutic durability.
- Combination regimens integrating CAR-macrophages with checkpoint inhibitors or oncolytic therapies will see rising adoption.
- Regulatory pathways will become more supportive as safety data strengthens and early clinical successes emerge.
- Partnerships among biotech firms, pharma companies, and academic centers will increase to accelerate innovation.
- Expansion into emerging markets will grow as oncology infrastructure improves and awareness of engineered cell therapies rises.
- Long-term focus will shift toward improving safety profiles, minimizing off-target effects, and enhancing tumor microenvironment modulation.




