Market Overview
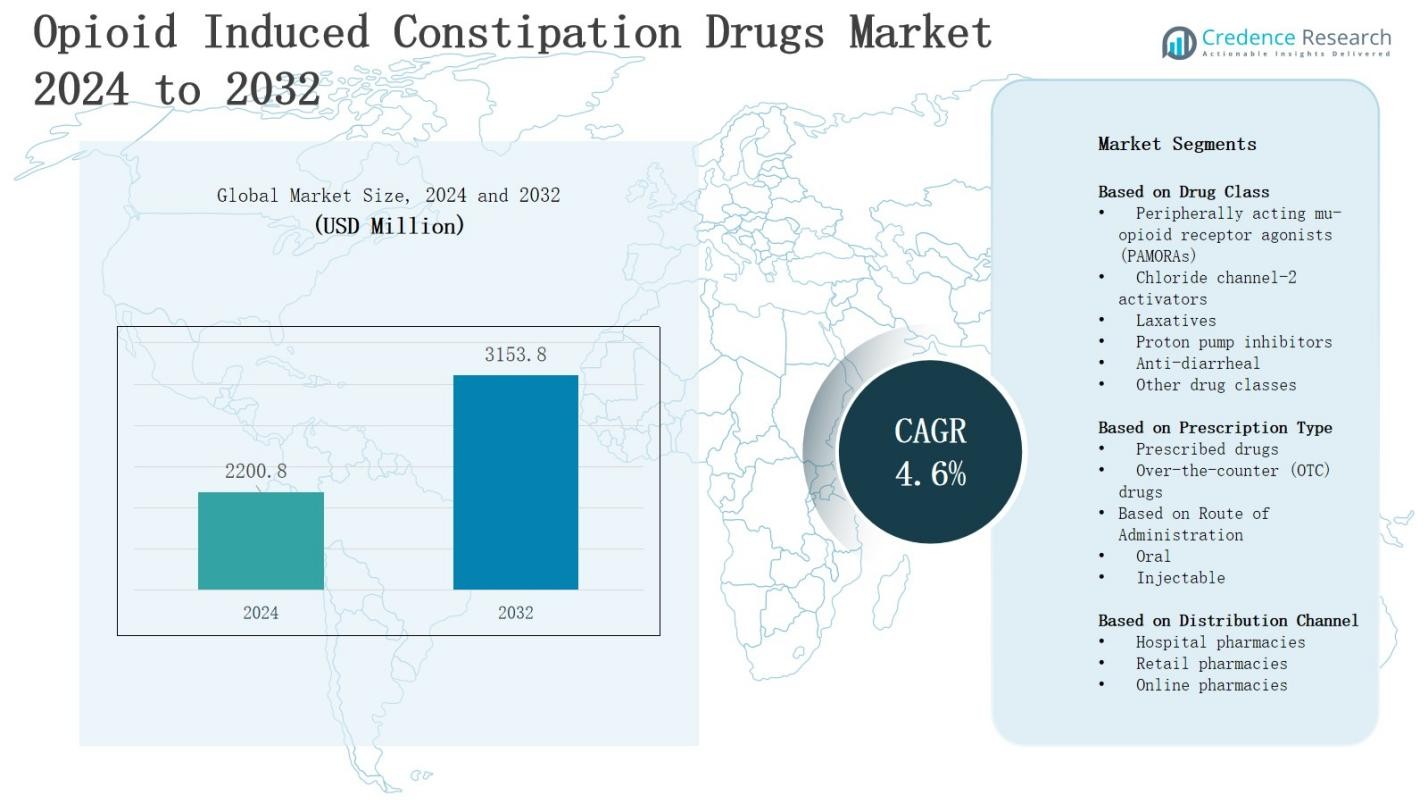
The opioid induced constipation drugs market is projected to grow from USD 2200.8 million in 2024 to USD 3153.8 million by 2032, registering a CAGR of 4.6% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2024 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Opioid Induced Constipation Drugs Market Size 2024 |
USD 2200.8 Million |
| Opioid Induced Constipation Drugs Market, CAGR |
4.6% |
| Opioid Induced Constipation Drugs Market Size 2032 |
USD 3153.8 Million |
The opioid induced constipation drugs market is driven by the growing use of opioids for chronic pain management and the rising prevalence of opioid-induced side effects among patients. Increasing awareness of gastrointestinal complications and the need for improved patient quality of life support demand for targeted treatments. Favorable regulatory approvals and the availability of peripherally acting mu-opioid receptor antagonists (PAMORAs) are strengthening market adoption. Trends highlight the shift toward non-invasive, patient-friendly therapies, the introduction of novel formulations, and strong investments in R&D. Expanding healthcare access in emerging economies also fosters market growth and wider treatment adoption.
The opioid induced constipation drugs market shows diverse regional dynamics, with North America leading at 41% due to high opioid use and advanced healthcare, followed by Europe with 28% supported by strong infrastructure and regulatory approvals. Asia-Pacific holds 20%, driven by expanding access in China, India, and Japan. Latin America accounts for 6%, led by Brazil and Mexico, while the Middle East & Africa holds 5% with gradual adoption. Key players include Pfizer, Roche, Viatris, Fresenius Kabi, Hikma, Novartis, Teva, Bristol Myers Squibb, GSK, Bayer, Aurobindo, and S.L.A. Pharma.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The opioid induced constipation drugs market is projected to grow from USD 2200.8 million in 2024 to USD 3153.8 million by 2032, registering a CAGR of 4.6% during the forecast period.
- PAMORAs dominate the drug class segment with 42% share, followed by laxatives at 25% and chloride channel-2 activators at 18%, highlighting rising adoption of advanced and targeted therapies.
- Prescribed drugs hold 67% of the market, reflecting strong physician reliance on advanced treatments, while OTC drugs account for 33%, largely driven by widespread use of affordable laxatives.
- Oral drugs lead with 72% market share due to convenience and higher compliance, while injectables represent 28%, mainly used in hospitals for severe cases requiring immediate relief.
- Regionally, North America leads with 41%, Europe follows at 28%, Asia-Pacific accounts for 20%, Latin America holds 6%, and the Middle East & Africa captures 5% share.
Market Drivers
Rising Opioid Consumption and Related Side Effects
The opioid induced constipation drugs market is fueled by the rising use of opioids in managing chronic pain conditions, including cancer and musculoskeletal disorders. Increased prescription rates have led to a higher prevalence of opioid-related gastrointestinal issues, particularly constipation, which reduces patient compliance and quality of life. It drives the demand for specialized treatments that address side effects without limiting pain relief. Growing awareness among healthcare providers further strengthens adoption and treatment penetration.
- For instance, Lubiprostone is anticipated to show the fastest growth due to its widespread use in treating both opioid-induced and chronic idiopathic constipation.
Growing Demand for Targeted Therapies
The market is expanding due to the increasing preference for targeted therapies that offer effective relief from constipation without interfering with central analgesic effects. Peripherally acting mu-opioid receptor antagonists (PAMORAs) are gaining strong acceptance due to their safety and efficiency. It benefits patients who cannot rely on traditional laxatives for sustainable relief. The wider availability of advanced prescription drugs positions the market for steady growth, especially in developed healthcare systems with supportive policies.
- For instance, AstraZeneca’s MOVENTIG (naloxegol), approved by the European Medicines Agency in 2014, is widely prescribed for opioid-induced constipation in adults who do not respond adequately to laxatives.
Favorable Regulatory Support and Approvals
The opioid induced constipation drugs market benefits from favorable regulatory frameworks and timely drug approvals by agencies like the FDA and EMA. Streamlined approval pathways encourage pharmaceutical companies to invest in innovative formulations with improved safety profiles. It allows faster introduction of advanced products that meet growing patient needs. Regulatory backing not only enhances competitive differentiation but also boosts global commercialization opportunities, supporting broader adoption in both hospital and retail pharmacy settings.
Expansion in Emerging Healthcare Markets
Rising healthcare access in emerging economies strengthens the market by opening new avenues for adoption. Growing awareness of opioid-related side effects and increasing investments in healthcare infrastructure improve diagnosis and treatment rates. It creates significant opportunities for both branded and generic drug makers to expand presence. The shift toward patient-centric healthcare and rising focus on improving treatment adherence also fuel market penetration, supporting sustainable growth in underserved regions worldwide.
Market Trends
Shift Toward Peripherally Acting Mu-Opioid Receptor Antagonists (PAMORAs)
The opioid induced constipation drugs market is witnessing a clear shift toward PAMORAs, which effectively relieve constipation without reducing the analgesic benefits of opioids. These drugs are increasingly preferred over conventional laxatives that fail to provide long-term relief. It has created strong opportunities for pharmaceutical companies to expand product portfolios. Clinical adoption continues to rise as physicians recommend PAMORAs for improved patient compliance, better outcomes, and reduced risks linked to gastrointestinal complications.
Rising Focus on Patient-Centric and Non-Invasive Treatments
A major trend involves the growing demand for patient-friendly and non-invasive treatment options. Healthcare providers are prioritizing oral formulations that offer ease of use and improved adherence compared to invasive alternatives. It strengthens market acceptance among patients managing chronic opioid use. Companies are focusing on research to develop therapies with fewer side effects, aligning with the shift toward safer and more convenient drug delivery approaches that improve long-term patient satisfaction.
- For instance, The Smart Lollipop offers a painless saliva-based diagnostic tool that digitizes biomarker data for easier patient and professional use, especially benefiting pediatric patients.
Increasing Research and Development Investments
The opioid induced constipation drugs market benefits from rising R&D investments aimed at discovering novel formulations and expanding therapeutic options. Pharmaceutical companies are channeling resources into developing advanced drugs with higher efficacy and fewer adverse effects. It has led to ongoing clinical trials and pipeline expansion, creating expectations for steady product launches. Collaborative efforts between biotech firms and large pharmaceutical players are also driving innovation, ensuring continuous advancement of effective treatment solutions.
- For instance, Kyowa Kirin Co. Ltd., a Japan-based biotech company, partnered with Germany’s Grünenthal GmbH in 2022 to expand and globalize their portfolio of pain management medications, including OIC treatments.
Growing Penetration in Emerging Economies
Emerging economies are becoming important growth drivers for the market, supported by expanding healthcare infrastructure and greater accessibility to advanced therapies. Rising opioid use in these regions increases the incidence of constipation-related complications, fueling demand for effective solutions. It opens opportunities for both branded and generic products, strengthening overall market presence. Governments and private healthcare providers are increasingly investing in awareness campaigns and improved distribution networks, creating favorable conditions for wider drug adoption.
Market Challenges Analysis
High Treatment Costs and Limited Patient Awareness
The opioid induced constipation drugs market faces significant challenges due to the high cost of advanced therapies, particularly PAMORAs, which limits affordability for patients in low- and middle-income regions. Traditional laxatives remain widely used because they are inexpensive and easily accessible, even though they offer limited effectiveness. It creates a barrier for newer drugs to gain widespread adoption. Limited awareness among patients regarding available specialized treatments further restricts growth, particularly in underserved healthcare systems.
Regulatory Hurdles and Safety Concerns
Strict regulatory frameworks and lengthy approval processes create obstacles for pharmaceutical companies seeking to introduce innovative drugs. The opioid induced constipation drugs market also contends with ongoing concerns about potential side effects linked to advanced therapies, which can reduce physician confidence in prescribing them. It impacts overall adoption, especially in markets with limited clinical evidence. Intense competition from generics further pressures pricing and profitability, challenging companies to balance affordability with sustainable research and development.
Market Opportunities
Expansion of Advanced Therapies and New Drug Development
The opioid induced constipation drugs market presents strong opportunities through the development of advanced therapies that address unmet clinical needs. Pharmaceutical companies are focusing on expanding product portfolios with safer, more effective drugs designed to improve long-term patient outcomes. It allows firms to differentiate their offerings while capturing a larger share of the growing patient base. The rising adoption of PAMORAs, combined with ongoing research into novel drug formulations, creates significant room for future growth and innovation.
Growing Opportunities in Emerging Economies
Expanding healthcare infrastructure and rising opioid prescriptions in emerging economies create favorable conditions for market penetration. Increasing awareness of gastrointestinal complications linked to opioid use encourages wider adoption of targeted treatments. It provides opportunities for both branded and generic drugs to strengthen their presence in underserved markets. Governments and private healthcare providers are also investing in awareness campaigns, distribution improvements, and reimbursement policies, further supporting accessibility. These factors make emerging regions highly attractive for long-term expansion.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Drug Class
Peripherally acting mu-opioid receptor antagonists (PAMORAs) hold the dominant share of around 42% in the opioid induced constipation drugs market, driven by their targeted action that relieves constipation without impacting opioid analgesia. Chloride channel-2 activators account for nearly 18%, supported by their effectiveness in improving intestinal fluid secretion. Laxatives capture about 25% due to affordability and accessibility, while proton pump inhibitors and anti-diarrheal drugs together contribute close to 10%. Other drug classes make up the remaining 5%, reflecting niche applications.
By Prescription Type
Prescribed drugs dominate this segment with a market share of approximately 67%, supported by strong physician preference for advanced therapies like PAMORAs and chloride channel activators that require medical oversight. It reflects the growing demand for regulated and effective solutions that improve treatment outcomes. Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs hold around 33%, largely represented by laxatives, which remain widely accessible and cost-effective. Their popularity is sustained by patient self-management practices, although limited efficacy drives reliance on prescribed options.
- For instance, Sucampo Pharmaceuticals (acquired by Mallinckrodt) developed Amitiza (lubiprostone), a chloride channel activator approved in over 30 countries, which demonstrates clinical efficacy but is only available via prescription.
By Route of Administration
Oral drugs command a leading share of about 72% in the opioid induced constipation drugs market, driven by ease of use, better patient compliance, and strong adoption of oral PAMORAs and laxatives. It highlights the preference for convenient, non-invasive administration methods. Injectable drugs account for nearly 28%, supported by use in hospital settings for severe cases requiring immediate relief. While smaller in share, injectables offer critical options in advanced clinical management.
- For instance, AstraZeneca’s Movantik® (naloxegol), an oral once-daily PAMORA, has been widely prescribed since its FDA approval in 2014 for treating OIC in adult patients with chronic non-cancer pain.
Segments:
Based on Drug Class
- Peripherally acting mu-opioid receptor agonists (PAMORAs)
- Chloride channel-2 activators
- Laxatives
- Proton pump inhibitors
- Anti-diarrheal
- Other drug classes
Based on Prescription Type
- Prescribed drugs
- Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs
Based on Route of Administration
Based on Distribution Channel
- Hospital pharmacies
- Retail pharmacies
- Online pharmacies
Based on the Geography:
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Regional Analysis
North America
North America dominates the opioid induced constipation drugs market with a share of 41%. Strong opioid prescription rates, advanced healthcare systems, and early adoption of novel therapies such as PAMORAs drive regional leadership. It is supported by favorable reimbursement frameworks and high awareness among physicians and patients. The presence of leading pharmaceutical companies also ensures rapid product availability. Rising investments in clinical research continue to strengthen market adoption. Growing emphasis on patient safety and adherence further sustains growth in this region.
Europe
Europe holds 28% of the opioid induced constipation drugs market, supported by strong healthcare infrastructure and growing awareness of opioid-related side effects. Regulatory support from the European Medicines Agency has encouraged the entry of advanced treatment options. It benefits from expanding adoption of non-invasive therapies, particularly oral drugs that enhance compliance. Increasing demand for prescription-based therapies drives consistent growth across key countries such as Germany, France, and the United Kingdom. Efforts to reduce gastrointestinal complications support long-term market expansion.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific accounts for 20% of the opioid induced constipation drugs market, driven by rising opioid prescriptions and expanding healthcare access. Increasing disposable incomes and urbanization have contributed to higher diagnosis and treatment rates. It is supported by growing adoption of oral therapies, which remain the preferred route of administration. Strong growth is expected from China, India, and Japan due to government investments in healthcare and rising awareness of gastrointestinal disorders. Expanding pharmaceutical manufacturing also supports affordability and accessibility.
Latin America
Latin America represents 6% of the opioid induced constipation drugs market, with growth influenced by increasing adoption of advanced drugs in urban centers. Rising healthcare spending in Brazil and Mexico strengthens regional demand. It benefits from growing awareness of opioid side effects, though access challenges persist in rural areas. Prescription drugs account for the majority of sales, supported by physician recommendations. Expansion of private healthcare networks enhances treatment availability and patient adherence in the region.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa captures 5% of the opioid induced constipation drugs market, supported by growing investments in healthcare modernization. Rising opioid use in pain management is driving increased incidence of related side effects. It encourages demand for specialized treatments, particularly in hospital-based settings. Access remains limited in certain regions due to affordability constraints, yet urban markets demonstrate steady adoption. Expanding distribution networks and international collaborations help improve availability. The region shows potential for long-term growth.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Novartis AG (Switzerland)
- Bristol Myers Squibb Company (U.S.)
- Aurobindo Pharma (India)
- Bayer AG (Germany)
- Hikma Pharmaceuticals PLC (U.K.)
- Pfizer Inc (U.S.)
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. (Israel)
- Fresenius Kabi AG (Germany)
- GSK Plc. (U.K.)
- Viatris Inc. (U.S.)
- Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd (Switzerland)
- L.A. Pharma AG (U.K.)
Competitive Analysis
The opioid induced constipation drugs market is highly competitive, shaped by the presence of global and regional pharmaceutical companies investing in advanced therapies. Key players such as Pfizer Inc., F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Viatris Inc., Fresenius Kabi AG, Hikma Pharmaceuticals PLC, Novartis AG, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Bristol Myers Squibb Company, GSK Plc., Bayer AG, Aurobindo Pharma, and S.L.A. Pharma AG focus on expanding their product portfolios to strengthen market positioning. It benefits from innovation in peripherally acting mu-opioid receptor antagonists (PAMORAs), which are gaining preference over conventional laxatives. Companies actively pursue strategies including partnerships, regulatory approvals, and product launches to enhance global reach and competitiveness. Established firms leverage strong research capabilities and distribution networks, while emerging players target affordability in cost-sensitive regions. Market competition is further influenced by growing generic penetration, encouraging established players to balance innovation with pricing strategies. Strong investment in research and development, combined with efforts to expand access in emerging economies, underscores the dynamic and evolving nature of this competitive landscape.
Recent Developments
- In May 2025, Shionogi & Co., Ltd. announced that its New Drug Application (NDA) for naldemedine tosylate, a PAMORA treatment for opioid-induced constipation, was accepted in China.
- In July 2024, Grünenthal acquired Valinor Pharma for $250 million, adding the opioid-induced constipation drug Movantik (naloxegol) to its portfolio.
- In March 2025, Mallinckrodt and Endo announced a nearly $7 billion merger, combining opioid-related portfolios. The merger may indirectly impact OIC drug strategies.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Drug Class, Perception Type, Route of Administartion, Distribution Channel and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Rising opioid prescriptions will continue to drive strong demand for constipation management drugs worldwide.
- Development of safer and more effective PAMORAs will strengthen treatment adoption across healthcare systems.
- Increasing preference for oral formulations will enhance patient compliance and boost long-term market growth.
- Expanding healthcare infrastructure in emerging economies will create new opportunities for drug accessibility and adoption.
- Pharmaceutical companies will invest heavily in research pipelines to develop innovative and patient-friendly treatment solutions.
- Growing physician awareness of advanced therapies will encourage wider prescription of targeted constipation management drugs.
- Generic drug penetration will intensify competition, pushing companies to balance affordability with innovation strategies.
- Regulatory support and streamlined approval pathways will accelerate market entry of novel therapeutic formulations globally.
- Partnerships between global and regional players will strengthen distribution networks and expand market presence internationally.
- Rising focus on patient-centric healthcare will drive adoption of convenient, safe, and effective drug options.




