Market Overview
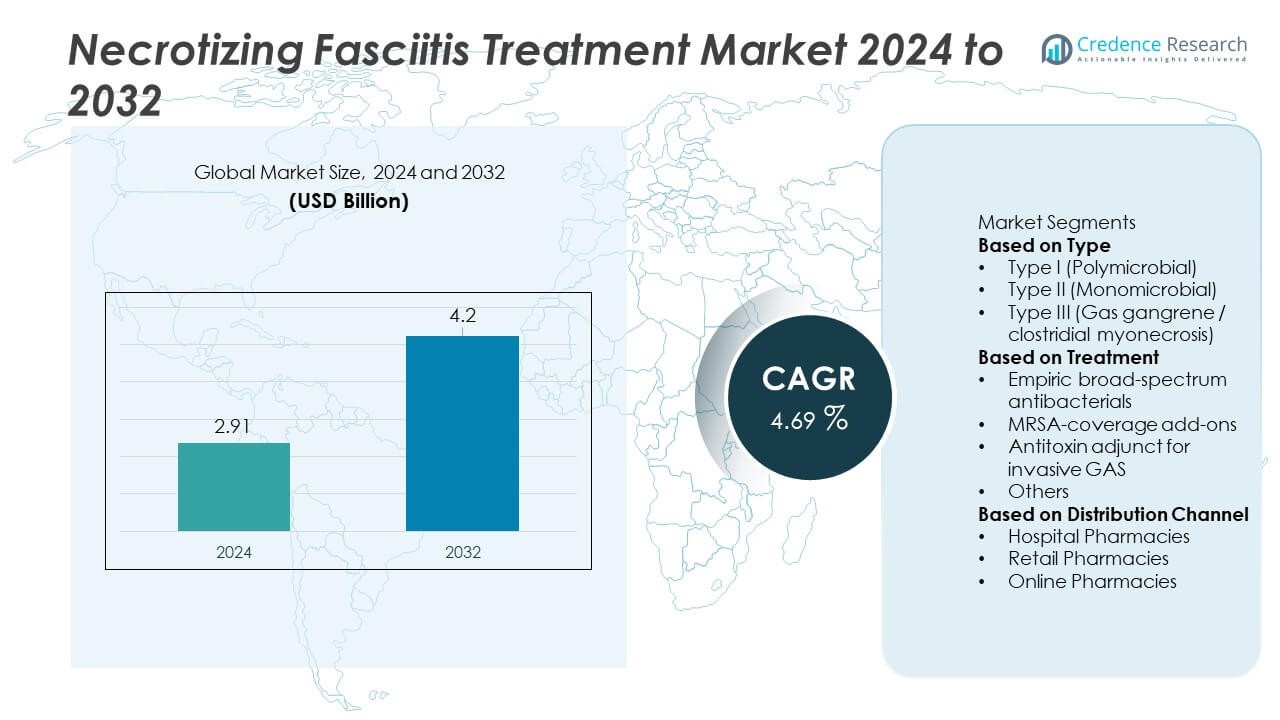
Necrotizing Fasciitis Treatment market size was valued at USD 2.91 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 4.2 billion by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 4.69% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Necrotizing Fasciitis Treatment Market Size 2024 |
USD 2.91 Billion |
| Necrotizing Fasciitis Treatment Market, CAGR |
4.69% |
| Necrotizing Fasciitis Treatment Market Size 2032 |
USD 4.2 Billion |
The Necrotizing Fasciitis Treatment market is driven by key players including Pfizer, Merck & Co. (MSD), Gilead Sciences, Astellas Pharma, Basilea Pharmaceutica, Takeda, CSL Behring, Grifols, Octapharma, and Hikma Pharmaceuticals, all contributing to critical antimicrobial, antitoxin, and supportive-therapy advancements. These companies strengthen hospital treatment capabilities through broad-spectrum antibiotics, MRSA-directed agents, and immune-supportive products used in severe cases. North America leads the market with 39% share, supported by advanced critical-care infrastructure, while Europe holds 31% share due to strong clinical guidelines and early diagnostic adoption. Asia Pacific follows with 22% share, driven by increasing prevalence and expanding hospital capacity.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The Necrotizing Fasciitis Treatment market reached USD 2.91 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 4.20 billion by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 4.69% during the forecast period.
- Key drivers include rising cases among diabetic, immunocompromised, and elderly patients, with Type I (Polymicrobial) leading the type segment with 49% share due to its higher clinical burden and need for broad-spectrum therapy.
- Major trends include growing adoption of rapid diagnostics, increased use of antitoxin adjuncts for invasive GAS, and expansion of advanced wound-care technologies that support faster stabilization.
- The competitive landscape is shaped by Pfizer, Merck & Co. (MSD), Gilead Sciences, Astellas Pharma, Basilea Pharmaceutica, Takeda, CSL Behring, Grifols, Octapharma, and Hikma, all enhancing antimicrobial and immune-supportive portfolios.
- Regionally, North America leads with 39% share, Europe holds 31%, and Asia Pacific follows with 22%, while Latin America and the Middle East & Africa account for 5% and 3%, driven by improving hospital capacity and rising chronic disease prevalence.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Type
Type I (Polymicrobial) accounted for the dominant 49% share, driven by its high prevalence in diabetic, immunocompromised, and elderly patients. This subtype often requires aggressive intervention due to multiple bacterial pathogens, increasing demand for broad-spectrum and combination-based therapy. Type II (Monomicrobial) cases, mainly linked to Streptococcus pyogenes, also grew due to rising invasive GAS infections across hospital settings. Type III (Gas gangrene) remained less common but required rapid surgical and antimicrobial management. The strong clinical burden of polymicrobial cases continues to shape treatment protocols and expand the need for advanced diagnostic and therapeutic approaches.
- For instance, Smith & Nephew introduced a debridement system (the VERSAJET Hydrosurgery System) that uses a high-velocity, focused jet of saline to tangentially cut and remove devitalized tissue and foreign matter via the Venturi effect, supporting a faster surgical response.
By Treatment
Empiric broad-spectrum antibacterials held the largest 58% share, as clinicians initiate immediate coverage to manage rapidly spreading necrotizing infections. These regimens target mixed aerobic and anaerobic organisms, making them essential for early stabilization. MRSA-coverage add-ons gained adoption due to increasing community and hospital MRSA cases. Antitoxin adjunct therapy for invasive GAS showed growth as guidelines encouraged clindamycin and IVIG use for toxin suppression. Other supportive treatments, including wound care and debridement adjuncts, continued to support overall management. The dominance of empiric therapy reflects urgent care needs and guideline-driven broad antimicrobial use.
- For instance, Grifols has significantly expanded its global immunoglobulin (IVIG) purification and manufacturing capacity, with its flagship Clayton, North Carolina, site alone capable of processing 12 million liters of plasma annually.
By Distribution Channel
Hospital pharmacies dominated the market with a 64% share, driven by the critical nature of necrotizing fasciitis, which requires immediate hospitalization, IV antibiotics, and surgical intervention. These settings manage most acute cases, ensuring rapid drug availability and specialist oversight. Retail pharmacies saw moderate uptake for post-discharge prescriptions and supportive medications. Online pharmacies observed gradual growth as patients accessed follow-up therapies and wound-care supplies after stabilization. The strong share of hospital pharmacies highlights the emergency-driven nature of treatment and the dependence on in-facility drug administration for severe soft-tissue infections.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Incidence in High-Risk Populations
Cases increase as more patients face diabetes, obesity, and weakened immunity. Hospitals report higher admissions linked to polymicrobial infections in aging populations. Early detection tools improve identification, pushing demand for rapid treatment. Growing awareness among clinicians supports faster use of advanced antibiotics and surgical care. The expanding pool of vulnerable patients strengthens long-term need for optimized therapy plans.
- For instance, bioMérieux advanced hospital readiness with its BIOFIRE BCID2 Panel, capable of detecting 43 targets (including bacteria, yeast, and antimicrobial resistance genes) associated with bloodstream infections in one test cycle of about an hour from a positive blood culture.
Advancements in Antimicrobial and Adjunctive Therapies
Broader antibacterial regimens improve survival by targeting mixed pathogens. New combinations support faster stabilization in severe presentations. Antitoxin therapies reduce tissue damage in invasive GAS cases. Updated guidelines promote aggressive, evidence-based treatment across emergency settings. These improvements increase drug utilization and drive demand for specialized options.
- For instance, the antibiotic daptomycin (Cubicin), which is now owned by Merck, uses a 6 mg/kg once-daily IV dosing strategy to treat S. aureus bloodstream infections, including MRSA bacteremia, and this is supported by guideline-based recommendations.
Strengthening Hospital Infrastructure for Critical Care
More hospitals expand emergency and surgical capacity for complex infections. Improved access to IV therapy and advanced wound care boosts treatment outcomes. Rapid debridement teams reduce complications and improve patient survival. Investments in intensive care units support recovery for severe cases. Better-equipped centers strengthen reliance on hospital-based pharmacy channels.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Growing Adoption of Rapid Diagnostic and Imaging Tools
Hospitals adopt faster diagnostic systems to detect early soft-tissue damage. Point-of-care imaging supports swift decisions during critical stages. Early confirmation encourages immediate initiation of broad-spectrum therapy. Rising demand for speed boosts adoption of molecular panels and AI-supported scans. Better detection creates opportunities for integrated treatment platforms.
- For instance, Siemens Healthineers improved emergency imaging by deploying its SOMATOM go.Up CT system, a 32 to 64-slice detector scanner that can perform a low-dose lung protocol scan in as little as 9 seconds for a 33 cm length.
Expansion of Post-Acute and Supportive Care Solutions
Recovery care supports long-term healing after initial stabilization. Demand increases for wound therapies, infection-control supplies, and rehabilitation services. Retail and online pharmacies supply follow-up medications for continued recovery. Patient education programs support better compliance and improve outcomes. This growing segment unlocks new commercial opportunities across outpatient care.
- For instance, Walgreens utilizes micro-fulfillment centers that, in one automated facility, can process 35,000 prescription orders per day to allow pharmacists more time to provide care and other services for patients.
Key Challenges
Rising Antimicrobial Resistance Across Key Pathogens
Resistance reduces effectiveness of standard regimens in many regions. Clinicians face difficulty choosing optimal therapy under urgent conditions. Increased MRSA and resistant anaerobes complicate empirical coverage. Hospitals require stronger stewardship to preserve drug efficacy. These issues raise treatment complexity and increase healthcare burdens.
Delayed Diagnosis and Limited Awareness in Early Stages
Early symptoms often resemble minor infections, leading to late intervention. Delayed care increases tissue loss and raises mortality. Many regions lack rapid diagnostic tools for timely detection. Limited clinical training adds risk in under-resourced facilities. These gaps create serious challenges for consistent treatment success.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America held the largest 39% share, supported by strong critical-care infrastructure and high awareness among clinicians. The region reports a rising number of cases linked to diabetes, obesity, and invasive GAS infections, increasing demand for rapid diagnostics and broad-spectrum therapies. Hospitals maintain well-established emergency pathways that enable immediate surgical intervention and IV antimicrobial use. Expansion of advanced wound-care centers further strengthens treatment capacity. Favorable reimbursement frameworks and access to specialist teams contribute to improved outcomes. These factors reinforce North America’s leading role in necrotizing fasciitis treatment adoption.
Europe
Europe accounted for 31% share, driven by well-developed hospital networks and strong adherence to early intervention guidelines. Countries across Western Europe adopt standardized protocols that combine rapid debridement, broad-spectrum therapy, and intensive post-operative care. Increasing cases linked to aging populations and chronic comorbidities strengthen treatment demand. Enhanced diagnostic systems such as MRI and rapid blood markers support timely diagnosis. Research initiatives across Germany, France, and the UK promote evidence-based therapy optimization. Europe’s expanding antimicrobial stewardship programs also guide effective treatment choices, sustaining the region’s strong market contribution.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific captured 22% share, supported by rising disease prevalence, growing healthcare access, and expanding hospital capacity. Large populations with increasing rates of diabetes and soft-tissue infections drive higher case volumes. Countries such as India, China, and Indonesia report improved emergency responsiveness and expanded surgical care availability. Investments in ICU facilities, infection control, and antimicrobial access strengthen treatment adoption. Governments promote awareness programs that encourage early hospital visits, reducing severe complications. Rapid urbanization and improving diagnostic tools further accelerate demand for comprehensive necrotizing fasciitis management.
Latin America
Latin America represented 5% share, influenced by increasing healthcare modernization and higher recognition of soft-tissue infections. Brazil and Mexico lead adoption due to expanding tertiary hospitals equipped for emergency surgical care. However, delayed diagnosis remains common in remote regions, increasing reliance on aggressive antimicrobial therapy once patients reach advanced facilities. Growth in public-health investments improves access to debridement and wound-care services. Rising chronic disease burden elevates infection risks, strengthening treatment demand. The region continues to expand critical-care services, supporting gradual improvement in clinical outcomes.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region held 3% share, shaped by rising hospital investment and growing attention to severe bacterial infections. Gulf countries enhance emergency and surgical capabilities, enabling faster response to necrotizing infections. African nations rely heavily on public hospitals, where late diagnosis remains a barrier. Increasing training programs for early symptom recognition support improved intervention rates. International partnerships boost access to broad-spectrum antibiotics and wound-care supplies. Despite infrastructure gaps, expanding healthcare facilities and rising chronic disease prevalence drive steady growth in treatment adoption.
Market Segmentations:
By Type
- Type I (Polymicrobial)
- Type II (Monomicrobial)
- Type III (Gas gangrene / clostridial myonecrosis)
By Treatment
- Empiric broad-spectrum antibacterials
- MRSA-coverage add-ons
- Antitoxin adjunct for invasive GAS
- Others
By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
Competitive landscape analysis highlights leading companies such as Pfizer, Merck & Co. (MSD), Gilead Sciences, Astellas Pharma, Basilea Pharmaceutica, Takeda, CSL Behring, Grifols, Octapharma, and Hikma Pharmaceuticals, which contribute significantly to advancements in necrotizing fasciitis treatment. These players focus on broad-spectrum antimicrobials, MRSA-targeted therapies, antitoxin adjuncts, and immune-supportive products essential for managing severe soft-tissue infections. Many companies invest in expanding IV antibiotic portfolios, developing faster-acting formulations, and improving availability of critical care biologics. Strategic collaborations with hospitals and healthcare networks strengthen access to life-saving therapies. Vendors also enhance clinical data generation to support evidence-based treatment protocols. As disease burden grows among high-risk populations, competition intensifies around advanced therapeutics, supportive-care solutions, and comprehensive hospital treatment packages.
Key Player Analysis
- Grifols
- Astellas Pharma
- Octapharma
- Takeda
- CSL Behring
- Pfizer
- Basilea Pharmaceutica
- Hikma Pharmaceuticals
- Merck & Co. (MSD)
- Gilead Sciences
Recent Developments
- In October 2025, Astellas Pharma presented new advances in its oncology portfolio at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) congress, highlighting data from innovative trials and new indications.
- In June 2024, GSK plc announced the acquisition of Elsie Biotechnologies, a San Diego based private biotechnology company focusing on realizing the full promise of oligonucleotide medicines.
- In January 2024, Merck’s Life Science division and Mycenax Biotech signed a non binding Memorandum of Understanding to explore cooperation on new, high capacity bioprocessing solutions for Taiwan and other markets. The MoU aims to integrate Merck’s BioContinuum™ Platform into Mycenax’s bioprocessing, focusing on automation and digitalization.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Type, Treatment, Distribution Channel and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Demand for rapid broad-spectrum therapies will grow as early intervention becomes standard practice.
- Hospitals will expand critical-care units and emergency response pathways to improve treatment speed.
- Adoption of rapid molecular diagnostics will rise to support faster identification of pathogens.
- Use of antitoxin adjuncts for invasive GAS infections will increase as guidelines evolve.
- Wound-care innovations and advanced debridement tools will play a larger role in recovery management.
- MRSA-targeted therapies will see higher demand due to rising resistant infections.
- Clinical training programs will expand to reduce delays in recognizing early symptoms.
- More healthcare systems will invest in multidisciplinary care teams for complex soft-tissue infections.
- Biologic and immune-supportive therapies will gain traction for severe and toxin-mediated cases.
- Emerging markets will strengthen treatment capacity as hospital infrastructure and diagnostic access improve.




