Market Overview
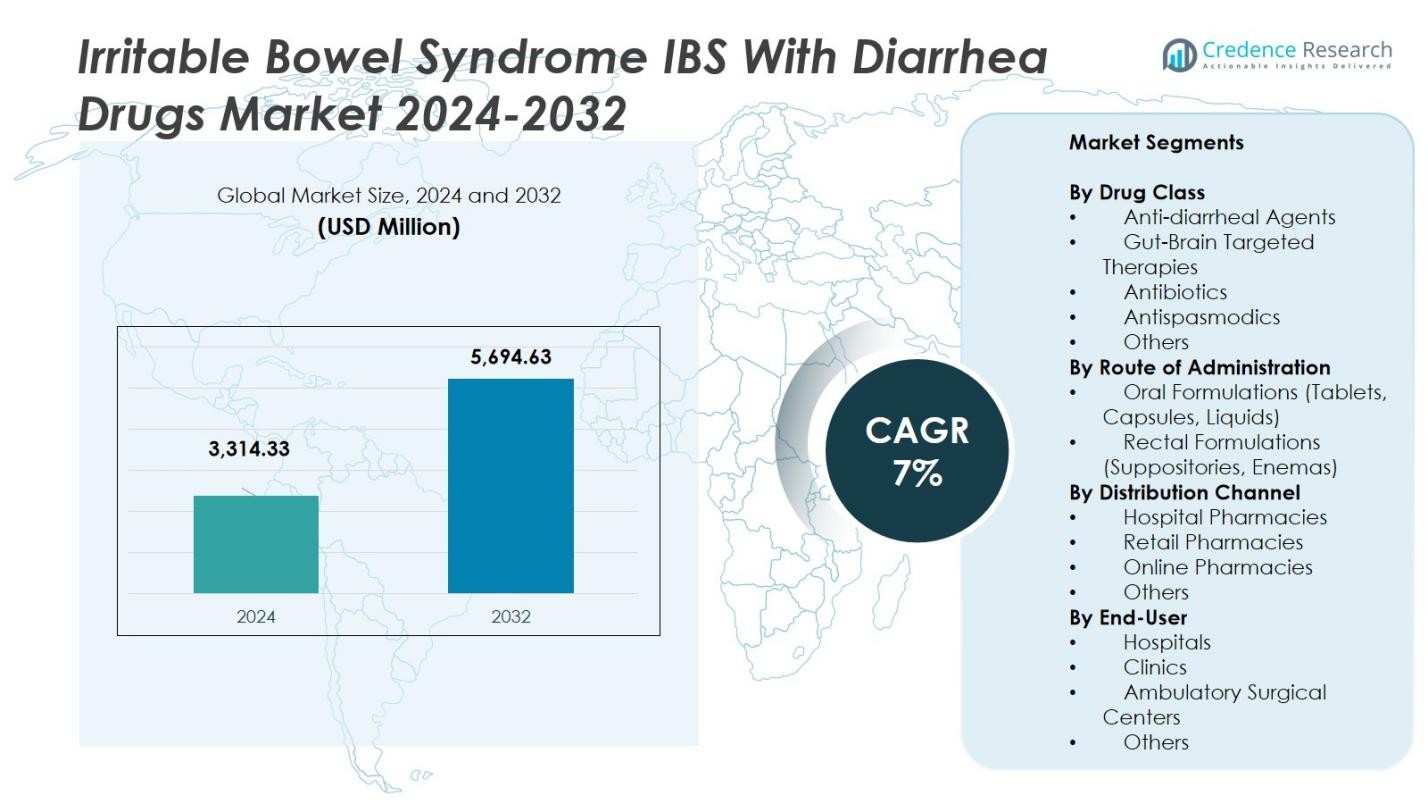
The Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) with Diarrhea Drugs Market size was valued at USD 3,314.33 Million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 5,694.63 Million by 2032, at a CAGR of 7% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) with Diarrhea Drugs Market Size 2024 |
USD 3,314.33 Million |
| Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) with Diarrhea Drugs Market, CAGR |
7% |
| Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) with Diarrhea Drugs Market Size 2032 |
USD 5,694.63 Million |
TheIrritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS with Diarrhea Drugs Market features leading players such asBausch Health Companies (Salix Pharmaceuticals), Ironwood Pharmaceuticals, Allergan (AbbVie), Sebela Pharmaceuticals, RedHill Biopharma, Ardelyx, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Mylan Pharmaceuticals, Astellas Pharma and Takeda Pharmaceutical Company. North America leads the market with a 37.5% share in 2024, driven by advanced healthcare infrastructure, high disease awareness and early therapeutic adoption. Europe follows closely, supported by strong regulatory frameworks and rising prevalence in key countries. The Asia Pacific region, growing rapidly, shows promise due to improving healthcare access, urbanisation, and increasing focus on novel therapies in markets such as China, Japan and India.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) with Diarrhea Drugs Market was valued at USD 3,314.33 Million in 2024 and is forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 7% through 2032.
- The gut‑brain targeted therapies segment holds the largest share at around 22.6%, driven by increased understanding of the gut–brain axis in IBS‑D.
- The oral formulations route dominates with over 60% share, reflecting high patient compliance and preference for tablets and capsules.
- Major companies such as Bausch Health (Salix Pharmaceuticals), Ironwood, Allergan (AbbVie) and Takeda are leading the market, though limited approved therapies and high treatment costs restrain growth.
- Regionally, North America commands 37.5% of the market, followed by Europe, while Asia‑Pacific offers strong growth potential thanks to rising healthcare access and emerging patient demand.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Drug Class
Within the drug‑class segment for the Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Diarrhea (IBS‑D) drugs market, the gut‑brain targeted therapies sub‑segment currently holds the largest share, estimated at approximately 22.6% of the total. This dominance stems from growing evidence linking the gut–brain axis to IBS‑D symptoms, and the entry of targeted agents such as mixed opioid receptor modulators which address both diarrhea and abdominal pain. The rising preference for treatments beyond mere antidiarrheals those that also relieve key functional and neurological pathways is driving this sub‑segment’s growth, while broader awareness of the gut‑brain connection in gastrointestinal disorders further accelerates adoption.
- For instance, ramosetron, a serotonin 5-HT3 antagonist, has demonstrated effectiveness in relieving global IBS symptoms, including abdominal pain and abnormal bowel habits, with favorable safety outcomes observed in multiple randomized clinical trials.
By Route of Administration
In the route‑of‑administration segment, oral formulations dominate, accounting for the majority of market value (well in excess of 60% of the total). This preference reflects the convenience, widespread physician familiarity, and strong patient compliance associated with tablets, capsules and liquids. Oral delivery enables broad outpatient treatment of IBS‑D and supports high volumes of prescriptions. The ease of administration and the ability to deliver extended‑release and controlled‑release dosage forms further support the oral sub‑segment’s dominance over less convenient routes such as suppositories or enemas, which remain niche.
- For instance, RedHill Biopharma’s BEKINDA (RHB-102) is a once-daily, bimodal extended-release oral tablet of ondansetron. It showed clinically meaningful improvement in stool consistency and abdominal pain in Phase II IBS-D studies, positioning it as a promising oral treatment with a patient-friendly dosing schedule.
By Distribution Channel
For distribution channels in the IBS‑D drugs market, the hospital pharmacies channel leads with around 44.7% share of total revenue. The dominance of hospital pharmacies is driven by the concentration of specialist gastroenterology care within hospital settings, where novel therapies are frequently initiated and monitored. These settings often facilitate specialist prescribing, diagnostic confirmation, and multidisciplinary support, making them preferred for higher‑cost or newer agents. Meanwhile, retail and online channels are growing, but hospital pharmacies maintain the largest share due to their structured care environments and ability to handle complex cases.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Prevalence of IBS-D
The increasing prevalence of IBS-D is a major driver of market growth. As lifestyle changes, stress, and dietary shifts contribute to higher diagnosis rates, more patients seek pharmaceutical treatments. This growing patient base fuels the demand for IBS-D drugs, prompting pharmaceutical companies to innovate and expand their offerings. The heightened focus on managing IBS-D symptoms effectively further accelerates market growth as healthcare providers and patients search for more targeted and efficient therapies.
- For instance, pharmaceutical companies are innovating with drugs like alosetron, a selective 5-HT3 antagonist approved specifically for IBS-D, providing targeted relief by slowing gut transit and alleviating pain.
Advancements in Targeted Therapies
Recent advancements in targeted therapies have significantly impacted the IBS-D drug market. Innovative treatments focusing on the gut-brain axis, microbiome imbalance, and neurotransmitter regulation are gaining traction. These therapies offer improved efficacy by addressing the root causes of IBS-D rather than just managing symptoms. With the increasing availability of such therapies, both patients and healthcare providers are more inclined to adopt them, leading to greater market penetration and sustained growth in the IBS-D segment.
- For instance, Rifaximin, a gut-selective antibiotic, reduces IBS-D symptoms by altering the intestinal microbiota, with documented efficacy shown in two Phase 3 clinical trials.
Improved Diagnosis and Awareness
Rising awareness among both patients and clinicians is driving growth in the IBS-D drug market. Better diagnostic tools and increased understanding of IBS-D contribute to earlier and more accurate diagnoses. With healthcare systems becoming more adept at identifying and treating IBS-D, the market sees an uptick in the prescription of effective drugs. The heightened focus on IBS-D and its management encourages both physicians and patients to actively seek therapeutic options, further promoting market expansion.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Personalised Medicine and Biomarkers
prominent trend in the IBS-D drug market is the move towards personalised medicine. The use of biomarkers and individual patient profiles to tailor treatments is gaining momentum. This approach promises higher treatment efficacy, fewer side effects, and better overall patient outcomes. By developing therapies that are customized to an individual’s specific condition, pharmaceutical companies can distinguish their products in a crowded market, creating significant opportunities for growth and innovation.
- For instance, Alosetron, a 5-HT3 antagonist approved for severe IBS-D in the US, shows higher efficacy in women with specific symptom profiles, demonstrating targeted therapy based on patient characteristics.
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Emerging markets present a significant growth opportunity for the IBS-D drug market. With increasing healthcare access and awareness in regions like Asia-Pacific, pharmaceutical companies are finding new avenues for growth. As these markets develop and patient awareness rises, the demand for effective IBS-D treatments is expected to soar. Expanding into these regions with targeted therapies and affordable options allows companies to tap into a previously underserved population, further boosting global market expansion.
- For instance, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company has also been investing heavily in personalized medicine in the region, developing innovative gastrointestinal drugs tailored to local patient needs.
Key Challenges
Limited Number of Approved Therapies
The IBS-D drug market faces challenges due to the limited number of approved therapies. Despite growing demand, relatively few treatments have been formally approved by regulatory authorities, which restricts available options. Many drugs are used off-label, causing hesitation among healthcare providers. This limited approval landscape creates barriers for both patients seeking optimal treatment and pharmaceutical companies looking to expand their product portfolios in the IBS-D segment.
High Treatment Costs and Access Barriers
The high costs of IBS-D treatments pose a significant challenge to market growth. For many patients, especially in developing regions, these costs present a substantial barrier to access. Insurance coverage and reimbursement policies also vary widely, which can limit the affordability and availability of these treatments. These economic challenges hinder widespread adoption, particularly in lower-income markets, where the cost of new therapies can impede broader market penetration and patient access.
Regional Analysis
North America
The North America region holds a dominant position in the global IBS‑D drugs market, accounting for a market share of 37.5% in 2024. This strong share is driven by advanced healthcare infrastructure, high level of disease awareness, and early adoption of novel therapeutics. The presence of major pharmaceutical players and significant investment in gastroenterology research further reinforce regional leadership. Patients in North America benefit from better access to diagnostic services and specialist care, which supports higher uptake of targeted treatment options for IBS‑D and contributes to sustained market momentum.
Europe
Europe comprises a significant portion of the IBS‑D drugs market, contributing a substantial share (though slightly below North America’s lead). The region’s growth is supported by widespread health awareness campaigns, strong regulatory frameworks and increasing healthcare spending in countries like Germany, the UK, and France. Diet and lifestyle changes among European populations are elevating the prevalence of IBS‑D, stimulating demand. Moreover, reimbursement policies in many European markets encourage treatment uptake. These combined factors enable Europe to maintain a stable and growing segment of the global IBS‑D drugs market.
Asia Pacific
The Asia Pacific region is emerging rapidly in the IBS‑D drugs market, with growth driven by increasing healthcare access, urbanisation and awareness of gastrointestinal disorders. Although its current market share is smaller than that of North America and Europe, Asia Pacific’s growth rate exceeds many mature regions. Countries such as China, Japan and India are seeing rising incidence of IBS‑D, expanding pharmaceutical infrastructure and a greater focus on novel therapies. These developments position Asia Pacific as a key growth frontier for IBS‑D drug manufacturers seeking expansion beyond established markets.
Latin America
Latin America holds a moderate share of the global IBS‑D drugs market, supported by improving healthcare systems and rising patient awareness of bowel disorders. While its market size remains smaller compared with North America and Europe, the region demonstrates potential for expansion due to increasing diagnostic capabilities and pharmaceutical penetration in countries like Brazil and Argentina. Economic constraints and variable reimbursement remain hurdles, yet the growing demand for effective IBS‑D treatments and generics presents an attractive opportunity for manufacturers targeting this region.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region has the smallest share of the global IBS‑D drugs market, reflecting limited healthcare infrastructure, low awareness of IBS‑D and constrained access to advanced therapies. Nonetheless, gradual improvements in public health spending, rising urbanisation and expanding private healthcare services are laying the foundation for future growth. Manufacturers developing cost‑effective treatment options and engaging in education campaigns may unlock latent demand. With increased investment and better diagnostics, this region could achieve higher uptake of IBS‑D therapies in the coming years.
Market Segmentations:
By Drug Class
- Anti-diarrheal Agents
- Gut-Brain Targeted Therapies
- Antibiotics
- Antispasmodics
- Others
By Route of Administration
- Oral Formulations (Tablets, Capsules, Liquids)
- Rectal Formulations (Suppositories, Enemas)
By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
- Others
By End-User
- Hospitals
- Clinics
- Ambulatory Surgical Centers
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape in the IBS‑D drugs market led by Bausch Health Companies (Salix Pharmaceuticals), Ironwood Pharmaceuticals, Allergan (AbbVie), Sebela Pharmaceuticals, RedHill Biopharma, Ardelyx, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Mylan Pharmaceuticals, Astellas Pharma and Takeda Pharmaceutical Company features both established pharma giants and agile biotech players. These companies differentiate through strategic product launches, patent protections, and licensing alliances focused on novel mechanisms such as gut‑microbiome modulation or opioid receptor targeting. Pricing strategy, clinical trial success, and formulary inclusion determine competitive positioning, with generics and off‑label alternatives adding pressure on margins. Collaboration with academic bodies and investment in pipelines help new entrants challenge incumbents, while regulatory hurdles and IP defense remain critical battlegrounds.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Bausch Health Companies (Salix Pharmaceuticals)
- Ironwood Pharmaceuticals
- Allergan (AbbVie)
- Sebela Pharmaceuticals
- RedHill Biopharma
- Ardelyx
- Alnylam Pharmaceuticals
- Mylan Pharmaceuticals
- Astellas Pharma
- Takeda Pharmaceutical Company
Recent Developments
- In February 2025, RedHill Biopharma Ltd. entered into an exclusive worldwide licensing agreement (excluding North America) with Hyloris Pharmaceuticals SA for the development and commercialization of RHB-102 (Bekinda®) for IBS-D.
- In March 2025, Zydus Lifesciences received final approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (USFDA) to manufacture generic tablets of Eluxadoline (75 mg and 100 mg) for adults with Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Diarrhea (IBS‑D).
- In February 2024, CinPhloro Pharma, a portfolio company of CinRx Pharma, dosed the first patient in the Phase 2 “enviva” study of CIN-103, a novel phloroglucinol formulation for Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Diarrhea (IBS-D) .
- In October 2023, Roche entered into a definitive agreement to acquire Telavant Holdings, Inc., a company specializing in gastrointestinal disorders. This acquisition, which includes a novel TL1A-directed antibody, strengthens Roche’s presence in the GI therapeutic space, indirectly impacting IBS-D treatment development .
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Drug Class, Route of Administration, Distribution Channel, End User and Region. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Continuous growth in the IBS‑D drugs market will result from rising diagnosis rates and increased treatment uptake.
- Innovation in therapies targeting the gut‑brain axis, microbiome modulation, and personalized medicine will reshape the competitive landscape.
- Emerging markets will see faster growth as healthcare access and awareness improve in Asia‑Pacific and Latin America.
- Healthcare providers will shift toward early intervention and preventive management strategies, boosting demand for effective treatments.
- Biotech and pharma firms will invest more heavily in clinical trials and drug pipeline development for novel IBS‑D drugs.
- Digital health tools and telemedicine will enhance patient engagement and adherence to IBS‑D treatment regimens.
- Generic entrants and biosimilars will increase market pressure on branded therapies, driving cost‑effective alternatives.
- Regulatory agencies will streamline approval pathways for new mechanisms of action, accelerating market entry of advanced therapies.
- Patient preference for oral formulations and convenient dosing will drive formulation innovation and market growth.
- Affordability and reimbursement dynamics will become critical, with companies needing strategies to ensure access in diverse economic environments.




