Market Overviews
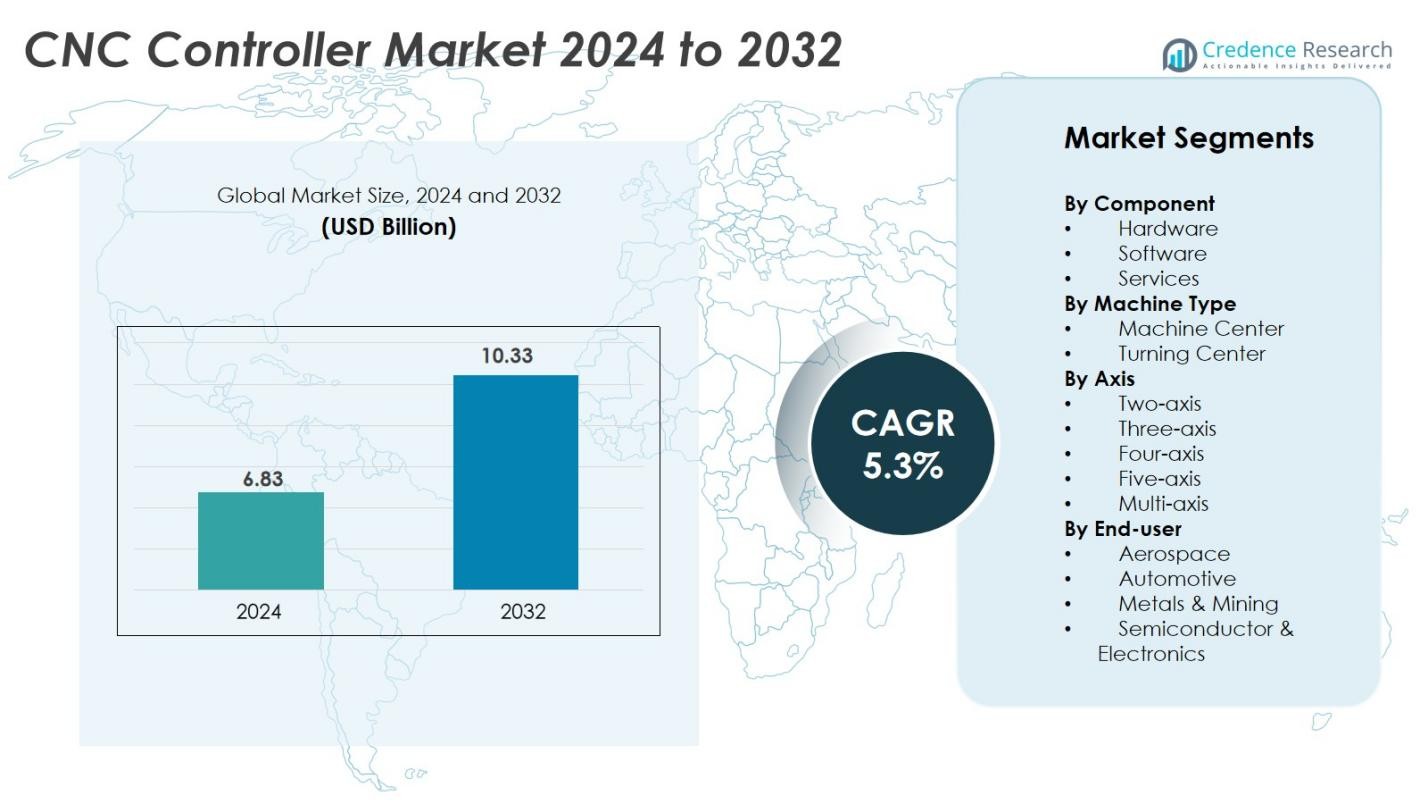
CNC Controller market size was valued USD 6.83 Billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 10.33 Billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 5.3% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| CNC Controller Market Size 2024 |
USD 6.83 Billion |
| CNC Controller Market, CAGR |
5.3% |
| CNC Controller Market Size 2032 |
USD 10.33 Billion |
The CNC Controller Market is dominated by key players such as Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, FANUC Corporation, Siemens AG, Bosch Rexroth AG, Heidenhain Corporation, NUM Group, Okuma Corporation, HAAS Automation Inc., Hurco Companies Inc., and Fagor Automation. These companies compete through advanced multi-axis controllers, high-speed processing, and software-driven automation features that support smart factory operations. Product strategies focus on precision machining, cloud connectivity, predictive maintenance, and retrofit-ready platforms to upgrade legacy equipment. Asia-Pacific leads the market with over 45% share, driven by strong machine tool production, rapid industrial automation, and large-scale manufacturing in automotive, electronics, and metalworking sectors.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The CNC controller market reached USD 6.83 Billion in 2024 and is projected to hit USD 10.33 Billion by 2032 at a 5.3% CAGR.
- Rising demand for automation in automotive, aerospace, and precision engineering drives strong adoption of CNC-controlled machining centers and multi-axis systems.
- Key trends include digital retrofitting of aging equipment, cloud-based monitoring, and integration of AI for real-time toolpath optimization and predictive maintenance.
- Competition is shaped by Mitsubishi Electric, FANUC, Siemens, Bosch Rexroth, and HAAS Automation, with companies upgrading hardware, motion control, and software platforms to support Industry 4.0.
- Asia-Pacific leads with over 45% market share, supported by large machine tool manufacturing bases and investments in smart factories, while hardware remains the dominant component with above 60% share, driven by controller upgrades and new installations.
Market Segmentation Analysis
By Component
Hardware holds the dominant position in the CNC controller market, accounting for over 60% share. Controllers, servo drives, and motors form the core of CNC machine functionality, making hardware indispensable for accuracy, rigidity, and high-speed machining. Rising deployment of automated milling, cutting, and grinding machines in automotive and aerospace plants strengthens demand. Software and services show steady growth as factories add programming platforms, remote diagnostics, and predictive maintenance. However, hardware remains the clear leader due to mandatory replacement cycles and continuous upgrades in high-volume production facilities.
- For instance, FANUC’s Series 30i/31i/32i Model B controllers are widely adopted in automotive and aerospace milling operations, enabling high accuracy and rigidity.
By Machine Type
Machine centers lead the segment with more than 65% market share, supported by their ability to perform milling, drilling, and cutting in a single setup. These machines allow unattended, continuous machining, which lowers production time and operational cost across automotive, metal fabrication, and precision engineering. Turning centers grow steadily as powertrain and shaft machining rises, but machine centers stay ahead due to their flexibility with three-axis and five-axis configurations. Their higher throughput and capability to manufacture complex geometries continue to drive large-scale industrial adoption.
- For instance, Mazak’s Variaxis i-700 five-axis machining center allows simultaneous precision machining of automotive transmission components, enhancing operational efficiency and minimizing manual intervention.
By Axis
Three-axis CNC machines dominate this segment, holding above 50% share, driven by extensive use in metal fabrication, woodworking, furniture, and plastic molding. They offer a cost-efficient balance of precision and speed, making them ideal for mid-complexity components in automotive, consumer electronics, and packaging industries. Two-axis machines continue to serve basic lathe operations, whereas demand for five-axis and multi-axis systems accelerates in aerospace, mold making, and medical implants. Despite the growth of advanced machining, three-axis controllers maintain the lead due to wide affordability and easy integration for small and medium manufacturers.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Demand for Industrial Automation Across Manufacturing
Industrial automation remains the strongest driver for the CNC controller market as manufacturers move toward fully automated and precision-driven production. Automotive, aerospace, and metal fabrication plants increase CNC integration to boost accuracy, repeatability, and output consistency. Faster production cycles reduce labor dependency and downtime, while multi-axis machining supports complex designs at scale. The rising shift from manual processes to automated cutting, drilling, and milling drives controller deployments in both new installations and retrofits. Small and medium manufacturers also adopt CNC to improve part quality and reduce scrap rates.
- For instance, Mitsubishi Electric’s M800 series CNC controllers are widely adopted in Asian automotive and metal cutting industries for their high-speed and high-accuracy processing.
Rapid Growth of Multi-Axis and High-Precision Machining
The demand for high-accuracy machining supports strong adoption of five-axis and multi-axis CNC controllers. These systems help produce intricate components for aerospace structures, turbine blades, defense parts, medical implants, and automotive molds. Multi-axis control reduces setup time, improves tolerances, and enables machining from multiple angles without repositioning. Manufacturers value shorter lead times, precision in complex geometries, and reduced material wastage. Growing investments in aerospace and electric vehicle production further strengthen multi-axis implementation. Precision machining also rises in medical manufacturing as CNC supports titanium, stainless steel, and polymer implant shaping with tight tolerances. As innovation advances, controller suppliers introduce real-time tool monitoring, adaptive feed control, and AI-based error prevention to improve machining efficiency and tool life.
- For instance, Lockheed Martin employs true 5-axis simultaneous machining in aerospace R&D for parts like landing gear, allowing intricate geometry machining in one setup without repositioning.
Increased Retrofits and Digitalization of Legacy Equipment
Retrofitting older machines with modern CNC controllers presents a major growth avenue, driven by cost efficiency and sustainability goals. Many factories extend the life of existing mechanical systems by upgrading controls, drives, and software instead of buying new equipment. Retrofitted CNC units improve spindle control, speed, toolpath accuracy, and diagnostics, bringing outdated line operations closer to smart factory standards. Predictive maintenance, real-time data capture, and remote troubleshooting help manufacturers reduce unplanned downtime and improve asset utilization. Adoption grows especially in small and mid-sized workshops that seek automation without heavy capital investment. In addition, digital retrofits support IoT connectivity, allowing operators to track machine health and performance.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Expansion of Connected CNC and Cloud-Based Monitoring
CNC controllers increasingly integrate IoT, cloud analytics, and edge computing to support connected machining. Factories adopt smart CNC systems that track tool wear, energy use, and spindle performance in real time. Cloud-based platforms analyze machine data and optimize production schedules, enabling predictive maintenance and continuous improvement. Remote monitoring becomes valuable in multi-plant operations, reducing on-site service needs and enabling centralized control. The trend aligns with smart factory adoption, offering machine-level intelligence and reduced downtime. Controller manufacturers invest in sensors, digital twins, and AI-based optimization to capture this emerging opportunity in high-volume and precision machining facilities.
- For instance, MachineMetrics uses IIoT sensors and edge computing to track real-time machine condition data, allowing manufacturers to set automatic alerts for maintenance before downtime occurs, improving overall equipment effectiveness.
Growing Penetration of CNC in Small and Medium Enterprises
Cost-efficient controller models, modular hardware, and simplified programming software support CNC adoption in small and medium enterprises. SMEs use CNC to improve accuracy, reduce scrap, and shorten delivery timelines for custom parts and low-batch production. Affordable three-axis and compact machining centers attract woodworking, furniture, signage, and consumer goods producers. The rise of digital training platforms, operator-friendly HMIs, and cloud programming widens accessibility. Government programs that promote local manufacturing, export capacity, and skill development further accelerate SME integration. The shift also creates opportunities for retrofit specialists and service providers offering cost-effective automation upgrades.
- For instance, CubeBOX, a modular digital twin solution designed to integrate with legacy machines in SMEs incrementally, enabling gradual adoption of advanced monitoring without full system overhaul.
Key Challenges
High Initial Investment and Integration Cost
Despite clear operational advantages, CNC controllers require substantial capital investment in hardware, software, and skilled installation. Many small manufacturers find cost barriers difficult, especially when upgrading to multi-axis or high-speed systems. Integration into existing workflows can also require downtime, facility redesign, or operator retraining. Advanced controllers with AI-based monitoring and IoT connectivity add licensing costs and subscription fees. These financial challenges slow adoption in cost-sensitive sectors and emerging manufacturing economies. Vendors respond by offering leasing models, modular upgrades, and retrofit kits, but high upfront expense remains a key constraint for widespread deployment.
Shortage of Skilled CNC Programmers and Maintenance Experts
The CNC controller market faces a global skill gap, as factories struggle to hire experienced programmers, operators, and maintenance specialists. Complex multi-axis machining demands advanced G-code knowledge, tooling expertise, and familiarity with CAD/CAM platforms. Without trained staff, manufacturers experience slower setup times, higher scrap rates, and machine downtime. This skill shortage impacts both large and small plants, especially in regions with limited technical training infrastructure. Controller vendors introduce operator-friendly HMIs, automated toolpath generation, and online training modules to reduce dependency on specialized staff. However, workforce readiness remains a significant challenge for scaling CNC adoption in high-growth manufacturing markets.
Regional Analysis
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific holds the largest share of the CNC controller market, accounting for over 45% of global revenue. China, Japan, South Korea, and India drive strong demand due to rapid industrial automation, expanding automotive production, and growth in metalworking industries. Government initiatives encouraging smart factories and robotics adoption accelerate CNC deployment across manufacturing clusters. Local machine tool manufacturers and competitive pricing increase accessibility for small and medium enterprises. The region also benefits from strong export activity in machinery and precision components. Rising investments in aerospace, EV manufacturing, and electronics further strengthen regional dominance.
North America
North America commands more than 25% of the CNC controller market, supported by advanced aerospace, defense, and automotive manufacturing. The United States leads adoption with high demand for multi-axis machining and high-precision metal fabrication. Strong investments in automation, retrofits, and Industry 4.0 projects modernize production lines in automotive parts and industrial machinery plants. Technological leadership in cloud monitoring, digital twins, and predictive maintenance platforms promotes next-generation CNC upgrades. Demand for medical devices and customized engineered components also contributes to market growth. Supportive manufacturing policies and reshoring activities keep CNC adoption strong across major industries.
Europe
Europe accounts for around 20% of market share, driven by strong machine tool production in Germany, Italy, and Switzerland. The region focuses on precision engineering, aerospace, renewable energy, and industrial automation, which require high-performance CNC systems. Adoption of five-axis and multi-axis machining continues to expand in toolmaking and automotive component production. Government support for digital transformation and energy-efficient manufacturing also boosts modernization of existing facilities. European manufacturers emphasize sustainability, resulting in rising demand for retrofits and CNC upgrades to reduce waste and improve efficiency. Strong exports of industrial machinery further reinforce the region’s position.
Latin America
Latin America secures below 7% of global market share, with growth concentrated in Brazil and Mexico. Rising adoption of CNC systems in automotive parts, metal fabrication, and industrial equipment manufacturing supports gradual expansion. Multinational manufacturers establish production bases in Mexico to supply North American markets, leading to increased demand for automated machining centers. Local industries modernize production lines to improve output quality and reduce labor-intensive processes. However, high import costs and limited access to skilled operators slow widespread adoption. The market continues to grow as SMEs invest in cost-efficient controllers and refurbished CNC systems.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa holds under 5% of market share but shows steady growth driven by industrial diversification and infrastructure development. GCC countries invest in aerospace, automotive parts, metal fabrication, and renewable energy projects, creating demand for precision machining. Construction equipment and oil-and-gas component manufacturers adopt CNC systems to improve reliability and reduce import reliance. South Africa leads regional adoption, supported by mining equipment manufacturing and aerospace component machining. Limited local machine tool production and dependence on imported systems create cost barriers, yet ongoing industrial expansion strengthens long-term opportunities.
Market Segmentations:
By Component
- Hardware
- Software
- Services
By Machine Type
- Machine Center
- Turning Center
By Axis
- Two-axis
- Three-axis
- Four-axis
- Five-axis
- Multi-axis
By End-user
- Aerospace
- Automotive
- Metals & Mining
- Semiconductor & Electronics
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The CNC controller market features strong competition among global automation leaders and specialized machine tool manufacturers, including FANUC Corporation, Hurco Companies, Inc., HAAS AUTOMATION, INC., Siemens AG, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, and Bosch Rexroth AG. Companies focus on precision control, real-time monitoring, multi-axis capability, and software integration to differentiate their portfolios. Major players offer modular controllers, compact drive systems, and cloud-connected platforms to support smart factory adoption. They also expand through partnerships with OEM machine builders, robotics suppliers, and CAD/CAM software providers. Product upgrades emphasize faster processing, vibration control, and adaptive feed optimization. Retrofitting solutions gain strategic importance as manufacturers modernize legacy equipment. Firms invest in training services and digital programming tools to address the industry skill gap. Price competition increases in emerging economies, where cost-efficient, mid-range controllers attract small and medium enterprises. Leading companies adopt localization of production and service centers to shorten delivery timelines and strengthen after-sales support.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- FANUC Corporation
- Hurco Companies, Inc.
- HAAS AUTOMATION, INC.
- Siemens AG
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Bosch Rexroth AG
- NUM Group
- Okuma Corporation
- Heidenhain Corporation
- Fagor Automation Corporation
Recent Developments
- In May 2024, Fagor Automation and GEKA announced a collaboration to advance the digitalization of production processes with the Fagor Digital Suite. This modular platform is designed to enhance manufacturing processes, including those involving CNC controllers.
- In March 2024, FANUC America Corporation introduced its new combined PLC/CNC motion controller, the Power Motion i-MODEL A Plus (PMi-A Plus), at MODEX 2024 in Atlanta, Georgia (booth B-4026). The PMi-A Plus allows users to operate FANUC controls for general motion control applications.
- In September 2023, ESAB introduced its Vision T6 CNC controller, a next-generation solution for automated plasma and oxy-fuel cutting machines. Its user-friendly interface, similar to a smartphone or tablet, makes it easy to operate while improving cutting efficiency.
- In August 2023, the OSP-P500 was launched to improve user experiences and optimize modern manufacturing operations. Featuring dual-core processors for enhanced machine processing power, Digital Twin Technology for precise machining simulations, and strong data protection measures, it is designed for advanced performance.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Component, Machine Type, Axis, End-User and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Demand for multi-axis CNC systems will rise as manufacturers produce complex and high-precision components.
- Retrofitting of old machines with modern CNC controllers will increase across small and medium industries.
- Cloud-enabled CNC monitoring and predictive maintenance will become standard in smart factories.
- Integration of AI and digital twins will enhance toolpath accuracy and reduce machining errors.
- Adoption of CNC systems will grow in EV manufacturing, medical implants, and aerospace parts production.
- User-friendly programming interfaces will reduce skill barriers and expand CNC usage in SMEs.
- Controller makers will focus on energy-efficient hardware and faster real-time processing.
- Compact and modular CNC systems will gain traction in workshops with space and cost constraints.
- Service-based business models and subscription software will increase vendor revenue streams.
- Asia-Pacific will continue leading market expansion due to strong machine tool production and industrial automation.




