Market Overview
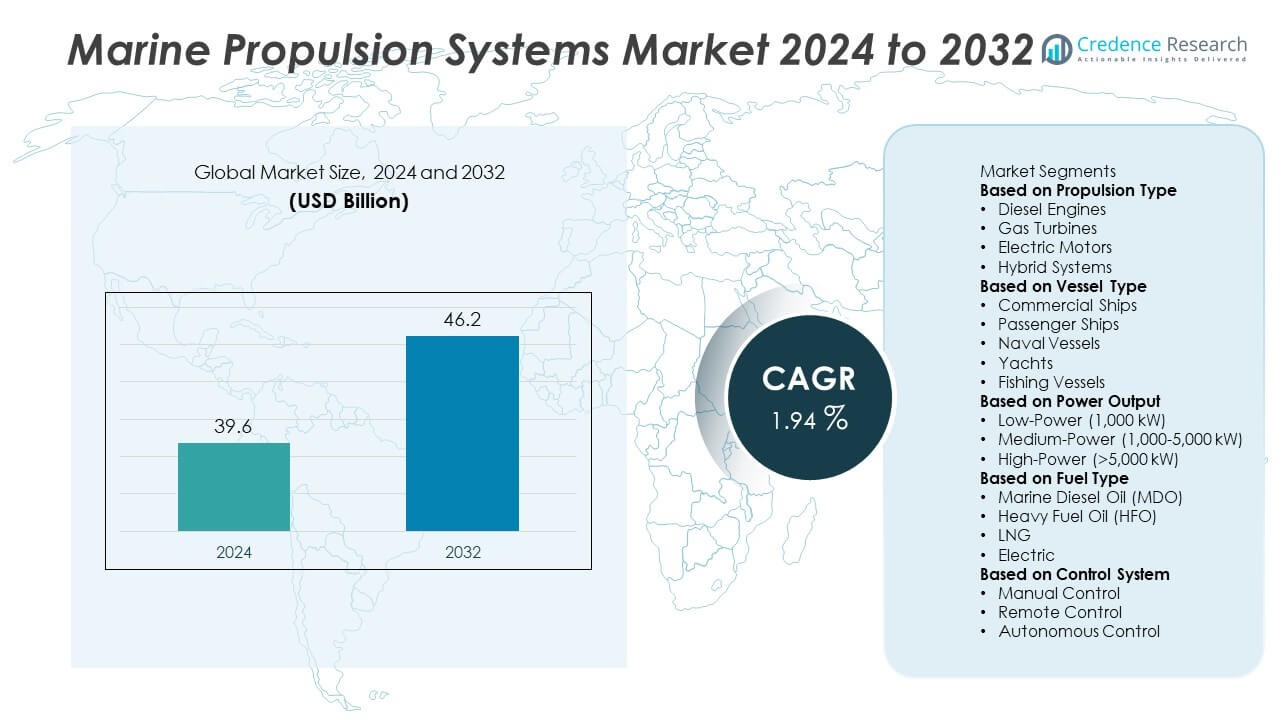
The Marine Propulsion Engine Market was valued at USD 39.6 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 46.2 billion by 2032, registering a CAGR of 1.94% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2024 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Marine Propulsion Engine Market Size 2024 |
USD 39.6 Million |
| Marine Propulsion Engine Market, CAGR |
1.94% |
| Marine Propulsion Engine Market Size 2032 |
USD 46.2 Million |
The Marine Propulsion Engine Market grows through rising demand for fuel-efficient and low-emission technologies, supported by strict International Maritime Organization regulations. Increasing global trade and fleet modernization boost adoption of advanced propulsion across commercial vessels.
The Marine Propulsion Engine Market demonstrates strong geographical presence across major regions, with Asia-Pacific leading due to its dominance in shipbuilding industries in China, Japan, and South Korea. Europe advances rapidly with its focus on green shipping, hybrid propulsion, and strict emission regulations that accelerate adoption of alternative fuels. North America shows steady growth supported by commercial shipping activity and significant naval investments in nuclear-powered and turbine-based propulsion. Latin America and the Middle East & Africa gain traction through offshore oil, gas, and defense programs, where modernization drives demand for advanced systems. Key players shaping the market include Caterpillar Inc., known for its high-performance diesel propulsion engines, MAN Energy Solutions, which specializes in dual-fuel and LNG systems, and ABB Group, a leader in hybrid-electric and automation technologies. Companies such as Hyundai Heavy Industries also contribute through integrated propulsion solutions supporting both commercial and naval applications worldwide.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The Marine Propulsion Engine Market was valued at USD 39.6 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 46.2 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 1.94%.
- Rising demand for fuel-efficient and low-emission propulsion systems drives growth, supported by global regulations set by the International Maritime Organization.
- The market shows strong trends toward hybrid and fully electric propulsion in ferries and cruise ships, along with growing adoption of LNG, hydrogen, and biofuel-powered systems in commercial fleets.
- Competition remains intense with players such as Caterpillar Inc., MAN Energy Solutions, ABB Group, Hyundai Heavy Industries, and Cummins focusing on sustainable propulsion technologies and global fleet modernization projects.
- High upfront costs for advanced propulsion systems, infrastructure limitations for LNG and hydrogen, and uncertainty around fuel availability act as restraints, slowing rapid adoption across developing regions.
- Asia-Pacific leads due to its strong shipbuilding base in China, Japan, and South Korea, while Europe focuses on green shipping initiatives and North America benefits from naval propulsion programs.
- Latin America and the Middle East & Africa show gradual expansion through offshore oil and gas projects, naval modernization, and regional shipping activities, offering new opportunities for propulsion system providers.
Market Drivers
Rising Demand for Fuel-Efficient and Low-Emission Technologies
The Marine Propulsion Engine Market benefits from the rising focus on fuel efficiency and emission reduction. International Maritime Organization (IMO) regulations set strict limits on sulfur oxide and greenhouse gas output, driving adoption of cleaner systems. Shipbuilders and operators invest in dual-fuel engines, LNG propulsion, and hybrid-electric solutions to comply with global standards. It creates consistent demand for advanced propulsion designs that balance performance with sustainability. Manufacturers work to integrate efficient combustion, optimized hull interaction, and renewable integration into vessel operations. These efforts strengthen industry alignment with long-term environmental goals.
- For instance, In May 2025, MAN Energy Solutions announced it would deliver its most powerful two-stroke methanol engine, the MAN B&W 12G95ME-C10.5-LGIM, in June 2025. The engine was confirmed to have an output of 82,440 kW and is destined for a new series of twelve 24,000 TEU container vessels. The first of these engines, built by licensee CSSC-MES Diesel in China, passed its Factory Acceptance Test before the delivery announcement.
Expanding Global Trade and Fleet Modernization Programs
The Marine Propulsion Engine Market grows with global trade expansion and modernization of commercial fleets. Container ships, bulk carriers, and tankers require reliable and high-output propulsion systems for long voyages. Governments and private operators replace aging fleets with vessels designed for higher efficiency and compliance. It ensures steady orders for propulsion technologies across commercial shipping sectors. Rising offshore oil and gas exploration also supports demand for powerful marine engines. Modernization programs encourage adoption of digital monitoring and predictive maintenance, enhancing propulsion system reliability.
- For instance, In May 2024, Caterpillar Marine and Damen Shipyards Group signed an MoU to deploy the first field demonstration of dual-fuel Cat 3500E series methanol marine engines in new tugs in 2026. A version of the 3500E platform can deliver up to 2,525 kW, and the new methanol engines are designed to meet upcoming emissions standards.
Technological Advancements in Hybrid and Electric Propulsion
The Marine Propulsion Engine Market advances through rapid adoption of hybrid and fully electric propulsion. Shipbuilders integrate battery storage, electric motors, and energy management systems into vessels across multiple classes. Ferries, cruise ships, and naval vessels explore electrification to meet sustainability targets. It enables lower operational costs, quieter operations, and reduced maintenance requirements. Advances in energy storage capacity allow larger vessels to explore extended-range electric solutions. Partnerships between propulsion system providers and energy technology firms accelerate innovation and market penetration.
Increasing Investment in Naval and Defense Applications
The Marine Propulsion Engine Market secures growth from rising investments in naval fleets and defense programs. Governments prioritize propulsion technologies that enhance maneuverability, stealth, and endurance of naval vessels. Demand for nuclear propulsion in submarines and advanced turbine systems in destroyers drives steady progress. It highlights the strategic role of propulsion technology in national security objectives. Naval modernization programs stimulate continuous research into high-power-density systems and noise-reduction techniques. These investments reinforce the market’s importance in both commercial and defense applications.
Market Trends
Adoption of Alternative Fuels and Cleaner Energy Sources
The Marine Propulsion Engine Market shows a strong shift toward alternative fuels and cleaner technologies. LNG, hydrogen, and biofuels gain importance due to their ability to reduce emissions. Shipbuilders invest in propulsion systems compatible with multiple fuel options to increase flexibility. It encourages operators to reduce dependency on conventional marine diesel. Hybrid systems combining conventional engines with renewable sources also gain traction in passenger and cargo fleets. This trend reflects industry-wide alignment with global sustainability goals.
- For instance, The AIDAnova, an LNG dual-fuel cruise ship delivered in 2018, was equipped with four Caterpillar dual-fuel engines that have a combined output of 61,760 kW. While it was the first cruise ship capable of running entirely on LNG both at sea and in port.
Integration of Digitalization and Smart Control Solutions
The Marine Propulsion Engine Market evolves with digital technologies integrated into propulsion design and management. Smart sensors, IoT platforms, and advanced analytics enable real-time performance monitoring. Operators use digital twins and predictive maintenance to improve operational efficiency and reduce downtime. It drives adoption of data-driven solutions across commercial and defense fleets. Automated control systems also enhance energy optimization and compliance with emission standards. Digitalization continues to redefine propulsion operations with a focus on cost control and reliability.
- For instance, ABB announced the launch of its next-generation dynamic positioning (DP) system, the ABB Ability Marine Pilot Control, at the SMM maritime trade fair in September 2018. In a successful trial in November 2018, an ice-class passenger ferry in Helsinki harbor was remotely piloted with the system.
Growing Popularity of Hybrid and Fully Electric Propulsion Systems
The Marine Propulsion Engine Market experiences rising adoption of hybrid and fully electric systems across vessel classes. Ferries and cruise ships deploy battery-powered propulsion for short-distance travel and port operations. It improves energy efficiency while lowering operating costs and noise levels. Naval fleets also explore hybrid propulsion to strengthen endurance and tactical flexibility. Advances in battery technology extend range capabilities, making electrification viable for larger vessels. This trend accelerates as governments and private operators pursue green shipping objectives.
Expansion of Global Shipbuilding and Retrofit Activities
The Marine Propulsion Engine Market benefits from expansion in shipbuilding and retrofitting programs worldwide. New vessel construction projects in Asia-Pacific and Europe drive demand for modern propulsion solutions. Operators retrofit existing fleets with advanced engines to comply with IMO emission rules. It creates sustained demand for propulsion technologies offering improved efficiency and compliance. Investments in offshore oil, gas, and renewable energy projects further strengthen market prospects. These activities reinforce propulsion as a central component of maritime modernization efforts.
Market Challenges Analysis
High Costs of Advanced Propulsion Technologies and Infrastructure
The Marine Propulsion Engine Market faces challenges from high costs linked to advanced propulsion solutions. LNG, hydrogen, and hybrid-electric systems require heavy investment in vessel design, fueling stations, and port infrastructure. Shipowners struggle to justify expenses when fuel prices fluctuate and profit margins remain tight. It limits adoption, especially in developing markets with budget constraints and slower regulatory enforcement. Maintenance and crew training also increase operational costs, further slowing the transition toward cleaner propulsion. This financial barrier continues to restrict widespread deployment of next-generation marine technologies.
Complex Regulatory Compliance and Technological Uncertainty
The Marine Propulsion Engine Market confronts difficulties from complex regulations and uncertain technological pathways. IMO emission rules demand compliance, yet varied regional policies create confusion for ship operators. It forces companies to choose between LNG, biofuels, electrification, or emerging hydrogen solutions without clear long-term direction. Uncertainty in future fuel availability and safety standards complicates investment decisions. Rapid technological changes add pressure, as vessels risk obsolescence if systems become outdated. Regulatory and technical uncertainty creates hesitation among operators and investors, slowing industry-wide adoption of innovative propulsion solutions.
Market Opportunities
Advancement of Green Shipping and Alternative Fuel Adoption
The Marine Propulsion Engine Market presents strong opportunities through the shift toward green shipping. Growing adoption of LNG, hydrogen, and biofuels creates demand for propulsion systems compatible with multiple fuels. It allows operators to align with global emission reduction goals and secure long-term regulatory compliance. Rising investment in renewable energy corridors and green port infrastructure further expands this opportunity. Hybrid-electric propulsion also strengthens appeal in passenger and cargo vessels by offering efficiency and cost savings. Companies that lead in fuel-flexible propulsion technologies stand to capture significant growth.
Expansion of Naval Programs and Commercial Fleet Modernization
The Marine Propulsion Engine Market gains opportunities from ongoing naval upgrades and commercial fleet replacement programs. Governments invest heavily in advanced propulsion for submarines, destroyers, and aircraft carriers to improve endurance and tactical performance. It creates sustained demand for nuclear and turbine-based propulsion technologies with high power density. Commercial operators replace aging fleets with vessels that prioritize efficiency and compliance, driving orders for advanced systems. Retrofitting of existing ships also opens avenues for hybrid and digital propulsion integration. These modernization efforts ensure long-term growth across both defense and commercial maritime sectors.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Propulsion Type
The Marine Propulsion Engine Market is segmented by propulsion type into diesel, gas turbine, nuclear, hybrid, and fully electric systems. Diesel engines remain dominant due to their established infrastructure and reliability in commercial fleets. Hybrid and fully electric propulsion gain traction in ferries, cruise ships, and short-sea vessels, driven by emission targets and operational savings. LNG and gas turbine systems attract interest for large vessels requiring high power and cleaner performance. Nuclear propulsion continues to hold strategic importance in naval fleets, particularly submarines and aircraft carriers. It highlights a market moving toward diversification, with hybrid and electric systems expected to grow steadily alongside conventional technologies.
- For instance, the MAN Energy Solutions 49/60DF dual-fuel engine delivers a power output of up to 18,200 kW per unit, supporting LNG, diesel, and heavy fuel oil use in large cargo vessels
By Vessel Type
The Marine Propulsion Engine Market covers vessel types such as commercial, naval, and offshore support vessels. Commercial ships including bulk carriers, tankers, and container vessels drive strong demand for propulsion systems with high efficiency and endurance. Cruise ships and ferries adopt hybrid and electric propulsion to improve sustainability and reduce port emissions. Naval fleets prioritize advanced technologies that enhance stealth, speed, and operational range, with nuclear propulsion remaining vital. Offshore support vessels demand compact and robust systems capable of performing under harsh conditions. It ensures steady demand across multiple vessel categories, with defense and passenger vessels leading innovation adoption.
By Power Output
The Marine Propulsion Engine Market is segmented by power output into low, medium, and high ranges. Low-power systems serve ferries, yachts, and smaller vessels requiring efficiency and flexibility. Medium-power systems support mid-sized ships such as naval patrol vessels, offshore service ships, and regional cargo carriers. High-power propulsion dominates in tankers, container ships, and large naval vessels, where endurance and heavy-load capacity are critical. Advances in energy storage and hybrid designs expand applications for low and medium-power categories. It creates a balanced demand spectrum where both smaller sustainable systems and large-scale high-power propulsion continue to advance.
- For instance, Wärtsilä supplied its 6L26 engine rated at 2,040 kW for offshore patrol vessels, ensuring operational reliability and fuel efficiency for medium-range maritime needs. High-power propulsion dominates in tankers, container ships, and large naval vessels, where endurance and heavy-load capacity are critical.
Segments:
Based on Propulsion Type
- Diesel Engines
- Gas Turbines
- Electric Motors
- Hybrid Systems
Based on Vessel Type
- Commercial Ships
- Passenger Ships
- Naval Vessels
- Yachts
- Fishing Vessels
Based on Power Output
- Low-Power (1,000 kW)
- Medium-Power (1,000-5,000 kW)
- High-Power (>5,000 kW)
Based on Fuel Type
- Marine Diesel Oil (MDO)
- Heavy Fuel Oil (HFO)
- LNG
- Electric
Based on Control System
- Manual Control
- Remote Control
- Autonomous Control
Based on the Geography:
- North America
- Europe
- UK
- France
- Germany
- Italy
- Spain
- Russia
- Belgium
- Netherlands
- Austria
- Sweden
- Poland
- Denmark
- Switzerland
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Thailand
- Indonesia
- Vietnam
- Malaysia
- Philippines
- Taiwan
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Peru
- Chile
- Colombia
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East
- UAE
- KSA
- Israel
- Turkey
- Iran
- Rest of Middle East
- Africa
- Egypt
- Nigeria
- Algeria
- Morocco
- Rest of Africa
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds a market share of around 21% in the Marine Propulsion Engine Market, supported by strong commercial shipping activity and advanced naval programs. The United States leads the region with heavy investments in defense, including nuclear-powered submarines and aircraft carriers, which create consistent demand for high-performance propulsion systems. Canada contributes through its naval modernization projects and growing focus on sustainable shipping technologies. LNG adoption in regional shipping routes and retrofitting initiatives in commercial fleets also fuel system upgrades. It benefits from established infrastructure, advanced technology providers, and a strong regulatory framework driving cleaner propulsion adoption. Partnerships between shipbuilders and propulsion manufacturers enhance innovation and ensure reliable supply for both defense and commercial applications.
Europe
Europe accounts for approximately 26% of the Marine Propulsion Engine Market, reflecting its leadership in green shipping and sustainability regulations. The region is home to major shipbuilding hubs in Germany, Norway, and Italy, which emphasize hybrid and electric propulsion systems for cruise ships and ferries. Strict International Maritime Organization (IMO) compliance drives operators to adopt LNG, hydrogen, and battery-based propulsion technologies. It also sees growing retrofitting projects in older fleets to align with decarbonization policies. Northern Europe leads investment in offshore wind projects, boosting demand for support vessels equipped with advanced propulsion solutions. The region benefits from collaboration between maritime technology companies and governments, accelerating innovation and deployment of alternative fuel systems.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific dominates the Marine Propulsion Engine Market with a market share of around 34%, driven by large-scale shipbuilding industries in China, Japan, and South Korea. The region serves as the global hub for commercial vessel production, ranging from bulk carriers to container ships. Rising trade activity across the region fuels demand for efficient propulsion systems in large cargo vessels. It witnesses strong adoption of LNG propulsion and increasing exploration of hybrid solutions in ferries and coastal ships. Government-backed naval modernization programs in India, China, and South Korea further support defense-related propulsion demand. Growing investments in port infrastructure and regional dominance in ship exports ensure that Asia-Pacific remains the largest market for propulsion systems.
Latin America
Latin America represents about 9% of the Marine Propulsion Engine Market, supported by growing maritime trade and offshore exploration projects. Brazil dominates regional demand due to its offshore oil and gas activities, which require powerful propulsion systems in support vessels. Mexico contributes through naval expansion and increased regional shipping activities. It faces challenges from limited technological infrastructure but steadily embraces cleaner propulsion through LNG and hybrid adoption in commercial fleets. Regional governments encourage modernization programs to improve fleet efficiency and reduce emissions. Latin America’s position strengthens further through international partnerships that expand access to advanced marine technologies.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa account for nearly 10% of the Marine Propulsion Engine Market, driven by offshore oil, gas, and defense programs. The Middle East invests in advanced propulsion systems for naval fleets to enhance maritime security. Offshore projects in the Gulf region stimulate demand for heavy-duty propulsion systems in support vessels. Africa sees growth through expanding port activities and rising demand for smaller commercial vessels in trade corridors. It continues to face infrastructure limitations, but new LNG and hybrid systems gain attention in regional shipping. Investment in maritime defense and energy projects supports steady growth, while partnerships with global technology providers strengthen system adoption.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Kohler
- MAN Energy Solutions
- Doosan Infracore
- ABB Group
- Caterpillar Inc.
- ZF Marine Propulsion
- Hyundai Heavy Industries
- GE Power
- Volvo Penta
- Cummins
Competitive Analysis
The competitive landscape of the Marine Propulsion Engine Market features leading players such as Caterpillar Inc., MAN Energy Solutions, ABB Group, Hyundai Heavy Industries, Cummins, GE Power, ZF Marine Propulsion, Volvo Penta, Kohler, and Doosan Infracore. These companies focus on delivering advanced propulsion technologies that balance performance, efficiency, and regulatory compliance. Strong emphasis is placed on hybrid and electric propulsion systems, as well as LNG and dual-fuel engines, to align with global emission standards. Strategic partnerships, investments in R&D, and expansion of product portfolios help strengthen their positions in both commercial and naval sectors. Players also integrate digital solutions, including smart monitoring and predictive maintenance, to enhance operational reliability and cost-effectiveness. Regional dominance is shaped by technological capabilities and shipbuilding collaborations, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Europe. Intense competition encourages continuous innovation, with each company working to capture opportunities from fleet modernization, offshore projects, and growing demand for sustainable maritime operations.
Recent Developments
- In April 2025, its 32/44CR engines and Alpha propellers were selected for Indian Navy fleet support ships.
- In May 2024, Caterpillar signed an MoU with Damen Shipyards to include its Cat 3516E methanol dual‑fuel engines in a tug, targeting deployment in 2026.
- In May 2023, ABB introduced the ABB Dynafin cycloidal propulsion concept to boost marine efficiency.
- In April 2023, Kohler transformed its power business into “Kohler Energy,” prioritizing decarbonization, alternative fuels, electrification, and hybrid solutions.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Propulsion Type, Vessel Type, Power Output, Control System and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Demand for hybrid and electric propulsion will grow with stricter emission norms.
- LNG, hydrogen, and biofuels will gain wider adoption in commercial and naval fleets.
- Digital monitoring and predictive maintenance will become standard for propulsion systems.
- Shipbuilders will focus on fuel-flexible propulsion to meet uncertain fuel availability.
- Naval programs will drive innovation in nuclear and high-power propulsion technologies.
- Retrofitting older vessels with cleaner systems will increase across global shipping.
- Battery advancements will extend range and performance of fully electric vessels.
- Asia-Pacific will remain the key hub for large-scale shipbuilding and propulsion adoption.
- Europe will lead in green shipping initiatives and hydrogen-based propulsion solutions.
- Partnerships between technology providers and shipbuilders will accelerate market transformation.




