Market Overview
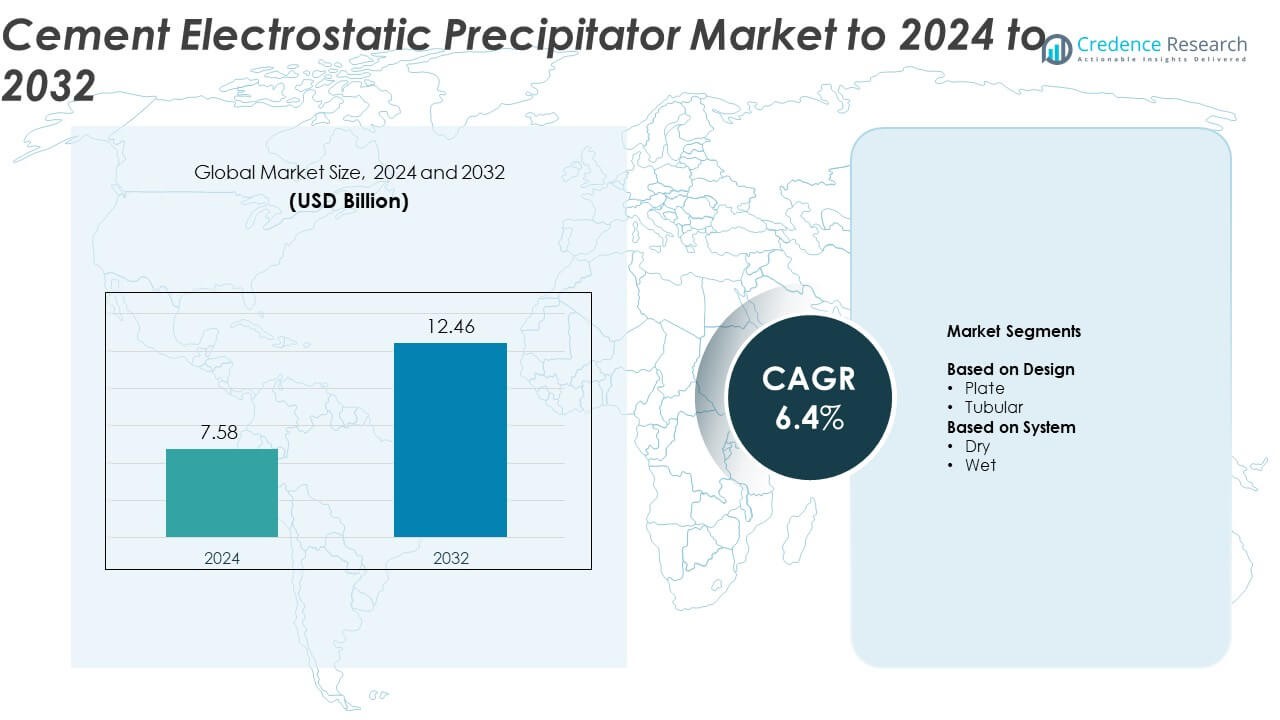
Cement Electrostatic Precipitator Market size was valued at USD 7.58 Billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 12.46 Billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 6.4% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Cement Electrostatic Precipitator Market Size 2024 |
USD 7.58 Billion |
| Cement Electrostatic Precipitator Market, CAGR |
6.4% |
| Cement Electrostatic Precipitator Market Size 2032 |
USD 12.46 Billion |
The cement electrostatic precipitator market is led by prominent players such as Siemens Energy, Fuji Electric, GEA Group, AGICO Cement, Valmet, KC Cottrell India, ANDRITZ Group, Sumitomo Heavy Industries, Babcock & Wilcox, Kraft Powercon, PPC AIR, Elex, and McGill AirClean. These companies compete through advanced product portfolios, energy-efficient systems, and digital emission control technologies. Asia Pacific dominates the global market with a 38.6% share in 2024, driven by expanding cement production and strict pollution control norms. Europe follows with 24.7% share, supported by strong regulatory frameworks and technological upgrades in cement plants.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The cement electrostatic precipitator market was valued at USD 7.58 Billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 12.46 Billion by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 6.4%.
- Rising enforcement of air pollution control regulations and expansion of cement production facilities are driving strong market growth worldwide.
- Increasing adoption of energy-efficient and digitally controlled ESP systems is shaping industry trends toward sustainable and low-maintenance emission solutions.
- The market remains moderately competitive with global players focusing on system upgrades, automation, and long-term service contracts to maintain market share.
- Asia Pacific leads with 38.6% share in 2024, followed by Europe at 24.7% and North America at 21.4%, while the plate design segment accounts for 68.3% and the dry system segment holds 72.6% share, reflecting strong dominance in high-volume cement operations.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Design
The plate design segment dominates the cement electrostatic precipitator market, accounting for nearly 68.3% share in 2024. Its dominance is driven by high efficiency in capturing fine particulate emissions and lower maintenance requirements compared to tubular designs. Plate-type ESPs are widely deployed in large cement kilns and clinker coolers due to their robust structure, adaptability, and superior dust removal capacity. Their modular configuration enables easy installation and scalability, making them ideal for high-volume operations focused on meeting stringent environmental standards.
- For instance, Tai & Chyun’s electrostatic precipitator (ESP) upgrades often exceed customer requirements, with various power and cement plant case studies showing achieved emissions of less than 10 mg/Nm³ or around 10-11 mg/Nm³ after upgrades.
By System
The dry system segment leads the market with approximately 72.6% share in 2024. This segment’s strength lies in its suitability for high-temperature gas treatment and lower operational costs. Dry ESPs are preferred in cement manufacturing plants where gas streams contain low moisture levels, ensuring efficient particulate collection. Rising adoption of dry systems is supported by improved emission control technologies and regulatory emphasis on reducing particulate matter. Manufacturers are increasingly upgrading dry ESP units to enhance collection efficiency and energy performance across cement production lines.
- For instance, Mitsubishi Power’s dry ESP lists outlet dust ≤ 10 mg/m³N and 1,050 MW capacity.
Key Growth Drivers
Stringent Environmental Regulations
Tightening global emission standards for particulate matter in the cement industry is a primary growth driver. Governments across major economies are enforcing stricter limits on air pollution, compelling cement manufacturers to adopt high-efficiency electrostatic precipitators. This regulatory pressure is accelerating modernization of existing plants and the installation of advanced ESP systems, particularly in Asia Pacific and Europe. Compliance with environmental laws and sustainability targets continues to drive steady investment in emission control technologies.
- For instance, Schenck Process documented a specific upgrade to a clinker cooler electrostatic precipitator (ESP) originally designed for a gas flow rate of 519,400 Am³/h and a maximum inlet dust concentration of 22,000 mg/Nm³ (with an original design outlet of 50 mg/Nm³).
Expansion of Cement Production Facilities
Rising infrastructure development and urbanization across emerging economies are fueling cement production expansion, boosting ESP demand. Countries in Asia, Africa, and the Middle East are increasing investments in new cement plants and upgrading existing units to meet growing construction needs. This production surge is generating consistent demand for durable, energy-efficient electrostatic precipitators capable of operating under high dust load conditions. The need for operational reliability and emission control supports long-term market growth.
- For instance, environmental reports for the JK Lakshmi Cement Durg plant show that the coal mill bag house is specified for a maximum permissible dust emission of 30 mg/Nm³, and overall operations strive for this lower emission level.
Technological Advancements in ESP Systems
Advances in design and materials are improving the performance and efficiency of electrostatic precipitators in cement applications. Innovations such as high-voltage power supplies, advanced rapping systems, and automated controls are enhancing dust collection rates and system longevity. Integration of IoT-based monitoring and predictive maintenance tools enables real-time performance tracking and reduced downtime. These advancements are encouraging cement producers to adopt next-generation ESP systems for improved energy use and compliance efficiency.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Shift Toward Energy-Efficient ESP Designs
Manufacturers are emphasizing low-energy ESP models that optimize power consumption without compromising collection efficiency. This shift aligns with the cement industry’s push toward sustainability and cost control. The adoption of energy-efficient ESP systems is particularly strong among large cement producers aiming to meet carbon reduction goals. Developments in power management technologies are also lowering operational expenses and enhancing return on investment, positioning energy-efficient ESPs as a preferred choice for new installations.
- For instance, FLSmidth reports ESP dust well below 5 mg/Nm³ and ~150 Pa pressure drop.
Integration with Digital Monitoring Systems
Digitalization is reshaping ESP performance management in cement plants. The use of smart sensors, data analytics, and cloud-based monitoring enables predictive maintenance and precise emission control. These systems allow operators to track parameters like voltage, temperature, and dust concentration, reducing unplanned shutdowns. Growing adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies presents new opportunities for manufacturers to offer intelligent, data-driven ESP solutions tailored for modern cement production environments.
- For instance, Neundorfer documented a specific electrostatic precipitator (ESP) performance study for a taconite induration furnace where computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling was used to analyze the gas flow patterns for a flow of 420,000 SCFM, with the process generating a raw material throughput (often referred to as ‘loading’) of 45 t/hour.
Key Challenges
High Installation and Maintenance Costs
Electrostatic precipitators involve significant capital and operational expenses, posing challenges for small and mid-sized cement manufacturers. The cost of system installation, high-voltage equipment, and periodic maintenance can limit adoption in cost-sensitive markets. Upgrading older plants to comply with advanced emission standards further increases financial pressure. This cost barrier often drives manufacturers toward alternative filtration technologies in regions with weaker regulatory enforcement.
Performance Limitations Under High Moisture Conditions
The efficiency of electrostatic precipitators can decline when treating gas streams with high moisture or variable particulate properties. Moisture-related issues such as re-entrainment and corrosion affect collection performance and system reliability. Cement plants operating in humid climates face added maintenance and material selection challenges to sustain long-term efficiency. Addressing these technical limitations remains essential for improving system durability and maintaining consistent emission control.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds nearly 21.4% share of the cement electrostatic precipitator market in 2024. Growth is supported by strict environmental standards from the Environmental Protection Agency and modernization of cement plants across the United States and Canada. Manufacturers are investing in advanced ESP systems with automated controls to enhance emission performance. The region’s focus on energy-efficient and low-maintenance systems is encouraging upgrades in existing production lines. Ongoing infrastructure investments and the replacement of aging industrial assets continue to strengthen market expansion.
Europe
Europe accounts for around 24.7% share of the global market in 2024. The region’s leadership is driven by stringent EU emission norms and increasing adoption of sustainable cement production technologies. Countries such as Germany, Italy, and France are integrating next-generation ESP systems to comply with industrial decarbonization targets. Continuous upgrades in plant operations and emphasis on low-carbon manufacturing practices further support demand. Technological innovation, supported by government-funded clean air initiatives, enhances the region’s competitive position in advanced emission control systems.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific dominates the cement electrostatic precipitator market with approximately 38.6% share in 2024. The region’s dominance is driven by rapid urbanization, large-scale infrastructure projects, and high cement output in China and India. Growing government focus on reducing industrial air pollution is accelerating adoption of ESP systems across new and existing cement plants. Rising investments in energy-efficient and automated systems further strengthen the market outlook. The continuous expansion of production capacity and favorable industrial policies keep Asia Pacific the key contributor to global growth.
Latin America
Latin America represents about 8.3% share of the market in 2024. The demand is supported by growing construction activity and modernization of cement facilities in Brazil, Mexico, and Chile. Manufacturers are adopting advanced ESP designs to meet emerging air quality regulations and improve production efficiency. Government-backed infrastructure programs and increasing awareness of environmental sustainability drive regional installations. Despite moderate growth, limited capital availability and economic fluctuations pose challenges to faster technology adoption in smaller markets.
Middle East & Africa
Middle East & Africa holds around 7% share of the cement electrostatic precipitator market in 2024. Expanding cement production capacity in Gulf Cooperation Council countries and North Africa supports demand for reliable emission control systems. Ongoing construction projects, including industrial and urban developments, are encouraging the use of efficient ESP solutions. Regulatory reforms aimed at minimizing particulate emissions further drive market growth. However, cost sensitivity among regional producers and dependency on imported technology continue to restrain rapid expansion.
Market Segmentations:
By Design
By System
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the cement electrostatic precipitator market includes leading companies such as Siemens Energy, Fuji Electric, GEA Group, AGICO Cement, Valmet, KC Cottrell India, ANDRITZ Group, Sumitomo Heavy Industries, Babcock & Wilcox, Kraft Powercon, PPC AIR, Elex, and McGill AirClean. The market is characterized by continuous technological innovation, focusing on improving dust collection efficiency, energy optimization, and system automation. Companies are emphasizing digital integration, predictive maintenance, and modular ESP designs to meet stricter emission standards and enhance plant reliability. Strategic collaborations with cement manufacturers and regional distributors are helping expand service networks and strengthen aftersales support. Global players are also investing in R&D to develop sustainable materials and high-voltage power systems that ensure better operational stability. Increasing demand for retrofitting existing systems and upgrading older plants to comply with new environmental norms continues to create opportunities for competitive differentiation across the industry.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Siemens Energy
- Fuji Electric
- GEA Group
- AGICO Cement
- Valmet
- KC Cottrell India
- ANDRITZ Group
- Sumitomo Heavy Industries
- Babcock & Wilcox
- Kraft Powercon
- PPC AIR
- Elex
- McGill AirClean
Recent Developments
- In 2025, Valmet secured an order to upgrade a Wet Electrostatic Precipitator (WESP) at Forestia AS’s chipboard plant in Norway, showcasing technological advances in ESP wastewater treatment and emission control.
- In 2025, Kraft Powercon Launched “NovaKraft” ESP power-supply platform. Targets higher efficiency and reliability for precipitators.
- In 2022, Babcock & Wilcox finalized the acquisition of Hamon Research‑Cottrell’s emissions control technologies, strengthening its position in air quality solutions.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Design, system and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Growing emphasis on sustainable cement manufacturing will drive wider adoption of advanced ESP systems.
- Integration of AI and IoT technologies will improve system monitoring and operational efficiency.
- Replacement of aging electrostatic precipitators will boost retrofit and upgrade demand across regions.
- Rising construction and infrastructure investments in Asia Pacific will sustain long-term market expansion.
- Energy-efficient ESP designs will gain preference as cement producers aim to cut operational costs.
- Increasing environmental regulations will accelerate installation of high-performance emission control equipment.
- Manufacturers will focus on modular and compact ESP designs for easier installation and maintenance.
- Partnerships between technology providers and cement producers will enhance innovation and customization.
- Growing public awareness of air quality issues will strengthen regulatory compliance across emerging economies.
- Continuous R&D investments will lead to improved durability, automation, and dust collection performance in next-generation systems.




