Market Overview
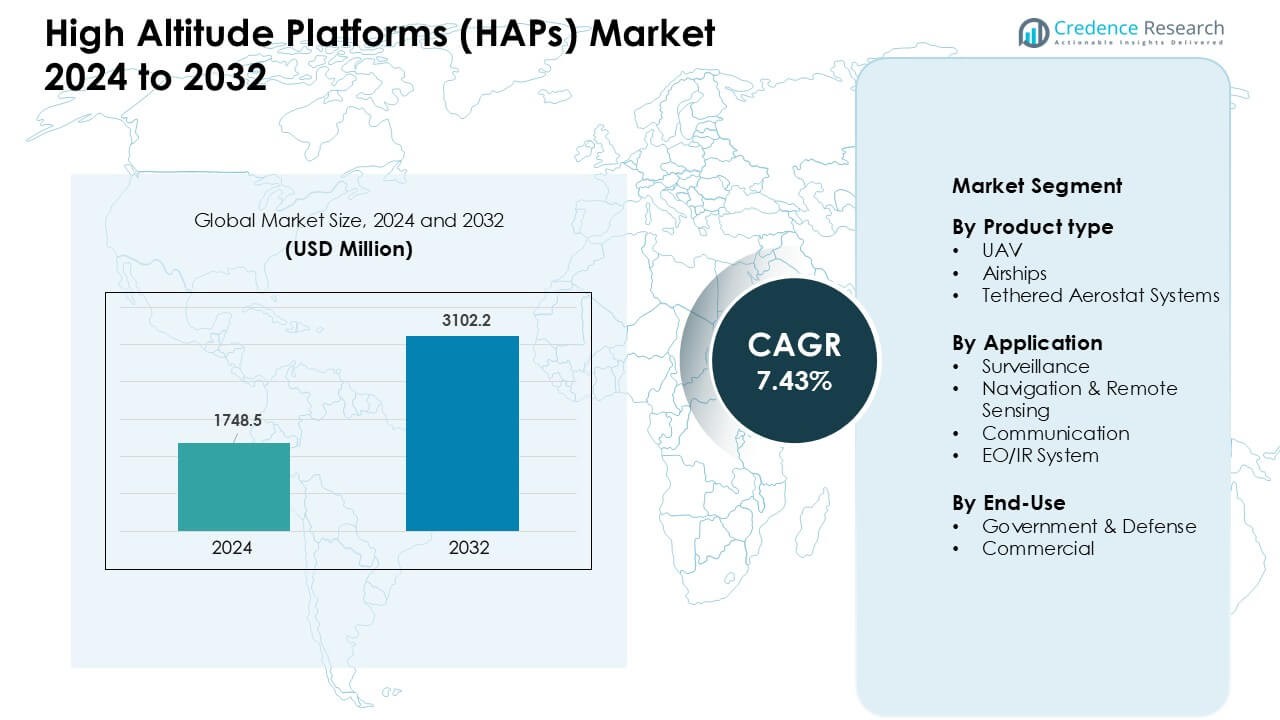
High Altitude Platforms (HAPs) Market was valued at USD 1748.5 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 3102.2 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 7.43 % during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| High Altitude Platforms (HAPs) Market Size 2024 |
USD 1748.5 Million |
| High Altitude Platforms (HAPs) Market, CAGR |
7.43 % |
| High Altitude Platforms (HAPs) Market Size 2032 |
USD 3102.2 Million |
The High Altitude Platforms (HAPs) Market is shaped by major players such as Thales, AeroVironment, Inc., ILC Dover LP, Rafael Advanced Defense Systems, AIRBUS, Israel Aerospace Industries, Aeros, TCOM, L.P., Northrop Grumman, and Lindstrand Technologies Limited. These companies strengthen their positions through long-endurance UAV development, advanced aerostat systems, and multi-mission payload integration for surveillance, communication, and environmental monitoring. North America remained the leading region in 2024 with a 38% share, supported by strong defense budgets, early technology adoption, and extensive testing of HAP-based connectivity solutions.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The High Altitude Platforms (HAPs) Market reached USD 5 million in 2024 and is projected to hit USD 3102.2 million by 2032, registering a CAGR of 7.43%.
- Growing demand for persistent surveillance, long-endurance communication systems, and real-time monitoring drives adoption across defense, telecom, and environmental agencies.
- Rising use of solar-powered UAVs, stratospheric connectivity platforms, and 5G-NTN integration shapes market trends, with communication-focused HAPs holding the largest segment share at about 41% in 2024.
- Competition remains strong among Thales, Northrop Grumman, AIRBUS, AeroVironment, and ILC Dover as companies develop multi-week endurance platforms, advanced payloads, and high-altitude airships while facing cost, regulatory, and operational challenges.
- North America led the market with 38% in 2024, followed by Europe at 27% and Asia-Pacific at 24%, supported by rising defense modernization, remote connectivity expansion, and high-altitude research programs.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Product Type
UAVs held the dominant share in 2024 with nearly 61% of the High Altitude Platforms (HAPs) Market. Demand grew as UAVs offered long-endurance flights, flexible payload capacity, and rapid deployment for defense and commercial uses. UAV platforms also supported cost-effective operations compared to manned systems, which attracted governments seeking persistent aerial coverage. Airships followed due to rising interest in long-duration communication missions, while tethered aerostat systems gained use in border monitoring and stationary surveillance projects across developing regions.
- For instance, the Airbus Zephyr a high-altitude solar-powered UAV achieved a continuous flight endurance of 624 hours (about 26 days) during tests, carrying a payload of 5 kg.
By Application
Surveillance captured the largest share in 2024 at about 47% of the High Altitude Platforms (HAPs) Market. Agencies favored high-altitude systems for wide-area observation, real-time threat tracking, and disaster assessment. Growth also came from rising investments in homeland security and cross-border intelligence programs. Navigation and remote sensing expanded with higher adoption in climate monitoring and agricultural mapping. Communication platforms advanced as telecom firms tested stratospheric networks for rural connectivity, while EO/IR systems gained interest for precision imaging in defense missions.
- For instance, the Airbus Zephyr, a stratospheric high-altitude UAV, operates around 21 km (70,000 ft) altitude, has a 25-meter wingspan, and weighs less than 75 kg, yet it can remain aloft for over 67 days (more than 1,600 hours) while providing continuous Earth-observation and intelligence data coverage.
By End-Use
Government and defense dominated the market in 2024 with roughly 68% share. Demand stayed high as defense agencies required persistent ISR coverage, high-altitude communication relays, and rapid-response aerial systems. Funding for border protection, strategic surveillance, and military modernization boosted platform procurement. The commercial segment grew as companies explored HAPs for broadband delivery, environmental studies, disaster support, and logistics mapping. Rising interest in stratospheric connectivity and Earth-observation services continued to pull new private players into the market.
Key Growth Drivers:
Rapid Demand for Persistent Surveillance
Growing security needs drive strong adoption of High Altitude Platforms. Governments use long-endurance UAVs and aerostats for border monitoring and disaster assessment. These platforms provide wide-area coverage without the high operating cost of satellites. Defense agencies prefer HAPs because the systems stay aloft for weeks and offer real-time intelligence. Civil agencies also deploy them for wildfire tracking and coastal management as climate risks rise. The steady expansion of smart-surveillance programs in the US, China, India, and the EU strengthens demand. Rising cross-border tensions, urban crowd monitoring, and national security modernization plans support steady growth across military and civil segments.
- For instance, the Indian Air Force (IAF) recently issued a request for information to acquire three stratospheric high-altitude platform (HAPS) aircraft capable of operating around 20 km altitude for persistent ISR (intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance) missions.
Growing Use in Broadband and Connectivity Expansion
Global connectivity programs boost HAP deployment across rural and underserved regions. Telecom operators use stratospheric platforms to extend 4G/5G coverage at lower cost than terrestrial towers. The technology supports high-capacity backhaul links for remote mining, offshore energy sites, and island economies. Governments and private networks explore HAPs as an alternative to satellites for temporary connectivity during natural disasters. The rise of remote work, digital government programs, and cloud-based services also increases network load, pushing operators to adopt flexible airborne infrastructure. Major investments in non-terrestrial networks (NTN) strengthen adoption as countries target universal digital coverage.
- For instance, HAP-based broadband architectures studied in academic literature show that HAPs can serve as wireless backhaul links for IoT sensors and remote ground networks, enabling data aggregation and transmission from rural, mountainous or forested regions directly to a HAP node bypassing ground infrastructure constraints.
Advances in Lightweight Materials and Solar-Powered Designs
Modern HAP systems benefit from rapid innovation in materials, batteries, and propulsion. New composite materials reduce airframe weight and improve resistance to stratospheric conditions. Solar-powered UAVs deliver multi-week endurance with minimal fuel needs. High-density batteries extend nighttime operations and support stronger payloads for communication, imaging, and sensing. These improvements lower operating costs and expand mission profiles for telecom, defense, and environmental monitoring. R&D programs in the US, Japan, South Korea, and Europe continue pushing longer endurance and higher altitude stability. Better payload integration makes HAPs viable for many industries that once relied only on satellites or ground-based towers.
Key Trends & Opportunities:
Rising Integration with 5G and NTN Ecosystems
The market benefits from strong alignment with emerging non-terrestrial networks. HAPs support seamless integration with 5G radio units, cloud-core networks, and edge-computing architectures. Telecom operators deploy them to strengthen coverage in sparsely populated zones without waiting for fiber expansion. Standardization by 3GPP encourages wider commercial adoption and reduces risk for operators. Many governments now include airborne platforms in national digital-inclusion plans, which opens new contract opportunities. As network slicing and low-latency services spread across industries, HAPs help deliver reliable connectivity for logistics, telemedicine, and disaster-response operations.
- For instance, the 3GPP — the global standard-setting body for mobile networks — formally included NTN (which covers satellites, high-altitude platform systems (HAPS), and drones) in its Release 17 specifications, enabling 5G NR over non-terrestrial links.
Expanding Use in Environmental and Climate Monitoring
Climate programs create new opportunities for atmospheric sensing and disaster management. HAPs support high-resolution imaging of glaciers, flood zones, forests, and pollution hotspots. These systems operate above commercial air traffic and collect continuous data that satellites cannot always capture due to orbital gaps. Environmental agencies use HAPs for methane tracking, crop health analysis, and early wildfire detection. Countries facing rising climate risks, such as Japan, Australia, and the US, invest in high-altitude sensing to improve preparedness. Commercial firms explore HAP-based analytics for insurance, agriculture, and energy sectors, expanding the market beyond traditional defense use.
- For instance, HAP-based air-quality monitoring studies envision platforms operating at stratospheric altitudes that provide near-continuous observations of both surface-level pollution and atmospheric constituents enabling detection of pollution “hotspots” over cities or industrial regions that ground-based sensors might miss.
Emerging Opportunities in Stratospheric IoT Networks
IoT growth drives interest in large-area sensor connectivity from the stratosphere. HAP networks support thousands of sensors for pipeline monitoring, maritime tracking, and precision farming. Industries rely on HAP-IoT links to monitor equipment in deserts, oceans, and mountains, where terrestrial towers are impractical. New low-power protocols allow cost-effective long-distance communication. Energy firms and logistics companies test HAP-based asset-tracking programs to cut losses and improve supply-chain visibility. As global IoT deployments grow, demand for wide-area, low-cost, and low-latency airborne connectivity continues to increase.
Key Challenges:
High Operational and Maintenance Complexity
HAP systems face technical challenges due to extreme stratospheric conditions. Maintaining structural stability, temperature control, and energy efficiency requires advanced engineering. Sudden wind shifts or prolonged cloud cover can reduce endurance for solar-powered UAVs. Airships and aerostats need careful handling, logistics support, and skilled operators. Many operators struggle with high maintenance needs and limited availability of specialized components. These factors increase lifecycle cost and slow adoption among smaller telecom operators or civil agencies. The need for frequent inspection, payload calibration, and safety compliance adds further complexity.
Regulatory Barriers and Airspace Integration Issues
Airspace rules remain a major bottleneck for large-scale HAP adoption. Many countries lack clear frameworks for long-endurance platforms operating above commercial aviation lanes. Approvals for cross-border flights, payload operation, and spectrum allocation often take months. Telecom-focused HAP missions require coordination with national spectrum agencies, which slows deployment. Defense-related missions face restrictions tied to surveillance concerns. Operating in the stratosphere also requires harmonized standards across regions, which remain limited. These regulatory gaps create uncertainty for investors and delay commercial projects in both communication and surveillance segments.
Regional Analysis:
North America
North America held the leading share in the High Altitude Platforms (HAPs) Market in 2024 with about 38%. Defense modernization programs in the US drove strong procurement of surveillance-focused UAVs and aerostats. Telecom operators also tested HAP-based connectivity to expand coverage in rural regions. Federal agencies used high-altitude systems for disaster mapping and wildfire monitoring, which reinforced adoption. Canada advanced trials for remote-area broadband and environmental observation. The presence of major aerospace contractors, strong funding programs, and early regulatory progress supported the region’s sustained leadership and continued technology development.
Europe
Europe accounted for nearly 27% of the High Altitude Platforms (HAPs) Market in 2024, driven by rising investments in defense surveillance, climate monitoring, and 5G extension programs. The UK, Germany, and France expanded trials of high-endurance solar UAVs for persistent intelligence and communication support. The EU’s focus on non-terrestrial networks encouraged deployment models for emergency connectivity and environmental sensing. European agencies also funded HAP-based research for border monitoring and disaster-response operations. Strong aerospace manufacturing capabilities and cross-border research projects helped strengthen regional adoption.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific held roughly 24% of the High Altitude Platforms (HAPs) Market in 2024, supported by rapid investments in security, telecom expansion, and atmospheric monitoring. China, Japan, India, and South Korea led procurement of long-endurance UAVs and tethered aerostats for surveillance, communication, and disaster-response missions. Telecom operators in emerging economies explored HAPs to extend broadband into remote islands and mountainous regions. Government-backed programs for stratospheric research and solar-electric UAV development also grew. Expanding military budgets and digital-infrastructure programs strengthened adoption across both defense and commercial sectors.
Latin America
Latin America captured about 6% of the High Altitude Platforms (HAPs) Market in 2024. Brazil and Mexico led regional adoption, using HAPs for border monitoring, Amazon-region surveillance, and emergency communication support. Several countries tested tethered aerostat systems for coastal security and environmental mapping. Rural telecom expansion plans created interest in HAP-based connectivity, though large-scale deployments remained limited due to budget constraints. Growing environmental risks increased the need for high-resolution monitoring across forests, rivers, and farmland. Gradual regulatory improvements and partnerships with global OEMs supported the region’s emerging demand.
Middle East & Africa
Middle East & Africa held around 5% of the High Altitude Platforms (HAPs) Market in 2024. Gulf nations invested in high-altitude surveillance platforms for border protection and critical-infrastructure monitoring. Countries like the UAE and Saudi Arabia supported trials for communication-focused HAPs to enhance remote-area connectivity. African markets showed early adoption for wildlife tracking, disaster assessment, and rural broadband support. However, budget limits and regulatory gaps restricted wide deployment. Growing security needs and infrastructure expansion plans are expected to drive gradual adoption as more nations modernize their surveillance and communication capabilities.
Market Segmentations:
By Product type
- UAV
- Airships
- Tethered Aerostat Systems
By Application
- Surveillance
- Navigation & Remote Sensing
- Communication
- EO/IR System
By End-Use
- Government & Defense
- Commercial
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape:
The High Altitude Platforms (HAPs) Market features strong competition among leading aerospace and defense companies developing advanced UAVs, airships, and tethered aerostat systems. Key players such as Thales, AeroVironment, Inc., ILC Dover LP, Rafael Advanced Defense Systems, AIRBUS, Israel Aerospace Industries, Aeros, TCOM, L.P., Northrop Grumman, and Lindstrand Technologies Limited focus on high-endurance platforms, multi-mission payloads, and integrated communication solutions. These firms strengthen their positions through long-duration solar UAV programs, improved aerostat designs, and stratospheric connectivity projects. Defense demand for surveillance and intelligence systems drives steady procurement, while telecom operators and environmental agencies expand trials for broadband extension and climate monitoring. Strategic partnerships with government agencies, cross-border R&D programs, and investments in lightweight materials support innovation. Leading players compete on endurance, payload efficiency, operational reliability, and cost optimization as the market shifts toward multi-week, autonomous stratospheric platforms.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Thales
- AeroVironment, Inc.
- ILC Dover LP
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- AIRBUS
- Israel Aerospace Industries
- Aeros
- TCOM, L.P.
- Northrop Grumman
- Lindstrand Technologies Limited
Recent Developments
- In September 2025, TCOM announced it will showcase its latest elevated-ISR aerostat platforms at the 33rd International Defence Industry Exhibition (MSPO 2025).
- In April 2025, Thales Alenia Space showcased its space/HAP capabilities at the 40th Space Symposium (April 2025), highlighting continued program activity and outreach for stratospheric missions.
- In October 2024, AeroVironment, Inc.: flight-tested an upgraded Sunglider™ HAPS (announced Oct 1, 2024); the upgrade (branded Horus™ A for government use in some materials) boosts payload and power for long-duration, stratospheric HAPS missions.
Report Coverage:
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Product Type, Application, End-Use and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook:
- HAP adoption will rise as defense agencies expand long-endurance surveillance programs.
- Telecom operators will use stratospheric platforms to strengthen remote and rural connectivity.
- Solar-powered UAVs will gain wider use due to longer endurance and lower operating cost.
- Integration with 5G non-terrestrial networks will accelerate commercial deployment.
- Environmental agencies will rely more on HAPs for climate, pollution, and disaster monitoring.
- Stratospheric airships will advance as materials and propulsion technologies improve.
- Multi-mission payloads will support growth across communication, imaging, and sensing tasks.
- Industry partnerships between aerospace firms and telecom operators will increase.
- Regulatory frameworks will evolve to support cross-border stratospheric operations.
- Emerging economies will adopt HAPs for border security and digital-infrastructure expansion.




