Market Overview
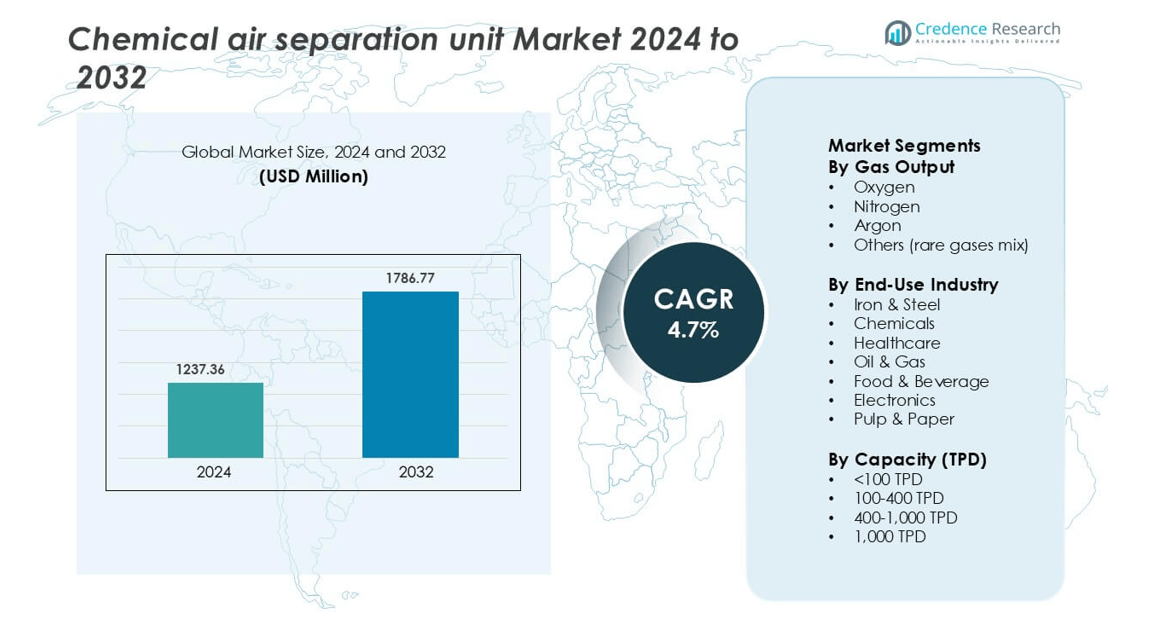
Chemical air separation unit Market was valued at USD 1237.36 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 1786.77 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 4.7% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Chemical Air Separation Unit Market Size 2024 |
USD 1237.36 million |
| Chemical Air Separation Unit Market, CAGR |
4.7% |
| Chemical Air Separation Unit Market Size 2032 |
USD 1786.77 million |
Top players in the chemical air separation unit market include Linde plc, Air Liquide, Air Products and Chemicals, Inc., Taiyo Nippon Sanso (Nippon Sanso Holdings), Messer Group, Yingde Gases, Hangyang, AMCS Corporation, Technex and Universal Industrial Gases (UIG). These firms focus on large‑capacity cryogenic units, modular onsite systems, and long‑term gas supply contracts to serve steel, petrochemical, electronics and healthcare sectors. They expand globally through build‑own‑operate models, digital monitoring platforms and strategic partnerships. The leading region is Asia Pacific, which holds approximately 40% of this market, driven by major industrial gas demand from China, India, Japan and South Korea.
Market Insights
- The chemical air separation unit market reached USD 1237.36 million in 2024 and will grow at a CAGR of 4.7% through 2032.
- Rising demand for oxygen in steelmaking and petrochemical processing drives new installations, while healthcare and food processing increase consumption of high-purity nitrogen for medical supply and packaging applications.
- Energy-efficient cryogenic systems, digital monitoring, and build-own-operate supply models are key trends, with many end users shifting to onsite gas generation to reduce transport costs and ensure stable purity levels.
- Competition remains strong among Linde, Air Liquide, Air Products, and Messer Group, all expanding capacity, signing long-term gas contracts, and deploying automation-based ASUs for cost optimization.
- Asia Pacific leads with around 40% share, driven by steel, electronics, and chemicals; North America holds close to 25%; Europe has nearly 20%. Oxygen dominates by output, and units above 1,000 TPD hold the largest capacity share due to large industrial consumption
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Gas Output
Oxygen holds the dominant share in the chemical air separation unit market, driven by its wide use across steelmaking, refining, pharmaceuticals, and wastewater treatment. The steel industry consumes oxygen to enhance furnace efficiency, lower fuel use, and boost output, which increases demand for large-scale air separation facilities. Nitrogen is the next major output, favored in electronics, chemicals, and food packaging due to its inert properties. Argon and other rare gas mixes continue to grow in welding, metal fabrication, and semiconductor processes, supported by rising demand for high-purity gases in precision manufacturing.
- For instance, Air Liquide operates the world’s largest oxygen production unit in Secunda, South Africa, supplying 5,000 tons of oxygen per day using advanced cryogenic distillation technology.
By End-Use Industry
Iron and steel is the leading end-use industry, holding the highest market share due to continuous oxygen demand for blast furnaces, converters, and direct reduced iron plants. Growth in infrastructure and automotive production strengthens consumption. The chemicals sector also drives steady installations for nitrogen, oxygen, and argon use in synthesis and inerting applications. Healthcare and food & beverage segments grow with rising use of medical-grade gases and modified atmosphere packaging. Oil & gas and electronics industries are expanding adoption for refining processes and semiconductor fabrication.
- For instance, Linde supplies integrated air separation units to ArcelorMittal’s steel facilities, delivering more than 4,000 tons of oxygen per day to support basic oxygen furnace operations and continuous casting.
By Capacity (TPD)
Air separation units above 1,000 TPD dominate the market, supported by large steel mills, petrochemical complexes, and integrated industrial gas networks. These high-capacity systems deliver continuous output, lower unit production costs, and meet bulk gas requirements. The 400–1,000 TPD category is expanding with mid-sized manufacturing clusters and industrial parks installing dedicated plants. Smaller units below 400 TPD serve regional demand, captive use in healthcare, food processing, and specialty gas production. Adoption of energy-efficient cryogenic and non-cryogenic technologies supports installations across all capacity segments.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Industrial Oxygen Demand from Steel and Metallurgy
Steelmaking requires large volumes of oxygen for blast furnaces, basic oxygen furnaces, and direct reduced iron units. This drives continuous expansion of high-capacity air separation units across major steel-producing regions. Oxygen injection improves combustion efficiency, increases furnace productivity, and lowers fuel consumption, making it a preferred option for both fully integrated steel plants and mini-mills. Growth in construction, shipbuilding, and automotive production increases steel output, which strengthens demand for industrial gases. Many steel plants also choose onsite oxygen generation to reduce dependency on bulk gas transport and ensure uninterrupted availability. As a result, new greenfield steel investments and plant expansions directly support the installation of large-scale chemical air separation systems to meet long-term oxygen supply requirements.
- For instance, Air Liquide installed very large units, including two ASUs each with a production capacity of 3,700 tons per day of oxygen for the Gwangyang and Pohang sites, which were the largest capacities ever installed for a steelmaker at that time.
Increasing Use of High-Purity Nitrogen in Chemicals, Electronics, and Food Packaging
Nitrogen is widely used as an inert gas in petrochemicals, fertilizers, plastics, and synthesis processes to prevent oxidation and contamination. The electronics industry expands nitrogen demand for semiconductor fabrication, component manufacturing, and wafer handling. Food and beverage processors are adopting nitrogen for modified atmosphere packaging, which extends shelf life and prevents spoilage. These industries prefer onsite air separation units because they provide high-purity nitrogen, stable pressure control, and lower operating costs compared to cylinder deliveries. Growing investments in chemical clusters, semiconductor fabs, and food processing plants accelerate adoption of medium- and large-capacity ASUs. As manufacturers expand product lines, the requirement for reliable nitrogen supply strengthens the need for continuous-operation air separation facilities.
- For instance, Taiyo Nippon Sanso operates nitrogen generators for Toshiba’s semiconductor facilities in Oita, supplying more than 50,000 Nm³ of ultra-high-purity nitrogen per hour for wafer cleaning and lithography.
Growing Healthcare Applications and Medical Oxygen Infrastructure
Hospitals, clinics, and emergency care facilities are investing in continuous oxygen supply systems, which boosts demand for air separation plants and onsite generation solutions. Medical oxygen is essential for intensive care, anesthesia, respiratory treatment, and emergency response systems. Many countries are upgrading healthcare infrastructure, leading to installation of dedicated oxygen production units for regional medical supply. Pharmaceutical manufacturing also uses oxygen and nitrogen for fermentation, packaging, and clean-room environments. In addition, governments and private healthcare operators prefer onsite oxygen systems to avoid supply shortages and logistics issues. This shift creates long-term demand for small and medium-capacity chemical air separation units designed for hospital networks and medical gas distributors.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Shift Toward Energy-Efficient and Low-Carbon ASU Technology
Energy consumption is the largest operating cost in air separation. Modern ASUs now integrate advanced compressors, optimized cryogenic cycles, waste-heat recovery, and digital automation to reduce electricity use. High-efficiency turbo expanders and variable-speed drives improve productivity while maintaining purity and pressure stability. Green hydrogen, renewable steelmaking, and eco-friendly chemical processing require large oxygen volumes, creating opportunities for sustainable and low-carbon ASUs. Many industrial gas companies are installing renewable-powered separation units to support emissions-reduction goals. This trend opens long-term growth for manufacturers offering energy-optimized designs and digital monitoring platforms for predictive maintenance.
- For instance, Air Liquide and Siemens Energy inaugurated a joint electrolyzer gigafactory in Berlin in November 2023 for the mass production of Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) electrolyzer modules, which produce green hydrogen, not an Air Separation Unit (ASU).
Expansion of Onsite Gas Generation and Build-Own-Operate Models
Manufacturers increasingly prefer onsite ASU installations to avoid supply disruptions and high transportation costs. Build-own-operate and long-term gas supply agreements allow companies to secure stable gas availability without high upfront capital investment. Steel plants, refineries, chemical parks, and semiconductor fabs are shifting from liquid gas deliveries to onsite continuous-flow systems. The growing industrialization of emerging economies creates opportunities for medium and large-capacity onsite ASUs. Packaged and modular systems also gain traction among food processors, healthcare facilities, and small manufacturers that need high-purity gases with minimal installation time. This business model strengthens industry partnerships and supports recurring revenue for gas suppliers.
- For instance, the plants at the JSW Bellary complex were part of a joint venture named Bellary Oxygen Company Private Limited (BOCPL), initially a 50:50 venture between Linde India (previously BOC India/BOC Group) and INOX Air Products.
Key Challenges
High Capital and Energy Costs Affect Profitability
Cryogenic ASUs require heavy investment in compressors, distillation columns, heat exchangers, and control systems. The capital cost of building large-scale units and associated utilities can be a major financial barrier, especially for smaller manufacturers. Electricity is the biggest running expense, and rising energy prices increase production costs for oxygen and nitrogen. Industries with low profit margins may struggle to justify new installations. As a result, cost-optimized and energy-efficient designs become essential to remain competitive. Financial viability often depends on long-term gas supply contracts and guaranteed production volumes from end-users.
Operational Complexity and Need for Skilled Workforce
Air separation involves cryogenic processing, continuous monitoring, purity management, and complex safety requirements. Plants require skilled technicians to manage cooling cycles, compressors, and instrument controls. Sudden fluctuations in demand, power supply issues, or equipment failures can disrupt gas purity and flow levels. Smaller industries face difficulty handling maintenance and operational risks without trained workforce support. To address this challenge, manufacturers are adopting remote monitoring, automated controls, and predictive maintenance systems, but integration and training still require significant time and cost.
Regional Analysis
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific holds the largest market share of around 40% in the chemical air separation unit market, driven by strong steel production, petrochemical expansion, and rapid electronics growth. China, India, Japan, and South Korea operate high-capacity oxygen and nitrogen plants supporting steel mills, refineries, fertilizers, and semiconductor fabs. Many industries prefer onsite ASUs to reduce transport costs and ensure uninterrupted gas supply. Growing infrastructure and LNG terminal investments strengthen long-term demand. Rising industrialization and large manufacturing clusters make Asia Pacific the leading region for high-purity oxygen and nitrogen production, supporting continuous capacity additions.
North America
North America accounts for close to 25% of the global market share, supported by mature chemical, refining, food processing, and healthcare industries. The U.S. hosts a large installed base of ASUs supplying oxygen, nitrogen, and argon to steelmaking, semiconductor plants, and pharmaceutical networks. Expansion of chip fabrication and clean-energy projects boosts demand for high-purity nitrogen and continuous-flow onsite systems. Industrial gas suppliers also operate build-own-operate models and long-term contracts across key manufacturing hubs. Advanced digital controls, strong automation adoption, and energy-efficient cryogenic designs sustain regional growth.
Europe
Europe represents nearly 20% of the market share, with Germany, France, Italy, and the U.K. leading adoption. Steelmaking, petrochemicals, food processing, and pharmaceuticals drive consistent consumption of oxygen and nitrogen. The region invests heavily in low-emission and energy-efficient ASUs due to strict environmental regulations and high electricity prices. Growth of green hydrogen, renewable steelmaking, and carbon-capture projects supports large oxygen units. Many European companies shift to onsite supply contracts to reduce logistics costs and stabilize purity levels. Strong technological maturity and semiconductor expansion maintain steady demand.
Middle East & Africa
Middle East & Africa hold around 8% of the market share, led by refinery expansions, natural gas processing, and petrochemical projects in Saudi Arabia, UAE, Qatar, and Oman. High demand for nitrogen blanketing and oxygen-based refining processes drives ASU installations. Africa sees rising demand from steel plants, healthcare suppliers, and food packaging industries. Many facilities adopt onsite ASUs to overcome logistic challenges and secure continuous supply. Government-backed industrial zones and diversification initiatives continue to support long-term growth for medium- and large-capacity systems.
Latin America
Latin America accounts for approximately 7% of the global market share, with Brazil and Mexico leading deployments. Steel, chemical processing, food & beverage, and healthcare sectors generate steady demand for nitrogen and oxygen. Food processors expand nitrogen use for modified-atmosphere packaging, while hospitals and medical suppliers increase oxygen consumption. Rising industrial projects encourage onsite gas production and reduce reliance on transported cylinders. Local distributors also add mid-capacity ASUs to serve regional industrial clusters. Growing manufacturing investments help the region maintain a gradual but stable expansion rate.
Market Segmentations
By Gas Output
- Oxygen
- Nitrogen
- Argon
- Others (rare gases mix)
By End-Use Industry
- Iron & Steel
- Chemicals
- Healthcare
- Oil & Gas
- Food & Beverage
- Electronics
- Pulp & Paper
By Capacity (TPD)
- <100 TPD
- 100-400 TPD
- 400-1,000 TPD
- 1,000 TPD
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the chemical air separation unit market features prominent global firms such as Linde plc, Air Liquide, Air Products and Chemicals, Inc., Taiyo Nippon Sanso (Nippon Sanso Holdings), Messer Group, Yingde Gases, Hangyang, AMCS Corporation, Technex, and Universal Industrial Gases (UIG). These companies compete by offering large‑capacity cryogenic plants, energy‑efficient compressors, and modular onsite ASU systems to serve high‑demand sectors such as steel, petrochemicals, electronics, and healthcare. They establish long‑term gas supply agreements, deploy build‑own‑operate models, and invest in automation and digital monitoring to improve uptime and purity. Innovation in sustainable technologies and expansion into emerging industrial hubs, especially in Asia Pacific, strengthen their market positions. This competition underpins broader market dynamics and reinforces growth in the chemical air separation unit segment.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
Recent Developments
- In October 2025, Nippon Gases opened a new ASU in Caserta, Italy. The plant produces oxygen and nitrogen for regional industries.
- In July 2025, Yingde Gases Commissioned a new liquid ASU in Shaoxing, Phase II of its gas hub. The unit boosts supply for steel, chemicals, and electronics.
- In July 2024, Air Products and Chemicals, Inc. did announce plans to build and operate two new Air Separation Units (ASUs) at its existing facilities in Conyers, Georgia, and Reidsville, North Carolina.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Gas Output, End-Use Industry, Capacity (TPD) and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Demand for large-capacity ASUs will rise as steel and petrochemical plants expand.
- Onsite gas generation models will grow due to supply reliability and lower logistics costs.
- Energy-efficient compressors and cryogenic cycles will reduce operating expenses.
- Digital control systems and predictive maintenance will improve uptime and purity.
- Semiconductor and battery manufacturing will boost high-purity nitrogen consumption.
- Green hydrogen and low-carbon steel projects will increase oxygen requirements.
- Healthcare networks will adopt more medical oxygen units to ensure continuous availability.
- Modular and packaged ASUs will gain traction among mid-size manufacturers.
- Regional gas suppliers will invest in build-own-operate contracts for long-term demand.
- Integration of renewable power with ASUs will support sustainability goals.




