Market Overview
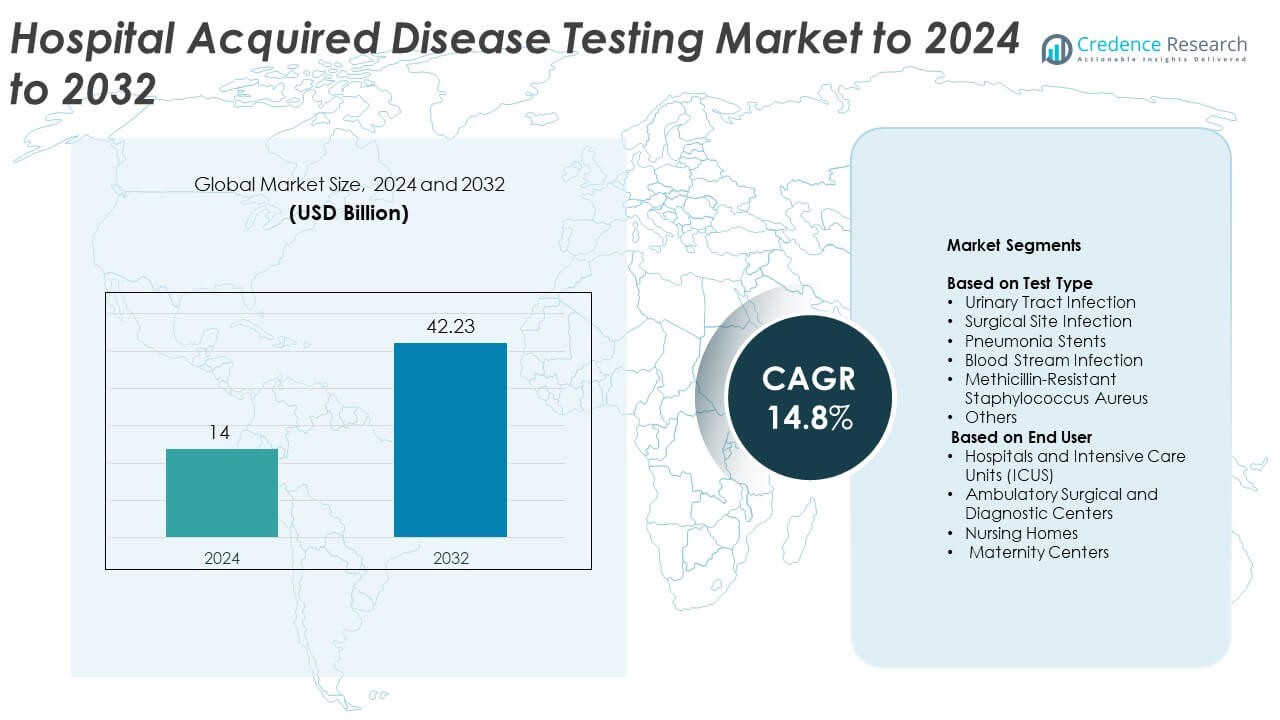
Hospital Acquired Disease Testing market size was valued at USD 14 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 42.23 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 14.8% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Hospital Acquired Disease Testing Market Size 2024 |
USD 14 Billion |
| Hospital Acquired Disease Testing Market, CAGR |
14.8% |
| Hospital Acquired Disease Testing Market Size 2032 |
USD 42.23 Billion |
Leading companies in the Hospital Acquired Disease Testing market strengthen adoption through rapid molecular platforms, automated lab systems, and advanced pathogen-detection technologies. These players focus on improving turnaround time, expanding resistance-marker panels, and supporting infection-control programs in high-risk clinical units. Their solutions gain traction as hospitals work to reduce outbreaks and enhance surveillance accuracy. North America led the market in 2024 with a 38% share due to strong diagnostic infrastructure and strict regulatory standards. Europe followed with 30% share, supported by advanced healthcare systems, while Asia Pacific accounted for 24% share driven by rising hospital admissions and expanding ICU capacity.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The Hospital Acquired Disease Testing market reached USD 14 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit USD 42.23 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 14.8%.
- Strong demand grows as hospitals adopt rapid molecular tests to reduce infection spread and improve early detection, supporting high use in urinary tract infection testing, which held about 31% share in 2024.
- Trends include expansion of point-of-care diagnostics, increasing adoption of AI-enabled platforms, and wider use of multiplex resistance panels across critical care units.
- Leading companies compete through automation, advanced assay development, integration of antimicrobial resistance panels, and partnerships with healthcare networks to expand diagnostic capacity.
- North America held 38% share in 2024, followed by Europe at 30%, while Asia Pacific reached 24% and demonstrated the fastest growth due to rising hospital admissions and ICU expansion.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Test Type
Urinary tract infection led the test type segment in 2024 with about 31% share. Its strong lead came from high case prevalence in catheterized patients and routine screening needs in acute care units. Hospitals rely on rapid UTI panels to reduce diagnostic delays and prevent complications linked to prolonged catheter use. Surgical site infection and bloodstream infection tests also expanded with rising antimicrobial resistance, while MRSA testing gained wider adoption due to infection-control mandates. Pneumonia stent testing and other panels grew steadily as respiratory-linked hospital infections increased in critical care settings.
- For instance, BD’s BACTEC FX stack configuration uses four drawers with 100 vials each, giving capacity for 400 blood culture vials in a common hospital setup.
By End User
Hospitals and intensive care units dominated the end-user segment in 2024 with nearly 54% share. Their lead stems from high patient density, invasive procedures, and greater exposure to multidrug-resistant pathogens. ICUs adopt rapid diagnostic platforms to shorten detection time and limit outbreak spread. Ambulatory surgical and diagnostic centers increased use of screening tests to comply with safety protocols, while nursing homes expanded adoption due to rising infection-control requirements. Maternity centers contributed modest growth as prenatal and postnatal units strengthened preventive testing for high-risk infections.
- For instance, bioMérieux’s BioFire Pneumonia Panel detects 33 respiratory targets in about 1 hour, covering bacteria, viruses, and resistance genes for ICU pneumonia cases.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising burden of hospital acquired infections
Hospitals face growing clinical pressure as infection rates rise across critical care units. Higher use of catheters, ventilators, and surgical implants increases exposure to pathogens, which boosts demand for faster diagnostic tools. Hospitals adopt advanced tests to prevent outbreaks, cut care delays, and meet safety standards. The rising need for early and accurate detection strengthens adoption of automated and molecular testing platforms, allowing care teams to control infection spread.
- For instance, Abbott’s ID NOW COVID-19 assay delivers molecular results for SARS-CoV-2 in 13 minutes or less, helping emergency units act faster on suspected hospital infections.
Expansion of rapid molecular diagnostic technologies
Rapid molecular systems offer shorter turnaround times and high accuracy for detecting resistant organisms. Hospitals choose these platforms to support timely treatment decisions and reduce broad-spectrum antibiotic use. Many facilities integrate point-of-care molecular technologies into infection-control workflows to improve patient outcomes. Faster detection also helps lower hospitalization duration, which encourages wider investment in high-throughput assays and automated lab solutions.
- For instance, Cepheid’s Xpert Xpress SARS-CoV-2 test reports nucleic acid results in about 45 minutes on the GeneXpert system, combining sample prep and amplification in a single cartridge.
Growing regulatory focus on infection prevention
Governments and health agencies continue to tighten standards around infection surveillance and reporting. Mandatory screening protocols push hospitals to increase testing frequency for high-risk cases. Compliance with quality audits and accreditation programs drives adoption of modern diagnostic panels. Stronger enforcement of safety rules supports market growth as facilities allocate higher budget shares for infection prevention and diagnostic upgrades.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Adoption of AI-enabled testing platforms
AI tools help labs detect patterns in infection spread and optimize testing workflows. These platforms support faster review of diagnostic data and provide predictive insights for outbreak management. Hospitals explore AI systems that enhance test interpretation and reduce manual errors. Integration of smart analytics with molecular platforms offers new opportunities for improving infection surveillance efficiency.
- For instance, Philips’ IntelliVue Guardian Solution with automated early warning scoring has been deployed across 3 Lakeland Health hospitals, using continuous vital-sign analytics to flag clinical deterioration earlier.
Growth of decentralized and point-of-care testing models
Care providers shift toward decentralized testing to reduce pressure on central labs and speed up clinical decisions. Point-of-care systems support rapid screening in emergency units, ICUs, and surgical wards. This trend opens opportunities for compact, automated devices that work with minimal sample preparation. Strong interest in bedside testing encourages manufacturers to deliver more portable and user-friendly diagnostic solutions.
- For instance, QuidelOrtho’s Sofia 2 Flu + SARS Antigen FIA produces automated results for influenza A, influenza B, and SARS-CoV-2 in 15 minutes at the point of care.
Rising demand for antimicrobial resistance panels
Pathogen resistance continues to increase, creating strong need for panels that detect multiple resistance markers. Hospitals use these tests to guide targeted therapies and reduce misuse of antibiotics. Expanded adoption of multiplex assays offers opportunities for companies to introduce broader panels. This trend supports improved infection management in high-risk clinical environments.
Key Challenges
High cost of advanced diagnostic systems
Modern molecular platforms and automated systems require significant upfront investment, which limits adoption in smaller facilities. Ongoing maintenance, consumable expenses, and skilled staff needs increase operational cost. Many providers struggle to balance cost with diagnostic accuracy, slowing the transition from conventional methods. Budget constraints remain a major barrier in developing economies.
Shortage of trained laboratory professionals
Healthcare systems face difficulty in maintaining skilled staff capable of handling advanced diagnostic tools. Limited training resources slow integration of new technologies and increase test turnaround times. Workforce gaps strain labs during infection surges, reducing system efficiency. The shortage of qualified personnel challenges sustained and widespread adoption of high-complexity testing platforms.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America led the Hospital Acquired Disease Testing market in 2024 with about 38% share. The region benefits from strong adoption of rapid molecular tests, strict infection-control policies, and high hospital spending. Large healthcare networks use automated diagnostic platforms to reduce detection time and manage antimicrobial resistance. Growing reporting obligations further increase testing volumes. The United States contributes most of the demand due to advanced clinical infrastructure and widespread ICU capacity. Canada adds steady growth through national infection-surveillance programs and greater use of point-of-care screening solutions across acute care facilities.
Europe
Europe followed with nearly 30% share in 2024, supported by robust infection-prevention frameworks and strong regulatory oversight. Hospitals in major markets such as Germany, the United Kingdom, and France rely on rapid diagnostic panels to maintain clinical safety standards. Increased focus on antimicrobial stewardship drives demand for resistance-specific assays. Investment in laboratory automation enhances testing output across public and private hospitals. Expansion of centralized diagnostic networks in Nordic and Western European countries also supports sustained adoption. Eastern Europe records emerging growth as facilities upgrade testing capabilities and align with European healthcare quality guidelines.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific held about 24% share in 2024 and recorded the fastest growth due to rising hospital admissions and higher incidence of device-associated infections. Expanding ICU capacity across China and India increases demand for rapid pathogen identification tools. Hospitals shift toward molecular testing to manage resistant organisms and reduce mortality linked to late diagnosis. Government programs promoting infection surveillance improve adoption across public hospitals. Growing private healthcare investment in Southeast Asia supports new diagnostic installations. Partnerships between global manufacturers and regional distributors accelerate access to advanced testing systems in developing markets.
Latin America
Latin America accounted for around 5% share in 2024, driven by gradual improvement in healthcare infrastructure and increased awareness of infection-control practices. Major countries such as Brazil and Mexico invest in modernizing diagnostic labs to manage rising hospital infection cases. Adoption of rapid tests grows as hospitals work to reduce treatment delays and strengthen surveillance efforts. However, budget limitations slow adoption of high-cost molecular systems. Public health agencies support training programs to improve diagnostic competency and expand use of standardized testing protocols across regional healthcare networks.
Middle East and Africa
The Middle East and Africa held nearly 3% share in 2024, supported by selective investments in advanced hospital diagnostics in the Gulf countries. Nations such as Saudi Arabia and the UAE adopt rapid infection-testing tools to enhance clinical quality and reduce ICU-related risks. Broader regional adoption remains limited due to infrastructure gaps and financial constraints across low-income countries. Infection-prevention programs and international partnerships help improve testing access in select African markets. Gradual expansion of private hospitals and medical tourism in the Middle East also supports higher adoption of modern diagnostic platforms.
Market Segmentations:
By Test Type
- Urinary Tract Infection
- Surgical Site Infection
- Pneumonia Stents
- Blood Stream Infection
- Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus
- Others
By End User
- Hospitals and Intensive Care Units (ICUS)
- Ambulatory Surgical and Diagnostic Centers
- Nursing Homes
- Maternity Centers
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
BD (U.S.), BIOMÉRIEUX (France), Meridian Bioscience, Inc. (U.S.), Eurofins Scientific (Luxembourg), Siemens Healthcare Private Limited (Germany), F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd (Switzerland), QIAGEN (Germany), Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. (U.S.), Hologic, Inc. (U.S.), Cantel Medical (U.S.), and Abbott (U.S.) lead the competitive landscape of the Hospital Acquired Disease Testing market. These companies compete through advanced molecular technologies, rapid diagnostic panels, and integrated infection-surveillance solutions. Their strategies focus on improving detection speed, expanding antimicrobial resistance testing, and strengthening laboratory automation. Many players invest in AI-driven analytics to support early outbreak identification and enhance result accuracy. Product portfolios continue to broaden with multiplex assays, point-of-care platforms, and automated lab instruments designed to handle rising test volumes. Partnerships with healthcare facilities and research institutions help increase adoption across high-risk care units. Strong regulatory compliance capabilities and global distribution networks further reinforce competitive strength in this evolving market.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- BD (U.S.)
- BIOMÉRIEUX (France)
- Meridian Bioscience, Inc. (U.S.)
- Eurofins Scientific (Luxembourg)
- Siemens Healthcare Private Limited (Germany)
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd (Switzerland)
- QIAGEN (Germany)
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. (U.S.)
- Hologic, Inc. (U.S.)
- Cantel Medical (U.S.)
- Abbott (U.S.)
Recent Developments
- In 2025, Roche received FDA clearance and CLIA waiver for its cobas liat sexually transmitted infection (STI) multiplex assay panels, including CT/NG and CT/NG/MG.
- In 2024, bioMérieux SA Acquired the LUMED start-up to leverage data in the fight against antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
- In 2023, Thermo Fisher Scientific unveiled real-time PCR kits in India for the detection of infectious diseases
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Test Type, End-User and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Demand for rapid molecular testing will rise as hospitals prioritize faster diagnosis.
- Automated platforms will gain wider use to improve accuracy and reduce manual workload.
- AI-driven analytics will support early outbreak prediction and better infection surveillance.
- Point-of-care testing will expand across ICUs and emergency departments for quicker decisions.
- Adoption of antimicrobial resistance panels will increase to guide targeted therapy.
- Hospitals will invest more in integrated lab systems to meet regulatory compliance needs.
- Decentralized testing models will grow to reduce pressure on central laboratories.
- Emerging economies will upgrade diagnostic infrastructure to lower infection-related mortality.
- Partnerships between hospitals and diagnostic companies will rise to improve test access.
- Innovation in multiplex assays will drive broader detection of hospital-based pathogens.




