Market Overview:
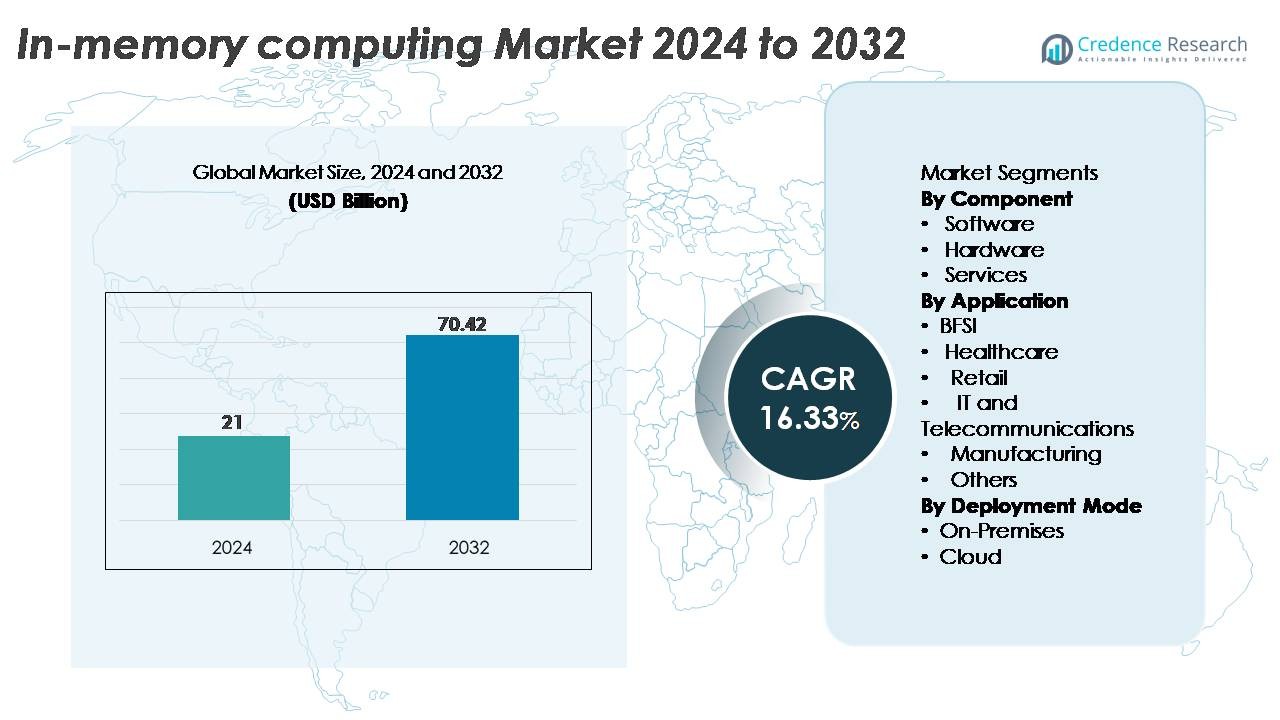
The In-Memory Computing Market was valued at USD 21 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 70.42 billion by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 16.33% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| In-Memory Computing Market Size 2024 |
USD 21 Billion |
| In-Memory Computing Market, CAGR |
16.33% |
| In-Memory Computing Market Size 2032 |
USD 70.42 Billion |
North America leads the in-memory computing market with an exact 37% market share, supported by mature digital infrastructure, rapid cloud adoption, and strong demand for real-time analytics. The competitive landscape includes major global players such as Oracle Corporation, SAP SE, Microsoft Corporation, IBM Corporation, and TIBCO Software Inc., which dominate through extensive in-memory database portfolios, cloud-native platforms, and enterprise-grade data grids. Emerging innovators like GridGain Systems, Hazelcast Inc., GigaSpaces Technologies, Altibase Corporation, and Software AG strengthen competition by offering high-performance distributed caching engines and scalable in-memory architectures. These companies focus on accelerating transaction processing, AI-driven analytics, and mission-critical workloads, driving sustained market expansion.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights:
- The in-memory computing market was valued at USD 21 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 70.42 billion by 2032, registering a CAGR of 16.33% during the forecast period.
- Strong market growth is driven by rising adoption of real-time analytics, ultra-low-latency processing, and cloud-native architectures, with software emerging as the dominant component due to its scalability and integration with enterprise data platforms.
- Key trends include expansion of AI and machine learning workloads, adoption of persistent memory technologies, and increasing deployment of IMC across BFSI, telecom, retail, and manufacturing for high-speed decisioning and automation.
- Competitive intensity grows as leading players Oracle, SAP, Microsoft, IBM, TIBCO, Hazelcast, GridGain, GigaSpaces, Altibase, and Software AG expand in-memory databases and distributed data grids while addressing restraints such as high memory costs and architectural complexity.
- Regionally, North America holds 35%, followed by Europe at 26% and Asia-Pacific at 23%, while BFSI remains the leading application segment with the highest adoption share.
 Market Segmentation Analysis:
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Component
Software represents the dominant component in the in-memory computing market, driven by rising adoption of in-memory data grids, real-time analytics engines, and distributed caching solutions across enterprise workloads. Organizations prioritize software-based platforms due to their scalability, low-latency processing, and ability to integrate with big data frameworks and cloud-native architectures. Hardware demand continues to expand with the deployment of high-capacity DRAM, persistent memory modules, and optimized processors that accelerate in-memory workloads. Services gain traction as enterprises require consulting, deployment, and performance tuning support to align in-memory implementations with digital transformation initiatives.
- For instance, Hazelcast IMDG performance can scale linearly as nodes are added, with benchmarks demonstrating throughputs of over 600,000 operations per second per node for simple put/get scenarios, enabling consistent low-latency analytics (often achieving sub-millisecond latency at the 99.99th percentile).
By Application
BFSI stands as the leading application segment, supported by the need for millisecond-level transaction processing, fraud detection, and real-time risk modeling. Banks and financial institutions increasingly rely on in-memory platforms to accelerate high-frequency computations and enhance customer experience through instant decisioning engines. Healthcare and retail also expand rapidly as providers utilize in-memory architectures for clinical data integration, e-prescription analytics, inventory forecasting, and personalized customer engagement. IT and telecommunications deploy these solutions for network optimization and billing analytics, while manufacturing leverages them for predictive maintenance and digital twin simulations.
- For instance, GigaSpaces’ in-memory platform has been deployed by major banks to process more than 100,000 trades per second while maintaining sub-10-millisecond latency during peak load.
By Deployment Mode
Cloud deployment emerges as the dominant mode due to the scalability, cost efficiency, and simplified resource provisioning offered by hyperscale cloud providers. Enterprises increasingly favor cloud-native in-memory platforms to support elastic data processing, real-time analytics, and distributed application workloads without heavy capital investment. On-premises deployment remains significant among organizations prioritizing stringent data governance, low-latency internal processing, and regulatory compliance, particularly in BFSI, healthcare, and government sectors. Hybrid adoption also influences market growth as enterprises integrate both models to balance security, performance, and scalable computing requirements.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Demand for Real-Time Analytics and Ultra-Low Latency Processing
The in-memory computing market grows significantly as enterprises shift toward real-time decision-making, demanding sub-millisecond data processing speeds. As transaction volumes surge across BFSI, e-commerce, telecom, and logistics, traditional disk-based systems fail to support the required throughput. In-memory platforms eliminate I/O bottlenecks by storing operational datasets in DRAM or persistent memory, improving query performance for fraud detection, dynamic pricing, customer personalization, and supply chain optimization. The expansion of IoT, edge analytics, and AI-driven workloads further accelerates IMC adoption as businesses increasingly rely on instantaneous insights to remain competitive. Additionally, digital-native companies prioritize architectures that support complex event processing and real-time streaming pipelines, driving demand for scalable in-memory databases and data grids. This shift reinforces the importance of IMC as a foundational technology for speed-sensitive analytics environments.
- For instance, SAP HANA’s in-memory engine has demonstrated scan throughput exceeding 1.2 million operations per second on certified appliance configurations, enabling real-time analytical workloads.
Growing Adoption of Distributed Architectures and Cloud-Native Computing
The transition toward distributed and cloud-native architectures drives the adoption of in-memory computing, enabling organizations to scale horizontally and support large, dynamic workloads. Microservices-based applications require fast-access data layers for efficient inter-service communication, making IMC a critical infrastructure element. Cloud platforms provide elastic compute and memory resources, enabling enterprises to deploy high-performance in-memory clusters without major capital expenditure. As hybrid and multi-cloud environments gain traction, IMC solutions support seamless data sharing across nodes while maintaining consistency and resilience. Distributed caching, in-memory data grids, and replicated memory architectures are increasingly prioritized in AI training, recommendation engines, and operational analytics. Enterprises adopting DevOps and container orchestration also benefit from IMC’s ability to accelerate CI/CD tasks and service interactions. This widespread modernization fuels sustained IMC demand.
- For instance, GridGain’s distributed in-memory platform has demonstrated linear scaling across clusters exceeding 100 nodes, supporting aggregated memory pools above 50 terabytes for real-time compute workloads.
Expansion of AI, Machine Learning, and Real-Time Automation Use Cases
AI and machine learning workloads increasingly depend on high-speed data access, driving demand for in-memory computing as a performance accelerator. Training models, executing inference tasks, and running data-heavy algorithms require rapid access to large in-memory datasets. IMC significantly reduces data retrieval latency, allowing AI systems to process high-frequency data streams and complex patterns in real time. Industries such as healthcare, finance, retail, and manufacturing integrate IMC to support predictive modeling, anomaly detection, robotics automation, and autonomous system operations. Real-time automation in Industry 4.0 environments benefits from IMC-powered digital twins and sensor-heavy simulations that require instant state updates. As businesses deploy AI at scale, IMC becomes essential for ensuring responsiveness, throughput, and high-volume data ingestion capabilities.
Key Trends & Opportunities:
Integration of Persistent Memory and Next-Generation Memory Technologies
A major trend reshaping the IMC landscape is the rapid adoption of persistent memory technologies that merge the durability of storage with the performance of DRAM. Solutions such as Intel Optane persistent memory, NVDIMMs, and upcoming storage-class memory architectures enable significantly larger in-memory datasets at lower cost per gigabyte. These advancements reduce system bottlenecks and improve recovery time after power interruptions by allowing data to be retained even when the system is off. Enterprises view persistent memory as an opportunity to optimize large-scale analytics, real-time processing, and high-throughput workloads without relying exclusively on expensive DRAM. As memory-centric architectures evolve, IMC providers can capitalize on delivering platforms that support hybrid memory tiers, enabling better scalability and cost efficiency.
- For instance, Intel Optane Persistent Memory modules support capacities of 128 gigabytes, 256 gigabytes, and 512 gigabytes per DIMM, enabling total memory pools exceeding 24 terabytes in multi-socket servers far beyond what DRAM-only configurations allow.
Growing Use of IMC in Edge Computing, IoT, and High-Frequency Workloads
Edge computing and IoT deployments increasingly adopt in-memory processing to support ultra-low latency requirements. With billions of connected devices generating continuous data streams, centralized systems struggle to keep pace with real-time analytics demands. By enabling computation at or near the data source, IMC reduces data transmission delays and supports mission-critical applications such as autonomous vehicles, smart manufacturing, remote diagnostics, and intelligent retail. Edge AI models benefit from rapid memory access and accelerated inference, creating opportunities for IMC vendors to introduce lightweight, scalable solutions optimized for constrained environments. The growth of 5G and distributed edge networks further enhances this opportunity by enabling high-frequency workloads that rely heavily on in-memory architectures.
- For instance, Hazelcast’s edge-optimized in-memory engine has demonstrated end-to-end processing latency below 2 milliseconds for streaming sensor workloads exceeding 400,000 operations per second across distributed nodes.
Increasing Adoption of In-Memory Databases for Digital Transformation
As organizations accelerate digital transformation, they adopt in-memory databases (IMDBs) to modernize legacy systems and improve data accessibility. IMDBs enable organizations to handle mixed workloads—transactional, analytical, and hybrid—within a single platform, supporting real-time insights and operational efficiency. Industries such as BFSI, retail, and telecommunications increasingly replace disk-based systems with IMDBs to handle rising data complexity and user expectations for instantaneous responses. This trend creates significant opportunities for IMC vendors to deliver optimized, cloud-ready, and AI-integrated in-memory database solutions.
Key Challenges:
High Infrastructure Costs and Memory Scalability Limitations
Despite its performance benefits, the high cost of DRAM and advanced memory technologies poses a major barrier to widespread IMC adoption. Organizations implementing large in-memory clusters must invest heavily in high-capacity servers, persistent memory modules, and optimized compute architectures. These expenses limit adoption among small and mid-sized enterprises with constrained budgets. Additionally, scaling memory capacity while maintaining performance and fault tolerance presents engineering challenges. Large in-memory nodes require robust redundancy mechanisms, increasing infrastructure complexity and operational costs. As data volumes expand, maintaining cost-efficient memory scaling becomes even more difficult, slowing adoption rates in cost-sensitive sectors.
Data Security Concerns and Complexity of Memory-Centric Architectures
In-memory computing environments face heightened security risks due to the volatile and centralized nature of data storage. Sensitive information residing in memory can become vulnerable if proper encryption, access control, and memory isolation mechanisms are not enforced. Implementing such safeguards increases architectural complexity and requires specialized expertise. Additionally, transitioning from disk-based to memory-centric architectures often involves major operational changes, integration challenges, and potential downtime. Organizations with legacy systems may struggle to adapt existing workflows and applications to new in-memory models. Managing real-time replication and ensuring data consistency across distributed memory nodes further complicates deployment. These challenges create adoption friction, especially in regulated industries.
Regional Analysis:
North America
North America holds the largest share of the in-memory computing market, accounting for around 35% of global revenue, driven by strong enterprise digitization and widespread adoption of real-time analytics across BFSI, retail, and healthcare sectors. The region benefits from early cloud adoption, advanced data infrastructure, and high investment in AI, machine learning, and edge analytics. Tech giants in the U.S. accelerate IMC penetration through in-memory databases, distributed caching engines, and real-time data platforms integrated into cloud-native ecosystems. The region’s focus on fraud detection, recommendation engines, and operational intelligence sustains its leadership in IMC adoption.
Europe
Europe captures approximately 26% of the IMC market, supported by rapid digital transformation across financial services, manufacturing, automotive, and telecom industries. The region’s stringent data governance and adoption of in-memory platforms for compliance analytics, risk modeling, and predictive maintenance strengthen demand. Germany, the U.K., and France lead adoption as enterprises deploy IMC for real-time supply chain visibility, industrial automation, and smart production systems. Ongoing investments in Industry 4.0 and cloud acceleration further enhance market potential. Growing interest in persistent memory and distributed in-memory architectures positions Europe as a strong, innovation-driven market.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, holding around 23% of the global IMC market, fueled by expanding digital economies in China, India, Japan, and South Korea. Rapid growth in e-commerce, fintech, telecommunications, and manufacturing drives adoption of in-memory architectures to support real-time personalization, transaction processing, and predictive automation. Cloud-first strategies and investments in AI, 5G, and IoT ecosystems significantly boost demand for IMC-enabled high-speed analytics. Regional enterprises leverage IMC to manage large-scale workloads from rising customer bases and high data velocity. Government-led digital transformation and smart city initiatives further accelerate market expansion.
Latin America
Latin America accounts for about 6% of the IMC market, with steady adoption across banking, retail, and telecommunications. Enterprises in Brazil, Mexico, and Chile increasingly deploy in-memory platforms to enhance real-time fraud detection, mobile banking performance, and customer analytics. Rising cloud adoption and digital payments drive the need for scalable, low-latency infrastructures. Although adoption lags behind mature markets due to budget constraints, IMC demand is growing as organizations modernize IT systems and embrace hybrid cloud models. The region’s expanding fintech ecosystem and digital commerce accelerate interest in IMC technologies for high-speed processing.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region represents approximately 4% of the global IMC market, with momentum building in the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa. Investments in smart cities, digital banking, government modernization, and cloud infrastructure foster IMC adoption for real-time analytics and operational decisioning. BFSI and telecommunications remain key adopters as organizations seek to improve fraud monitoring, customer engagement, and network optimization. Although overall adoption is relatively nascent, rising cloud migration and national digital transformation agendas are creating strong opportunities for IMC providers. Growing data-intensive sectors, including energy, logistics, and retail, further support regional growth.
Market Segmentations:
By Component
- Software
- Hardware
- Services
By Application
- BFSI
- Healthcare
- Retail
- IT and Telecommunications
- Manufacturing
- Others
By Deployment Mode
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape:
The in-memory computing market features a highly competitive landscape dominated by global technology providers specializing in high-performance data platforms, distributed architectures, and real-time analytics engines. Leading vendors focus on expanding their IMC capabilities through in-memory data grids, in-memory databases, persistent memory integration, and cloud-native compute acceleration. Companies strengthen portfolios through partnerships with hyperscale cloud providers to deliver scalable, low-latency platforms aligned with enterprise modernization initiatives. Innovation centers on reducing memory costs, improving horizontal scalability, and enabling hybrid memory architectures that combine DRAM with next-generation persistent memory. Competitors also emphasize security, multi-cloud interoperability, and high-availability features to meet demand from BFSI, telecom, and manufacturing industries. With enterprises increasingly adopting AI-driven analytics and real-time automation, vendors differentiate through enhanced query performance, distributed caching engines, and seamless integration with container orchestration frameworks. As the market evolves, strategic acquisitions, R&D investments, and cloud ecosystem expansion remain central to maintaining competitive advantage.
Key Player Analysis:
- GridGain Systems
- Oracle Corporation
- GigaSpaces Technologies
- Software AG
- SAP SE
- Hazelcast Inc.
- Altibase Corporation
- IBM Corporation
- Microsoft Corporation
- TIBCO Software Inc.
Recent Developments:
- In October 2025, SAP released its “SAP Cloud ERP Private 2025” package, enhancing its cloud-ERP suite with a strengthened data foundation, embedded AI and intelligent-agent capabilities to support end-to-end business processes.
- In 2025, GridGain continues to be recognized among the leading in-memory computing providers. A 2025 industry overview report cites GridGain for its open-source and enterprise-grade in-memory platforms supporting real-time analytics and distributed computing.
- In September 2023, Altibase Corporation According to public information, Altibase released version 7.3 of its hybrid in-memory database That version introduced a “hybrid partition” architecture — allowing data to reside either in memory or on disk at the partition level — along with parallel processing enhancements aimed at improving performance under mixed load conditions.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Report Coverage:
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Component, Application, Deployment mode and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook:
- In-memory computing will expand rapidly as enterprises prioritize real-time analytics and ultra-low-latency processing.
- Adoption of AI, machine learning, and automation will accelerate demand for high-speed in-memory data architectures.
- Cloud-native IMC platforms will gain prominence as organizations shift to hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
- Persistent memory and next-generation memory technologies will enhance scalability and reduce dependence on DRAM.
- BFSI, telecom, and e-commerce will continue driving IMC use for instant transaction processing and fraud detection.
- Edge computing growth will increase deployment of lightweight IMC solutions for real-time inference and IoT workloads.
- In-memory databases will replace legacy disk-based systems across digital-first enterprises.
- Vendors will focus on improving interoperability with container orchestration and microservices frameworks.
- Security enhancements and real-time encryption will become critical as more sensitive data resides in memory.
- Emerging markets will adopt IMC more rapidly as digital transformation and cloud penetration accelerate.

 Market Segmentation Analysis:
Market Segmentation Analysis:

