Market Overview
The Biomethane Biogas market reached USD 14.23 billion in 2024. The market is expected to increase to USD 24.23 billion by 2032. The industry will expand at a CAGR of 6.88% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Biomethane Biogas Market Size 2024 |
USD 14.23 billion |
| Biomethane Biogas Market, CAGR |
6.88% |
| Biomethane Biogas Market Size 2032 |
USD 24.23 billion |
The Biomethane Biogas market is led by major players such as ENGIE SA, Veolia Environnement SA, EnviTec Biogas AG, Air Liquide, Bright Renewables, Wärtsilä Corporation, Schmack Biogas GmbH, Ameresco Inc., Xebec Adsorption Inc., and Future Biogas Ltd. These companies expand production capacity, invest in advanced upgrading technologies, and secure long-term supply agreements for renewable natural gas. Europe leads the global market with a 41% share, driven by strong policy support, mature waste-to-energy infrastructure, and large-scale biomethane grid injection projects. North America follows with a growing network of renewable natural gas facilities supported by transport decarbonization initiatives.
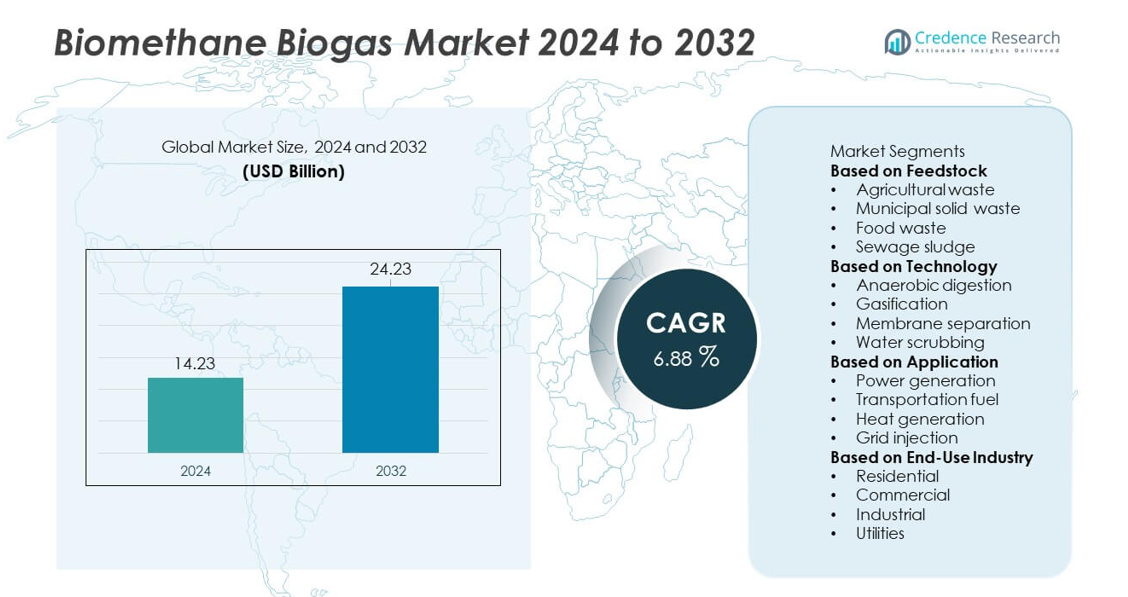
Market Insights
- The Biomethane Biogas market reached USD 14.23 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit USD 24.23 billion by 2032 at a CAGR of 6.88%, supported by strong demand for renewable energy solutions.
- Key growth drivers include rising decarbonization targets, expansion of waste-to-energy programs, and strong adoption of agricultural waste feedstock, which leads the segment with a 42% share due to high availability and lower processing costs.
- Trends highlight rapid upgrades in membrane separation and water scrubbing technologies, along with increasing biomethane use in power generation, which dominates applications with a 38% share.
- Competitive activity intensifies as major players expand production capacity and invest in high-purity upgrading systems to strengthen renewable natural gas supply across industrial and transport sectors.
- Europe dominates regional demand with a 41% share, followed by North America at 34%, driven by strong grid-injection projects and supportive renewable gas policies that encourage wider biomethane deployment.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Feedstock
Agricultural waste leads this segment with a 42% share, supported by strong availability of crop residues and wide adoption in rural and industrial biogas facilities. This feedstock delivers consistent methane output and lower processing costs, which encourages developers to expand farm-based digester installations. Municipal solid waste grows steadily due to rising waste-to-energy projects, while food waste adoption increases through organized collection systems. Sewage sludge demand also rises as utilities upgrade digestion capacity. Supportive waste management policies strengthen agricultural waste leadership in global biomethane production.
- For instance, Waga Energy supplies high-efficiency WAGABOX® units for upgrading landfill gas into grid-quality biomethane (Renewable Natural Gas). Waga Energy’s technology uses a unique heating, cooling, and distillation process to achieve nearly pure methane from the raw landfill gas.
By Technology
Anaerobic digestion dominates the technology segment with a 57% share, driven by its high conversion efficiency and flexibility across diverse organic feedstocks. This method reduces operational expenses and enables scalable deployment, making it the preferred choice for agricultural, municipal, and industrial plants. Gasification adoption rises as industries seek cleaner syngas pathways, while membrane separation and water scrubbing gain traction for high-purity biomethane upgrading. Strong investment in renewable natural gas keeps anaerobic digestion at the forefront of technology selection.
- For instance, EnviTec Biogas deployed a modular AD system in Germany that processes 35,000 tons of feedstock annually, while its membrane upgrading unit delivers 700 Nm³ of biomethane per hour using a three-stage separation system.
By Application
Power generation holds the leading position with a 38% share, supported by growing demand for renewable electricity and expanded deployment of combined heat and power systems. This application benefits from government incentives that promote clean grid integration and reduced carbon intensity. Transportation fuel demand rises quickly as fleets shift to compressed biomethane, while heat generation gains adoption in industries seeking low-carbon thermal solutions. Grid injection expands with upgraded gas networks, but power generation continues to dominate due to strong energy security and decarbonization priorities.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Focus on Renewable Energy and Decarbonization
Global decarbonization goals increase demand for biomethane as industries shift away from fossil fuels. Governments introduce incentives such as feed-in tariffs, carbon credits, and renewable energy mandates to support large-scale biomethane deployment. Utilities integrate biomethane into power grids to lower carbon intensity, while industrial users adopt it for sustainable heat generation. This shift accelerates investments in digestion and upgrading plants across regions. Strong climate commitments position biomethane as a reliable renewable fuel that supports long-term emission reduction strategies.
- For instance, Air Liquide operates a biomethane plant in Delavan, Wisconsin, which became operational in 2022 and injects upgraded biomethane into the local natural gas grid.
Expanding Waste-to-Energy Projects
Municipalities strengthen waste-to-energy programs to manage rising organic waste and reduce landfill pressure. Cities adopt structured waste segregation and collection systems, improving feedstock supply for digestion facilities. Agricultural and food processing industries convert residues into biomethane to reduce disposal costs and generate clean energy. Landfill diversion policies and circular waste mandates further enhance project viability. This expansion accelerates the development of new biomethane plants across urban, agricultural, and industrial centers.
- For instance, Veolia utilizes various anaerobic digestion systems and upgrading technologies, such as its MemGas™ membrane separation process which can achieve high purification efficiencies of up to 99.5% methane purity, to convert organic waste and sewage sludge into biomethane.
Growing Adoption in Transportation and Industrial Uses
Transport fleets shift toward biomethane as a cleaner and more economical alternative to diesel, especially for buses, logistics trucks, and municipal vehicles. Fuel providers expand compressed biomethane refueling stations to support fleet transitions. Industrial users adopt biomethane for boilers and process heat to meet sustainability targets. This adoption diversifies demand and strengthens biomethane’s presence across mobility and industrial sectors. The shift bolsters long-term consumption and supports market expansion.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Advancements in Biogas Upgrading Technologies
Modern upgrading systems such as membrane separation, pressure swing adsorption, and water scrubbing deliver higher purity biomethane with better efficiency. These technologies reduce operating costs, increase methane recovery, and enable modular plant development in farms and municipal units. Manufacturers design compact upgrading units to simplify maintenance and improve plant adaptability. High-purity biomethane supports broader use across transport, power generation, and pipeline injection. Technological progress creates strong opportunities for scalable renewable gas production.
- For instance, Xebec Adsorption has installed numerous biogas upgrading systems in Canada and globally, utilizing both membrane and pressure swing adsorption (PSA) technologies to produce renewable natural gas (RNG).
Integration of Biomethane into Existing Gas Infrastructure
Utilities expand renewable gas infrastructure to support biomethane injection into existing natural gas networks. Pipeline blending improves distribution efficiency and increases access for industrial, commercial, and residential users. Investments in monitoring systems, injection points, and pressure control units enhance supply reliability. End-users benefit from lower carbon intensity without altering existing equipment. This integration supports large-scale adoption and strengthens biomethane’s role in national energy systems.
- For instance, ENGIE connected a biomethane plant in Hauts-de-France to the regional grid with an injection capacity of 300 Nm³ per hour, supported by an automated odorization and pressure-regulation skid capable of handling inlet pressures up to 67 bar for safe pipeline blending.
Key Challenges
High Initial Capital and Operating Costs
Biomethane projects require substantial investment in digestion systems, upgrading units, and grid-connection infrastructure. Smaller developers face financing barriers due to high equipment and installation costs. Operations become more expensive in areas lacking efficient waste collection or stable feedstock supply. Maintenance requirements and regulatory compliance add further financial pressure. These cost burdens slow project rollout and reduce participation from small and mid-scale producers.
Feedstock Availability and Supply Chain Constraints
Reliable feedstock supply remains challenging due to seasonal agricultural residues, inconsistent waste segregation, and competing biomass uses. Municipal waste systems often lack strong organic collection networks, reducing feedstock consistency for plants. Transportation and storage remain costly, particularly in rural or distant regions. Irregular feedstock availability reduces methane yields and disrupts plant operations. These constraints limit large-scale biomethane production and hinder expansion in new regions.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds a 34% share driven by strong renewable energy targets, supportive incentives, and rapid expansion of renewable natural gas projects. The United States leads growth with increasing deployment of anaerobic digestion units across farms, wastewater plants, and food processing facilities. Canada strengthens biomethane integration through utility-driven procurement programs and carbon reduction policies. Growing demand for low-carbon transportation fuel accelerates investment in compressed biomethane stations. Waste management reforms and corporate sustainability commitments further support market penetration. Expansion of grid-injection capacity and rising interest from industrial users reinforce regional growth momentum.
Europe
Europe accounts for a 41% share, supported by strict emission regulations, advanced waste-to-energy policies, and strong adoption of circular economy frameworks. Countries such as Germany, France, Italy, and the Netherlands expand biomethane injection into national gas grids and lead in large-scale upgrading facilities. The region benefits from mature feedstock collection systems and strong collaboration between utilities, municipalities, and agricultural cooperatives. Growth in renewable transportation fuels, especially bio-CNG and bio-LNG, further boosts demand. EU-wide decarbonization goals and long-term renewable gas strategies ensure stable investment and sustained market leadership.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific holds a 16% share, driven by rising energy demand, expanding waste-to-energy infrastructure, and supportive government programs for rural biogas development. China leads growth through large agricultural waste conversion projects, while India accelerates adoption under national biogas and clean fuel initiatives. Southeast Asian countries invest in converting food waste and palm residues into biomethane, improving energy security. Industrial clusters increasingly adopt renewable gas to reduce carbon emissions. Growing urbanization and pressure to improve waste management systems fuel wider project development across the region, strengthening market potential.
Latin America
Latin America captures a 6% share supported by expanding agricultural and livestock waste conversion projects. Brazil leads with increasing biomethane production for transport and industrial use, backed by strong bioenergy policies. Mexico and Chile invest in municipal waste digestion systems to support clean energy targets. Growing interest from the transport sector drives adoption of biomethane-fuelled fleets in select cities. Agricultural cooperatives deploy digester units to reduce waste disposal costs and generate additional revenue. However, limited infrastructure and financing challenges slow large-scale adoption across several countries.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East and Africa region holds a 3% share, driven by gradual adoption of waste-to-energy programs and rising interest in renewable gas solutions. Gulf countries explore biomethane potential through municipal waste and sewage treatment projects, supporting diversification beyond fossil fuels. South Africa and Kenya increase investment in agricultural biogas plants to improve rural energy access. Industrial clusters also evaluate biomethane for low-carbon process heat. Despite strong resource availability, limited upgrading infrastructure and policy gaps restrain faster growth. Ongoing sustainability initiatives are expected to support steady project development in the coming years.
Market Segmentations:
By Feedstock
- Agricultural waste
- Municipal solid waste
- Food waste
- Sewage sludge
By Technology
- Anaerobic digestion
- Gasification
- Membrane separation
- Water scrubbing
By Application
- Power generation
- Transportation fuel
- Heat generation
- Grid injection
By End-Use Industry
- Residential
- Commercial
- Industrial
- Utilities
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape features major players such as ENGIE SA, Veolia Environnement SA, EnviTec Biogas AG, Air Liquide, Bright Renewables, Wärtsilä Corporation, Schmack Biogas GmbH, Ameresco Inc., Xebec Adsorption Inc., and Future Biogas Ltd. Companies focus on expanding biomethane production capacity through new digestion plants, advanced upgrading systems, and strategic partnerships with utilities and agricultural operators. Technology providers strengthen their portfolios with high-efficiency membrane separation, water scrubbing, and pressure swing adsorption solutions to improve methane purity and project economics. Several operators invest in long-term supply agreements for renewable natural gas to serve transport fleets and industrial users. Mergers, acquisitions, and joint ventures support market expansion across Europe, North America, and Asia Pacific. Rising emphasis on decarbonization and waste-to-energy integration drives companies to enhance operational efficiency, secure feedstock supply chains, and increase grid injection capabilities. This competitive environment encourages continuous innovation and broader adoption of biomethane solutions.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- ENGIE SA
- Veolia Environnement SA
- EnviTec Biogas AG
- Air Liquide
- Bright Renewables
- Wärtsilä Corporation
- Schmack Biogas GmbH
- Ameresco Inc.
- Xebec Adsorption Inc.
- Future Biogas Ltd.
Recent Developments
- In October 2025, Wärtsilä Corporation (via Wärtsilä Gas Solutions) won a contract to build a high-capacity biogas upgrading plant in Denmark for the renewable-energy firm Bigadan AS.
- In October 2025, EnviTec Biogas AG announced it is entering its 23rd financial year confident. The firm plans to expand into additional European markets beyond existing operations.
- In April 2024, ENGIE SA acquired two biomethane-production sites in the Netherlands to expand its green-gas capacity in Europe
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Feedstock, Technology, Application, End-Use Industry and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Demand for biomethane will rise as countries strengthen long-term decarbonization plans.
- Adoption in heavy-duty transportation will expand due to cleaner fuel requirements.
- Grid injection capacity will grow as utilities upgrade renewable gas infrastructure.
- Advanced upgrading technologies will increase methane purity and reduce operating costs.
- Agricultural and municipal waste projects will scale as circular economy policies tighten.
- Industrial users will shift to biomethane for low-carbon heat and process energy.
- Emerging markets will invest more in rural biogas and waste-to-energy systems.
- Partnerships between utilities, technology firms, and waste operators will accelerate project development.
- Digital monitoring solutions will enhance plant efficiency and boost long-term reliability.
- Government incentives and carbon credit programs will continue to support large-scale biomethane expansion.




