| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Smart Transformers Market Size 2024 |
USD 3,330.52 million |
| Smart Transformers Market, CAGR |
9.39% |
| Smart Transformers Market Size 2032 |
USD 6,795.32 million |
Market Overview:
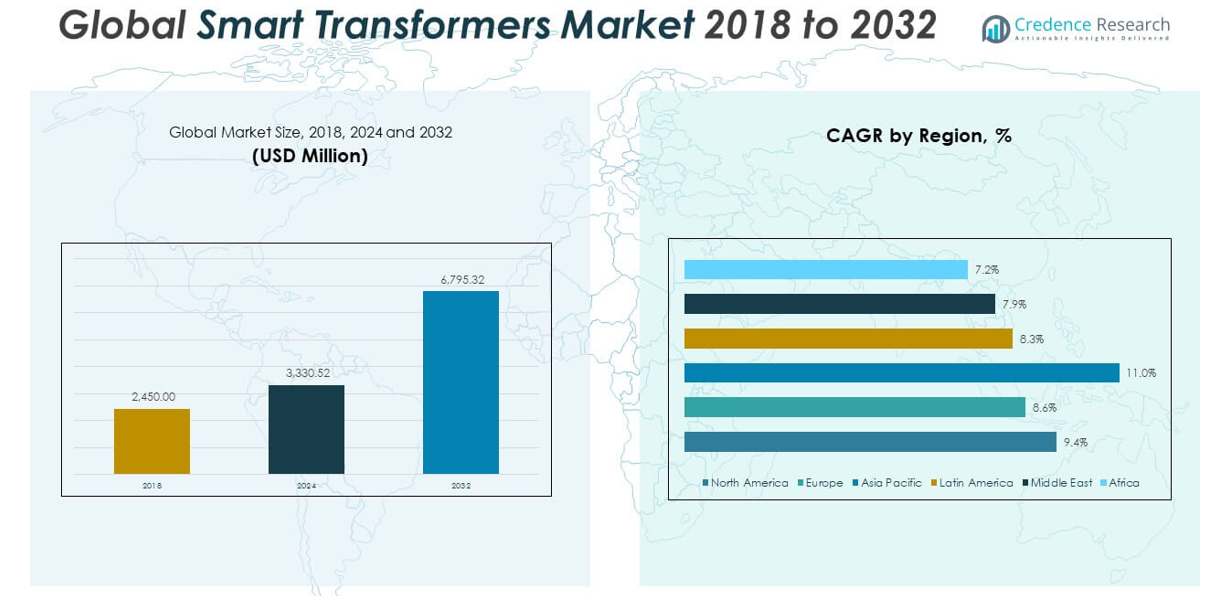
The Global Smart Transformers Market size was valued at USD 2,450.00 million in 2018 to USD 3,330.52 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 6,795.32 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 9.39% during the forecast period.
Key drivers propelling the market include the global emphasis on grid modernization and the integration of smart grids, which require adaptive and intelligent systems like smart transformers to ensure grid stability and efficiency. Governments across developed and emerging economies are heavily investing in grid infrastructure upgrades, where smart transformers serve as a core component. The growing shift toward renewable energy generation—particularly solar and wind—demands advanced distribution systems that can handle fluctuating input and allow bi-directional energy flow, roles that smart transformers are uniquely positioned to fulfill. Additionally, the rapid growth of electric vehicles and industrial automation has heightened the need for reliable and intelligent power delivery systems. The rising adoption of IoT-enabled power equipment, AI-powered diagnostics, and remote monitoring capabilities is also contributing to market expansion. However, recent supply chain constraints have led to a shortage of transformer components globally. Industry leaders such as Hitachi Energy are increasing investment in production capacity to meet rising demand, although supply tightness is expected to continue in the near term.
Regionally, the Asia-Pacific region holds the largest market share in the global smart transformers market. Countries like China, India, Japan, and South Korea are at the forefront of smart grid implementation and urban electrification, driving robust demand. North America follows closely, supported by the U.S. government’s initiatives to modernize grid infrastructure, promote clean energy, and expand EV charging networks. Europe ranks third, bolstered by aggressive sustainability goals, aging infrastructure replacement, and the European Union’s energy efficiency mandates under the Green Deal. Meanwhile, markets in the Middle East & Africa and Latin America, though smaller in size, are witnessing increased adoption due to ongoing investments in renewable energy projects, regulatory reforms, and the expansion of electrification in underserved regions. Overall, the global smart transformers market is positioned for sustained growth, fueled by the convergence of digital transformation, decarbonization efforts, and rising energy demand across both developed and emerging economies.
Market Insights:
- The Global Smart Transformers Market grew from USD 2,450.00 million in 2018 to USD 3,330.52 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 6,795.32 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 9.39%.
- Government-backed grid modernization programs in countries like the U.S., China, and Germany are boosting demand for smart transformers that support real-time monitoring and energy efficiency.
- Rising integration of solar and wind energy has increased the need for intelligent transformers that regulate voltage and enable two-way power flow for grid stability.
- Expanding EV infrastructure and smart city initiatives in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific are creating sustained demand for adaptive, intelligent power delivery systems.
- The market faces challenges such as high initial investment costs and long payback periods, which restrict adoption in developing and cost-sensitive regions.
- Global supply chain disruptions and shortages of electronic components are delaying project timelines and driving up costs, prompting manufacturers to diversify sourcing and expand local production.
- Asia-Pacific dominates the market share, followed by North America and Europe, while Latin America and the Middle East & Africa show rising potential due to renewable energy investments and electrification efforts.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Drivers:
Government-Led Grid Modernization Initiatives Are Fueling Transformer Innovation and Replacement:
Governments around the world are prioritizing energy infrastructure upgrades to meet rising electricity demand and address aging transmission networks. Investments in smart grids are at the core of these initiatives, and smart transformers are critical to enabling advanced grid capabilities. These devices allow for dynamic voltage regulation, real-time fault detection, and improved system reliability. National energy strategies in countries like the United States, Germany, China, and India are allocating significant funding for intelligent grid deployments. The Global Smart Transformers Market benefits directly from these programs, which mandate the replacement of legacy transformers with intelligent and digital units. It supports utility companies in reducing transmission losses, managing distributed energy resources, and improving power quality across all grid levels.
- For instance, Sensformer™ platform supports data-driven asset management, allowing grid operators to make informed decisions and extend transformer life cycles, as documented in Siemens’ deployment reports.
Integration of Renewable Energy Sources Requires Intelligent Voltage Regulation and Grid Flexibility:
The rapid expansion of renewable energy sources is a significant force behind the demand for smart transformers. Solar and wind installations introduce variable and decentralized power into the grid, which creates volatility in supply and requires smarter control at the distribution level. Smart transformers play a key role in stabilizing this variability by enabling automated voltage control, load balancing, and two-way power flow. It helps maintain consistent power delivery and prevents outages or equipment damage. Markets with aggressive renewable goals—such as the European Union, India, and California—are witnessing strong deployment of smart transformers to support grid decentralization. The Global Smart Transformers Market is aligning with the clean energy transition, offering scalable and responsive infrastructure solutions.
- For instance, Hitachi Energy’s TXpert™ Ecosystem, launched in 2023, incorporates the TXpert Hub, which aggregates and analyzes data from multiple sensors embedded in transformers. This system has been deployed in projects supporting over 1 GW of renewable capacity, enabling utilities to achieve a 25% improvement in voltage stability and a 20% reduction in reactive power losses.
Surge in Electric Vehicle Infrastructure and Smart City Development Supports Demand:
The electrification of transportation and the rise of smart cities are expanding the operational requirements of distribution networks. High EV adoption requires resilient charging infrastructure, which in turn depends on smart transformers for efficient energy distribution and grid balancing. Cities integrating IoT, real-time monitoring, and automation into urban planning are also deploying these transformers for better control and energy optimization. It enables grid operators to support sudden spikes in demand while maintaining voltage stability. Public and private investments in EV charging stations and intelligent urban infrastructure are increasing across North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific. The Global Smart Transformers Market is seeing growing interest from municipal utilities and private grid operators that seek flexibility, responsiveness, and scalability.
Digital Transformation and Predictive Maintenance Are Reshaping Utility Asset Management:
The adoption of advanced sensors, AI algorithms, and communication technologies in smart transformers is redefining how utilities monitor and manage grid assets. Real-time data collection enables predictive maintenance, helping reduce unplanned outages and extend equipment life. Utilities gain visibility into performance metrics, fault conditions, and operational anomalies, allowing for proactive intervention. It reduces operating costs and enhances reliability without manual inspections. With rising expectations for power reliability, especially in industrial zones and data centers, digitalized power systems are no longer optional. The Global Smart Transformers Market is evolving rapidly to deliver embedded intelligence, network connectivity, and automation to modern energy infrastructure.
Market Trends:
Growing Preference for Solid-State Transformers Reflects Shift Toward Advanced Power Electronics:
Solid-state transformers (SSTs) are gaining traction due to their superior functionality and compact design. Unlike traditional transformers, SSTs use power electronic components to achieve voltage regulation, frequency conversion, and power flow control with greater precision. Their ability to operate in both AC and DC environments supports the evolution of modern grids. High-efficiency transmission, smaller footprint, and adaptability to smart grids make them attractive for utilities and industrial users. Research institutions and manufacturers are focusing on advancing SST technology for commercial deployment. The Global Smart Transformers Market is gradually incorporating solid-state units, setting a trend for future-ready power systems that combine hardware innovation with digital intelligence.
- For instance, ABB’s Ability™ TXpert™ Dry is the world’s first dry-type digital transformer, featuring smart sensors for power quality monitoring, self-diagnostics, and lifecycle assessment. In recent field trials, TXpert™ Dry units demonstrated a 15% reduction in energy losses and eliminated oil-related maintenance, supporting safer and more environmentally friendly operations.
Rise of Edge Computing Integration Enhances Real-Time Control and Decision-Making:
Edge computing is becoming a key feature in next-generation smart transformers, enabling localized data processing and quicker decision-making. By analyzing data directly at the transformer level, utilities can reduce latency and improve grid responsiveness during disturbances. This trend supports applications like fault detection, load forecasting, and energy management without relying solely on centralized data centers. It helps optimize operational efficiency and enhances network resilience during peak load or emergencies. Smart transformers with built-in edge computing capabilities offer better security, faster analytics, and adaptive performance. The Global Smart Transformers Market is responding to this trend by integrating decentralized computing resources into core transformer designs.
- For instance, Schneider Electric’s EcoStruxure™ Transformer Expert, launched in 2024, is an IoT-based platform that continuously monitors transformer health and predicts maintenance needs. Deployed at CERN, this solution provided a 40% reduction in maintenance-related outages and allowed for accurate prediction of transformer lifespan, optimizing replacement schedules and reducing operational disruptions.
Adoption of Cybersecurity Protocols Is Becoming a Core Design Element in Smart Transformers:
The increasing digitalization of transformers introduces new vulnerabilities, prompting strong emphasis on cybersecurity. Manufacturers are embedding advanced encryption, secure firmware, and network protection protocols within smart transformer architectures. Regulatory frameworks in the U.S., EU, and APAC markets now require utilities to address cyber threats at the component level. The rising threat of grid-focused cyberattacks has accelerated the development of secure communication channels and intrusion detection systems. It is encouraging utilities and suppliers to prioritize cyber-resilient transformer models in procurement. The Global Smart Transformers Market is moving toward standardized cybersecurity integration, ensuring data integrity, secure grid operations, and regulatory compliance.
Use of Digital Twin Technology Supports Lifecycle Optimization and Remote Diagnostics:
Digital twin models are emerging as a transformative trend in transformer lifecycle management. By creating virtual replicas of smart transformers, utilities can simulate performance, detect anomalies, and plan maintenance more effectively. These models help identify failure risks, extend service life, and reduce downtime. Remote diagnostics through digital twins also streamline asset monitoring, especially for equipment deployed in remote or hazardous environments. It improves operational planning and reduces manual inspection costs for large utility networks. The Global Smart Transformers Market is embracing digital twin technology to deliver smarter asset management, predictive maintenance, and improved return on infrastructure investments.
Market Challenges Analysis:
High Initial Investment Costs and Long Payback Periods Restrain Adoption in Cost-Sensitive Markets:
Smart transformers require significant upfront capital due to their advanced components, embedded software, and communication systems. These costs are substantially higher than those of conventional transformers, which deters adoption in developing regions and among small utility providers. For many utilities, the return on investment depends on long-term operational savings and system efficiency improvements, which may not be immediately quantifiable. Budget constraints and uncertain regulatory incentives make financial justification difficult. It limits large-scale deployment, especially in markets where electricity pricing and infrastructure spending remain tightly controlled. The Global Smart Transformers Market must navigate cost pressures and promote flexible financing models to encourage broader uptake.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Component Shortages Delay Project Execution and Raise Costs:
Global disruptions in the supply of critical electronic components, such as semiconductors and sensors, have negatively impacted transformer production timelines. Manufacturers face extended lead times and rising input costs, complicating procurement strategies and delaying smart grid projects. Ongoing geopolitical tensions, raw material shortages, and limited supplier diversity contribute to this bottleneck. It poses operational risks for utilities relying on timely upgrades and replacements. Project delays can affect power reliability and slow the digital transformation of grid infrastructure. The Global Smart Transformers Market is addressing these challenges by diversifying supply chains and investing in localized manufacturing capabilities, though recovery remains gradual.
Market Opportunities:
Expansion of Rural Electrification and Microgrid Projects Creates Untapped Demand:
The global push for rural electrification and energy access in underserved regions opens significant avenues for smart transformer deployment. Governments and development agencies are prioritizing decentralized energy systems, where microgrids and renewable integration play a key role. Smart transformers support voltage regulation and energy balancing in isolated networks, making them ideal for off-grid and hybrid setups. It enables stable and efficient power supply in remote communities, reducing reliance on diesel-based solutions. The Global Smart Transformers Market stands to benefit from this shift, particularly in parts of Africa, South Asia, and Latin America where grid extension remains costly and challenging.
Smart Transformer Role in EV Charging Infrastructure Enhances Long-Term Growth Potential:
The accelerating growth of electric vehicles and the corresponding need for robust charging infrastructure present strong market opportunities. Smart transformers enable dynamic load management, bi-directional power flow, and peak demand mitigation across EV charging networks. Urban planners and power utilities are incorporating intelligent transformers to handle fluctuating loads and ensure grid stability. It positions the technology as a foundational element of future-ready transport ecosystems. The Global Smart Transformers Market can leverage this trend to expand its reach across transportation hubs, commercial corridors, and residential neighborhoods deploying next-generation charging stations.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
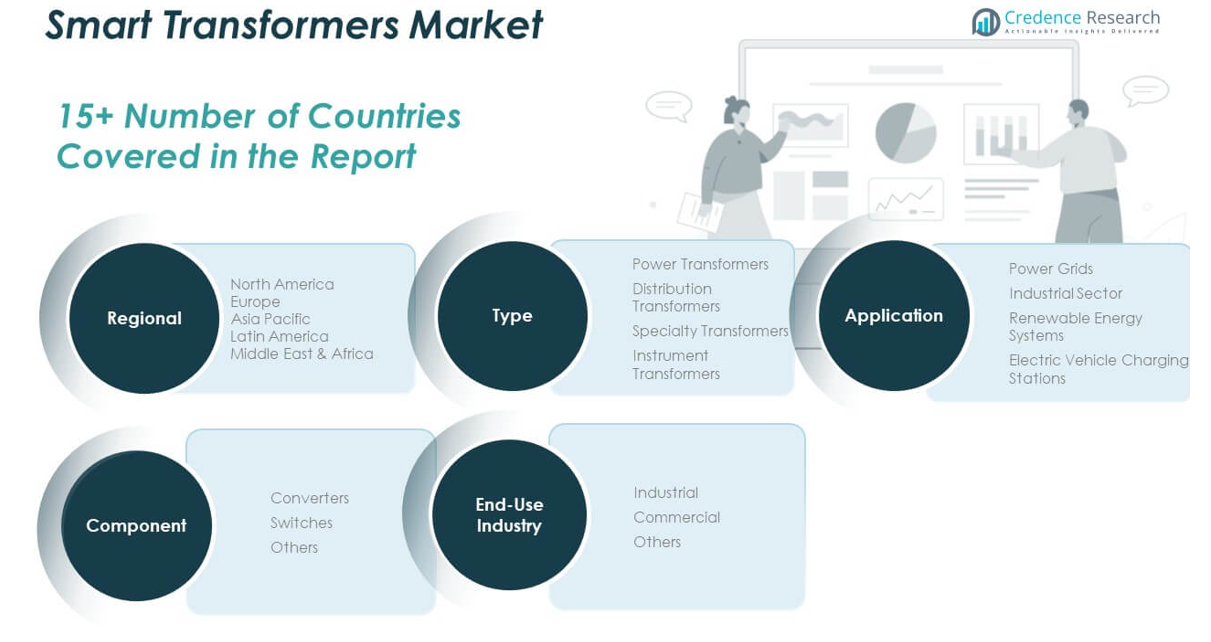
By Component
Converters dominate the component segment due to their ability to manage voltage levels and support AC/DC power conversion across dynamic grid environments. Switches play a vital role in isolating faults and ensuring safe power distribution. Other components, including sensors and communication modules, contribute to system automation and intelligent monitoring.
- For instance, Prolec, in partnership with Ubicquia, developed the UbiGrid™ DTM+ platform, integrating real-time grid analytics and health monitoring. Over 30,000 units equipped with this technology have been deployed across the US and Latin America, providing utilities with actionable insights that have led to a 20% reduction in transformer failures and a 15% improvement in grid reliability.
By Type
Power transformers lead the market, driven by their necessity in high-voltage transmission infrastructure. Distribution transformers hold substantial share across urban and rural distribution networks. Specialty transformers cater to unique industrial requirements such as railways and renewable plants. Instrument transformers support accurate measurement and protection in grid operations.
- For instance, Toshiba Transmission & Distribution Systems increased its manufacturing capacity by 1.5 times in 2024, focusing on 400kV/765kV transformers for both conventional and renewable grid applications.
By Application
Power grids constitute the largest application segment, propelled by global investments in smart grid infrastructure. The industrial sector relies on smart transformers for uninterrupted power, real-time diagnostics, and load efficiency. Renewable energy systems use them to handle bidirectional power flow and voltage variability. Electric vehicle charging stations represent a fast-growing area, requiring intelligent load management and stable output.
By End-Use Industry
The industrial segment dominates end-use, driven by automation, high energy demand, and the need for predictive maintenance. The commercial sector is expanding due to smart infrastructure developments in offices, malls, and data centers. Other sectors, including government utilities and transportation, are adopting smart transformers for grid resilience and energy optimization. The Global Smart Transformers Market continues to expand across all segments, aligned with energy transition and digital transformation goals.
Segmentation:
By Component
- Converters
- Switches
- Others
By Type
- Power Transformers
- Distribution Transformers
- Specialty Transformers
- Instrument Transformers
By Application
- Power Grids
- Industrial Sector
- Renewable Energy Systems
- Electric Vehicle Charging Stations
By End-Use Industry
- Industrial
- Commercial
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Regional Analysis:
North America
The North America Smart Transformers Market size was valued at USD 1,036.35 million in 2018 to USD 1,394.14 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 2,841.14 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 9.4% during the forecast period. North America holds approximately 20.6% of the Global Smart Transformers Market revenue in 2024. Strong federal support for grid modernization, electrification of transport, and renewable energy integration drives growth. The U.S. leads regional adoption, followed by Canada and Mexico, with utilities investing in advanced infrastructure. It benefits from regulatory clarity, innovation hubs, and robust capital spending by energy companies. Rising EV adoption and digital utility transformation are key accelerators. The region continues to advance toward flexible, resilient grid systems supported by intelligent transformer deployment.
Europe
The Europe Smart Transformers Market size was valued at USD 631.61 million in 2018 to USD 824.55 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 1,587.06 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 8.6% during the forecast period. Europe accounts for 12.2% of global revenue in 2024, with strong growth led by Germany, the UK, and France. EU mandates for carbon neutrality and energy efficiency support widespread adoption of smart transformers. It is a mature market focused on replacing aging infrastructure with advanced solutions that meet digital grid requirements. Renewable energy integration and cross-border energy distribution enhance demand. Smart city initiatives and regulatory compliance further drive deployment. The market maintains steady growth with advanced technological integration and public-private collaboration.
Asia Pacific
The Asia Pacific Smart Transformers Market size was valued at USD 498.58 million in 2018 to USD 713.88 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 1,636.32 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 11.0% during the forecast period. Asia Pacific holds the largest share in the Global Smart Transformers Market, at approximately 21.4% in 2024. China, India, Japan, and South Korea lead with large-scale electrification, renewable integration, and smart grid expansion. Rapid industrialization and urban development fuel consistent demand. Governments are investing heavily in infrastructure upgrades, grid automation, and electric mobility. It sees widespread deployment in transmission, distribution, and EV charging networks. Regional momentum continues with policy support and strong manufacturing ecosystems.
Latin America
The Latin America Smart Transformers Market size was valued at USD 139.16 million in 2018 to USD 187.14 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 351.11 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 8.3% during the forecast period. Latin America contributes around 5.6% of global market revenue in 2024. Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina are key contributors, focusing on power grid upgrades and renewable energy projects. Smart transformers support energy reliability in both urban and rural sectors. It sees increasing utility investment in automation and load management. Funding challenges and policy uncertainty affect pace but not long-term potential. The market is steadily evolving with regional infrastructure needs.
Middle East
The Middle East Smart Transformers Market size was valued at USD 84.53 million in 2018 to USD 106.89 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 194.38 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 7.9% during the forecast period. The region holds 3.5% of the Global Smart Transformers Market share in 2024. Saudi Arabia, UAE, and Israel lead in deploying smart grid technologies to enhance energy security and reduce losses. Projects focused on clean energy and digital utilities support demand. It benefits from urban infrastructure development and smart city investments. Governments aim to diversify energy sources and modernize transmission assets. The region continues expanding adoption in line with national energy transformation agendas.
Africa
The Africa Smart Transformers Market size was valued at USD 59.78 million in 2018 to USD 103.93 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 185.30 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 7.2% during the forecast period. Africa represents 3.1% of the global market in 2024. South Africa, Egypt, and Nigeria are early adopters, with a focus on grid reliability and rural electrification. Smart transformers are being used in mini-grid and hybrid power systems to improve voltage regulation and reduce losses. It faces adoption challenges from financing and infrastructure limitations. International aid and private partnerships are improving access to technology. Market growth remains positive, supported by increasing electrification and energy reform.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis:
- ABB Ltd. (Switzerland)
- Emerson Electric Co. (U.S.)
- Siemens AG (Germany)
- Schneider Electric SE (France)
- General Electric Company (U.S.)
- Eaton Corporation plc (Ireland)
- Wilson Transformers (Australia)
- Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (India)
- CG Power & Industrial Solutions Ltd. (India)
- HPL Electric & Power Ltd. (India)
- Howard Industries (U.S.)
- Alstom SA (France)
- Cree, Inc. (U.S.)
- Toshiba Corporation (Japan)
- KONCAR – Electrical Industry Inc. (Croatia)
- HD Hyundai Electric Co., Ltd. (South Korea)
- Rockwell Automation, Inc. (U.S.)
- Nexans S.A. (France)
Competitive Analysis:
The Global Smart Transformers Market features strong competition among multinational corporations with established expertise in power systems and grid automation. Key players include ABB Ltd., Siemens AG, Schneider Electric SE, General Electric Company, and Eaton Corporation, all offering comprehensive smart transformer portfolios integrated with digital monitoring and control technologies. These companies invest heavily in R&D to enhance performance, grid compatibility, and cybersecurity. Regional players such as CG Power, Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited, and Wilson Transformers strengthen domestic supply and serve specific regulatory requirements. It is shaped by strategic collaborations, grid modernization contracts, and participation in renewable integration projects. Competitive focus remains on technological innovation, product reliability, and lifecycle service offerings. Market participants are expanding manufacturing capacity to address global supply constraints and rising demand from EV infrastructure, industrial automation, and decentralized energy networks. The Global Smart Transformers Market continues to evolve with heightened focus on energy efficiency, automation, and digital intelligence.
Recent Developments:
- In June 2025, Siemens Energy announced plans to begin production of large industrial power transformers in the United States by 2027. The expansion of its Charlotte, North Carolina facility will support domestic grid modernization and address the high demand for large power transformers, particularly in light of the growing need for AI-driven data center infrastructure.
- In March 2025, Eaton signed an agreement to acquire Fibrebond Corporation for $1.4 billion. This acquisition expands Eaton’s capabilities in modular power enclosures, supporting the integration of smart transformers and accelerating deployment for data centers, utilities, and industrial customers. Eaton also announced a $340 million investment in a new transformer manufacturing facility in South Carolina, with production expected to begin in 2027.
- In March 2024, Wilson Power Solutions introduced the Wilson e4 Ultimate Low Loss Amorphous® Transformer, recognized as the most efficient transformer in the UK and Europe. This product targets industrial and commercial clients seeking reduced energy losses and enhanced grid performance.
Market Concentration & Characteristics:
The Global Smart Transformers Market is moderately concentrated, with a mix of global giants and regional specialists competing across diverse application areas. It features a strong presence of established players like ABB, Siemens, Schneider Electric, and GE, which collectively hold a significant market share due to their broad portfolios and global distribution networks. It is characterized by high capital intensity, long product lifecycles, and a strong emphasis on innovation and system integration. Barriers to entry remain high due to technological complexity, certification requirements, and long utility procurement cycles. The market favors companies with advanced R&D capabilities, strategic partnerships, and the ability to deliver end-to-end grid solutions. Demand concentration is higher in industrialized regions, though emerging markets are accelerating adoption through infrastructure development and electrification programs. The Global Smart Transformers Market continues to shift toward digital, connected, and sustainable solutions aligned with evolving grid modernization goals.
Report Coverage:
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on component, type, application, and end-use industry. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook:
- Rising global investments in smart grids will drive long-term demand for intelligent transformer systems.
- Integration of distributed renewable energy sources will require advanced voltage regulation and two-way power flow capabilities.
- Expansion of electric vehicle charging infrastructure will increase adoption of load-balancing smart transformers.
- Digital twin technology and AI-driven diagnostics will become standard features in future product offerings.
- Governments will implement stricter energy efficiency regulations, accelerating transformer modernization.
- Emerging markets in Asia, Africa, and Latin America will provide new growth avenues through electrification initiatives.
- Strategic partnerships between OEMs and utilities will reshape service delivery and grid asset management.
- Supply chain diversification and regional manufacturing expansion will reduce lead times and enhance resilience.
- Cybersecurity integration will gain importance to protect digital grid infrastructure from evolving threats.
- The Global Smart Transformers Market will continue to evolve toward modular, scalable, and interoperable solutions.





