Market overview
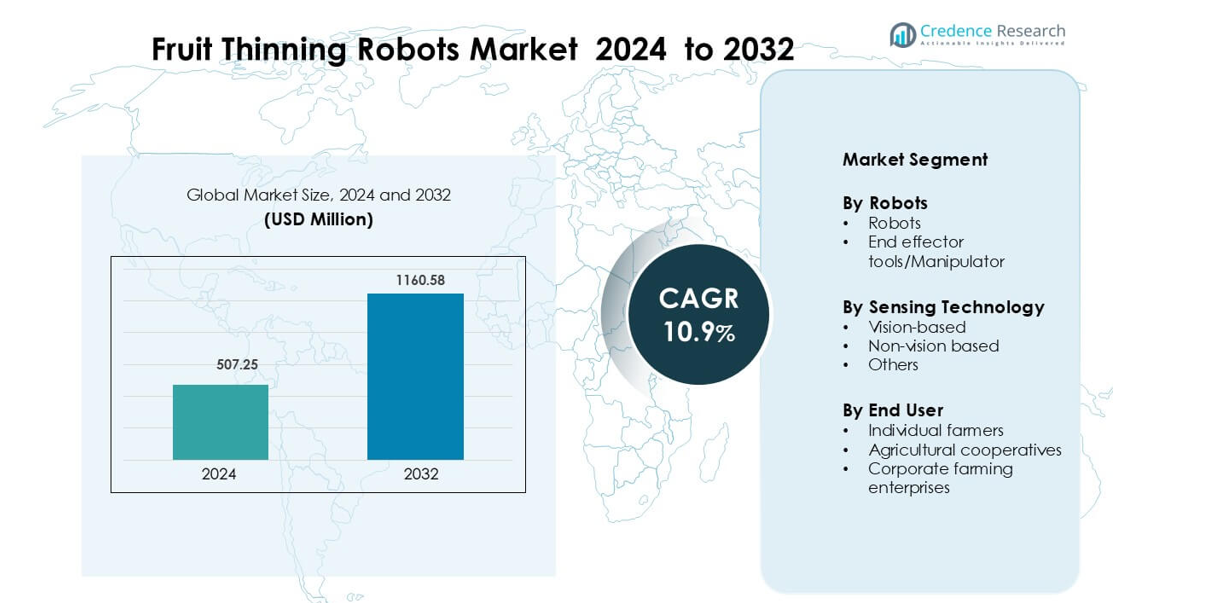
Fruit Thinning Robots Market was valued at USD 507.25 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 1160.58 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 10.9 % during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Fruit Thinning Robots Market Size 2024 |
USD 507.25 million |
| Fruit Thinning Robots Market, CAGR |
10.9% |
| Fruit Thinning Robots Market Size 2032 |
USD 1160.58 million |
The Fruit Thinning Robots Market is driven by key players such as FFRobotics, EcoRobotix, Bakus Robotics, Harvest CROO Robotics LLC, Clearpath Robotics, Abundant Robotics, Advanced Farm Technologies, Aigritec, Fieldwork Robotics, and Harvest Automation Inc. These companies strengthen market growth through advanced vision systems, precise end-effector tools, and autonomous mobility platforms designed for large orchards. Their focus on AI-driven detection and consistent thinning performance helps growers address rising labor shortages and quality demands. North America leads the market with a 37% share in 2024, supported by rapid orchard automation, strong ag-tech adoption, and large commercial fruit farms.
Market Insights
- The Fruit Thinning Robots Market was valued at USD 507.25 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 1160.58 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 10.9 %.
- Rising labor shortages and increasing pressure for uniform fruit quality drive demand, with robots holding the dominant segment share at 63% due to higher field efficiency and consistent thinning accuracy.
- Vision-based systems show strong momentum as improved AI detection, multispectral imaging, and adaptive sensing support better performance in dense canopies and varying light conditions.
- Competition intensifies as players introduce lightweight autonomous platforms, modular end-effectors, and cloud-linked diagnostics, while high upfront cost remains a key restraint for small and mid-sized orchards.
- North America leads with 37% share in 2024 due to rapid orchard mechanization, followed by Europe at 29% and Asia Pacific at 23%, with individual farmers representing the largest adopter category at 46%.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Robots
Robots lead this segment with about 63% share in 2024 due to higher adoption of autonomous thinning systems that reduce labor dependence during peak seasons. Growers prefer full robotic units because they offer faster cycle times, stable precision, and continuous 24/7 operation in orchards. Demand rises as producers shift toward automation to offset rising labor shortages and improve crop load uniformity. End-effector tools and manipulators grow at a steady pace as farmers upgrade older systems for better grip control and damage reduction in delicate fruit varieties.
- For instance, Washington State University’s robotic blossom-thinning system, using a UR5e industrial arm and depth-camera vision, thinned 67.2% of flowers in a cluster in “boundary thinning” mode with a cycle time of just 9.0 seconds per cluster.
By Sensing Technology
Vision-based systems dominate this segment with nearly 58% share in 2024 due to strong accuracy in fruit identification, spacing assessment, and selective thinning tasks. Growers adopt RGB-D, multispectral, and stereo-vision modules because these tools provide real-time data for precise robotic movements. Adoption rises as imaging systems improve under variable lighting and canopy density. Non-vision and other sensing methods expand with use in harsh weather conditions and low-light environments, but uptake remains slower due to lower spatial accuracy.
- For instance, a LiDAR‑camera fusion system developed by researchers at Monash University achieved fruit‑localisation standard deviations of just 0.253 cm at 0.5 m, 0.230 cm at 1.2 m, and 0.285 cm at 1.8 m in bright sunlight by combining high‑resolution solid‑state LiDAR with RGB imagery.
By End User
Individual farmers hold the leading share at about 46% in 2024 as small and mid-sized orchards adopt compact robotic thinning solutions to replace seasonal labor. These farmers prefer affordable autonomous units that improve productivity and reduce human error in early fruit-load control. Agricultural cooperatives grow steadily because shared-equipment models lower ownership costs. Corporate farming enterprises increase adoption as large orchards scale automated thinning fleets to improve uniformity and optimize yield consistency across wide acreage.
Key Growth Drivers
Labor Shortages Accelerating Automation Demand
Labor scarcity remains the strongest driver in the fruit thinning robots market as orchards struggle to secure reliable seasonal workers during peak thinning periods. Rising wages, aging rural labor populations, and stricter immigration controls push growers toward automated thinning solutions. Robotic systems reduce dependence on manual labor while offering predictable performance, which helps maintain fruit size uniformity and yield quality. Autonomous units also operate longer hours with higher precision, lowering the risk of inconsistent thinning. As global orchard acreage expands, especially in apples, peaches, and pears, growers adopt automated tools to stabilize operations and minimize production delays. The shift toward continuous and timely thinning reinforces adoption, making labor shortages a central growth catalyst.
- For instance, Tevel Aerobotics raised US$ 20 million for its FAR (Flying Autonomous Robot) drones that can pick fruit on demand the company explicitly cites labor shortages (especially in orchard workforces) as a key reason for the technology’s deployment.
Need for Higher Yield Quality and Uniformity
Demand for premium-grade fruit drives strong investment in robotic thinning systems that improve size uniformity and reduce overload stress on trees. Traditional manual thinning often suffers from inconsistency and timing delays, which affects fruit quality. Robotic platforms equipped with vision-guided tools allow producers to control fruit load more accurately, improving grading outcomes and market value. Growers also adopt automation to reduce crop losses linked to late or uneven thinning, which can impact ripening and reduce pack-out rates. With global retailers tightening quality specifications, orchard managers view automated thinning as a strategic tool to deliver consistent produce. The link between uniform thinning and higher revenue strengthens the long-term adoption of fruit thinning robots.
- For instance, Penn State’s UGV-based chemical thinning system detected flower clusters with 93.8% precision and produced an average fruit set of 2.2 fruits per cluster, closely matching optimal targets and demonstrating improved load control.
Rising Adoption of Precision Orchard Management
Digital orchard management is expanding rapidly, and thinning robots play a key role in precision practices. Growers use robots equipped with multispectral imaging, AI-based detection, and cloud-linked analytics to thin fruit with greater accuracy than manual methods. Robots provide real-time data on fruit density, branch load, and canopy conditions, enabling smarter orchard planning. Precision thinning helps optimize inputs such as fertilizers, water, and pruning effort by balancing tree vigor. Integrating robots with orchard management software boosts traceability and improves decision-making through data-driven insights. As farms invest in smart irrigation, automated spraying, and yield monitoring systems, thinning robots align naturally with broader digital transformation trends, reinforcing market growth.
Key Trends and Opportunities
Advancements in Vision and Sensing Technologies
Progress in camera systems, multispectral imaging, LiDAR, and AI-based classification drives key market trends, allowing robots to operate with higher accuracy in dense canopies. New deep-learning algorithms enhance fruit detection even under shadow, glare, or irregular tree structures. These improvements reduce error rates and allow robots to adapt across varying fruit varieties and orchard architectures. As sensing modules become smaller, more affordable, and more power-efficient, manufacturers integrate them into compact robot platforms suitable for small and mid-sized farms. This trend supports wider adoption and opens new opportunities to develop robots tailored for diverse fruit crops.
- For instance, a LiDAR–camera fusion system demonstrated by Kang et al. achieved fruit‑localization standard deviations of just 0.245 cm at 0.5 m, 0.227 cm at 1.2 m, and 0.275 cm at 1.8 m, which is over five times more precise than a conventional Realsense D455 sensor.
Growth of Modular and Retrofittable Robotic Tools
Manufacturers increasingly design modular robotic arms and end-effector tools that attach to existing farm machinery or autonomous carriers. This trend enables farmers to upgrade older thinning systems without purchasing full robots, reducing capital barriers. Retrofittable tools also support flexible deployment across different orchard zones. As growers look for cost-effective automation, modular solutions create strong opportunities for vendors offering interchangeable grippers, adaptive manipulators, or toolkits optimized for crop-specific thinning. These innovations broaden access for small farms and cooperatives while expanding the serviceable market.
- For instance, researchers from Carnegie Mellon developed Hefty, a modular reconfigurable robot platform with interchangeable modules for mobility, sensing, power, and end‑effectors they demonstrated five different configurations (e.g., for grasping, pruning, or sensing) for various orchard tasks.
Key Challenges
High Initial Investment and Integration Costs
High upfront costs remain a major challenge as fruit thinning robots require advanced sensing hardware, AI processors, rugged mobility platforms, and orchard-specific customization. Many small and mid-sized orchards struggle with the capital needed for full robotic systems. Integration into existing farm layouts, especially older orchards with narrow rows or irregular canopies, adds additional cost and complexity. Growers also face expenses related to software updates, maintenance, and operator training. These investment barriers slow adoption despite long-term labor savings, particularly in emerging markets with limited automation budgets.
Operational Limitations in Complex Orchard Environments
Robot performance can be constrained by varying fruit densities, irregular branch geometry, inconsistent lighting, and weather conditions such as dust or rain. Vision-based systems can experience reduced accuracy in dense canopies, leading to missed or incorrect thinning actions. Terrain unevenness, slopes, and narrow rows in traditional orchards limit robotic mobility and reduce productivity. Additionally, some fruit varieties require delicate handling that current end-effector tools cannot always manage reliably. These operational challenges push manufacturers to enhance robustness, sensing accuracy, and adaptive algorithms, but they continue to affect field performance and real-world adoption.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America leads the fruit thinning robots market with about 37% share in 2024 due to strong adoption of orchard automation in the U.S. and Canada. Apple and peach growers invest heavily in robotic thinning to reduce labor shortages and improve yield uniformity. Supportive ag-tech funding, rising wages, and advanced digital farming ecosystems further accelerate adoption. High penetration of precision orchard tools, including vision-based robotic systems, positions the region as the early adopter. Increasing expansion of large commercial orchards strengthens long-term demand for autonomous thinning platforms across major fruit-producing states.
Europe
Europe holds nearly 29% share in 2024, driven by strong modernization of orchards in Italy, Spain, France, and the Netherlands. Strict labor regulations, higher wages, and sustainability goals encourage farmers to shift toward automated thinning solutions. European orchards benefit from structured layouts suited for robotic navigation, enabling consistent performance. Government incentives supporting smart farming and AI-driven agriculture drive market growth. Demand increases as fruit producers focus on premium-grade apples, pears, and stone fruits, where uniform thinning directly enhances export quality and profitability.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific captures around 23% share in 2024 as China, Japan, South Korea, and Australia increase investments in agricultural robotics. Large orchard areas, rising labor scarcity, and rapid digital transformation push growers toward autonomous thinning systems. Japan leads high-tech orchard automation, while China increases adoption through domestic robotics production. Expanding commercial fruit farming, especially in apples and citrus, boosts demand across the region. Government programs aimed at reducing manual dependence and promoting smart agriculture accelerate growth. Adoption continues rising as farmers seek improved productivity and consistent fruit size.
Latin America
Latin America accounts for nearly 7% share in 2024, supported by orchard expansion in Chile, Brazil, and Argentina. Growers increasingly adopt robotic thinning to improve export-quality fruit, especially apples, grapes, and citrus. Labor shortages during peak seasons and rising operational costs encourage interest in automated thinning systems. Investment grows slowly due to high upfront costs, but large commercial farms adopt new technologies faster. As export markets raise quality standards, orchard managers view robotic thinning as a strategic tool to increase pack-out rates and reduce seasonal workforce dependence.
Middle East & Africa
Middle East & Africa hold about 4% share in 2024, with adoption driven mainly by high-value orchard development in Israel, South Africa, and the UAE. Precision agriculture technologies gain traction as growers face water scarcity, high labor expenses, and the need for efficient resource use. Israel leads innovation with advanced sensing and AI-based orchard tools. South Africa expands adoption in commercial fruit farms focused on global exports. While adoption is gradual due to capital constraints, interest grows as robotic thinning helps improve fruit uniformity under challenging climate conditions.
Market Segmentations:
By Robots
- Robots
- End effector tools/Manipulator
By Sensing Technology
- Vision-based
- Non-vision based
- Others
By End User
- Individual farmers
- Agricultural cooperatives
- Corporate farming enterprises
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The Fruit Thinning Robots Market is shaped by leading companies such as FFRobotics, EcoRobotix, Bakus Robotics, Harvest CROO Robotics LLC, and Clearpath Robotics, Inc., all of which compete through advanced sensing technologies, autonomous navigation, and crop-specific robotic tools. These manufacturers focus on improving fruit detection accuracy, end-effector precision, and thinning speed to support large orchard operations. Many companies invest in AI-driven vision systems to adapt robots to variable canopy densities and lighting conditions. Partnerships with orchard operators, research institutions, and ag-tech integrators help vendors test robots across diverse fruit varieties. Companies also expand modular toolkits that allow growers to customize robots for apples, peaches, pears, and citrus crops. As competition grows, players strengthen aftermarket services, remote diagnostics, and fleet-management platforms to improve uptime. Continuous innovation in lightweight mobility platforms and battery efficiency positions these companies to accelerate market penetration in regions facing severe labor shortages.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- FFRobotics
- EcoRobotix
- Bakus Robotics
- Harvest CROO Robotics LLC
- Clearpath Robotics, Inc.
- Abundant Robotics
- Advanced Farm Technologies
- Aigritec
- Fieldwork Robotics
- Harvest Automation Inc
Recent Developments
- In November 2025, FFRobotics an orchard technology article reported their robotic harvester matches six pickers. It achieves about 85% harvesting efficiency in structured orchards, showing near-commercial maturity.
- In September 2025, EcoRobotix New Ultra-High Precision crop algorithms were announced for vegetable farming. The update allows non-selective herbicides with plant-by-plant targeting, cutting manual weeding and input waste.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Robots, Sensing Technology, End User and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Adoption of fruit thinning robots will rise as labor scarcity increases across major orchard regions.
- Vision-based AI systems will improve detection accuracy and support faster thinning decisions.
- Robots will expand to more fruit varieties, including citrus, plums, and apricots.
- Modular end-effectors will gain traction as growers seek crop-specific customization.
- Integration with digital orchard management platforms will boost data-driven yield planning.
- Autonomous navigation will become more reliable in dense canopies and uneven terrains.
- Leasing and shared-equipment models will grow to reduce high ownership costs.
- Battery efficiency and lightweight designs will enhance field coverage and operating hours.
- Regional expansion will accelerate in Asia Pacific and Europe as local manufacturers scale production.
- Continuous field trials and partnerships with growers will speed technological refinement and commercialization.




