Market Overview
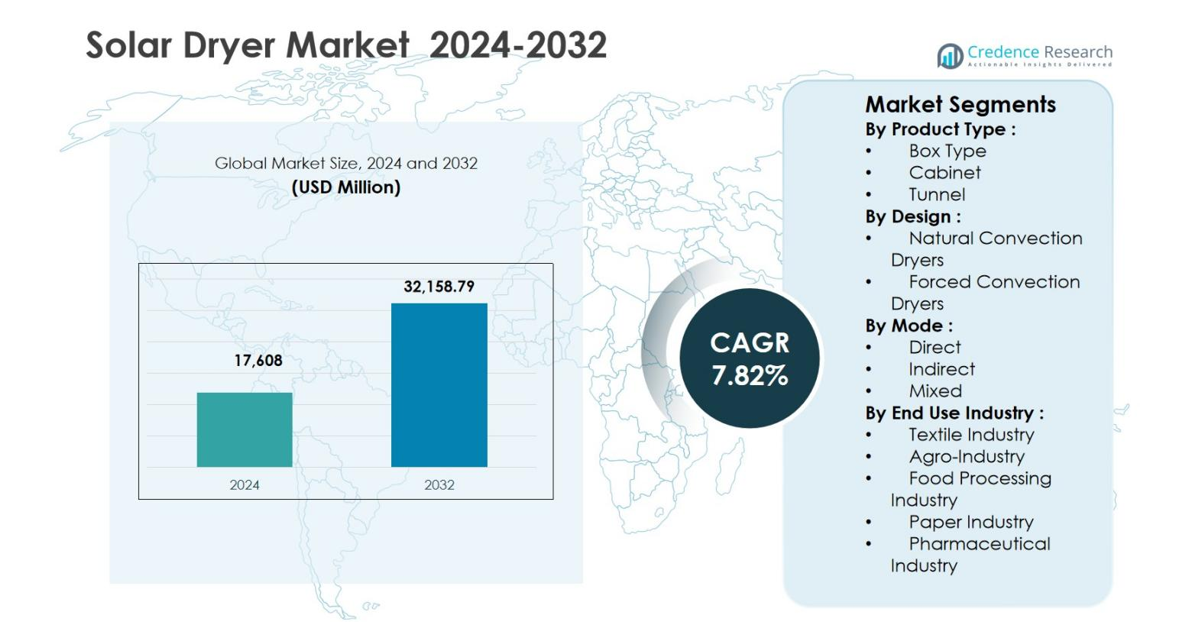
The Solar Dryer Market size was valued at USD 17,608 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 32,158.79 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 7.82% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Solar Dryer Market Size 2024 |
USD 17,608 million |
| Solar Dryer Market, CAGR |
7.82% |
| Solar Dryer Market Size 2032 |
USD 32,158.79 millio |
The Solar Dryer Market is characterized by the presence of established regional manufacturers and technology-focused organizations offering product-specific and application-oriented solutions. Key players such as Solar Dryers Australia, Solar Conduction Dryer Pvt. Ltd., Sun Best, Ecosolaris, SolarTech Solutions, SolarFlex, Green Heat Uganda Limited, SRR Aqua Suppliers, Futurepump, and Hohenheim University (Solar Dryer Technology Division) focus on tunnel, forced-convection, and indirect solar dryer systems to address agricultural and food processing needs. These companies emphasize energy efficiency, modular design, and adaptability across farm and industrial scales. Asia Pacific led the Solar Dryer Market with a 37.8% share in 2024, driven by large agricultural output, strong government support, and high adoption across agro-processing and rural applications.
Market Insights
- The Solar Dryer Market was valued at USD 17,608 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 32,158.79 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 7.82% during the forecast period, supported by rising adoption of renewable-based post-harvest technologies.
- Market growth is driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient food preservation, reduction of post-harvest losses, and expanding agro-processing activities, with tunnel solar dryers holding a dominant 46.8% segment share in 2024 due to suitability for large-scale operations.
- Key market trends include growing adoption of forced-convection systems, which accounted for 58.6% share in 2024, along with rising preference for indirect solar dryers holding 51.9% share, driven by superior quality retention and food safety compliance.
- Market dynamics reflect a fragmented structure, where players focus on modular designs, hybrid systems, and localized manufacturing to address diverse agricultural and industrial drying needs across regions.
- Regionally, Asia Pacific led with a 37.8% share in 2024, followed by North America at 21.4% and Europe at 19.6%, while Latin America and Middle East & Africa together accounted for 21.2%, driven by favorable climate and rural adoption.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Product Type:
The Solar Dryer Market by product type is led by Tunnel solar dryers, which accounted for 46.8% market share in 2024, driven by their high throughput capacity, uniform heat distribution, and suitability for commercial-scale agricultural processing. Tunnel dryers support continuous drying operations for grains, fruits, vegetables, and spices, making them preferred in large farms and agro-processing units. Cabinet solar dryers follow due to their adoption in small and medium enterprises, while box-type dryers serve household and pilot-scale applications. Rising demand for scalable, energy-efficient post-harvest solutions continues to reinforce tunnel dryer dominance.
- For instance, E Three HVAC System & Solution offers a Vegetable Solar Tunnel Dryer with 500 kg capacity (8×28 ft dimensions), designed for commercial drying of vegetables, ginger, herbs, and spices using solar-powered fans even in monsoon conditions.
By Design:
By design, Forced convection solar dryers dominated the Solar Dryer Market with a 58.6% share in 2024, supported by superior temperature control, faster moisture removal, and consistent product quality. These systems use fans or blowers powered by solar energy, enabling controlled airflow essential for commercial food dehydration. Adoption is high in regions focusing on export-grade dried food products. Natural convection dryers maintain relevance in low-cost rural applications due to simple construction and zero operational energy cost, but limited drying efficiency restricts large-scale deployment compared to forced convection designs.
- For instance, an indirect solar dryer in Morocco, constructed with inexpensive materials and a solar air collector, achieved a maximum outlet temperature of 58°C and reduced the mass of banana slices from 549.76 g to 138.41 g during the drying process, proving effective for small-scale, off-grid use.
By Mode:
Based on mode, Indirect solar dryers held the leading position with a 51.9% market share in 2024, driven by their ability to preserve nutritional value, color, and flavor by preventing direct exposure to sunlight. Indirect systems are widely used for high-value crops such as herbs, medicinal plants, and fruits. Mixed-mode dryers are gaining traction due to operational flexibility, while direct solar dryers remain limited to low-cost drying applications. Growing emphasis on quality retention and food safety standards continues to accelerate adoption of indirect solar drying systems globally.
Key Growth Driver
Rising Demand for Energy-Efficient Food Preservation
The Solar Dryer Market is strongly driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient and cost-effective food preservation solutions. Growing post-harvest losses in fruits, vegetables, grains, and fisheries have intensified the need for sustainable drying technologies that reduce dependency on fossil fuels. Solar dryers offer significant operational cost savings, particularly in off-grid and rural regions, while maintaining product quality and shelf life. Government initiatives promoting renewable energy adoption in agriculture, combined with rising awareness among farmers and cooperatives, continue to accelerate deployment across both small-scale and commercial food processing operations.
- For instance, the Jadhav couple in Pimpri, Nashik, installed a solar dryer in January 2023 after rain damaged black grape yields, saving 750 kg of grapes and generating profit.
Expansion of Commercial Agro-Processing Activities
Rapid expansion of commercial agro-processing and food export industries is a key growth catalyst for the Solar Dryer Market. Increasing global demand for dried fruits, spices, herbs, and seafood has encouraged processors to adopt controlled solar drying systems that ensure consistent quality and compliance with food safety standards. Tunnel and forced-convection solar dryers support high-volume operations while reducing energy expenses. The integration of solar dryers into value-added agricultural supply chains enhances profitability for producers, processors, and exporters, driving widespread adoption across developing and developed economies.
- For instance, Raheja Solar Food Processing provided foldable solar dryers to pineapple farmers in Odisha’s Gajapati district, enabling dehydration of fresh fruit into shelf-stable slices with retained color and nutrition.
Supportive Government Policies and Rural Electrification Gaps
Supportive government policies promoting renewable energy and sustainable agriculture significantly contribute to Solar Dryer Market growth. Subsidies, rural development programs, and climate-resilient agriculture initiatives encourage the adoption of solar-based post-harvest technologies. In regions with limited grid access, solar dryers provide a reliable alternative to electric and fuel-based drying systems. Development agencies and NGOs increasingly deploy solar dryers in rural livelihoods programs, strengthening income generation and food security while aligning with national decarbonization and clean-energy targets.
Key Trend & Opportunity
Integration of Hybrid and Smart Solar Dryer Systems
The Solar Dryer Market is witnessing a growing trend toward hybrid and smart solar dryer systems that integrate auxiliary heating sources, sensors, and automated airflow controls. These advancements improve drying consistency, reduce dependence on weather conditions, and enable year-round operation. Digital monitoring of temperature and humidity enhances product quality and reduces spoilage risks. This trend presents strong opportunities for manufacturers to differentiate offerings and target high-value food processing segments, including pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, and export-oriented agricultural products.
- For instance, Synnefa’s smart solar dryers incorporate FarmShield IoT sensors for real-time temperature and humidity monitoring, linked to a cloud platform that sends alerts to operators’ phones. Solar-powered HVAC fans maintain consistent drying for premium-quality products.
Growing Adoption in Fisheries and Livestock Feed Processing
Expanding application of solar dryers in fisheries and livestock feed processing presents a major opportunity in the Solar Dryer Market. Coastal and inland aquaculture operations increasingly use solar dryers to preserve fish, shrimp, and seaweed while minimizing fuel costs. Similarly, solar drying of fodder and feed ingredients supports livestock productivity in arid and semi-arid regions. These applications create new revenue streams for equipment providers and strengthen the role of solar dryers beyond traditional agricultural produce.
- For instance, ICAR-CIFT developed hybrid solar dryers with capacities from 6 to 110 m² tray area, enabling hygienic drying of 10 to 500 kg of fish even in unfavorable weather using LPG or biomass backup. In Kumbalanghi, India, entrepreneur Shri.
Key Challenge
High Initial Capital Investment for Advanced Systems
High upfront capital investment remains a significant challenge in the Solar Dryer Market, particularly for advanced tunnel and forced-convection systems. Small and marginal farmers often face financial constraints that limit adoption despite long-term cost benefits. Lack of access to affordable financing and limited awareness of return-on-investment timelines further restrict market penetration. While subsidies and grants help offset costs, uneven policy implementation across regions continues to slow large-scale adoption of technologically advanced solar drying solutions.
Weather Dependency and Seasonal Performance Variability
Weather dependency and seasonal variability pose operational challenges for the Solar Dryer Market. Inconsistent solar radiation affects drying efficiency, cycle duration, and throughput, especially in regions with high humidity or prolonged monsoon seasons. Natural convection and direct-mode systems are particularly vulnerable to climatic fluctuations. Although hybrid designs mitigate these limitations, they increase system complexity and cost. Ensuring reliable performance across diverse climatic conditions remains a critical challenge for manufacturers and end users.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America accounted for 21.4% market share in 2024 in the Solar Dryer Market, supported by growing adoption of renewable energy technologies in food processing and agriculture. The region benefits from advanced agro-processing infrastructure, strong focus on reducing food waste, and increasing use of solar dryers in organic food, specialty crops, and fisheries. Government incentives promoting clean energy solutions and sustainability standards further support adoption. Commercial-scale forced convection and tunnel solar dryers are widely deployed across the United States and Canada, particularly in fruit, vegetable, and herb drying applications.
Europe
Europe held a 19.6% market share in 2024 in the Solar Dryer Market, driven by strict environmental regulations, strong emphasis on energy efficiency, and high demand for premium dried food products. Countries such as Germany, France, and Italy actively integrate solar drying technologies within sustainable agriculture and food preservation programs. Indirect and hybrid solar dryers are widely adopted to maintain product quality and nutritional value. Support from research institutions, agricultural cooperatives, and renewable energy funding frameworks continues to strengthen regional market growth.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific dominated the Solar Dryer Market with a 37.8% market share in 2024, supported by large agricultural output, high post-harvest losses, and widespread rural electrification gaps. Countries including India, China, Vietnam, and Thailand actively deploy solar dryers for grains, spices, fruits, vegetables, and fisheries. Government-backed rural development initiatives and renewable energy subsidies accelerate adoption among smallholder farmers and cooperatives. Tunnel and forced convection dryers see strong demand due to rising export-oriented agro-processing and growing food security concerns across the region.
Latin America
Latin America captured a 11.2% market share in 2024 in the Solar Dryer Market, driven by expanding agricultural exports and favorable climatic conditions for solar drying. Countries such as Brazil, Mexico, and Peru increasingly use solar dryers for coffee, cocoa, fruits, and seafood processing. Adoption is supported by initiatives aimed at reducing energy costs and improving rural livelihoods. While natural convection systems remain common, commercial operators are gradually shifting toward indirect and forced convection dryers to enhance consistency and meet export quality standards.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region accounted for 10.0% market share in 2024 in the Solar Dryer Market, supported by high solar irradiation levels and limited grid connectivity in rural areas. Solar dryers play a critical role in preserving agricultural produce, fish, and livestock feed while reducing reliance on diesel-powered systems. Development agencies, NGOs, and government-led food security programs actively promote solar drying solutions. Growing adoption of low-cost and modular solar dryers continues to strengthen market penetration across arid and semi-arid regions.
Market Segmentations:
By Product Type :
By Design :
- Natural Convection Dryers
- Forced Convection Dryers
By Mode :
By End Use Industry :
- Textile Industry
- Agro-Industry
- Food Processing Industry
- Paper Industry
- Pharmaceutical Industry
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
Solar Dryers Australia, Sun Best, Solar Conduction Dryer Pvt. Ltd., Green Heat Uganda Limited, Ecosolaris, SolarTech Solutions, SolarFlex, SRR Aqua Suppliers, Futurepump, and Hohenheim University (Solar Dryer Technology Division). The Solar Dryer Market is moderately fragmented, with competition shaped by technological differentiation, regional presence, and application-specific customization. Leading players focus on developing tunnel, forced-convection, and indirect solar dryers to address commercial agro-processing and export-quality food requirements. Companies emphasize energy efficiency, durability, and modular designs to serve both smallholder farmers and large processing units. Strategic collaborations with agricultural cooperatives, NGOs, and government programs strengthen market penetration, particularly in emerging economies. Innovation remains centered on hybrid systems, improved airflow management, and material optimization to enhance drying consistency. Regional manufacturers leverage cost advantages and localized designs, while established players invest in R&D and pilot projects to expand global footprints.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
Recent Developments
- In September 2025, Rudra Solar Energy promoted its Solar Fish Dryer as a sustainable solution for fishermen, highlighting high-efficiency designs available in various capacities for hygienic fish preservation.
- • In April 2025, Covestro and Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) launched a solar dryer initiative in Ethiopia to support coffee farmers by deploying innovative polycarbonate-based solar dryers for improved post-harvest drying efficiency and quality.
- In January 2025, GITAM Technology Enabling Centre (GTEC) transferred its “Hybrid Solar Dryer with Automatic Temperature Controller” technology to the University of Ladakh to help reduce post-harvest losses of high-value crops and boost local agricultural processing capacity.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Product Type, Design, Mode, End Use Industry and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The Solar Dryer Market will witness increasing adoption across commercial agro-processing due to rising demand for energy-efficient food preservation.
- Integration of hybrid and forced-convection technologies will improve drying efficiency and year-round operational reliability.
- Growing focus on reducing post-harvest losses will accelerate deployment in fruits, vegetables, grains, and spice processing.
- Expansion of solar dryers in fisheries and aquaculture will support sustainable seafood preservation practices.
- Government-backed renewable energy and rural development programs will continue to support market penetration.
- Advancements in material design and insulation will enhance thermal performance and system durability.
- Increasing export of dried food products will drive demand for quality-controlled indirect drying systems.
- Adoption among farmer cooperatives and small enterprises will strengthen decentralized food processing models.
- Climate-resilient agricultural strategies will reinforce the role of solar dryers in food security initiatives.
- Ongoing innovation and localized manufacturing will improve affordability and accessibility across emerging markets.




