Market Overview
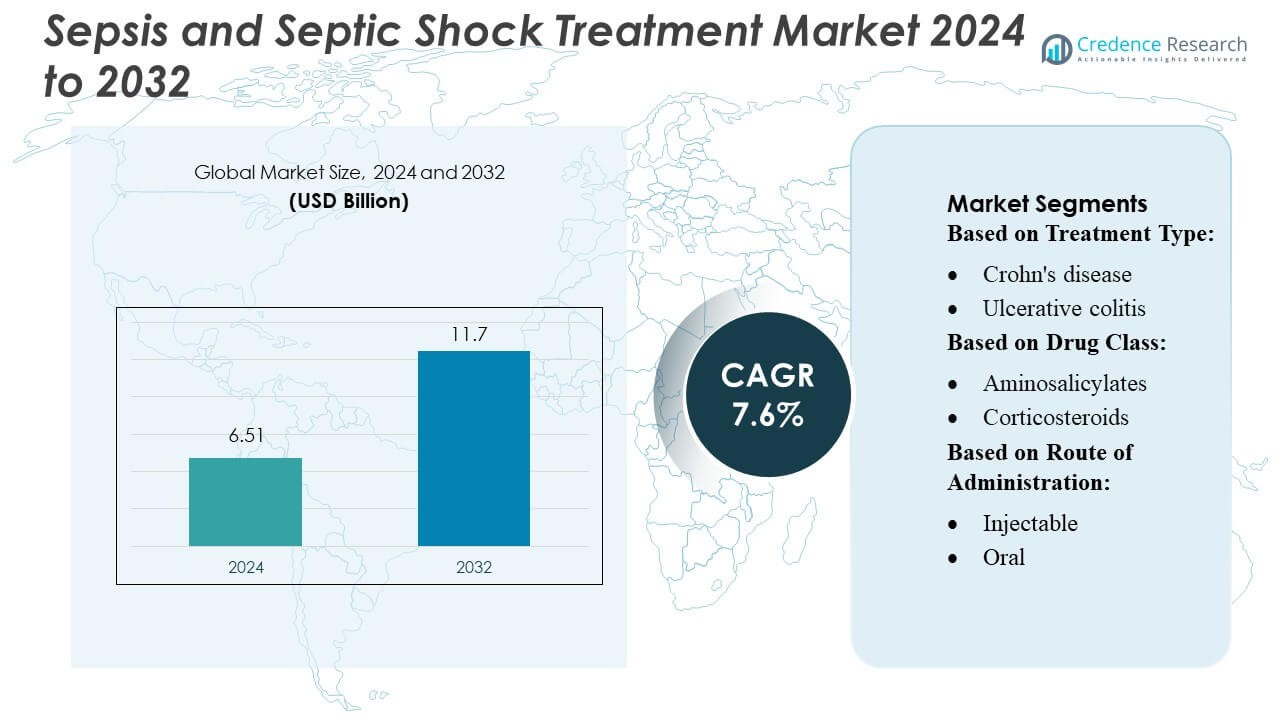
Sepsis and Septic Shock Treatment Market size was valued USD 6.51 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 11.7 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 7.6% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Sepsis and Septic Shock Treatment Market Size 2024 |
USD 6.51 Billion |
| Sepsis and Septic Shock Treatment Market, CAGR |
7.6% |
| Sepsis and Septic Shock Treatment Market Size 2032 |
USD 11.7 Billion |
In the global sepsis and septic shock treatment market, Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, and AM-Pharma stand out as leading players, leveraging broad antibiotic portfolios, advanced biologics, and immunotherapies. Pfizer leads the pack, especially in septic shock, with a commanding ~20% share. Merck & Co. and Johnson & Johnson follow with approximately 15% and 12%, respectively. Regionally, North America dominates the market, accounting for around 38.7% of global sepsis-therapeutics revenue, driven by its mature healthcare infrastructure and high R&D investment.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The sepsis and septic shock treatment market reached USD 6.51 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit USD 11.7 billion by 2032, expanding at a 7.6% CAGR, driven by rising global sepsis incidence and accelerated adoption of advanced therapeutics.
- Growing demand for broad-spectrum antibiotics, biologics, and immunomodulators fuels market growth, supported by rapid ICU infrastructure expansion and increased government focus on early sepsis intervention.
- The market experiences steady innovation, with players like Pfizer, Novartis, and AM-Pharma advancing pipeline biologics and combination therapies targeting severe septic shock and multi-organ complications.
- High treatment costs, limited diagnostic accuracy in low-income regions, and increasing antimicrobial resistance continue to restrain wider therapeutic adoption across developing markets.
- North America holds 38.7% of global revenue due to strong R&D capabilities, while Pfizer leads with ~20% share, followed by Merck at ~15% and Johnson & Johnson at ~12%, reinforcing a highly consolidated competitive landscape.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Treatment Type
Crohn’s disease remains the dominant sub-segment, accounting for an estimated over 55% of the treatment-type market share, driven by its higher global prevalence, recurrent flare frequency, and greater therapeutic intensity compared to ulcerative colitis. Demand continues to rise as biologic initiation rates increase in moderate to severe Crohn’s patients and as earlier diagnosis expands the eligible treatment pool. Ulcerative colitis follows with steady growth supported by improved diagnostic pathways and broader adoption of advanced immunomodulators, though overall market contribution remains comparatively smaller due to typically lower escalation to second-line biologics.
- For instance, Zydus Healthcare Limited strengthened therapeutic accessibility through its adalimumab biosimilar Exemptia (40 mg prefilled syringe), launched with a significantly reduced cost of ₹19,000 per dose compared to imported versions priced above ₹100,000, enabling wider biologic adoption in immune-mediated inflammatory conditions.
By Drug Class
TNF inhibitors lead the drug-class segment with roughly 35–40% market share, supported by long-established clinical efficacy, extensive physician familiarity, and wide insurance coverage. First-line therapies such as aminosalicylates and corticosteroids maintain significant usage in mild to moderate cases but exhibit limited revenue growth due to genericization and guideline-driven tapering. Among second-line biologics, IL inhibitors and JAK inhibitors are expanding rapidly as clinicians shift toward targeted, mechanism-specific agents, while anti-integrin and S1P receptor modulators grow steadily in patients with biologic intolerance. Combination therapy—particularly TNF inhibitors plus thiopurines—continues to strengthen outcomes but contributes a smaller share due to safety-monitoring requirements.
- For instance, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. has strengthened its biologics footprint through its partnership with Alvotech, this facility is equipped with a large-scale, flexible manufacturing setup that utilizes both 1,000-liter and 2,000-liter single-use bioreactor designs, achieving a total production capacity of 16,000 liters.
By Route of Administration
Injectable therapies dominate with over 60% market share, largely because leading biologics—including TNF inhibitors, IL inhibitors, and anti-integrin agents—are primarily delivered via subcutaneous or intravenous routes. Their strong clinical response rates and suitability for severe disease drive consistent adoption in hospital and specialty-care settings. Oral formulations are gaining traction with the rise of JAK inhibitors and S1P receptor modulators, offering convenience and rapid symptom control. Rectal formulations hold a niche share, mainly limited to localized ulcerative colitis, but remain relevant for cost-effective symptom management in mild distal disease.
Key Growth Drivers
- Rising Global Incidence of Sepsis
The increasing prevalence of sepsis across developed and emerging economies continues to accelerate treatment demand. Higher infection rates driven by aging populations, antimicrobial resistance, and postoperative complications contribute significantly to case volume. Hospitals report growing admissions of severe sepsis, prompting urgent adoption of evidence-based treatment protocols. Expanded ICU capacity and improved diagnostic recognition further increase identification and intervention rates. As countries refine sepsis surveillance systems, reported incidence continues to rise, supporting strong market growth for both broad-spectrum antimicrobials and advanced supportive-care therapeutics.
- For instance, Gedeon Richter Plc. has expanded its mammalian-cell bioreactors, encompassing both stainless steel (1000L and 2x5000L) and single-use technology systems (4x2000L), to achieve a total fermentation capacity of 18,000 liters.
- Advancements in Rapid Diagnostic Technologies
Innovations in rapid molecular assays and biomarker-based detection systems are strengthening sepsis management by reducing time to targeted therapy. Modern platforms enable pathogen identification within hours instead of days, supporting timely decisions on antibiotic selection and vasopressor use. Hospitals increasingly integrate automated blood culture systems, point-of-care inflammation markers, and AI-based decision-support tools that improve prediction accuracy. These advancements enhance clinical outcomes and encourage broader utilization of high-value therapeutics. As diagnostics accelerate treatment workflows, adoption of advanced antibiotics and organ-support therapies expands, directly fueling market growth.
- For instance, ObsEva reassigned contracts worth USD 6.2 million (including 1.7 million in payables) related to its linzagolix program to Kissei Pharmaceutical, according to its Q3 restructuring update.
- Growing Adoption of Novel Therapeutics and Supportive Care
The accelerating introduction of innovative immunomodulators, next-generation vasopressors, and organ-support modalities is reshaping treatment approaches for septic shock. Expanded clinical evidence supporting early vasopressor initiation, corticosteroid optimization, and adjunctive therapies is improving survival outcomes and boosting product adoption. Advanced ventilatory systems, renal replacement technologies, and hemodynamic monitoring platforms further enhance patient recovery. Pharmaceutical investment in host-response therapies and monoclonal antibodies strengthens the development pipeline. As hospitals prioritize standardized sepsis bundles and protocolized care, demand for newly approved and premium treatment options continues to rise.
Key Trends & Opportunities
1. Shift Toward Precision-Based and Biomarker-Guided Therapy
Healthcare systems are transitioning toward precision approaches that leverage biomarkers such as procalcitonin, lactate, and cytokine profiles to tailor therapy. This shift enables optimized dosing strategies, reduced antibiotic overuse, and earlier escalation to vasopressor or organ-support interventions. Personalized treatment pathways are gaining regulatory support and fostering investment in companion diagnostics. Opportunities arise for pharmaceutical companies to develop biomarker-linked therapeutics and monitoring tools that fit into precision sepsis-management algorithms, strengthening long-term market innovation and clinical adoption.
- For instance, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited has developed an investigational, highly selective oral allosteric tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) inhibitor, TAK-279 (zasocitinib). In Phase 2b studies, the treatment demonstrated statistically significant and clinically meaningful efficacy in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis and active psoriatic arthritis by inhibiting IL-12/IL-23 signaling.
2. Rising Use of AI-Enabled Clinical Decision Support
Artificial intelligence and machine-learning platforms increasingly support real-time monitoring, early warning scores, and predictive analytics for sepsis onset. Hospitals deploying AI-driven algorithms report improved identification of deterioration and faster initiation of sepsis bundles. Integration into electronic health records creates opportunities for solution providers to offer subscription-based decision-support tools. This trend aligns with value-based care initiatives and opens avenues for partnerships between technology firms, diagnostic developers, and healthcare systems seeking improved sepsis detection performance.
- For instance, Bayer’s proprietary compound library comprises 6 million unique chemical entities, which the company scans using AI-powered in-silico target-identification tools, as disclosed in its AI strategy report.
3. Expansion of Critical-Care Infrastructure in Emerging Markets
Developing regions are expanding ICU capacity, upgrading monitoring systems, and improving availability of vasopressors, mechanical ventilation, and blood-culture technologies. Government-led investments in tertiary-care hospitals and training programs create significant growth potential for therapeutic suppliers. International health organizations are supporting sepsis-quality initiatives, which stimulate adoption of standardized treatment protocols. As awareness and diagnostic capabilities strengthen, emerging economies represent a major opportunity for manufacturers of antimicrobials, rapid diagnostics, and critical-care equipment.
Key Challenges
1. Antimicrobial Resistance and Limited Novel Antibiotic Development
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) remains a central challenge, limiting the effectiveness of standard therapies and increasing morbidity in septic patients. The slow pace of new antibiotic development reduces therapeutic options, especially for multi-drug-resistant pathogens. Clinicians face rising treatment failures and must rely on combination regimens that increase cost and toxicity risks. Regulatory hurdles and low commercial incentives further discourage innovation in anti-infective R&D. As a result, AMR continues to strain clinical outcomes and restricts long-term progress in sepsis management.
2. High Treatment Costs and Resource Constraints in Low-Income Settings
The financial burden associated with advanced sepsis care—including ICU admission, continuous monitoring, mechanical ventilation, and renal-replacement therapy—limits access in resource-constrained regions. Many hospitals lack rapid diagnostics, vasopressors, and standardized sepsis protocols, leading to delayed diagnosis and higher mortality rates. Cost pressures also hinder adoption of innovative biologics and new supportive therapies. Limited reimbursement frameworks and inconsistent healthcare funding exacerbate disparities in treatment quality. These constraints remain a major barrier to market expansion in low- and middle-income countries.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds the largest share of the sepsis and septic shock treatment market, accounting for around 35–38%, supported by advanced critical-care infrastructure, high ICU bed density, and strong adoption of rapid diagnostic technologies. The region benefits from well-established sepsis management guidelines, early vasopressor adoption, and broad access to novel antimicrobial and immunomodulatory therapies. Increasing hospital investments in AI-enabled monitoring, expanded emergency-care capacity, and high sepsis awareness continue to reinforce market dominance. Continued clinical research activity and strong reimbursement frameworks sustain steady growth across both the U.S. and Canada.
Europe
Europe captures approximately 28–30% of the global market, driven by strong public healthcare systems, rising sepsis detection rates, and widespread implementation of standardized sepsis bundles across major countries. Investments in early warning systems, rapid microbial identification platforms, and expanded antimicrobial stewardship programs support market expansion. Several EU nations report increased incidence of antimicrobial-resistant infections, accelerating the need for advanced treatment options. The region’s mature regulatory environment and high adoption of critical-care equipment further strengthen demand, although overall growth remains moderate due to stringent cost controls in government-funded hospitals.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, holding roughly 22–24% of the market and expanding rapidly due to rising sepsis burden, improving diagnostic access, and substantial investments in intensive-care capacity. Countries such as China, India, and Japan are increasing ICU infrastructure, adopting automated blood-culture systems, and enhancing emergency-care readiness. Growing awareness programs, higher hospital admission rates, and rising antimicrobial resistance further intensify treatment needs. Supportive government initiatives to strengthen acute-care services and modernize hospital networks attract major global suppliers, positioning the region for sustained long-term growth and increasing market influence.
Latin America
Latin America accounts for about 6–7% of the global market, influenced by rising sepsis-related hospitalizations, expanding tertiary-care facilities, and improved training on early recognition protocols. Brazil and Mexico lead regional adoption, driven by upgrades in public-sector ICUs and increased access to broad-spectrum antibiotics and vasopressors. However, limited availability of rapid diagnostics and uneven healthcare quality across regions constrain faster growth. Strengthening public health initiatives, donor-funded hospital modernization, and targeted antimicrobial stewardship programs support gradual market expansion, although economic constraints and variable reimbursement continue to limit widespread adoption of advanced therapies.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region represents around 5–6% of the market, with growth concentrated in GCC countries that are investing heavily in modern critical-care infrastructure and high-acuity hospital services. Rising incidence of hospital-acquired infections and broader adoption of rapid detection technologies drive demand in urban centers. In contrast, large portions of Africa face limited ICU capacity, insufficient diagnostic tools, and delayed treatment initiation, resulting in high mortality and restricted market uptake. International health partnerships, donor-funded critical-care programs, and government initiatives are gradually improving access, but overall market penetration remains comparatively low.
Market Segmentations:
By Treatment Type:
- Crohn’s disease
- Ulcerative colitis
By Drug Class:
- Aminosalicylates
- Corticosteroids
By Route of Administration:
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the sepsis and septic shock treatment market features leading pharmaceutical companies such as Zydus Healthcare Limited, AstraZeneca, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Gedeon Richter Plc., AbbVie, Inc., Astellas Pharma, Inc., ObsEva SA, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Pfizer, Inc., and Bayer AG. The sepsis and septic shock treatment market continues to evolve as pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies intensify their focus on developing advanced antimicrobial agents, immunomodulators, and supportive-care therapeutics. Competition is driven by the rising need for rapid-acting treatments, improved survival outcomes, and solutions that address antimicrobial resistance. Companies are expanding clinical pipelines targeting host immune response, exploring novel biomarkers, and integrating precision-based therapeutic strategies. Strategic collaborations with diagnostic technology providers enhance early detection capabilities and strengthen treatment pathways. Additionally, increased investment in critical-care innovation, global manufacturing expansion, and regulatory approvals across high-growth regions are shaping a dynamic and highly competitive market environment.
Key Player Analysis
- Zydus Healthcare Limited
- AstraZeneca
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
- Gedeon Richter Plc.
- AbbVie, Inc.
- Astellas Pharma, Inc.
- ObsEva SA
- Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited
- Pfizer, Inc.
- Bayer AG
Recent Developments
- In May 2025, Teva Pharmaceuticals, a U.S. affiliate of Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., and Alvotech announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had approved SELARSDI (ustekinumab-aekn) injection as interchangeable with the reference biologic Stelara (ustekinumab). This approval may help the company acquire an enhanced customer base.
- In June 2024, Henkel is dedicated to increasing knowledge about the role advanced materials can play in enabling sustainability across the value chain, from R&D to manufacturing to field use, among heavy vehicle and equipment (heavy vehicle and equipment) designers, manufacturers, and tier suppliers.
- In April 2024, Prenosis, Inc. entered into a commercial distribution collaboration with Roche for the distribution of the Sepsis ImmunoScore, an AI-driven software as a medical device (AI SaMD) designed to support the rapid diagnosis of sepsis and predict adverse outcomes.
- In January 2024, Hera Biotech, Inc., a Texas-based biotechnology company specializing in tissue-based diagnostics for endometriosis, announced its acquisition of the endometriosis diagnostic assets and associated intellectual property from Scailyte AG, a Swiss firm known for its expertise in single-cell omics and AI-driven biomarker discovery.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Treatment Type, Drug Class, Route of Administration and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market will experience sustained demand as global sepsis incidence rises and diagnostic accuracy improves.
- Adoption of rapid molecular diagnostics will accelerate, enabling earlier and more targeted treatment interventions.
- Biologics and immunomodulators will gain greater traction as clinical evidence supports their role in severe septic shock management.
- AI-driven clinical decision tools will become standard in hospitals, improving early detection and treatment precision.
- Antimicrobial resistance will drive the need for new antibiotic classes and broaden the use of combination therapies.
- Critical-care infrastructure expansion in emerging economies will significantly increase treatment adoption.
- Industry investment in host-response and pathogen-neutralizing therapies will reshape future therapeutic pipelines.
- Tele-ICU and remote monitoring technologies will enhance early intervention capabilities in resource-limited settings.
- Regulatory agencies will push for standardized sepsis protocols, improving treatment consistency across regions.
- Strategic collaborations between pharmaceutical firms and diagnostic technology companies will strengthen integrated sepsis management solutions.




