Market Overview
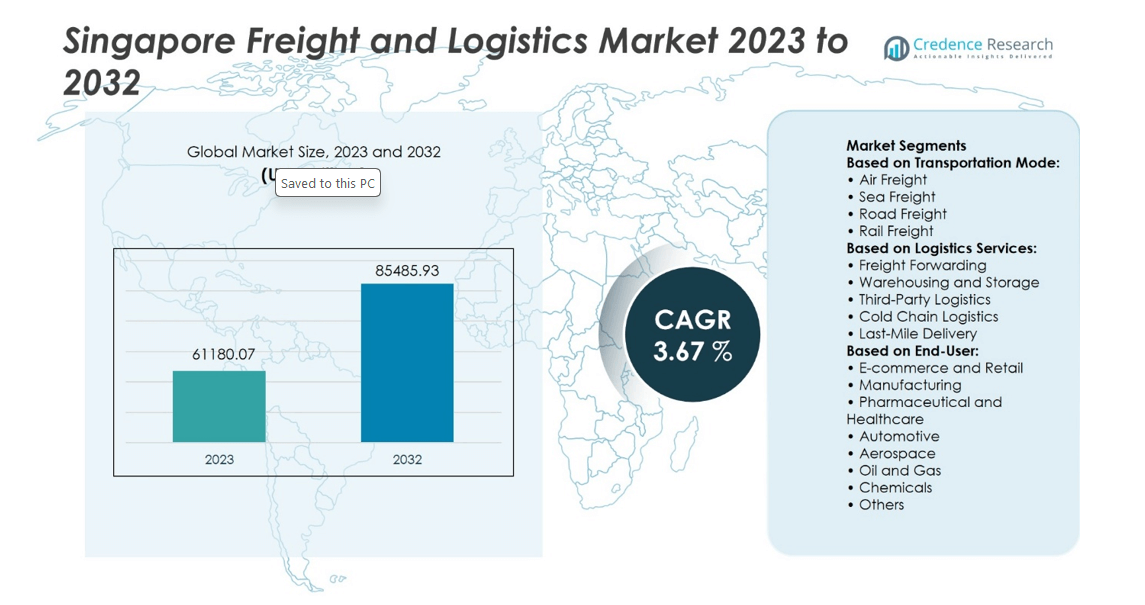
Singapore Freight and Logistics Market size was valued at USD 61180.07 million in 2023 and is anticipated to reach USD 85485.93 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 3.67% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Singapore Freight and Logistics Market Size 2024 |
USD 61180.07 million |
| Singapore Freight and Logistics Market, CAGR |
3.67% |
| Singapore Freight and Logistics Market Size 2032 |
USD 85485.93 million |
The Singapore Freight and Logistics Market is driven by its strategic location, world-class port and airport infrastructure, and strong government support for trade liberalization and digital transformation. Growing e-commerce demand, expanding cross-border trade, and the need for integrated logistics solutions further stimulate growth. It reflects key trends such as rising adoption of automation, AI, and blockchain to improve efficiency and transparency across supply chains. Sustainability initiatives, including green warehousing and low-emission transport, also shape the market’s evolution. The sector continues to adapt to shifting global trade flows while enhancing resilience through innovation and technology-led solutions.
The Singapore Freight and Logistics Market demonstrates strong geographical concentration in Central Singapore, supported by the CBD’s commercial demand, while Jurong anchors industrial and maritime activities with major port facilities. Other regions contribute through air freight at Changi and suburban logistics hubs that enhance last-mile delivery. Key players shaping the competitive landscape include United Parcel Service, Deutsche Post DHL Group, Singapore Post Limited, GEODIS, YCH Group Pte Ltd, CWT Pte Ltd, DSV A/S, Yamato Transport, ACW Logistics Pte Ltd, and Kuehne + Nagel International AG.
Market Insights
- The Singapore Freight and Logistics Market was valued at USD 61180.07 million in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 85485.93 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 3.67%.
- Strategic location, advanced port and airport infrastructure, and government-backed trade liberalization drive consistent market expansion.
- Rising adoption of automation, blockchain, and AI enhances supply chain transparency, speed, and efficiency.
- Competition intensifies with global leaders and regional firms offering integrated, specialized, and technology-driven services.
- High operating costs, land scarcity for warehousing, and global supply chain disruptions act as restraints.
- Central Singapore dominates with commercial concentration, while Jurong strengthens industrial and maritime logistics; other regions support air freight and suburban last-mile networks.
- Leading players include United Parcel Service, Deutsche Post DHL Group, Singapore Post Limited, GEODIS, YCH Group Pte Ltd, CWT Pte Ltd, DSV A/S, Yamato Transport, ACW Logistics Pte Ltd, and Kuehne + Nagel International AG.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Drivers
Strong Infrastructure and Connectivity
The Singapore Freight and Logistics Market benefits from world-class infrastructure and strategic geographical positioning. Singapore’s port remains one of the busiest globally, handling over 37.3 million TEUs in 2023, which strengthens its role as a leading transshipment hub. Changi Airport complements maritime trade with extensive air cargo operations that connect to more than 120 countries. It supports efficient integration of sea and air logistics, ensuring timely cargo movement for global supply chains. Advanced road and rail connectivity further enhances domestic and regional distribution. Continuous investment in smart port technologies and automated handling boosts reliability and operational capacity.
- For instance, PSA International launched 65 automated guided vehicles and 30 automated quay cranes at Pasir Panjang Terminal in 2023, enabling the port to handle over 500,000 additional TEUs annually through improved efficiency and reduced turnaround times.
Expanding E-commerce and Digital Trade
The rapid expansion of e-commerce across Southeast Asia drives sustained growth in the logistics sector. Rising consumer demand for same-day and next-day deliveries creates significant opportunities for freight operators. It encourages adoption of advanced warehouse automation, robotics, and last-mile solutions that ensure faster and more reliable order fulfillment. Singapore’s digital trade agreements with key partners support cross-border e-commerce, streamlining customs and compliance processes. Logistics firms benefit from government-led initiatives promoting digitalization and data exchange across the supply chain. This integration strengthens transparency, reduces delays, and improves customer satisfaction across regional markets.
- For instance, Singapore Post Limited reported handling 159 million e-commerce parcels in FY2023, supported by its new regional logistics hub equipped with automated systems that increase processing speed to 100,000 parcels per hour.
Government Policies and Trade Liberalization
Supportive government policies reinforce Singapore’s role as a global logistics hub. The nation’s pro-trade environment, transparent regulations, and extensive network of free trade agreements provide seamless access to major global markets. It ensures reduced tariffs, streamlined procedures, and higher competitiveness for freight operators. Initiatives such as the Logistics Industry Transformation Map encourage digital adoption, innovation, and workforce upskilling. Strategic collaborations with global logistics leaders enhance knowledge transfer and operational standards. These efforts align with long-term national strategies to secure Singapore’s position as a leading logistics gateway in Asia.
Technology Adoption and Sustainable Solutions
Widespread adoption of advanced technologies accelerates efficiency and competitiveness in the Singapore Freight and Logistics Market. Artificial intelligence, blockchain, and Internet of Things (IoT) solutions are integrated to optimize route planning, cargo tracking, and predictive maintenance. It supports greater accuracy and visibility across supply chain operations. Growing emphasis on sustainability drives investments in electric vehicles, green warehouses, and carbon-neutral shipping practices. Partnerships between logistics providers and technology firms enable scalable deployment of eco-friendly innovations. This transformation positions Singapore as a forward-looking logistics hub that balances efficiency with environmental responsibility.
Market Trends
Rising Demand for Integrated Logistics Solutions
The Singapore Freight and Logistics Market witnesses a clear trend toward integrated end-to-end logistics services. Customers increasingly seek single providers that can manage warehousing, transportation, and value-added services under one platform. It enables better cost efficiency, stronger supply chain visibility, and faster response to disruptions. Companies are consolidating operations to offer bundled services that reduce complexity for global shippers. Strategic partnerships between logistics firms and technology providers support this integration. The model strengthens Singapore’s position as a hub for seamless and efficient logistics operations.
- For instance, YCH Group expanded its Supply Chain City facility in Singapore to 50,000 square meters, integrating automated storage and retrieval systems capable of handling 600,000 pallets annually, which enhances efficiency for regional and global clients.
Growth of Cross-Border E-commerce Logistics
E-commerce expansion across Southeast Asia drives heightened demand for cross-border logistics capabilities. Singapore’s location makes it an ideal gateway for regional fulfillment and last-mile delivery networks. It supports streamlined customs procedures and improved connectivity to ASEAN and beyond. Logistics providers are investing in cross-border warehousing, bonded facilities, and express delivery services to capture this demand. Strong consumer appetite for international products sustains the need for agile and reliable logistics operations. Technology-driven platforms enhance coordination between retailers, freight forwarders, and customs authorities.
- For instance, DHL Express invested 104 million in its South Asia Hub at Changi Airfreight Centre, expanding capacity to handle 628,000 tons of cargo annually and enabling faster cross-border e-commerce delivery across 220 destinations.
Accelerated Adoption of Automation and Digitalization
Technology-driven transformation remains a defining trend across the logistics sector. Automation in warehouses, AI-powered forecasting, and IoT-enabled tracking improve speed and accuracy. It reduces operational costs and minimizes human error across supply chain processes. Logistics providers in Singapore are implementing blockchain solutions to enhance transparency and security of transactions. Digital freight platforms streamline booking, pricing, and shipment management for both enterprises and SMEs. Adoption of robotics and autonomous vehicles further strengthens efficiency in distribution networks.
Focus on Sustainability and Green Logistics
Environmental concerns shape long-term strategies within the Singapore Freight and Logistics Market. Companies are deploying electric fleets, renewable-powered warehouses, and energy-efficient storage solutions. It reflects increasing regulatory emphasis on sustainable operations and carbon neutrality goals. Shipping firms are exploring biofuels and alternative propulsion technologies to reduce emissions. Green certifications and eco-friendly logistics practices attract clients prioritizing responsible supply chains. The push for sustainability creates opportunities for innovation and competitive differentiation in Singapore’s logistics landscape.
Market Challenges Analysis
Rising Operating Costs and Infrastructure Pressures
The Singapore Freight and Logistics Market faces persistent challenges from escalating operating costs and infrastructure constraints. Rising fuel prices, labor shortages, and high real estate costs increase the burden on logistics providers. It creates pressure on profit margins, particularly for small and mid-sized operators that lack scale advantages. Limited land availability for new warehouses and distribution hubs further complicates expansion. Congestion at ports and increased demand for last-mile delivery add strain to existing infrastructure. Balancing capacity growth with cost efficiency remains a critical challenge for sustaining competitiveness.
Regulatory Complexity and Global Supply Chain Disruptions
Freight and logistics companies must navigate complex regulatory environments and frequent global disruptions. Shifts in international trade policies, compliance requirements, and customs procedures demand constant adaptation. It heightens administrative costs and creates delays in cross-border movement of goods. The sector also remains exposed to geopolitical tensions, climate-related risks, and fluctuating global demand. Supply chain disruptions from pandemics or conflicts highlight the vulnerability of tightly integrated networks. Ensuring resilience through diversification, risk management, and digital tools remains a key challenge for the industry.
Market Opportunities
Expansion of Digital Trade and Smart Logistics
The Singapore Freight and Logistics Market holds strong opportunities in digital trade and smart logistics adoption. Rapid growth in e-commerce and cross-border trade fuels demand for advanced digital platforms that streamline booking, tracking, and customs clearance. It allows logistics providers to enhance visibility, improve efficiency, and deliver faster services to clients. Investment in AI, blockchain, and IoT offers scope for predictive analytics, secure transactions, and real-time monitoring. Singapore’s government support for digital trade corridors and smart port initiatives further strengthens these opportunities. Companies that integrate technology-driven models can capture greater market share and establish long-term resilience.
Growing Focus on Sustainability and Regional Connectivity
Sustainability initiatives and regional integration create significant avenues for expansion. The push for carbon-neutral operations encourages adoption of electric fleets, renewable-powered warehouses, and low-emission shipping solutions. It enables logistics firms to align with global sustainability standards while appealing to environmentally conscious clients. Regional trade agreements and infrastructure projects across ASEAN enhance Singapore’s role as a central logistics hub. Demand for bonded warehouses, transshipment services, and green logistics solutions continues to rise in line with these developments. Companies that combine sustainable practices with regional connectivity will secure stronger positioning in the competitive market landscape.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Transportation Mode
The Singapore Freight and Logistics Market demonstrates strong diversification across transportation modes. Sea freight remains the backbone of trade, supported by the Port of Singapore’s advanced infrastructure and global connectivity. It manages a significant share of container transshipment, reinforcing the nation’s position as a maritime hub. Air freight contributes prominently through Changi Airport, which handles high-value and time-sensitive cargo with extensive global linkages. Road freight supports regional connectivity, particularly with Malaysia, while serving domestic distribution needs. Rail freight holds limited presence but continues to be explored through cross-border initiatives that may enhance long-term trade efficiency.
- For instance, PSA International handled 37.3 million TEUs in 2023, supported by its automated terminals equipped with 200 quay cranes. Air freight contributes prominently through Changi Airport, which handles high-value and time-sensitive cargo with extensive global linkages.
By Logistics Services
Logistics services exhibit wide-ranging specialization driven by evolving customer demands. Freight forwarding dominates through its role in coordinating international trade and streamlining customs clearance. Warehousing and storage services gain momentum with the growth of e-commerce, supported by automation and smart inventory systems. It fosters efficiency in managing complex supply chains while reducing delivery times. Third-party logistics providers expand rapidly, offering integrated solutions that combine transportation, warehousing, and value-added services. Cold chain logistics gains importance with the rising demand for pharmaceutical and food products requiring strict temperature control. Last-mile delivery strengthens its position as consumer expectations shift toward faster and more flexible fulfillment.
- For instance, FedEx processed more than 16 million packages per day, serving over 220 countries and territories using a massive fleet that includes more than 175,000 motor vehicles and 698 aircraft—demonstrating the scale of its integrated logistics capabilities.
By End-user
End-user industries provide diverse growth avenues across the market. E-commerce and retail emerge as primary drivers, creating sustained demand for express deliveries and efficient inventory management. Manufacturing contributes through continuous requirements for bulk freight and streamlined supply chain solutions. It ensures timely movement of raw materials and finished goods across global markets. Pharmaceutical and healthcare industries rely heavily on cold chain logistics to maintain product integrity. Automotive and aerospace segments demand specialized handling for high-value and oversized cargo. Oil and gas, alongside chemicals, require strict compliance and safety standards in transportation and storage. Other sectors, including consumer goods, also support steady logistics flows, reinforcing Singapore’s status as a critical trade gateway.
Segments:
Based on Transportation Mode:
- Air Freight
- Sea Freight
- Road Freight
- Rail Freight
Based on Logistics Services:
- Freight Forwarding
- Warehousing and Storage
- Third-Party Logistics
- Cold Chain Logistics
- Last-Mile Delivery
Based on End-User:
- E-commerce and Retail
- Manufacturing
- Pharmaceutical and Healthcare
- Automotive
- Aerospace
- Oil and Gas
- Chemicals
- Others
Based on the Geography:
- Central Singapore
- Jurong
- Other Regions
Regional Analysis
Central Singapore
Central Singapore accounts for around 48% of the market share, making it the largest contributor to the Singapore Freight and Logistics Market. The region’s dominance is underpinned by its proximity to the Central Business District (CBD), major commercial centers, and government institutions, which serve as key demand drivers for logistics and freight services. It houses a dense concentration of warehouses, distribution centers, and office headquarters of global logistics firms, creating an ecosystem that thrives on integrated supply chain solutions. The region also benefits from high connectivity to expressways, facilitating efficient access to ports and airports. It supports a large portion of last-mile delivery networks that cater to e-commerce and retail customers concentrated in urban hubs. High real estate costs in Central Singapore create challenges, yet they are offset by the premium value logistics providers deliver through strategic accessibility and service excellence. Central Singapore continues to lead in innovation, with widespread adoption of automation, robotics, and digital freight platforms to support efficiency and sustainability.
Jurong
Jurong contributes around 34% of the market share, positioning itself as the industrial backbone of the Singapore Freight and Logistics Market. The region is home to Jurong Port, one of the nation’s critical multipurpose ports, and the upcoming Tuas Mega Port, which is set to transform Singapore’s maritime landscape. This infrastructure underpins Jurong’s strength in sea freight, bulk cargo handling, and transshipment activities. Jurong Industrial Estate, the largest industrial hub in Singapore, creates steady demand for freight forwarding, warehousing, and specialized logistics services. The region also supports oil and gas, chemicals, and heavy industries, which require advanced logistics capabilities and strict compliance with safety standards. It plays a central role in manufacturing-related freight flows, supported by modern storage facilities and value-added logistics services. Jurong is also a focal point for green logistics, with the Tuas Mega Port designed for automation, smart technology integration, and carbon-efficient operations, strengthening the region’s competitiveness in the long term.
Other Regions
Other regions collectively account for around 18% of the market share, reflecting their growing importance in the Singapore Freight and Logistics Market. These regions, including the eastern and northern parts of Singapore, support expansion of warehousing, distribution, and last-mile delivery operations. The East, anchored by Changi Airport, plays a vital role in air freight, handling time-sensitive and high-value cargo for global markets. Northern areas, with increasing industrial and residential development, foster demand for logistics services that link businesses with regional distribution networks. It allows logistics operators to decentralize operations, easing the pressure on Central and Jurong regions while enhancing overall network efficiency. Growth in suburban logistics hubs also supports the rise of e-commerce, ensuring faster delivery to residential clusters.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- GEODIS
- Yamato Transport
- YCH Group Pte Ltd
- United Parcel Service
- Kuehne + Nagel International AG
- CWT Pte Ltd
- ACW Logistics Pte Ltd
- Singapore Post Limited
- DSV A/S
- Deutsche Post DHL Group
Competitive Analysis
The Singapore Freight and Logistics Market players include United Parcel Service, Deutsche Post DHL Group, Singapore Post Limited, ACW Logistics Pte Ltd, GEODIS, CWT Pte Ltd, YCH Group Pte Ltd, Yamato Transport, DSV A/S, and Kuehne + Nagel International AG. The Singapore Freight and Logistics Market reflects a competitive environment shaped by global connectivity, advanced infrastructure, and strong regional demand. Companies compete on the basis of service efficiency, technological adoption, and ability to deliver integrated end-to-end solutions. The sector emphasizes innovation in digital platforms, automation, and data-driven visibility to streamline operations and meet customer expectations. Sustainability also emerges as a defining factor, with logistics providers investing in electric fleets, renewable-powered warehouses, and low-emission shipping practices to align with regulatory standards and client preferences. Strong emphasis on e-commerce, cross-border trade, and time-sensitive delivery drives further differentiation, pushing market players to strengthen last-mile capabilities and expand specialized services such as cold chain and bonded warehousing. The overall competitive landscape highlights the balance between global scale, regional expertise, and technological transformation.
Recent Developments
- In August 2025, YCH Group signed a Memorandum of Understanding with National Trades Union Congress (NTUC) and SkillsFuture Singapore (SSG) to support workforce development and SME capability building in the supply chain and logistics sector in Singapore.
- In June 2025, Yamato Transport Singapore continues providing flexible freight and logistics solutions, leveraging its location at Changi Airfreight Centre to support customers using Singapore as a distribution hub.
- In June 2025, UPS Healthcare expanded its Asia-Pacific services with a new logistics facility in Singapore to better serve healthcare supply chains with advanced logistics capabilities.
- In January 2025, YCH Group partnered with Sime Darby Property Berhad to develop a logistics center in southern Vietnam’s Moc Bai Border Gate Economic Zone, aiming to enhance regional logistics capabilities and cross-border trade efficiency.
Market Concentration & Characteristics
The Singapore Freight and Logistics Market shows a moderately concentrated structure, with global leaders and established regional firms shaping competitive dynamics through scale, technology, and service specialization. It is characterized by a strong presence of multinational logistics providers that dominate international freight forwarding, contract logistics, and integrated supply chain solutions. Regional and domestic operators enhance competition by focusing on niche areas such as last-mile delivery, cold chain logistics, and warehousing tailored to e-commerce and retail demand. The market reflects high barriers to entry due to capital-intensive infrastructure, regulatory compliance, and the need for advanced digital platforms. It also demonstrates a strong orientation toward innovation, with players adopting automation, blockchain, and IoT-based solutions to enhance efficiency and transparency. Sustainability and green logistics practices emerge as defining characteristics, aligning with Singapore’s broader national objectives for carbon reduction. The balance between global scale, regional expertise, and technological advancement positions the market as both competitive and adaptive to evolving trade flows.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Transportation Mode, Logistics Services, End-User and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market will strengthen its role as a leading transshipment and regional trade hub.
- Technology adoption will expand with wider use of automation, blockchain, and AI-driven logistics solutions.
- E-commerce growth will drive continuous demand for last-mile delivery and express logistics.
- Cold chain logistics will expand to support pharmaceuticals, food, and healthcare industries.
- Sustainability initiatives will accelerate with investments in electric fleets and carbon-neutral warehousing.
- Digital trade corridors and smart port initiatives will enhance connectivity and efficiency.
- Regional integration with ASEAN markets will increase cross-border freight movement.
- Warehousing demand will rise with greater emphasis on automation and inventory optimization.
- Competition will intensify between global giants and regional firms offering specialized services.
- Resilience strategies will focus on diversifying supply chains and strengthening risk management.




