Market Overview
The Satellite and Space market reached USD 334.83 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 615.17 billion by 2032, reflecting a CAGR of 7.9% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Satellite and Space market Size 2024 |
USD 334.83 billion |
| Satellite and Space market, CAGR |
7.9% |
| Satellite and Space market Size 2032 |
USD 615.17 billion |
The satellite and space market is driven by leading players such as SpaceX, Airbus Defence and Space, Lockheed Martin Corporation, Boeing Defense, Space & Security, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Thales Alenia Space, Maxar Technologies, Blue Origin, CASC, and ISRO, all of which expand capabilities through advanced satellite manufacturing, high-throughput communication systems, and reliable launch services. These companies invest in reusable rockets, large satellite constellations, and high-resolution imaging technologies to address rising global demand for broadband, navigation, and Earth observation data. Regionally, North America leads the market with 38% share, supported by strong government programs and private-sector innovation, while Asia Pacific follows with 29% share, driven by expanding national space missions and rapid digital adoption.
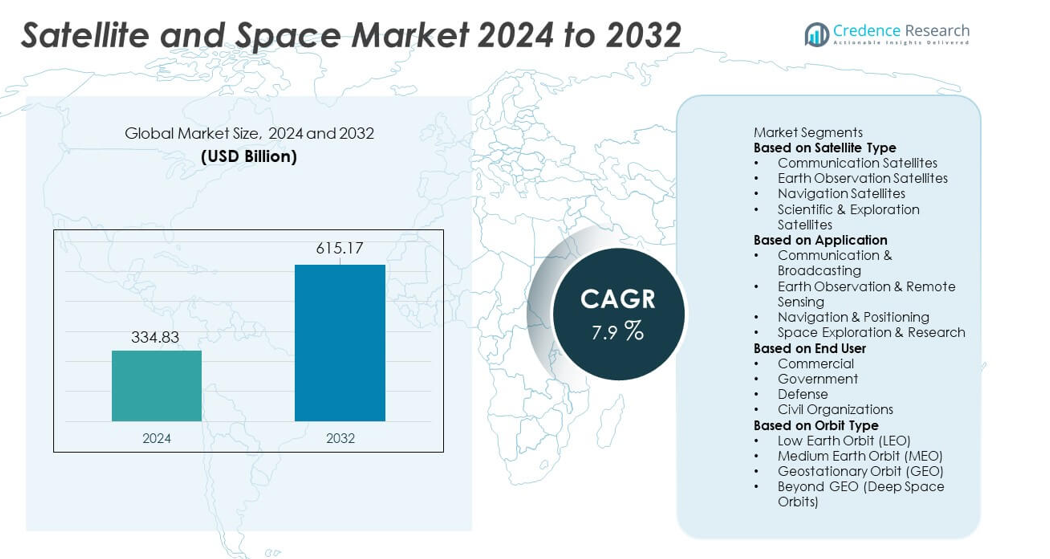
Market Insights
- The Satellite and Space market reached USD 334.83 billion in 2024 and will grow at a CAGR of 7.9% through 2032, supported by rising demand for connectivity and advanced satellite systems.
- Key drivers include growing investments in communication satellites, expanding Earth observation needs, and increasing government funding for national security, climate monitoring, and deep-space missions.
- Major trends include rapid growth of LEO mega-constellations, advancements in reusable launch vehicles, and rising commercial participation in satellite manufacturing, broadband services, and space exploration programs.
- Competitive activity intensifies as players such as SpaceX, Airbus, Lockheed Martin, Thales Alenia Space, and Maxar Technologies invest in high-throughput satellites, imaging technologies, and cost-efficient launch solutions.
- Regionally, North America leads with 38% share, followed by Asia Pacific at 29% and Europe at 27%. Segment-wise, communication satellites dominate with 44% share, while communication and broadcasting applications hold 41%, and the commercial end-user segment accounts for 48% across the global market.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Satellite Type
Communication satellites lead the segment with 44% share, driven by rising demand for broadband connectivity, growing adoption of IoT networks, and expanding use of high-throughput satellites for commercial and government communication needs. These satellites support data transmission, broadcasting, and real-time communication across remote and underserved regions. Earth observation satellites grow steadily due to increasing applications in agriculture, climate monitoring, and disaster management, while navigation satellites strengthen global positioning services. Scientific and exploration satellites continue to support deep-space missions and research programs. Continuous investment in advanced payloads and low-latency communication systems sustains the dominance of communication satellites.
- For instance, SpaceX boosted satellite capacity through Starlink Gen2, which carries approximately 96 Gbps of bandwidth per V2 Mini satellite and uses advanced phased-array antennas.
By Application
Communication and broadcasting dominate with 41% share, supported by strong demand for satellite TV, broadband services, secure communication networks, and mobility-based connectivity for aviation and maritime sectors. The shift toward high-speed satellite internet and global expansion of direct-to-home services drives steady adoption. Earth observation and remote sensing applications rise due to their use in defense surveillance, environmental monitoring, and commercial analytics. Navigation and positioning remain vital for transportation, autonomous systems, and precision mapping. Space exploration and research gain momentum as agencies and private companies invest in lunar missions and deep-space programs, broadening long-term growth opportunities.
- For instance, Maxar strengthened the remote sensing segment with its WorldView Legion satellites, designed to capture up to 15 revisits per day over key areas using 30 cm-class sensors.
By End User
The commercial segment holds the largest share at 48%, driven by rising demand for satellite broadband, imaging services, navigation support, and data-driven commercial applications. Private companies invest heavily in constellation launches, reusable rockets, and satellite-as-a-service models that expand accessibility. Government agencies remain key users for weather forecasting, public communication, and national space programs. Defense users rely on satellites for surveillance, secure communication, and navigation accuracy, contributing to steady procurement cycles. Civil organizations adopt satellite services for environmental protection, disaster response, and scientific research. Growing public–private partnerships and expanding commercial investments continue to reinforce the leadership of the commercial segment.
Key Growth Driver
Rising Demand for Global Connectivity
Growing demand for high-speed connectivity fuels strong adoption of communication satellites, especially in underserved and remote regions. Broadband expansion, 5G backhaul support, and rising IoT device integration increase the need for reliable satellite networks. Companies invest in high-throughput and low-earth-orbit constellations to enhance data capacity and reduce latency. Aviation, maritime, and mobility sectors depend on satellite communication for continuous coverage. As digital services expand and connectivity becomes essential for economic growth, satellite networks play a central role in bridging infrastructure gaps and meeting global communication needs.
- For instance, SES strengthened global connectivity with its O3b mPOWER constellation, deploying satellites capable of delivering up to 10,000 Mbps per beam.
Expansion of Earth Observation and Data Analytics
Earth observation satellites gain momentum as governments and industries rely on high-resolution imaging for agriculture, environmental monitoring, disaster response, and defense applications. Increased demand for climate intelligence, weather forecasting, and resource mapping drives the deployment of advanced remote-sensing satellites. Commercial users adopt satellite analytics for logistics, energy management, and urban planning. Technological advancements in synthetic aperture radar, hyperspectral imaging, and cloud-based analytics enhance data accuracy and real-time insights. As reliance on space-based intelligence rises, the Earth observation segment becomes a key driver of market growth.
- For instance, Planet Labs expanded monitoring capabilities with more than 200 Dove satellites capturing up to 1.2 million sq km of imagery daily at 3–5 meter resolution.
Growth of Space Exploration and Commercial Launch Services
Space exploration accelerates with growing investments in lunar missions, deep-space research, and spacecraft development. Commercial launch providers expand reusable rocket programs to reduce launch costs and increase mission frequency. Governments collaborate with private companies to advance exploration capabilities and support scientific missions. Rising interest in asteroid mining, space tourism, and long-term space habitats boosts demand for launch services and spacecraft manufacturing. As space becomes more accessible, exploration initiatives create significant opportunities for innovation, partnerships, and market expansion across multiple segments.
Key Trend & Opportunity
Rise of Mega-Constellations and Low-Earth-Orbit Systems
Mega-constellations in low-earth orbit create new opportunities for global broadband coverage, low-latency communication, and large-scale IoT integration. Companies invest in thousands of small satellites to deliver seamless internet access and support digital transformation across industries. These constellations reduce dependency on traditional geostationary systems and enable new commercial services such as autonomous vehicle support and remote industrial monitoring. As deployment costs decline and manufacturing scales, LEO-based networks reshape the competitive landscape and present strong long-term growth opportunities.
- For instance, Amazon’s Project Kuiper advanced constellation deployment by producing satellites using automated lines capable of assembling up to 5 satellites per day at peak capacity, each supporting 100 Gbps bandwidth per optical inter-satellite link.
Increased Commercialization and Private Sector Participation
Commercial players increasingly dominate satellite manufacturing, launch services, and data solutions, driving innovation and reducing operational costs. Private companies introduce flexible satellite platforms, reusable rockets, and satellite-as-a-service models that expand accessibility for businesses and governments. Venture capital investment supports startups developing navigation systems, imaging technologies, and space-based communication solutions. As commercialization accelerates, collaboration between public and private entities creates new opportunities in exploration, defense modernization, and global connectivity services.
- For instance, Rocket Lab improved commercial launch access by flying more than 70 Electron missions with payload capacities reaching 320 kg per launch.
Key Challenge
High Launch Costs and Capital-Intensive Infrastructure
The satellite and space market faces high financial barriers due to expensive launch operations, manufacturing costs, and ground infrastructure requirements. Despite advancements in reusable rockets, many small and emerging players struggle to enter the market. Long development cycles, technical risks, and high insurance costs further elevate operational challenges. These financial pressures limit scalability and slow expansion for companies that lack substantial investment backing. Managing cost efficiency while maintaining performance and reliability remains a core challenge.
Space Debris and Regulatory Constraints
Increasing satellite deployments create rising concerns about space debris, orbital congestion, and collision risks. Regulatory bodies impose strict guidelines for satellite disposal, orbital management, and spectrum allocation, increasing compliance burdens for operators. Coordination across nations remains complex, slowing deployment timelines. Debris-related risks threaten operational continuity and raise long-term sustainability concerns for both commercial and government missions. As space activity accelerates, balancing innovation with regulatory and environmental safeguards becomes a fundamental challenge for the industry.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds 38% share of the satellite and space market, driven by strong government funding, advanced space programs, and high commercial participation. The United States leads with extensive investments in satellite communication, national security systems, Earth observation projects, and deep-space exploration missions. Major aerospace companies and launch service providers expand LEO constellations, reusable rockets, and satellite-based broadband networks. Growing demand for defense surveillance, climate monitoring, and high-speed connectivity further strengthens regional dominance. Canada contributes through remote sensing programs and communication satellite development. Strong technological capabilities and space innovation ecosystems maintain North America’s leadership.
Europe
Europe accounts for 27% share, supported by strong institutional programs, collaborative research initiatives, and expanding commercial satellite activities. The European Space Agency (ESA) invests in Earth observation, navigation, and scientific missions that enhance regional technological strength. Countries such as Germany, France, and the United Kingdom lead satellite manufacturing, launch vehicle development, and advanced remote-sensing capabilities. Growing interest in sustainable space operations and regulatory frameworks strengthens regional competitiveness. Commercial players expand services in broadband, imaging, and navigation systems. Europe’s combined public–private investments and focus on strategic autonomy continue to drive stable growth in the satellite and space sector.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific holds 29% share, driven by rapid satellite deployment, strong government initiatives, and growing commercial launch activity. China and India lead the region with ambitious space programs, expanding launch capabilities, and large-scale satellite constellations supporting communication, navigation, and imaging. Japan and South Korea contribute through advanced R&D programs and commercial satellite solutions. Rising demand for broadband connectivity, disaster management tools, and agricultural monitoring accelerates adoption. Increasing investment from private companies strengthens innovation and manufacturing capacity. With large populations and fast-growing digital economies, Asia Pacific remains one of the most dynamic regions in the satellite and space market.
Latin America
Latin America captures 4% share, supported by rising demand for satellite broadband, remote sensing, and national security applications. Countries such as Brazil, Argentina, and Mexico expand satellite programs to strengthen communication networks and improve rural connectivity. Governments invest in Earth observation systems for agriculture, environmental monitoring, and climate risk management. Growing partnerships with global space agencies and private companies enhance regional capabilities. Despite budget limitations and slower adoption compared to major regions, increasing digital transformation and infrastructure needs continue to support stable market growth across Latin America.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East and Africa hold 2% share, driven by growing national space initiatives, rising communication needs, and expanding satellite-based services. Gulf countries such as the UAE and Saudi Arabia invest heavily in satellite manufacturing, space exploration missions, and geospatial intelligence. Africa shows increasing adoption of satellite broadband and Earth observation tools to support agriculture, disaster response, and connectivity in remote areas. Regional governments collaborate with international space agencies to develop local capabilities. Although infrastructure challenges persist, rising digitalization and strategic national programs support long-term market development.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Market Segmentations:
By Satellite Type
- Communication Satellites
- Earth Observation Satellites
- Navigation Satellites
- Scientific & Exploration Satellites
By Application
- Communication & Broadcasting
- Earth Observation & Remote Sensing
- Navigation & Positioning
- Space Exploration & Research
By End User
- Commercial
- Government
- Defense
- Civil Organizations
By Orbit Type
- Low Earth Orbit (LEO)
- Medium Earth Orbit (MEO)
- Geostationary Orbit (GEO)
- Beyond GEO (Deep Space Orbits)
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
Competitive landscape analysis shows a strong presence of major players such as SpaceX, Airbus Defence and Space, Lockheed Martin Corporation, Boeing Defense, Space & Security, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Thales Alenia Space, Maxar Technologies, Blue Origin, CASC, and ISRO. These organizations strengthen the market through advanced satellite manufacturing, high-frequency launch capabilities, and expanding involvement in Earth observation, communication networks, and space exploration missions. Leading companies invest heavily in reusable launch systems, next-generation satellite constellations, and high-throughput communication payloads to improve performance and reduce operational costs. Public–private partnerships support research, deep-space missions, and strategic national programs. Commercial players increasingly adopt satellite-as-a-service models, offering flexible access to imaging, broadband, and navigation solutions. Governments continue to drive demand through defense modernization, climate monitoring, and secure communication requirements. As competition intensifies, differentiation centers on launch reliability, technology innovation, constellation scaling, and sustainable space operations.
Key Player Analysis
- SpaceX
- Airbus Defence and Space
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- Boeing Defense, Space & Security
- Northrop Grumman Corporation
- Thales Alenia Space
- Maxar Technologies
- Blue Origin
- China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC)
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
Recent Developments
- In November 2025, Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) launched GSAT‑7R (CMS‑03) — India’s heaviest communication satellite — to boost naval communications.
- In November 2025, ISRO was reported to be in a major expansion phase and had plans for seven launches before the end of the financial year in March 2026.
- In November 2025, Blue Origin unveiled plans for a super-heavy variant of New Glenn, designated New Glenn 9×4, aimed to serve deep-space, lunar and large satellite constellation launches.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Satellite Type, Application, End User, Orbit Type and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Satellite constellations in low-earth orbit will expand to support global broadband coverage.
- Reusable launch vehicles will reduce mission costs and increase launch frequency.
- Earth observation services will grow as demand for climate and agricultural data rises.
- Defense agencies will increase investments in surveillance and secure communication satellites.
- Commercial players will drive innovation in small satellites and satellite-as-a-service models.
- Space exploration missions will accelerate with new lunar and deep-space programs.
- Navigation and positioning services will improve accuracy through upgraded satellite networks.
- Green propulsion and sustainable space operations will gain importance to reduce orbital debris.
- Partnerships between governments and private firms will strengthen global space capabilities.
- Advanced imaging and AI-driven satellite analytics will enhance real-time decision-making for multiple industries.




