Market Overview
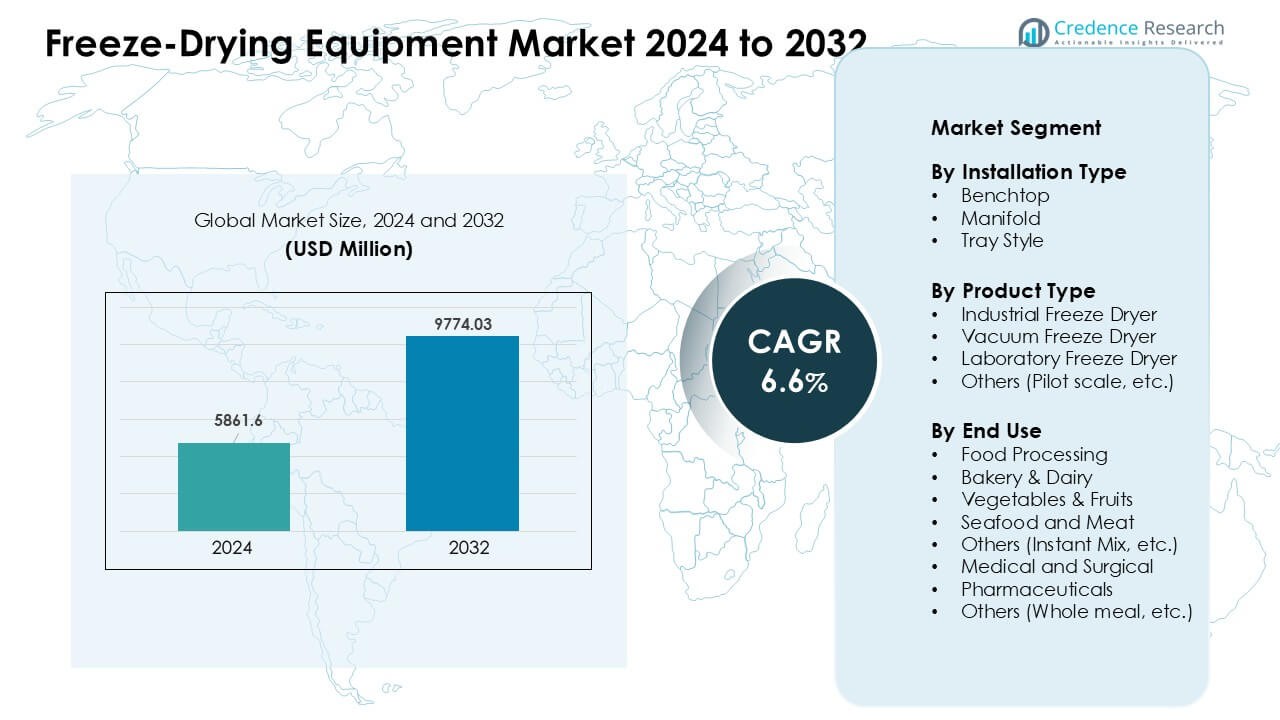
Freeze-Drying Equipment Market was valued at USD 5861.6 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 9774.03 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 6.6% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Freeze-Drying Equipment Market Size 2024 |
USD 5861.6 Million |
| Freeze-Drying Equipment Market, CAGR |
6.6% |
| Freeze-Drying Equipment Market Size 2032 |
USD 9774.03 Million |
The freeze-drying equipment market is shaped by key players such as Cuddon Freeze Dry, Optima Packaging Group GmBH, Azbil Corporation, BUCHI Corporation, Martin Christ Gefriertrocknungsanlagen GmbH, Senovatec, Hosokawa Micron BV, GEA Group, IMA SpA, and Syntegon. These companies advanced system precision, energy efficiency, and automation to meet rising demand in food, pharma, and biotech applications. Many focused on scalable pilot units, smart controls, and stronger global service networks to support diverse production needs. North America emerged as the leading region in 2024 with a 34% share, supported by strong pharmaceutical manufacturing and early adoption of high-performance lyophilization technologies.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The freeze-drying equipment market reached USD 5861.6 million in 2024 and is projected to hit USD 9774.03 million by 2032 at a CAGR of 6.6%.
- Strong demand grew from pharmaceuticals, which held the largest segment share at about 36% due to rising use in biologics and sterile injectables.
- Key trends included wider adoption of modular and pilot-scale units and rising use of freeze drying in premium, clean-label food products.
- Leading players focused on advanced automation, tighter temperature control, and energy-efficient designs, strengthening competition across global markets.
- North America led the market with a 34% share in 2024, supported by strong pharma manufacturing, while Asia Pacific grew fastest due to expanding biologics and food-processing capacity.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Installation Type
Benchtop units led the installation type segment in 2024 with about 42% share. Small labs and R&D teams used benchtop models due to easy setup and low space needs. Many buyers valued their quick cycle control, which helped speed early-stage testing. Manifold systems gained users where flexible flask handling mattered, while tray-style units grew in mid-scale food and pharma tasks. Strong demand for compact designs kept benchtop models ahead, supported by steady upgrades in temperature stability and vacuum precision.
- For instance, SP Scientific’s VirTis BenchTop Pro freeze dryer offers shelf areas up to 0.5 m², condenser capacities around 6 liters of ice, and temperature control down to −85 °C, supporting precise laboratory-scale lyophilization.
By Product Type
Industrial freeze dryers dominated the product type segment in 2024 with nearly 48% share. Large food and pharma plants preferred industrial systems because high-capacity chambers improved batch throughput and reduced cycle time. Many producers also used automated monitoring to enhance quality control. Vacuum freeze dryers expanded in biotech due to gentle drying needs, while laboratory units stayed key in small experiments. Rising focus on clean processing and long shelf life helped industrial dryers maintain leadership across global installations.
By End Use
Pharmaceuticals held the largest share in 2024 with about 36%. Drug makers relied on freeze drying to improve stability of vaccines, biologics, and sensitive injectables. Strong demand for sterile production and long storage life pushed higher adoption of large automated units. Food processing, bakery, and dairy also saw steady use due to rising demand for lightweight, shelf-stable products. Vegetables, fruits, and seafood users grew as freeze drying kept nutrients intact. The broad push for clean-label, preservative-free formats supported strong growth across all end-use groups.
- For instance, Telstar’s LyoBeta freeze dryer is a laboratory and pilot-scale system designed for pharmaceutical and biotech development. The unit offers shelf areas up to about 0.9 m² and achieves high vacuum levels suitable for lyophilization of vaccines, biologics, and injectable formulations during process development and scale-up.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Demand for Shelf-Stable Food and Pharma Products
Growth in shelf-stable goods pushed strong demand for freeze-drying systems. Many food brands used freeze drying to keep flavor, color, and nutrients intact, which helped support premium product launches. Pharma companies expanded freeze-drying use for vaccines, biologics, and injectables that required high purity and long storage life. The wider move toward clean-label goods encouraged firms to pick drying methods that avoided heat damage and chemical preservatives. Global trade in ready-to-eat meals also increased orders for large-capacity systems. This broad shift toward high-quality, long-life products remained a core driver for market expansion.
Expansion of Biologics and Advanced Therapies
Biologics and cell-based drugs needed gentle drying to keep structure stable, fueling rapid adoption of advanced freeze-drying equipment. Many biotech labs invested in systems with stronger temperature control and low-pressure uniformity to support research on mRNA, peptides, and protein drugs. Hospitals also relied on freeze-dried formulations for fast reconstitution during critical care. Growth in contract manufacturing created more demand for scalable units that handled frequent batch shifts. As global pipelines for specialty drugs expanded, freeze-drying systems became vital infrastructure to protect sensitive molecules and meet rising regulatory expectations.
- For instance, Samsung Biologics offers lyophilization services as part of its biomanufacturing infrastructure, integrating controlled freeze-drying, aseptic filling, and vial handling to stabilize high-concentration biologics under low-moisture conditions enabling long-term storage and transport of sensitive drugs.
Automation and Digital Control Advancements
New equipment designs with smart sensors, automated loading, and digital vacuum control improved accuracy and efficiency. Companies adopted these systems to lower cycle time and cut manual errors during batch handling. Real-time data tracking allowed operators to adjust drying stages and reduce waste. Predictive maintenance tools also reduced downtime and extended machine life. These upgrades improved quality consistency across large runs, making advanced units attractive for food and pharma producers. The move toward Industry 4.0 standards pushed wider investment in high-precision freeze-drying solutions.
- For instance, SP Scientific’s LyoStar® 4.0 freeze dryer integrates tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS) to measure water vapor flow in real time, enabling accurate end-point detection and tighter control of pharmaceutical lyophilization cycles.
Key Trend & Opportunity
Growth of Premium and Functional Food Categories
Demand for premium snacks, plant-based mixes, fruit powders, and nutrient-rich meals created major opportunities. Freeze-drying kept natural taste and vitamins intact, which helped brands market clean and healthy features. E-commerce growth boosted sales of freeze-dried fruits and instant meal kits, raising production needs for small and mid-scale processors. Sports nutrition and infant food producers also used freeze-drying to meet purity needs. Companies explored new flavors, single-serve packs, and travel-ready foods. This shift opened strong opportunities for flexible, energy-efficient systems that supported diverse product ranges.
- For instance, Büchi’s Lyovapor™ L-300 freeze dryer operates with condenser temperatures down to −105 °C and supports programmable shelf heating, enabling precise drying of fruit powders, plant-based ingredients, and nutrition-focused food products for premium and functional categories.
Rising Adoption of Modular and Pilot-Scale Systems
More companies used modular and pilot units to test new formulations and support small-batch innovation. These systems offered fast installation, lower capital cost, and easier scaling to full production. Startups in biotech, specialty foods, and personalized nutrition used pilot systems to validate new product lines before large investment. Growing interest in space-efficient units also helped modular systems gain traction. As firms pushed rapid product development, pilot-scale freeze dryers became key tools for experiment-focused production with quick cycle adjustments and strong repeatability.
- For instance, Labtron’s LPFD-E10 pilot freeze dryer is designed for small-batch R&D work and features a 4 kg ice condenser, silicone-oil-heated shelves with temperature control from −60 °C to +80 °C, and a freeze-drying area of about 0.256 m².
Key Challenge
High Equipment Cost and Energy Use
Freeze-drying systems required high upfront investment, which slowed adoption in small firms. Large chambers, vacuum pumps, and refrigeration parts increased cost, and energy use remained high during long cycles. Many producers struggled to balance operational cost with product quality needs. The market also faced pressure from cheaper drying alternatives, which attracted budget-focused buyers. Rising electricity prices made cost management harder, especially for 24/7 food operations. These financial barriers limited adoption in emerging regions and reduced upgrade speed for older facilities.
Long Cycle Time and Technical Complexity
Freeze-drying required skilled operators to manage temperature shifts, pressure control, and product load patterns. Long cycle time slowed throughput and limited daily batch capacity. Even small errors in freezing stage or vacuum calibration could affect texture, stability, or yield. Many companies needed strong training programs to reduce errors and handle diverse product profiles. Complex maintenance also added delays when vacuum seals, sensors, or refrigeration units failed. The technical burden made process optimization difficult and reduced production flexibility for high-mix operations.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America led the freeze-drying equipment market in 2024 with roughly 34% share. Strong adoption came from pharmaceutical and biotech firms that relied on lyophilization for biologics, vaccines, and high-purity injectables. Food producers also expanded freeze-dried fruit, dairy, and snack lines as demand for clean-label and long-shelf-life items grew. Advanced R&D facilities and strict regulatory standards pushed companies to invest in automated and high-precision systems. The region’s strong presence of contract manufacturing organizations further supported steady equipment upgrades and high-capacity installations across the U.S. and Canada.
Europe
Europe accounted for about 29% share in 2024, driven by strong pharma manufacturing and strict quality norms. Germany, France, Italy, and the U.K. expanded freeze-drying use for vaccines, specialty drugs, and high-value food ingredients. The region also saw rising adoption of modular and energy-efficient units due to sustainability goals. Growing demand for freeze-dried baby food, dairy powders, and premium fruit snacks supported investment across food plants. Continuous innovation in biologics and high funding for life-science research helped Europe maintain a strong, stable position in the global market.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific held nearly 27% share in 2024 and grew fastest due to expanding pharmaceutical production in China, India, Japan, and South Korea. Food companies increased freeze-dried vegetable, instant mix, and fruit exports, raising demand for large-capacity systems. Government support for vaccine development and biologics manufacturing also strengthened adoption. Rising consumer interest in premium nutrition products further boosted equipment needs. Lower labor cost and growing contract manufacturing activities helped Asia Pacific become a major hub for large-scale installations with strong long-term growth potential.
Latin America
Latin America captured around 6% share in 2024, supported by rising use of freeze-dried fruits, coffee, and meat products for export. Brazil, Mexico, and Chile expanded adoption as food processors shifted to long-shelf-life formats. Pharma firms showed gradual uptake for vaccines and specialty formulations but faced budget constraints that slowed large-scale upgrades. Growth remained steady due to increasing interest in clean-label food items. However, limited availability of advanced automation and high equipment cost kept adoption moderate compared to larger global regions.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa held nearly 4% share in 2024, driven by growing demand for freeze-dried dairy, meat, and ready-to-eat products. Gulf nations invested in food-processing capacity to reduce import reliance, which raised the need for freeze-drying systems. Pharma adoption remained limited but increased in markets like Saudi Arabia and the UAE as local drug production expanded. Africa showed early-stage growth focused on fruit and vegetable drying. High capital cost and limited technical expertise slowed broader uptake, but long-term prospects improved with rising food security initiatives.
Market Segmentations:
By Installation Type
- Benchtop
- Manifold
- Tray Style
By Product Type
- Industrial Freeze Dryer
- Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Freeze Dryer
- Others (Pilot scale, etc.)
By End Use
- Food Processing
- Bakery & Dairy
- Vegetables & Fruits
- Seafood and Meat
- Others (Instant Mix, etc.)
- Medical and Surgical
- Pharmaceuticals
- Others (Whole meal, etc.)
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the freeze-drying equipment market featured strong activity from leading companies such as Cuddon Freeze Dry, Optima Packaging Group GmBH, Azbil Corporation, BUCHI Corporation, Martin Christ Gefriertrocknungsanlagen GmbH, Senovatec, Hosokawa Micron BV, GEA Group, IMA SpA, and Syntegon. These players focused on improved chamber design, tighter temperature control, and high-efficiency vacuum systems to support food, pharma, and biotech needs. Many firms expanded digital tools that offered real-time monitoring and automated cycle adjustment. Product lines also shifted toward modular and pilot-scale units to help customers reduce cost and speed development. Strategic partnerships, service expansions, and regional manufacturing strengthened competitiveness in growth markets across Asia-Pacific and North America. Continuous R&D investment supported long-term gains as firms worked to deliver shorter cycles, cleaner operation, and lower energy use.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Cuddon Freeze Dry (New Zealand)
- Optima Packaging Group GmBH (Germany)
- Azbil Corporation (Japan)
- BUCHI Corporation (U.S.)
- Martin Christ Gefriertrocknungsanlagen GmbH (Germany)
- Senovatec (China)
- Hosokawa Micron BV (Japan)
- GEA Group (Germany)
- IMA SpA (Italy)
- Syntegon (Germany)
Recent Developments
- In November 2024, IMA SpA / IMA Life (Italy) IMA Life entered a strategic partnership with RheaVita to develop and commercialize continuous biopharmaceutical freeze-drying technology, aiming to industrialize highly controlled, low-volume high-value lyophilization lines.
- In October 2024, GEA Group (Germany) GEA launched its next-generation RAY® Plus batch freeze dryers for food, delivering higher energy efficiency, improved hygiene, and more flexible large-scale freeze-drying capacity for items such as fruits, pet food, and ready meals.
- In June 2024, IMA SpA / IMA Life (Italy) IMA Life introduced KryoAir, an air-based refrigeration system for pharmaceutical freeze dryers, developed with MIRAI Intex and ACT to replace high-GWP refrigerants and reach temperatures down to about −100 °C for biopharma lyophilization.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Installation Type, Product Type, End-Use and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Demand for high-capacity freeze dryers will rise as biologics and vaccines expand.
- Food processors will increase adoption to support clean-label and premium product lines.
- Automation and digital monitoring will strengthen consistency and reduce cycle time.
- Energy-efficient designs will gain traction as firms aim to cut operating costs.
- Modular and pilot-scale systems will grow due to flexible production needs.
- New entrants from Asia will intensify competition with cost-effective designs.
- Pharma firms will invest in advanced systems to meet strict regulatory standards.
- R&D labs will adopt compact units for rapid formulation testing.
- Service-based models, including maintenance packages, will gain wider use.
- Global capacity will expand as emerging economies build local food and drug manufacturing.




