Market Overview
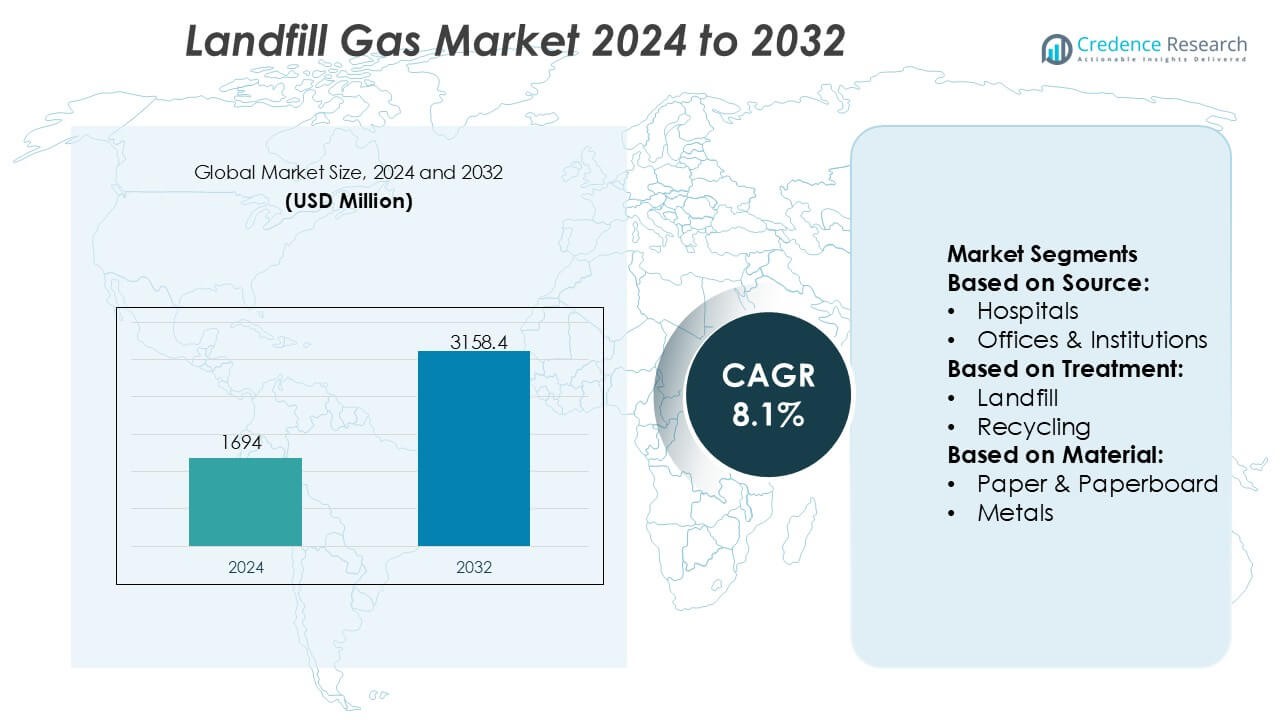
Landfill Gas Market size was valued USD 1694 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 3158.4 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 8.1% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Landfill Gas Market Size 2024 |
USD 1694 Million |
| Landfill Gas Market , CAGR |
8.1% |
| Landfill Gas Market Size 2032 |
USD 3158.4 Million |
The landfill gas market is characterized by the presence of established energy companies, midstream operators, and engineering service providers that compete through technological expertise, infrastructure integration, and project execution capabilities. These players focus on methane capture optimization, gas upgrading, and energy utilization to support power generation and renewable natural gas applications. Strategic priorities include long-term municipal contracts, expansion of gas processing capacity, and alignment with decarbonization objectives. Regionally, North America leads the landfill gas market with an exact 36% market share, driven by strict methane emission regulations, advanced landfill infrastructure, and widespread adoption of landfill gas-to-energy projects. Strong policy support and mature financing frameworks continue to reinforce the region’s leadership position.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The landfill gas market was valued at USD 1,694 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 3,158.4 million by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 8.1% due to rising methane recovery initiatives and energy utilization.
- Market growth is driven by stricter methane emission regulations, increasing municipal solid waste generation, and growing adoption of landfill gas-to-energy and renewable natural gas projects across urban waste facilities.
- Technology trends focus on advanced gas collection systems, upgrading landfill gas to pipeline-grade renewable natural gas, and integrating digital monitoring tools to improve capture efficiency and long-term operational performance.
- Competition centers on energy majors, midstream operators, and engineering firms leveraging gas processing expertise, long-term municipal contracts, and infrastructure integration to strengthen project scalability and execution capability.
- Regionally, North America leads with an exact 36% market share, while landfill-based treatment dominates by method, and food waste remains the leading material segment due to high methane generation potential.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Source
The Landfill Gas Market, by source, is primarily driven by Residential waste, which holds the dominant sub-segment with an estimated 42% market share. High population density, rapid urbanization, and consistent generation of organic household waste underpin this dominance. Residential waste streams contain a high proportion of biodegradable materials such as food scraps, paper, and yard waste, which generate methane-rich landfill gas under anaerobic conditions. Municipal solid waste collection systems are also more standardized for residential areas, improving feedstock reliability. Commercial establishments, hospitals, and offices contribute steadily, but their waste volumes and organic content remain comparatively lower.
- For instance, Centrica Business Solutions documents the deployment and operation of landfill-gas-fueled combined heat and power assets using reciprocating gas engines rated in the 1.0–3.0 MW electrical output range per unit, designed to operate on methane concentrations as low as 35 vol%.
By Treatment
By treatment, Landfill-based waste treatment emerges as the leading sub-segment, accounting for approximately 46% of the market share. The dominance stems from the widespread use of engineered sanitary landfills equipped with gas capture and control systems. These facilities enable efficient collection of methane for flaring or energy recovery, aligning with regulatory mandates to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Disposal and open dumping continue in developing regions but face regulatory pressure. Recycling, composting, anaerobic digestion, and incineration are expanding; however, landfill treatment remains central due to scalability, lower operational complexity, and existing infrastructure.
- For instance, Enterprise Products Partners operates large-scale gas gathering, compression, and processing infrastructure capable of handling gas streams with variable composition, including low-Btu methane-rich sources. Company technical filings describe the operation of more than 50,000 miles of onshore natural gas pipelines connected to processing facilities with individual plant capacities exceeding 2 billion cubic feet per day, supported by compression systems rated above 10,000 horsepower per station, enabling reliable integration of captured landfill gas into downstream treatment and utilization networks.
By Material
Based on material, Food waste represents the dominant sub-segment with an estimated 39% market share, driven by its high organic and moisture content that accelerates anaerobic decomposition and methane generation. Increasing volumes of discarded food from households, restaurants, and institutional sources significantly enhance landfill gas yield. Paper and paperboard also contribute meaningfully but decompose more slowly. Plastics, metals, and glass offer negligible gas potential and mainly act as inert components. The strong correlation between food waste volumes and methane output makes this segment the primary driver of landfill gas generation efficiency.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Regulatory Pressure to Reduce Methane Emissions
Stringent environmental regulations targeting methane emissions strongly drive the landfill gas market. Governments increasingly mandate landfill operators to install gas collection and control systems to limit greenhouse gas release. Methane’s high global warming potential has pushed regulators to enforce compliance through emission caps, monitoring requirements, and penalties for non-compliance. These policies encourage investments in gas capture, flaring, and utilization technologies. Regulatory clarity also improves project bankability, prompting municipalities and private operators to upgrade legacy landfills and integrate landfill gas recovery into long-term waste management strategies.
- For instance, ConocoPhillips has documented measurable progress in methane measurement and mitigation capabilities, reporting a methane emissions intensity of 3.2 kilograms of CO₂e per barrel of oil equivalent (kg CO₂e/BOE) as of year-end 2024, down from materially higher historical levels, supported by expanded use of aerial surveys, fixed-sensor technologies, and measurement campaigns conducted across hundreds of operational sites globally that incorporate source-level methane quantification consistent with Oil & Gas Methane Partnership (OGMP) 2.0 reporting protocols.
Growing Demand for Renewable and Low-Carbon Energy
The increasing focus on renewable energy sources supports landfill gas utilization for power generation, heat, and upgraded biomethane. Utilities and industrial users seek reliable, baseload renewable energy options that complement intermittent solar and wind sources. Landfill gas offers continuous energy output, making it attractive for grid injection and on-site energy use. Energy security concerns and decarbonization targets further strengthen demand. Incentives such as feed-in tariffs, renewable energy credits, and tax benefits improve project economics, accelerating adoption across municipal and privately operated landfill facilities.
- For instance, engineering firms specializing in environmental infrastructure have documented their role in the engineering and delivery of landfill gas–to–energy facilities. These projects typically include extensive gas collection networks involving several kilometers of horizontal and vertical piping, coupled with compression systems designed to handle significant landfill gas flow rates, sometimes exceeding 10,000 normal cubic meters per hour, to efficiently manage the site’s biogas output.
Expansion of Urban Waste Generation
Rapid urbanization and population growth significantly increase municipal solid waste volumes, expanding the feedstock base for landfill gas generation. Urban centers generate large quantities of organic waste, particularly food and paper, which enhances methane production potential. Developing economies, in particular, continue to rely on landfilling as a primary waste disposal method due to cost and infrastructure considerations. This sustained waste inflow ensures long-term gas generation, encouraging landfill operators to invest in gas capture systems to monetize waste streams while improving environmental performance.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Integration of Landfill Gas-to-Energy Projects
A key trend involves the integration of landfill gas-to-energy projects with local power and heating networks. Operators increasingly deploy combined heat and power systems to maximize energy recovery efficiency. Industrial parks, wastewater treatment plants, and district heating networks present attractive offtake opportunities. This integration improves project returns while reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Technological improvements in gas engines and turbines further enhance operational reliability, making energy recovery a central growth opportunity within the landfill gas market.
- For instance, Energy Transfer has documented growth in its RNG business where, as of end-of-2022, the company had eight renewable natural gas facilities/interconnects transporting over 5 billion cubic feet of conditioned gas into its pipeline network, demonstrating early incorporation of landfill and other biogas sources into midstream infrastructure.
Upgrading Landfill Gas to Renewable Natural Gas
The upgrading of landfill gas to renewable natural gas represents a growing opportunity. Advanced purification technologies remove impurities and carbon dioxide, enabling injection into natural gas grids or use as vehicle fuel. This trend aligns with transportation decarbonization goals and supports the development of low-carbon fuels. Renewable natural gas commands higher value compared to direct power generation, encouraging operators to invest in upgrading facilities. Expanding pipeline infrastructure and long-term supply contracts further support this opportunity.
- For instance, BP, through its acquisition and integration of Archaea Energy, has deployed modular RNG facilities that convert raw landfill gas into pipeline-ready biomethane. Archaea’s modular design RNG plant in Medora, Indiana, processes up to 3,200 cubic feet per minute (scfm) of landfill gas captured directly at a landfill site and upgrades it into RNG suitable for injection into existing natural gas infrastructure, with modular units engineered for rapid deployment and replication across multiple sites.
Key Challenges
High Capital and Maintenance Costs
The landfill gas market faces challenges related to high upfront capital investment and ongoing maintenance costs. Gas collection systems, upgrading equipment, and energy conversion units require significant financial resources. Smaller municipalities and developing regions often struggle to secure funding, delaying project implementation. Additionally, maintenance of wells, piping, and treatment systems is essential to prevent gas leakage and ensure safety. These cost pressures can limit adoption, particularly in regions with low energy prices or limited access to financial incentives.
Variability in Gas Quality and Generation Rates
Inconsistent landfill gas composition and declining generation rates over time pose operational challenges. Gas quality depends on waste composition, landfill age, moisture levels, and management practices, leading to fluctuations in methane concentration. This variability affects energy system efficiency and complicates long-term planning. Older landfills experience reduced gas output, impacting project viability. Managing these uncertainties requires advanced monitoring, flexible system design, and predictive modeling, increasing technical complexity for landfill operators.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America dominates the landfill gas market with an estimated 36% market share, supported by a mature waste management infrastructure and strict environmental regulations targeting methane emissions. The United States leads regional adoption due to federal and state-level mandates requiring landfill gas collection and utilization. A strong focus on landfill gas-to-energy and renewable natural gas projects strengthens market penetration, particularly in electricity generation and pipeline injection. Availability of financial incentives, tax credits, and long-term power purchase agreements further enhances project viability. Canada also contributes through sustainability-driven municipal initiatives and investments in gas upgrading technologies.
Europe
Europe accounts for approximately 29% of the global landfill gas market, driven by robust regulatory frameworks and aggressive climate targets. The European Union’s landfill and renewable energy directives strongly promote methane capture and utilization. Countries such as Germany, the United Kingdom, and France have advanced landfill gas recovery systems integrated with combined heat and power plants. A gradual shift toward waste diversion and recycling moderates long-term landfill volumes; however, existing landfills continue to generate significant gas output. Strong emphasis on renewable natural gas and grid injection supports sustained market activity across the region.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific holds an estimated 24% market share and represents the fastest-expanding regional market due to rapid urbanization and rising municipal solid waste generation. Countries such as China, India, and Indonesia rely heavily on landfilling, creating a large feedstock base for landfill gas production. Government initiatives focused on waste-to-energy and emission reduction are improving gas capture adoption. While infrastructure maturity varies widely across the region, large-scale urban landfill projects increasingly incorporate gas recovery systems. Growing energy demand and environmental awareness continue to drive investments in landfill gas utilization technologies.
Latin America
Latin America represents around 7% of the landfill gas market, supported by increasing adoption of controlled landfills and climate-focused development programs. Brazil and Mexico lead regional activity, driven by large urban waste volumes and participation in international carbon reduction initiatives. Landfill gas-to-energy projects are gaining traction, particularly for electricity generation near metropolitan areas. However, limited funding and uneven regulatory enforcement constrain broader adoption. Ongoing improvements in waste management practices and access to international financing are expected to gradually strengthen landfill gas recovery across the region.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region accounts for approximately 4% market share, reflecting early-stage development of landfill gas infrastructure. Rapid urban growth and increasing waste generation create long-term potential, particularly in Gulf countries and South Africa. Current adoption remains limited due to reliance on open dumping and lower regulatory enforcement in several markets. However, sustainability strategies, smart city initiatives, and renewable energy diversification plans are driving pilot landfill gas projects. International partnerships and technical assistance play a critical role in supporting gradual market development across the region.
Market Segmentations:
By Source:
- Hospitals
- Offices & Institutions
By Treatment:
By Material:
- Paper & Paperboard
- Metals
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the landfill gas market players such as Halliburton, Centrica, Enterprise Products Partners, Baker Hughes Company, ConocoPhillips, Hatch, Exxon Mobil Corporation, Energy Transfer, BP, Chevron Corporation. the landfill gas market is shaped by a combination of technological expertise, infrastructure capabilities, and long-term project development experience. Market participants compete by improving methane capture efficiency, expanding gas upgrading solutions, and integrating landfill gas into power generation and renewable natural gas value chains. Strategic focus areas include end-to-end project execution, from landfill gas collection and treatment to distribution and energy utilization. Companies increasingly emphasize partnerships with municipalities and waste management authorities to secure stable feedstock access. Investments in advanced monitoring, emissions control, and digital optimization tools further differentiate competitive positioning. Regulatory compliance, operational reliability, and the ability to deliver scalable, cost-effective solutions remain critical factors influencing competition in the landfill gas market.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
Recent Developments
- In October 2025, Manatee County partnered with Johnson Controls, Inc. (JCI), to capture methane gas from the Lena Road Landfill and convert it into clean energy. The initiative is called Renewable Natural Gas (RNG).
- In January 2025, Baker Hughes won a significant order from Tecnicas Reunidas (TR) – Devex, Spanish general contractor, for the Jafurah Oil and Gas Field (Saudi Arabia)’s third phase in Saudi Arabia, supplying gas compression trains and propane compressors, leveraging their local Dammam center to support Aramco’s major gas development.
- In November 2024, Centro Servizi Ambiente Impianti (CSAI), and Waga Energy entered into a 10-year partnership to produce renewable natural gas (RNG) at the Podere Rota Landfill in Terranuova Bracciolini, located in the province of Arezzo.
- In September 2024, Biffa, a UK waste firm, acquired L&S Waste Management, a Hampshire-based specialist in construction & demolition (C&D) waste, boosting Biffa’s recycling capabilities with L&S’s facilities, transfer station, and fleet, aligning with Biffa’s strategy to grow low-carbon solutions in the C&D sector.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Source, Treatment, Material and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Landfill gas recovery will gain priority as governments tighten methane emission regulations across municipal waste facilities.
- Investment in landfill gas-to-energy projects will increase to support baseload renewable power generation.
- Renewable natural gas upgrading will expand due to growing demand from transportation and industrial end users.
- Advanced gas collection and monitoring systems will improve methane capture efficiency and operational reliability.
- Municipalities will strengthen public–private partnerships to accelerate landfill gas project development.
- Integration of landfill gas into local power grids and heating networks will become more common.
- Digital monitoring and predictive maintenance tools will enhance long-term landfill gas asset performance.
- Developing regions will adopt engineered landfills, expanding the global landfill gas feedstock base.
- Lifecycle management of aging landfills will create sustained demand for gas optimization solutions.
- Alignment with circular economy and decarbonization strategies will reinforce the long-term relevance of landfill gas.




