Market overview
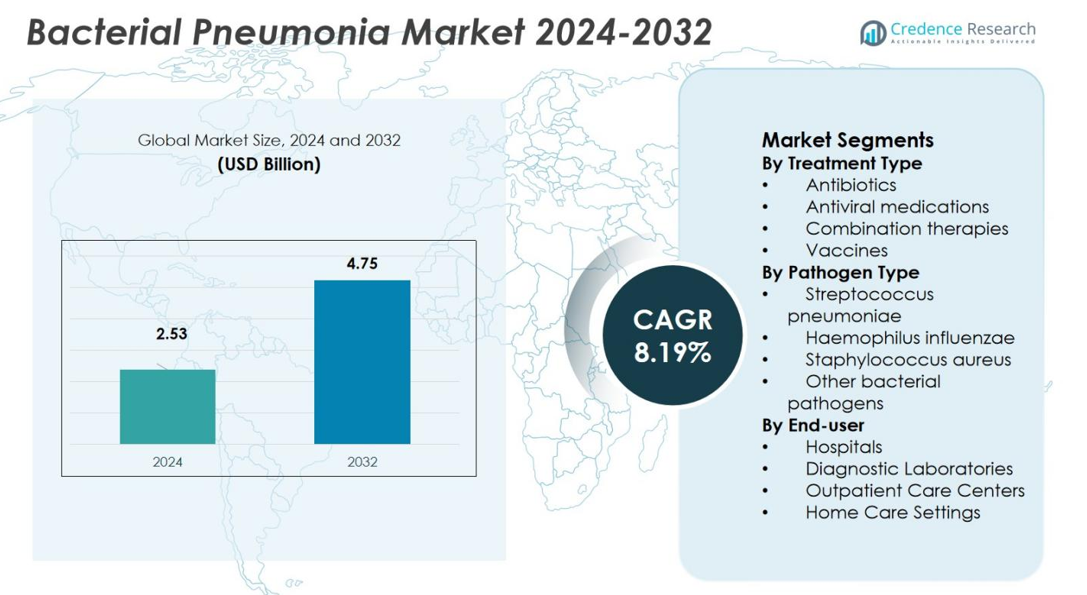
Bacterial Pneumonia Market size was valued USD 2.53 Billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 4.75 Billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 8.19% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Bacterial Pneumonia Market Size 2024 |
USD 2.53 Billion |
| Bacterial Pneumonia Market, CAGR |
8.19% |
| Bacterial Pneumonia Market Size 2032 |
USD 4.75 Billion |
The Bacterial Pneumonia Market features major players such as Pfizer Inc., Merck & Co., Inc., Bayer AG, AstraZeneca PLC, GlaxoSmithKline plc, bioMérieux SA and Abbott Laboratories, which maintain strong positions through broad portfolios of antibiotics, vaccines and diagnostics. Regionally, North America leads with a share of 35.4 %, supported by advanced healthcare systems, high R&D investment and early adoption of novel therapies. Europe follows with 28.0 % share, underpinned by mature immunisation programmes and hospital infrastructure. Asia‑Pacific holds 22.5 % of the market and offers significant growth potential thanks to expanding healthcare access and rising disease incidence.
Market Insights
- The Bacterial Pneumonia Market was valued at USD 2.53 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 4.75 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 8.19% during the forecast period.
- Key drivers of market growth include the rising incidence of bacterial pneumonia, the escalating threat of antibiotic resistance, and advancements in diagnostics and vaccines.
- Key trends include the shift towards precision medicine and tailored therapies, as well as expanding vaccination coverage to reduce disease burden.
- The market is highly competitive, with major players such as Pfizer Inc., Merck & Co., and Bayer AG driving innovation in antibiotics, vaccines, and diagnostic technologies.
- Regionally, North America leads with 35.4% market share, followed by Europe with 28.0%, while Asia‑Pacific holds 22.5%, showing the fastest growth potential in emerging markets due to improved healthcare access and infrastructure.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Treatment Type
The treatment‑type segment is dominated by antibiotics, which hold a significant share of 62% in the market. This dominance is driven by the high prevalence of bacterial pneumonia, the clinical effectiveness of antibiotics, and their status as the first‑line therapy for treating bacterial infections. Antibiotics remain the most commonly prescribed treatment, especially in hospitals and outpatient settings, due to their broad-spectrum efficacy. Although antiviral medications, combination therapies, and vaccines are important, antibiotics maintain the largest share of this segment.
- For instance, amoxicillin remains a cornerstone in pneumonia treatment, with the World Health Organization (WHO) designating amoxicillin dispersible tablets as the first-line antibiotic for childhood pneumonia globally.
By Pathogen Type
The Streptococcus pneumoniae sub‑segment dominates the pathogen type category, accounting for 29% of the market share. This pathogen is the leading cause of bacterial pneumonia, particularly in community‑acquired cases. The strong focus on Streptococcus pneumoniae in diagnostics and vaccination programs contributes to its high share. Other pathogens such as Haemophilus influenzae, Staphylococcus aureus, and other bacterial strains make up smaller shares but still play a role in specific patient populations or healthcare settings, contributing to the overall market diversity.
- For instance, Diagnostic advances for Haemophilus influenzae include rapid molecular assays like MCDA-LFB, which enable sensitive and specific detection of this pathogen in clinical samples, supporting tailored treatment approaches.
By End-user
Hospitals are the dominant sub‑segment in the end‑user category, holding 49.5% of the market share. Hospitals are the primary setting for the diagnosis and treatment of bacterial pneumonia, especially severe cases that require inpatient care and advanced diagnostics like PCR and multiplex testing. The high volume of pneumonia cases in hospitals, coupled with the complexity of managing severe bacterial infections, underpins their leading share. Other end‑users, such as diagnostic laboratories, outpatient care centers, and home care settings, follow, but hospitals remain the most crucial segment due to the acute care demand.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Incidence and High Disease Burden
The global burden of bacterial pneumonia drives demand for diagnostics, treatments and preventive measures within the market. The increasing incidence of lower‑respiratory infections and related hospitalisations underscores urgent clinical need, presenting a strong growth foundation. A heightened focus on vulnerable populations such as older adults, children and immunocompromised patients further elevates market size and expansion. This driver compels stakeholders to allocate resources toward product development and market penetration, creating sustained momentum for therapies, vaccines and supportive diagnostics. In effect, the high disease burden shapes the strategic priorities of industry, clinical practice and public‑health investment in bacterial pneumonia.
- For instance, Merck’s CAPVAXIVE, a 21-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine, is designed specifically for adults and covers serotypes responsible for about 84% of invasive pneumococcal disease in adults aged 50 and older, demonstrating robust immune responses across diverse adult populations in Phase 3 trials.
Escalating Antibiotic Resistance
The escalation of antibiotic‑resistant bacterial strains constitutes a powerful growth driver in the bacterial pneumonia market. As standard therapies become less effective, demand rises for next‑generation antimicrobials, combination regimens and adjunctive therapies capable of addressing resistant pathogens. This dynamic motivates pharmaceutical and biotech players to invest in research‑and‑development, licensing and collaboration to bring novel solutions to market. Regulatory and payer frameworks increasingly emphasise stewardship and innovation, which amplifies the commercial potential of new treatments. Consequently, resistance pressures not only create clinical urgency but also reshape market structure and segment growth in bacterial pneumonia.
- For instance, Wockhardt developed nafithromycin, India’s first indigenously developed antibiotic for drug-resistant community-acquired bacterial pneumonia, with a 96.7% clinical cure rate and higher lung exposure than existing drugs like azithromycin.
Advancements in Diagnostics and Vaccines
Advancements in diagnostic technologies and expanded vaccination programmes propel growth in the bacterial pneumonia market. Rapid molecular tests, point‑of‑care platforms and multiplex pathogen panels enhance early detection, appropriate therapy selection and improved outcomes. Meanwhile, broader immunisation efforts targeting key pathogens—such as Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae—reduce incidence and shift prophylaxis strategies. Together these forces stimulate provider adoption, reimbursement development and public‑health investment. As diagnostics become faster and more accurate, and as vaccines achieve wider uptake across age‑groups, the bacterial pneumonia market gains structural support for expanded treatment and prevention opportunities.
Key Trend & Opportunity
Precision Medicine and Tailored Therapies
The trend toward precision medicine in bacterial pneumonia opens a compelling opportunity for tailored therapies and diagnostics. Clinicians increasingly select treatment based on the specific bacterial pathogen, antibiotic‑susceptibility profile and patient risk‑factors, which encourages development of targeted antimicrobials, monoclonal antibodies and phage therapies. This shift not only enhances efficacy and reduces broad‑spectrum antibiotic use, but also distinguishes new products in the market. Manufacturers and diagnostic developers can capitalise on this opportunity by aligning development pipelines with stratified patient segments and offering integrated solutions that combine diagnostics and therapy.
- For instance, AR-301, a monoclonal antibody targeting the alpha-toxin of Staphylococcus aureus, is currently in Phase 3 trials as an adjunctive treatment for hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia, demonstrating specificity against a key virulence factor.
Expanding Vaccination and Preventive Care
An expanding trend in vaccination and preventive care represents a strong opportunity in the bacterial pneumonia market. Governments and healthcare systems are increasingly prioritising immunisation for high‑risk cohorts (elderly, children, underlying comorbidities), which drives vaccine development, deployment and uptake. Private‑public partnerships, outreach initiatives and inclusion of new conjugate or multivalent vaccines broaden market reach. Moreover, preventive strategies reduce disease incidence and hospital admissions, shifting market dynamics toward prophylaxis and early‑intervention models. Companies that offer comprehensive prevention solutions, supported by real‑world evidence, stand to capture substantial value.
- For instance, Pfizer has supplied over one billion doses of its pneumococcal conjugate vaccine to children in lower-income countries through Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance, highlighting the impact of public-private partnerships in expanding vaccine access and preventing pneumonia in vulnerable populations.
Key Challenge
Limited Access and Healthcare Infrastructure Gaps
One major challenge in the bacterial pneumonia market is uneven access and infrastructure limitations—particularly in emerging and low‑income regions. Availability of advanced diagnostics, novel therapies and vaccines often lags where healthcare resources, reimbursement systems and cold‑chain logistics are weak. These gaps inhibit market penetration, delay adoption and constrain commercial expansion. In such regions, reliance on older standard treatments remains common, reducing demand for innovative solutions. To succeed globally, companies must address these structural barriers, adapt offerings for lower‑resource settings and engage in value‑based delivery models.
Stringent Regulatory Approval and Antibiotic Stewardship
Another key challenge arises from stringent regulatory approval pathways, combined with antibiotic‑stewardship programmes that restrict broad‑spectrum antibiotic use. New antimicrobial agents must satisfy high thresholds for safety, efficacy and resistance‑risk mitigation, lengthening development timelines and increasing cost. Simultaneously, stewardship initiatives aim to curb overuse of antibiotics, which may reduce commercial volume for new antibiotics and force rethinking of business models. These factors heighten financial risk for developers and complicate market entry—even as clinical need grows. Navigating regulatory and policy landscapes thus presents a critical barrier for market participants in bacterial pneumonia.
Regional Analysis
North America
The North America region commands a dominant position in the global bacterial pneumonia market, holding a market share of 35.4% in 2023. This strong lead stems from well‑established healthcare infrastructure, robust R&D investment, and a high prevalence of pneumonia cases among ageing populations. Advanced diagnostics and treatment options—including novel antibiotics and vaccines are widely available, enabling rapid adoption. Regulatory support and reimbursed care further bolster market uptake. The region’s premium pricing environment and early access to innovation create a growth ecosystem that outpaces many emerging markets and reinforces North America’s leadership role.
Europe
In Europe, the bacterial pneumonia market captures a substantial share of 28.0%, reflecting the convergence of mature healthcare systems with broad immunisation programmes and preventive care initiatives. Key drivers include widespread vaccination against pneumococcal disease, strong hospital‑based care networks, and regulatory emphasis on antimicrobial stewardship. However, growth in this region is moderated by saturated markets and slower incremental diagnostics penetration compared with emerging markets. Treatment access and patient awareness remain high, yet the overall opportunity lies mainly in incremental gains, niche therapeutics for drug‑resistant infections and expanding outpatient care ecosystems.
Asia Pacific
The Asia Pacific region is on a strong growth trajectory in the bacterial pneumonia market, accounting for a market share of 22.5%. Rapid urbanisation, rising healthcare expenditure, expanding hospital infrastructure and increasing disease burden—particularly in ageing populations and emerging economies—fuel demand. Governments are enhancing immunisation coverage and improving access to diagnostics and care. While current base share remains behind North America and Europe, Asia Pacific offers the fastest growth potential due to large population size, improving insurance coverage and increased penetration of advanced therapies. This combination positions the region as a key future growth engine.
Latin America
Latin America contributes a market share of 8.3% in the bacterial pneumonia space, driven by growing awareness of respiratory disease burden and expanding public health programmes. While healthcare infrastructure improvements in countries such as Brazil and Argentina offer opportunity, challenges remain—limited access to advanced treatments, affordable diagnostics and under‑penetrated vaccination markets. Cost constraints and variable reimbursement pose hurdles. Nonetheless, rising incidence of pneumonia, increasing private healthcare penetration and government initiatives to boost immunisation and antibiotic access are strengthening the region’s market potential.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region holds the smallest market share of 5.8% for bacterial pneumonia. Constraints such as limited diagnostics infrastructure, lower immunisation rates, and constrained healthcare budgets restrict uptake of advanced therapies. However, rising urbanisation, increasing prevalence of comorbidities (e.g., HIV, malnutrition) and improved public‑sector investment in healthcare present growth headroom. International donor‑driven vaccination programmes and technology transfers are beginning to improve access. Given these structural shifts, this region represents an emerging frontier for growth albeit from a low base and with infrastructure‑driven tailwinds.
Market Segmentations:
By Treatment Type
- Antibiotics
- Antiviral medications
- Combination therapies
- Vaccines
By Pathogen Type
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Other bacterial pathogens
By End-user
- Hospitals
- Diagnostic Laboratories
- Outpatient Care Centers
- Home Care Settings
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape in the bacterial pneumonia market comprises key players such as Pfizer Inc., Merck & Co., Bayer AG, AstraZeneca PLC, GlaxoSmithKline plc, bioMérieux SA and Abbott Laboratories. These organizations maintain strong competitive positions through diversified portfolios encompassing antibiotics, conjugate vaccines and rapid diagnostics. They actively pursue research and development initiatives targeted at multi‑serotype coverage, antimicrobial resistance and point‑of‑care testing enhancements. Strategic collaborations, acquisitions and licensing deals enable them to expand geographically and strengthen pipelines. The ability to leverage global distribution networks and apply bundled diagnostic‑treatment approaches further differentiates these incumbents. Together, they create high entry barriers for newer players and set a high bar for innovation in treatment and prevention of bacterial pneumonia.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- GlaxoSmithKline (GSK)
- Bayer AG
- Becton Dickinson (BD)
- Johnson & Johnson (Janssen Pharmaceuticals)
- AstraZeneca
- Cipla
- Abbott Laboratories
- BioMérieux
- Merck & Co. (MSD outside North America)
- Bristol‑Myers Squibb
Recent Developments
- In June 2024, Merck & Co. (MSD) secured U.S. FDA approval for its 21‑valent pneumococcal vaccine Capvaxive, marking a major milestone in the fight against bacterial pneumonia caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- In April 2024, Pfizer Inc. and AbbVie Inc. gained European Commission approval for the antibiotic combination Emblaveo (aztreonam/avibactam), intended to treat hospital‑acquired pneumonia including cases caused by multidrug‑resistant organisms.
- In March 2024, CARB‑X launched a new funding solicitation to support early‑stage development of diagnostics for lower‑respiratory tract infections including bacterial pneumonia, advancing the pipeline for novel detection technologies.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Treatment Type, Pathogen Type, End User and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Demand for next‑generation antibiotics will accelerate as multi‑drug resistant bacterial strains emerge, prompting pharmaceutical firms to invest heavily in novel antimicrobial pipelines.
- Increased vaccination coverage for key pathogens will shift market dynamics toward prevention, reducing overall disease incidence while expanding immunisation‑programme opportunities.
- Rapid molecular diagnostics and point‑of‑care testing will become standard of care, enabling faster pathogen identification and guiding targeted therapy, thereby boosting diagnostic segment growth.
- Growth in emerging regions particularly Asia‑Pacific and Latin America will outpace mature markets as healthcare infrastructure expands, access improves and public‑health investment increases.
- Healthcare systems will move from reactive treatment toward preventive and early‑intervention models, emphasising outpatient care, home‑based monitoring and telehealth‑enabled management.
- Public‑private partnerships and global funding mechanisms will support large‑scale immunisation and awareness campaigns, facilitating broader market penetration in underserved regions.
- Precision medicine approaches including pathogen‑specific therapies and immunomodulators will gain traction, enabling differentiated product offerings and higher clinical efficacy.
- Cost‑pressure and antimicrobial‑stewardship programmes will force companies to adopt value‑based pricing and outcome‑linked contracts, reshaping commercial models across the value chain.
- Supply chain resilience, cold‑chain logistics and access to remote‑area healthcare will become strategic priorities for companies seeking to scale in low‑resource settings.
- Regulatory agencies will increasingly prioritise incentives for antibiotic innovation and novel vaccine approvals, shortening time‑to‑market and stimulating investment in underserved bacterial pneumonia segments.




