1. Preface
1.1. Report Description
1.1.1. Purpose of the Report
1.1.2. Target Audience
1.1.3. USP and Key Offerings
1.2. Research Scope
1.3. Market Introduction
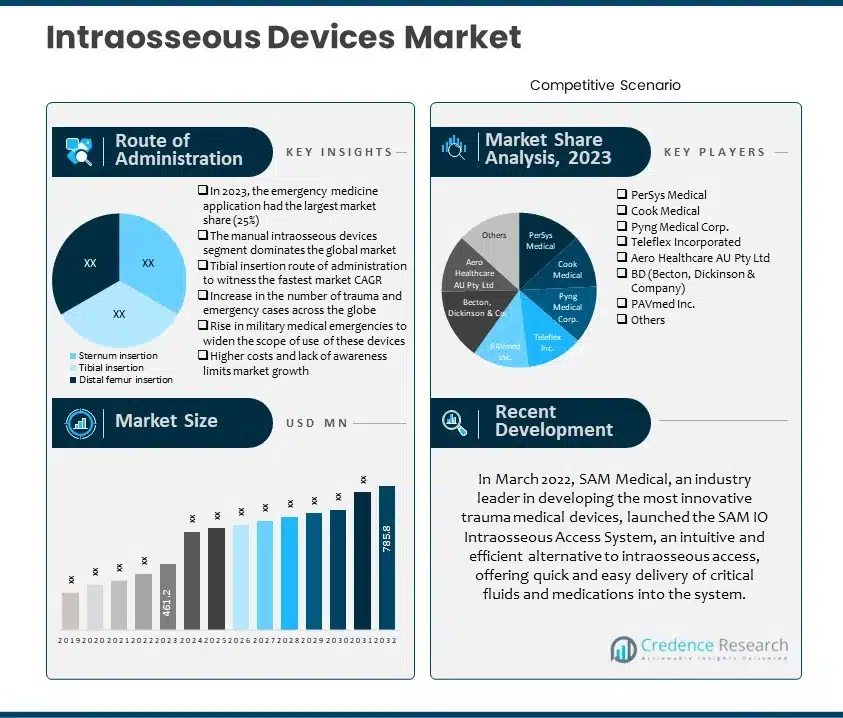
2. Executive Summary
2.1. Market Snapshot: Global Intraosseous Devices Market
2.1.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Product Type
2.1.2. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Route of Administration
2.1.3. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By End User
2.1.4. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Application
2.1.5. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Region
2.2. Insights from Primary Respondents
3. Market Dynamics & Factors Analysis
3.1. Introduction
3.1.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market Value, 2019-2032, (US$ Mn)
3.1.2. Y-o-Y Growth Trend Analysis
3.2. Market Dynamics
3.2.1. Intraosseous Devices Market Drivers
3.2.2. Intraosseous Devices Market Restraints
3.2.3. Intraosseous Devices Market Opportunities
3.2.4. Major Intraosseous Devices Industry Challenges
3.3. Growth and Development Patterns
3.4. Investment Feasibility Analysis
3.5. Market Opportunity Analysis
3.5.1. Product Type
3.5.2. Route of Administration
3.5.3. End User
3.5.4. Application
3.5.5. Geography
4. Market Competitive Landscape Analysis
4.1. Company Market Share Analysis, 2023
4.1.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market: Company Market Share, Value 2023
4.1.2. Global Intraosseous Devices Market: Top 6 Company Market Share, Value 2023
4.1.3. Global Intraosseous Devices Market: Top 3 Company Market Share, Value 2023
4.2. Global Intraosseous Devices Market: Company Revenue Share Analysis, 2023
4.3. Company Assessment Metrics, 2023
4.3.1. Stars
4.3.2. Emerging Leaders
4.3.3. Pervasive Players
4.3.4. Participants
4.4. Startups/SMEs Assessment Metrics, 2023
4.4.1. Progressive Companies
4.4.2. Responsive Companies
4.4.3. Dynamic Companies
4.4.4. Starting Blocks
4.5. Strategic Development
4.5.1. Acquisition and Mergers
4.5.2. New Product Launch
4.5.3. Regional Expansion
4.5.4. Partnerships
4.6. Key Player Product Matrix
4.7. Potential for New Players in the Global Intraosseous Devices Market
5. Premium Insights
5.1. STAR (Situation, Task, Action, Results) Analysis
5.2. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1. Threat of New Entrants
5.2.2. Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
5.2.3. Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.4. Threat of Substitute Types
5.2.5. Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5.3. PESTEL Analysis
5.3.1. Political Factors
5.3.2. Economic Factors
5.3.3. Social Factors
5.3.4. Technological Factors
5.3.5. Environmental Factors
5.3.6. Legal Factors
5.4. Key Market Trends
5.4.1. Demand Side Trends
5.4.2. Supply Side Trends
5.5. Value Chain Analysis
5.6. Technology Analysis
5.6.1. Research and development in the global market
5.6.2. Patent Analysis
5.6.3. Emerging technologies and their potential disruption to the market
5.7. Consumer Behaviour Analysis
5.7.1. Consumer Preferences and Expectations
5.7.2. Factors Influencing Consumer Buying Decisions
5.7.2.1. North America
5.7.2.2. Europe
5.7.2.3. Asia Pacific
5.7.2.4. Latin America
5.7.2.5. Middle East and Africa
5.7.3. Consumer Pain Points
5.8. Analysis and Recommendations
5.9. Adjacent Market Analysis
6. Market Positioning of Key Players, 2023
6.1. Company market share of key players, 2023
6.2. Competitive Benchmarking
6.3. Market Positioning of Key Vendors
6.4. Geographical Presence Analysis
6.5. Major Strategies Adopted by Key Players
6.5.1. Key Strategies Analysis
6.5.2. Mergers and Acquisitions
6.5.3. Partnerships
6.5.4. Product Launch
6.5.5. Geographical Expansion
6.5.6. Others
7. Impact Analysis of COVID 19 and Russia – Ukraine War on Intraosseous Devices Market
7.1. Ukraine-Russia War Impact
7.1.1. Uncertainty and Economic Instability
7.1.2. Supply chain disruptions
7.1.3. Regional market shifts
7.1.4. Shift in government priorities
7.2. COVID-19 Impact Analysis
7.2.1. Supply Chain Disruptions
7.2.2. Demand Fluctuations
7.2.3. Shift in Product Mix
7.2.4. Reduced Industrial Activity
7.2.5. Regional Impact Analysis
7.2.5.1. North America
7.2.5.2. Europe
7.2.5.3. Asia Pacific
7.2.5.4. Latin America
7.2.5.5. Middle East and Africa
8. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Product Type
8.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market Overview, by Product Type
8.1.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market Revenue Share, By Product Type, 2023 Vs 2032 (in %)
8.2. Manual intraosseous devices
8.2.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Manual intraosseous devices, By Region, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
8.2.2. Market Dynamics for Manual intraosseous devices
8.2.2.1. Drivers
8.2.2.2. Restraints
8.2.2.3. Opportunities
8.2.2.4. Trends
8.3. Automatic intraosseous devices
8.3.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Automatic intraosseous devices, By Region, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
8.3.2. Market Dynamics for Automatic intraosseous devices
8.3.2.1. Drivers
8.3.2.2. Restraints
8.3.2.3. Opportunities
8.3.2.4. Trends
8.4. Semi-automatic intraosseous devices
8.4.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Semi-automatic intraosseous devices, By Region, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
8.4.2. Market Dynamics for Semi-automatic intraosseous devices
8.4.2.1. Drivers
8.4.2.2. Restraints
8.4.2.3. Opportunities
8.4.2.4. Trends
9. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Route of Administration
9.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market Overview, by Route of Administration
9.1.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market Revenue Share, By Route of Administration, 2023 Vs 2032 (in %)
9.2. Sternum insertion
9.2.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Sternum insertion, By Region, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
9.2.2. Market Dynamics for Sternum insertion
9.2.2.1. Drivers
9.2.2.2. Restraints
9.2.2.3. Opportunities
9.2.2.4. Trends
9.3. Tibial insertion
9.3.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Tibial insertion, By Region, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
9.3.2. Market Dynamics for Tibial insertion
9.3.2.1. Drivers
9.3.2.2. Restraints
9.3.2.3. Opportunities
9.3.2.4. Trends
9.4. Distal femur insertion
9.4.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Distal femur insertion, By Region, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
9.4.2. Market Dynamics for Distal femur insertion
9.4.2.1. Drivers
9.4.2.2. Restraints
9.4.2.3. Opportunities
9.4.2.4. Trends
9.5. Others
9.5.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Others, By Region, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
9.5.2. Market Dynamics for Others
9.5.2.1. Drivers
9.5.2.2. Restraints
9.5.2.3. Opportunities
9.5.2.4. Trends
10. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By End User
10.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market Overview, by End User
10.1.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market Revenue Share, By End User, 2023 Vs 2032 (in %)
10.2. Hospitals
10.2.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Hospitals, By Region, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
10.2.2. Market Dynamics for Hospitals
10.2.2.1. Drivers
10.2.2.2. Restraints
10.2.2.3. Opportunities
10.2.2.4. Trends
10.3. Emergency medical services (EMS)
10.3.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Emergency medical services (EMS), By Region, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
10.3.2. Market Dynamics for Emergency medical services (EMS)
10.3.2.1. Drivers
10.3.2.2. Restraints
10.3.2.3. Opportunities
10.3.2.4. Trends
10.4. Ambulatory surgical centers
10.4.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Ambulatory surgical centers, By Region, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
10.4.2. Market Dynamics for Ambulatory surgical centers
10.4.2.1. Drivers
10.4.2.2. Restraints
10.4.2.3. Opportunities
10.4.2.4. Trends
10.5. Specialty clinics
10.5.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Specialty clinics, By Region, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
10.5.2. Market Dynamics for Specialty clinics
10.5.2.1. Drivers
10.5.2.2. Restraints
10.5.2.3. Opportunities
10.5.2.4. Trends
10.6. Others
10.6.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Others, By Region, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
10.6.2. Market Dynamics for Others
10.6.2.1. Drivers
10.6.2.2. Restraints
10.6.2.3. Opportunities
10.6.2.4. Trends
11. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Application
11.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market Overview, by Application
11.1.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market Revenue Share, By Application, 2023 Vs 2032 (in %)
11.2. Emergency medicine
11.2.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Emergency medicine, By Region, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
11.2.2. Market Dynamics for Emergency medicine
11.2.2.1. Drivers
11.2.2.2. Restraints
11.2.2.3. Opportunities
11.2.2.4. Trends
11.3. Pediatrics
11.3.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Pediatrics, By Region, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
11.3.2. Market Dynamics for Pediatrics
11.3.2.1. Drivers
11.3.2.2. Restraints
11.3.2.3. Opportunities
11.3.2.4. Trends
11.4. Geriatrics
11.4.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Geriatrics, By Region, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
11.4.2. Market Dynamics for Geriatrics
11.4.2.1. Drivers
11.4.2.2. Restraints
11.4.2.3. Opportunities
11.4.2.4. Trends
11.5. Military applications
11.5.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Military applications, By Region, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
11.5.2. Market Dynamics for Military applications
11.5.2.1. Drivers
11.5.2.2. Restraints
11.5.2.3. Opportunities
11.5.2.4. Trends
11.6. Veterinary medicine
11.6.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Veterinary medicine, By Region, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
11.6.2. Market Dynamics for Veterinary medicine
11.6.2.1. Drivers
11.6.2.2. Restraints
11.6.2.3. Opportunities
11.6.2.4. Trends
12. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Region
12.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market Overview, by Region
12.1.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Region, 2023 vs 2032 (in%)
12.2. Product Type
12.2.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Product Type, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
12.3. Route of Administration
12.3.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Route of Administration, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
12.4. End User
12.4.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By End User, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
12.5. Application
12.5.1. Global Intraosseous Devices Market, By Application, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
13. North America Intraosseous Devices Market Analysis
13.1. Overview
13.1.1. Market Dynamics for North America
13.1.1.1. Drivers
13.1.1.2. Restraints
13.1.1.3. Opportunities
13.1.1.4. Trends
13.2. North America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2032(US$ Mn)
13.2.1. Overview
13.2.2. SRC Analysis
13.3. North America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2032(US$ Mn)
13.3.1. Overview
13.3.2. SRC Analysis
13.4. North America Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2032(US$ Mn)
13.4.1. Overview
13.4.2. SRC Analysis
13.5. North America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2032(US$ Mn)
13.5.1. Overview
13.5.2. SRC Analysis
13.6. North America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Country, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
13.6.1. North America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Country, 2023 Vs 2032 (in%)
13.6.2. U.S.
13.6.3. Canada
13.6.4. Mexico
14. Europe Intraosseous Devices Market Analysis
14.1. Overview
14.1.1. Market Dynamics for North America
14.1.1.1. Drivers
14.1.1.2. Restraints
14.1.1.3. Opportunities
14.1.1.4. Trends
14.2. Europe Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2032(US$ Mn)
14.2.1. Overview
14.2.2. SRC Analysis
14.3. Europe Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2032(US$ Mn)
14.3.1. Overview
14.3.2. SRC Analysis
14.4. Europe Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2032(US$ Mn)
14.4.1. Overview
14.4.2. SRC Analysis
14.5. Europe Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2032(US$ Mn)
14.5.1. Overview
14.5.2. SRC Analysis
14.6. Europe Intraosseous Devices Market, by Country, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
14.6.1. Europe Intraosseous Devices Market, by Country, 2023 Vs 2032 (in%)
14.6.2. UK
14.6.3. France
14.6.4. Germany
14.6.5. Italy
14.6.6. Spain
14.6.7. Benelux
14.6.8. Russia
14.6.9. Rest of Europe
15. Asia Pacific Intraosseous Devices Market Analysis
15.1. Overview
15.1.1. Market Dynamics for North America
15.1.1.1. Drivers
15.1.1.2. Restraints
15.1.1.3. Opportunities
15.1.1.4. Trends
15.2. Asia Pacific Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2032(US$ Mn)
15.2.1. Overview
15.2.2. SRC Analysis
15.3. Asia Pacific Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2032(US$ Mn)
15.3.1. Overview
15.3.2. SRC Analysis
15.4. Asia Pacific Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2032(US$ Mn)
15.4.1. Overview
15.4.2. SRC Analysis
15.5. Asia Pacific Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2032(US$ Mn)
15.5.1. Overview
15.5.2. SRC Analysis
15.6. Asia Pacific Intraosseous Devices Market, by Country, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
15.6.1. Asia Pacific Intraosseous Devices Market, by Country, 2023 Vs 2032 (in%)
15.6.2. China
15.6.3. Japan
15.6.4. India
15.6.5. South Korea
15.6.6. South East Asia
15.6.7. Rest of Asia Pacific
16. Latin America Intraosseous Devices Market Analysis
16.1. Overview
16.1.1. Market Dynamics for North America
16.1.1.1. Drivers
16.1.1.2. Restraints
16.1.1.3. Opportunities
16.1.1.4. Trends
16.2. Latin America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2032(US$ Mn)
16.2.1. Overview
16.2.2. SRC Analysis
16.3. Latin America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2032(US$ Mn)
16.3.1. Overview
16.3.2. SRC Analysis
16.4. Latin America Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2032(US$ Mn)
16.4.1. Overview
16.4.2. SRC Analysis
16.5. Latin America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2032(US$ Mn)
16.5.1. Overview
16.5.2. SRC Analysis
16.6. Latin America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Country, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
16.6.1. Latin America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Country, 2023 Vs 2032 (in%)
16.6.2. Brazil
16.6.3. Argentina
16.6.4. Rest of Latin America
17. Middle East Intraosseous Devices Market Analysis
17.1. Overview
17.1.1. Market Dynamics for North America
17.1.1.1. Drivers
17.1.1.2. Restraints
17.1.1.3. Opportunities
17.1.1.4. Trends
17.2. Middle East Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2032(US$ Mn)
17.2.1. Overview
17.2.2. SRC Analysis
17.3. Middle East Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2032(US$ Mn)
17.3.1. Overview
17.3.2. SRC Analysis
17.4. Middle East Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2032(US$ Mn)
17.4.1. Overview
17.4.2. SRC Analysis
17.5. Middle East Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2032(US$ Mn)
17.5.1. Overview
17.5.2. SRC Analysis
17.6. Middle East Intraosseous Devices Market, by Country, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
17.6.1. Middle East Intraosseous Devices Market, by Country, 2023 Vs 2032 (in%)
17.6.2. UAE
17.6.3. Saudi Arabia
17.6.4. Rest of Middle East
18. Africa Intraosseous Devices Market Analysis
18.1. Overview
18.1.1. Market Dynamics for North America
18.1.1.1. Drivers
18.1.1.2. Restraints
18.1.1.3. Opportunities
18.1.1.4. Trends
18.2. Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2032(US$ Mn)
18.2.1. Overview
18.2.2. SRC Analysis
18.3. Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2032(US$ Mn)
18.3.1. Overview
18.3.2. SRC Analysis
18.4. Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2032(US$ Mn)
18.4.1. Overview
18.4.2. SRC Analysis
18.5. Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2032(US$ Mn)
18.5.1. Overview
18.5.2. SRC Analysis
18.6. Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by Country, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
18.6.1. Middle East Intraosseous Devices Market, by Country, 2023 Vs 2032 (in%)
18.6.2. South Africa
18.6.3. Egypt
18.6.4. Rest of Africa
19. Company Profiles
19.1. PerSys Medical
19.1.1. Company Overview
19.1.2. Products/Services Portfolio
19.1.3. Geographical Presence
19.1.4. SWOT Analysis
19.1.5. Financial Summary
19.1.5.1. Market Revenue and Net Profit (2019-2023)
19.1.5.2. Business Segment Revenue Analysis
19.1.5.3. Geographical Revenue Analysis
19.2. Cook Medical
19.3. Pyng Medical Corp.
19.4. Teleflex Incorporated
19.5. Aero Healthcare AU Pty Ltd
19.6. BD (Becton, Dickinson & Company)
19.7. PAVmed Inc.
19.8. Others
20. Research Methodology
20.1. Research Methodology
20.2. Phase I – Secondary Research
20.3. Phase II – Data Modelling
20.3.1. Company Share Analysis Model
20.3.2. Revenue Based Modelling
20.4. Phase III – Primary Research
20.5. Research Limitations
20.5.1. Assumptions
List of Figures
FIG. 1 Global Intraosseous Devices Market: Research Methodology
FIG. 2 Market Size Estimation – Top Down & Bottom up Approach
FIG. 3 Global Intraosseous Devices Market Segmentation
FIG. 4 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2023 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 5 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2023 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 6 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2023 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 7 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2023 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 8 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Geography, 2023 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 9 Attractive Investment Proposition, by Product Type, 2023
FIG. 10 Attractive Investment Proposition, by Route of Administration, 2023
FIG. 11 Attractive Investment Proposition, by End User, 2023
FIG. 12 Attractive Investment Proposition, by Application, 2023
FIG. 13 Attractive Investment Proposition, by Geography, 2023
FIG. 14 Global Market Share Analysis of Key Intraosseous Devices Market Manufacturers, 2023
FIG. 15 Global Market Positioning of Key Intraosseous Devices Market Manufacturers, 2023
FIG. 16 Global Intraosseous Devices Market Value Contribution, By Product Type, 2023 & 2032 (Value %)
FIG. 17 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Manual intraosseous devices, Value, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 18 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Automatic intraosseous devices, Value, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 19 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Semi-automatic intraosseous devices, Value, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 20 Global Intraosseous Devices Market Value Contribution, By Route of Administration, 2023 & 2032 (Value %)
FIG. 21 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Sternum insertion, Value, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 22 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Tibial insertion, Value, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 23 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Distal femur insertion, Value, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 24 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Others, Value, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 25 Global Intraosseous Devices Market Value Contribution, By End User, 2023 & 2032 (Value %)
FIG. 26 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Hospitals, Value, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 27 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Emergency medical services (EMS), Value, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 28 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Ambulatory surgical centers, Value, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 29 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Specialty clinics, Value, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 30 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Others, Value, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 31 Global Intraosseous Devices Market Value Contribution, By Application, 2023 & 2032 (Value %)
FIG. 32 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Emergency medicine, Value, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 33 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Pediatrics, Value, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 34 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Geriatrics, Value, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 35 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Military applications, Value, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 36 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Veterinary medicine, Value, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 37 North America Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 38 U.S. Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 39 Canada Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 40 Mexico Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 41 Europe Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 42 Germany Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 43 France Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 44 U.K. Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 45 Italy Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 46 Spain Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 47 Benelux Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 48 Russia Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 49 Rest of Europe Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 50 Asia Pacific Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 51 China Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 52 Japan Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 53 India Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 54 South Korea Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 55 South-East Asia Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 56 Rest of Asia Pacific Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 57 Latin America Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 58 Brazil Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 59 Argentina Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 60 Rest of Latin America Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 61 Middle East Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 62 UAE Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 63 Saudi Arabia Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 64 Rest of Middle East Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 65 Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 66 South Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 67 Egypt Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
FIG. 68 Rest of Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, 2019-2032 (US$ Mn)
List of Tables
TABLE 1 Market Snapshot: Global Intraosseous Devices Market
TABLE 2 Global Intraosseous Devices Market: Market Drivers Impact Analysis
TABLE 3 Global Intraosseous Devices Market: Market Restraints Impact Analysis
TABLE 4 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Competitive Benchmarking, 2023
TABLE 5 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Geographical Presence Analysis, 2023
TABLE 6 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Key Strategies Analysis, 2023
TABLE 7 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Manual intraosseous devices, By Region, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 8 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Manual intraosseous devices, By Region, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 9 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Automatic intraosseous devices, By Region, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 10 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Automatic intraosseous devices, By Region, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 11 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Semi-automatic intraosseous devices, By Region, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 12 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Semi-automatic intraosseous devices, By Region, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 13 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Sternum insertion, By Region, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 14 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Sternum insertion, By Region, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 15 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Tibial insertion, By Region, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 16 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Tibial insertion, By Region, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 17 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Distal femur insertion, By Region, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 18 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Distal femur insertion, By Region, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 19 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Others, By Region, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 20 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Others, By Region, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 21 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Hospitals, By Region, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 22 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Hospitals, By Region, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 23 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Emergency medical services (EMS), By Region, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 24 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Emergency medical services (EMS), By Region, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 25 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Ambulatory surgical centers, By Region, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 26 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Ambulatory surgical centers, By Region, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 27 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Specialty clinics, By Region, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 28 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Specialty clinics, By Region, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 29 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Others, By Region, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 30 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Others, By Region, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 31 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Emergency medicine, By Region, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 32 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Emergency medicine, By Region, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 33 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Pediatrics, By Region, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 34 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Pediatrics, By Region, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 35 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Geriatrics, By Region, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 36 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Geriatrics, By Region, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 37 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Military applications, By Region, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 38 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Military applications, By Region, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 39 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Veterinary medicine, By Region, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 40 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Veterinary medicine, By Region, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 41 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 42 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 43 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 44 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 45 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 46 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 47 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 48 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 49 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Region, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 50 Global Intraosseous Devices Market, by Region, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 51 North America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 52 North America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 53 North America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 54 North America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 55 North America Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 56 North America Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 57 North America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 58 North America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 59 North America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Country, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 60 North America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Country, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 61 United States Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 62 United States Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 63 United States Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 64 United States Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 65 United States Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 66 United States Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 67 United States Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 68 United States Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 69 Canada Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 70 Canada Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 71 Canada Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 72 Canada Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 73 Canada Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 74 Canada Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 75 Canada Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 76 Canada Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 77 Mexico Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 78 Mexico Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 79 Mexico Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 80 Mexico Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 81 Mexico Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 82 Mexico Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 83 Mexico Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 84 Mexico Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 85 Europe Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 86 Europe Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 87 Europe Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 88 Europe Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 89 Europe Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 90 Europe Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 91 Europe Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 92 Europe Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 93 Europe Intraosseous Devices Market, by Country, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 94 Europe Intraosseous Devices Market, by Country, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 95 Germany Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 96 Germany Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 97 Germany Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 98 Germany Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 99 Germany Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 100 Germany Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 101 Germany Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 102 Germany Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 103 France Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 104 France Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 105 France Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 106 France Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 107 France Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 108 France Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 109 France Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 110 France Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 111 United Kingdom Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 112 United Kingdom Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 113 United Kingdom Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 114 United Kingdom Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 115 United Kingdom Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 116 United Kingdom Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 117 United Kingdom Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 118 United Kingdom Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 119 Italy Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 120 Italy Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 121 Italy Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 122 Italy Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 123 Italy Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 124 Italy Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 125 Italy Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 126 Italy Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 127 Spain Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 128 Spain Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 129 Spain Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 130 Spain Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 131 Spain Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 132 Spain Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 133 Spain Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 134 Spain Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 135 Benelux Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 136 Benelux Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 137 Benelux Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 138 Benelux Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 139 Benelux Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 140 Benelux Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 141 Benelux Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 142 Benelux Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 143 Russia Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 144 Russia Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 145 Russia Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 146 Russia Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 147 Russia Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 148 Russia Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 149 Russia Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 150 Russia Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 151 Rest of Europe Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 152 Rest of Europe Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 153 Rest of Europe Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 154 Rest of Europe Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 155 Rest of Europe Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 156 Rest of Europe Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 157 Rest of Europe Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 158 Rest of Europe Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 159 Asia Pacific Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 160 Asia Pacific Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 161 Asia Pacific Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 162 Asia Pacific Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 163 Asia Pacific Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 164 Asia Pacific Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 165 Asia Pacific Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 166 Asia Pacific Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 167 China Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 168 China Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 169 China Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 170 China Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 171 China Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 172 China Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 173 China Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 174 China Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 175 Japan Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 176 Japan Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 177 Japan Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 178 Japan Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 179 Japan Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 180 Japan Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 181 Japan Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 182 Japan Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 183 India Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 184 India Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 185 India Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 186 India Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 187 India Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 188 India Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 189 India Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 190 India Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 191 South Korea Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 192 South Korea Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 193 South Korea Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 194 South Korea Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 195 South Korea Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 196 South Korea Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 197 South Korea Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 198 South Korea Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 199 South-East Asia Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 200 South-East Asia Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 201 South-East Asia Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 202 South-East Asia Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 203 South-East Asia Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 204 South-East Asia Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 205 South-East Asia Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 206 South-East Asia Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 207 Rest of Asia Pacific Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 208 Rest of Asia Pacific Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 209 Rest of Asia Pacific Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 210 Rest of Asia Pacific Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 211 Rest of Asia Pacific Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 212 Rest of Asia Pacific Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 213 Rest of Asia Pacific Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 214 Rest of Asia Pacific Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 215 Latin America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 216 Latin America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 217 Latin America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 218 Latin America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 219 Latin America Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 220 Latin America Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 221 Latin America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 222 Latin America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 223 Brazil Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 224 Brazil Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 225 Brazil Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 226 Brazil Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 227 Brazil Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 228 Brazil Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 229 Brazil Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 230 Brazil Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 231 Argentina Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 232 Argentina Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 233 Argentina Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 234 Argentina Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 235 Argentina Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 236 Argentina Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 237 Argentina Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 238 Argentina Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 239 Rest of Latin America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 240 Rest of Latin America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 241 Rest of Latin America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 242 Rest of Latin America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 243 Rest of Latin America Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 244 Rest of Latin America Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 245 Rest of Latin America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 246 Rest of Latin America Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 247 Middle East Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 248 Middle East Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 249 Middle East Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 250 Middle East Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 251 Middle East Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 252 Middle East Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 253 Middle East Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 254 Middle East Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 255 UAE Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 256 UAE Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 257 UAE Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 258 UAE Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 259 UAE Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 260 UAE Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 261 UAE Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 262 UAE Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 263 Saudi Arabia Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 264 Saudi Arabia Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 265 Saudi Arabia Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 266 Saudi Arabia Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 267 Saudi Arabia Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 268 Saudi Arabia Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 269 Saudi Arabia Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 270 Saudi Arabia Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 271 Rest of Middle East Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 272 Rest of Middle East Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 273 Rest of Middle East Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 274 Rest of Middle East Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 275 Rest of Middle East Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 276 Rest of Middle East Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 277 Rest of Middle East Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 278 Rest of Middle East Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 279 Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 280 Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 281 Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 282 Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 283 Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 284 Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 285 Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 286 Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 287 South Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 288 South Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 289 South Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 290 South Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 291 South Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 292 South Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 293 South Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 294 South Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 295 Egypt Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 296 Egypt Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 297 Egypt Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 298 Egypt Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 299 Egypt Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 300 Egypt Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 301 Egypt Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 302 Egypt Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 303 Rest of Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 304 Rest of Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by Product Type, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 305 Rest of Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 306 Rest of Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by Route of Administration, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 307 Rest of Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 308 Rest of Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by End User, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 309 Rest of Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2019-2023 (US$ Mn)
TABLE 310 Rest of Africa Intraosseous Devices Market, by Application, 2024-2032 (US$ Mn)