Market Overview
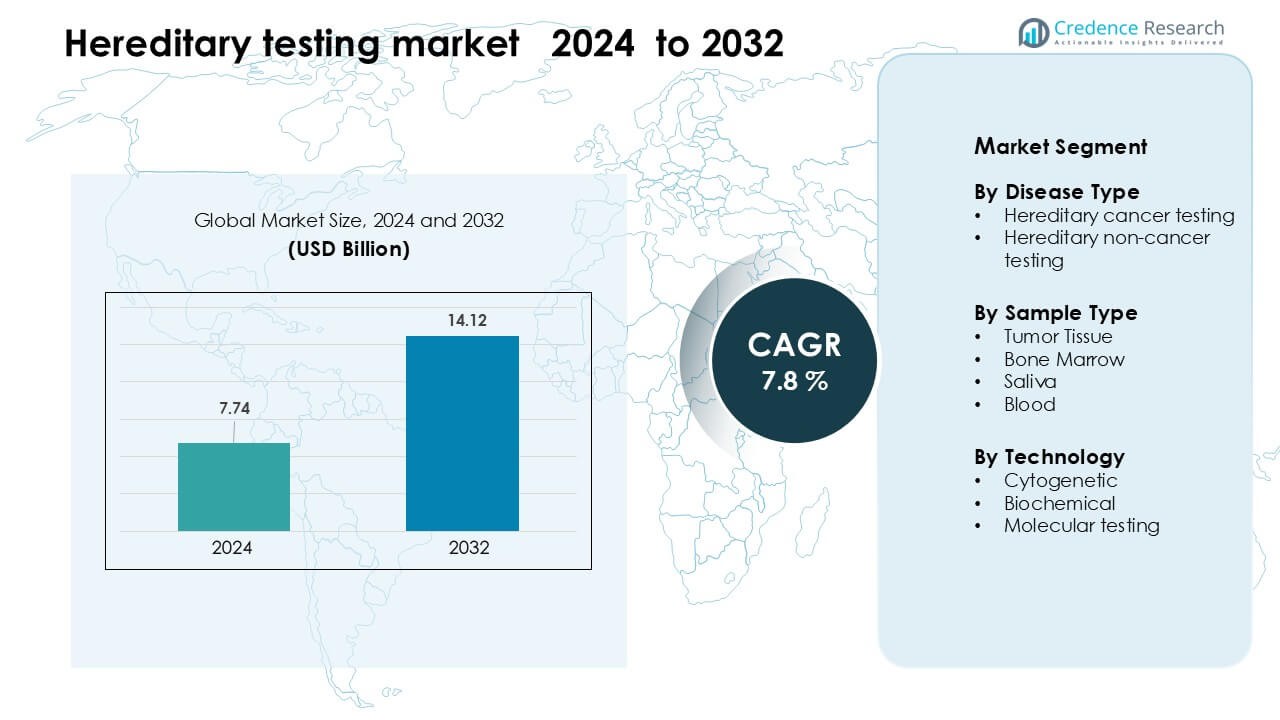
Hereditary testing market was valued at USD 7.74 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 14.12 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 7.8% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Hereditary Testing Market Size 2024 |
USD 7.74 Billion |
| Hereditary Testing Market, CAGR |
7.8% |
| Hereditary Testing Market Size 2032 |
USD 14.12 Billion |
The hereditary testing market is shaped by major players such as MedGenome Inc., SOPHiA GENETICS SA, Laboratory Corporation of America Holdings, Natera, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Myriad Genetics, Quest Diagnostics, Illumina, Fulgent Genetics, and F. Hoffmann-La Roche. These companies strengthen their positions through advanced NGS platforms, broad multi-gene panels, and expanding global laboratory networks. They focus on improving accuracy, reducing turnaround times, and integrating AI-based interpretation tools to support clinical decision-making. North America remained the leading region in 2024 with about 41% share, supported by strong healthcare infrastructure, high adoption of personalized medicine, and wider insurance coverage for hereditary risk testing.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The hereditary testing market reached USD 7.74 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit USD 14.12 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 7.8 %.
- Rising demand for early detection of hereditary cancers and rare genetic disorders drives strong adoption, supported by wider physician recommendations and declining sequencing costs.
- Molecular testing held the largest segment share at 71%, while blood samples led the sample type segment with about 54%, reflecting strong clinical preference for accuracy and faster processing.
- The market remains competitive with companies advancing NGS platforms, AI-driven interpretation, and high-throughput lab networks; price pressure and limited genetic counseling capacity continue to restrain growth.
- North America dominated with 41% share in 2024, followed by Europe at 30% and Asia Pacific at 22%, driven by robust screening programs, expanding genomic infrastructure, and rising awareness.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Disease Type
Hereditary cancer testing led the hereditary testing market in 2024 with about 62% share. Strong demand came from rising awareness of breast, ovarian, and colorectal cancer risks linked to BRCA1/BRCA2 and other high-risk genes. Healthcare programs promoted early detection, which pushed more patients toward genetic risk assessment. Wider test panels and falling sequencing costs also supported growth. Non-cancer testing expanded in areas such as cardiovascular and metabolic disorders, yet cancer-focused testing stayed ahead due to higher clinical urgency and broader physician adoption.
- For instance, Myriad Genetics’ myRisk Hereditary Cancer test screens 63 clinically recommended genes for more than 11 cancer types, including BRCA1/2, using next-generation sequencing.
By Sample Type
Blood-based testing dominated the hereditary testing market in 2024 with nearly 54% share. Clinicians preferred blood samples because they provide high-quality DNA, better accuracy, and faster processing compared with saliva or tissue samples. Demand rose as hospitals integrated routine hereditary screening into oncology and preventive care pathways. Saliva samples gained traction for at-home kits, while tumor tissue and bone marrow remained specialized for advanced diagnostic use. However, blood samples-maintained leadership due to strong reliability and ease of integration into clinical workflows.
- For instance, Invitae Common Hereditary Cancer Panel is validated on a 3 mL purple-top EDTA whole blood specimen and achieved ≥ 99% accuracy across 9,000+ clinical samples.
By Technology
Molecular testing accounted for the largest share in 2024 with about 71% of the hereditary testing market. Adoption grew as next-generation sequencing enabled detection of multiple gene variants in a single test, improving diagnostic depth and speed. Hospitals and labs favored molecular methods for identifying inherited risks across cancer, cardiac, and rare disease categories. Cytogenetic and biochemical tests supported specific cases but offered narrower insights. Molecular testing stayed dominant due to expanding panels, declining sequencing prices, and strong clinical validation across global health systems.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Adoption of Personalized Medicine
Growing adoption of personalized medicine remains a central driver for the hereditary testing market. Healthcare systems increasingly rely on genetic insights to tailor prevention, diagnosis, and treatment decisions. Clinicians use hereditary test panels to identify individuals at elevated risk for cancers, cardiovascular conditions, and rare genetic disorders, enabling earlier monitoring and targeted interventions. Pharmaceutical companies integrate genetic markers into therapy selection, especially in oncology, boosting the need for routine hereditary testing. Broader insurance coverage, improved patient education, and rising demand for precision-based care continue to strengthen market expansion across hospitals, diagnostic centers, and home-based testing platforms.
- For instance, Foundation Medicine’s FDA-approved FoundationOne CDx analyzes 324 genes and detects genomic signatures such as MSI-H and TMB, guiding therapy selection for targeted treatments in solid tumors.
Increasing Global Burden of Genetic Disorders
The rising incidence of hereditary cancers and non-cancer genetic disorders drives stronger testing adoption worldwide. Conditions such as hereditary breast and ovarian cancer, Lynch syndrome, and inherited cardiac disorders now receive greater attention due to improved clinical guidelines and national screening programs. Families with known risk factors seek multi-gene testing to clarify disease probability and guide preventive care. Additionally, growing newborn screening initiatives and earlier diagnostic interventions push governments and private providers to expand genetic testing infrastructure. Wider medical awareness and clinical acceptance create sustained demand for high-accuracy hereditary testing technologies.
- For instance, Ambry Genetics’ CancerNext panel evaluates 40 genes associated with hereditary colorectal, endometrial, gastric, and related cancers, supporting early diagnosis for families with Lynch syndrome and related disorders.
Advancement in Sequencing Technologies
Rapid advancements in sequencing platforms remain a key market growth accelerator. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) significantly reduces the cost per genome and speeds up detection of inherited mutations across large panels. Labs benefit from improved accuracy and the ability to detect rare variants, supporting widespread use in oncology, cardiology, and metabolic disease diagnostics. Automation and AI-supported analysis streamline workflows and reduce interpretation errors, making hereditary testing more accessible. As equipment becomes more scalable and cloud-integrated, both large hospitals and smaller labs adopt advanced testing, driving market penetration globally.
Key Trend and Opportunity
Expansion of At-Home Genetic Testing
The rise of at-home genetic testing kits marks a major trend reshaping consumer engagement in the hereditary testing market. Saliva-based kits enable easier access without clinical visits, aligning with growing demand for convenient and private health insights. Companies offer expanded hereditary panels that screen for cancer predisposition, carrier status, and lifestyle-related genetic markers. Increased comfort with telehealth and digital reports strengthens adoption. While clinical validation remains important, consumers now play a more active role in managing their hereditary risk profile, creating new commercial opportunities for hybrid clinical-consumer testing models.
- For instance, 23andMe’s FDA-authorized Health + Ancestry Service analyzes over 40 carrier status variants and includes three clinically relevant BRCA1/BRCA2 variants, with a customer base exceeding 12 million genotyped users, making it one of the largest consumer genetic datasets globally.
Integration of AI and Big Data in Genetic Interpretation
Rapid integration of AI and data-driven analytics presents significant market opportunities. Large genetic datasets help algorithms identify patterns, improve variant classification, and reduce uncertainty in hereditary risk assessments. AI-enabled reports support clinicians by simplifying complex genomic data into actionable recommendations. Cloud-based bioinformatics tools help labs scale operations while lowering operational costs. As global sequencing output grows, opportunities arise for interoperable platforms that unify electronic health records, family histories, and genetic data, driving more accurate and personalized hereditary disease predictions.
- For instance, Google DeepMind’s Alpha Missense model classifies 71 million human missense variants, labeling 89% as either pathogenic or benign, significantly reducing uncertainty in variant interpretation across hereditary disorders.
Key Challenge
Limited Genetic Counseling Capacity
A major challenge stems from limited availability of trained genetic counselors. Rising demand for hereditary testing places pressure on healthcare systems that lack sufficient specialists to explain results, guide patient decisions, and coordinate follow-up care. Many regions, especially developing markets, face shortages that slow test adoption and increase patient confusion. Without adequate counseling support, individuals may misinterpret risk levels or delay preventive actions. This gap restricts the full clinical impact of hereditary testing and reduces continuity across diagnostic and care pathways.
Complexity of Variant Interpretation
Interpreting genetic variants remains a key barrier in the hereditary testing market. Many detected variants fall into the “uncertain significance” category, requiring advanced expertise and larger population datasets to classify accurately. Differences in lab protocols, databases, and analytical tools lead to inconsistent outcomes, complicating clinical decisions. Limited global harmonization of reporting standards also increases risk of misinterpretation. These challenges hinder physician confidence, slow diagnosis, and restrict broader adoption of multi-gene hereditary testing panels across clinical settings.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America dominated the hereditary testing market in 2024 with about 41% share. Strong adoption came from well-established genomic programs, broad insurance coverage, and high awareness of hereditary cancer risks. Major hospitals integrated multi-gene panels into routine oncology and cardiovascular preventive care. The U.S. led growth due to rapid NGS adoption, while Canada expanded genetic counseling networks. Rising demand for personalized medicine and strong investment in genomic startups further strengthened the region’s position. Expanding direct-to-consumer testing and wider physician acceptance supported continued market leadership across clinical and home-based applications.
Europe
Europe held nearly 30% of the hereditary testing market in 2024, supported by national screening initiatives and strong regulatory frameworks. Countries such as Germany, the U.K., and France advanced hereditary cancer testing through public health programs and reimbursement reforms. Growing emphasis on rare disease diagnosis also increased use of molecular panels across hospitals and specialty clinics. Efforts to harmonize lab standards and integrate genomic data into universal healthcare systems strengthened clinical confidence. The region’s expanding genetic counseling capacity and rising investment in biobanks continued to support stable hereditary testing adoption.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific accounted for around 22% share in 2024 and remained the fastest-growing region. Higher incidence of hereditary cancers, improving diagnostic infrastructure, and rising awareness in countries such as China, Japan, South Korea, and India drove strong expansion. Governments increased support for population-level genomic programs, while private hospitals introduced affordable multi-gene panels. Growing medical tourism and lower sequencing costs accelerated adoption. The region’s large population base and rising disposable income strengthened demand for both clinical and home-based hereditary testing solutions, positioning Asia Pacific as a key future growth engine.
Latin America
Latin America captured about 4% share in 2024, supported by gradual improvements in genetic testing access and rising awareness of hereditary disease risks. Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina led adoption due to expanding oncology programs and partnerships with international diagnostic companies. Limited reimbursement and uneven access to genetic counseling remained challenges, yet private healthcare facilities increased use of hereditary cancer and cardiovascular panels. Growing interest in preventive care and ongoing investment in laboratory modernization helped strengthen the region’s market outlook. Educational initiatives also improved public understanding of genetic risk assessment.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region held close to 3% of the hereditary testing market in 2024. Growth came from rising investments in genomic medicine, particularly in the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa. National initiatives promoting rare disease diagnosis and hereditary risk screening supported early adoption. However, limited healthcare infrastructure and low availability of genetic counselors constrained widespread use. Private hospitals increasingly partnered with global labs to expand molecular testing access. Gradual improvements in sequencing capacity and awareness campaigns contributed to steady, though modest, regional growth.
Market Segmentations:
By Disease Type
- Hereditary cancer testing
- Hereditary non-cancer testing
By Sample Type
- Tumor Tissue
- Bone Marrow
- Saliva
- Blood
By Technology
- Cytogenetic
- Biochemical
- Molecular testing
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the hereditary testing market features leading companies such as MedGenome Inc., SOPHiA GENETICS SA, Laboratory Corporation of America Holdings, Natera, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Myriad Genetics, Quest Diagnostics, Illumina, Fulgent Genetics, and F. Hoffmann-La Roche. These companies compete through wide hereditary testing portfolios, advanced NGS technologies, and strong bioinformatics capabilities. Many players expand global reach by building high-throughput labs, improving variant interpretation tools, and strengthening partnerships with hospitals, oncology centers, and research institutions. Firms also focus on lowering sequencing costs and enhancing accuracy to support early risk detection across cancer and non-cancer conditions. Growing demand for personalized medicine encourages companies to invest in AI-driven analytics, integrated reporting platforms, and clinician-support tools. Mergers, acquisitions, and regional collaborations help broaden test accessibility, while continuous product innovation keeps competition strong in clinical and consumer genetic testing segments.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- MedGenome Inc.
- SOPHiA GENETICS SA
- Laboratory Corporation of America Holdings
- Natera, Inc.
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- Myriad Genetics, Inc.
- Quest Diagnostics Incorporated
- Illumina, Inc.
- Fulgent Genetics, Inc.
- Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
Recent Developments
- In May 2025, Illumina, Inc. expanded its clinical oncology portfolio (via the oncoReveal® CDx IVD kit) to detect genetic variations in 22 genes and received regulatory approval in Japan and U.S. Medicare coverage in the U.S.
- In February 2025, F. Hoffmann‑La Roche Ltd. unveiled its new sequencing by expansion (SBX) next-generation sequencing technology. This ultra-rapid sequencing platform may impact hereditary/genomic testing capabilities.
- In February 2025, Fulgent Genetics, Inc. announced that Foundation Medicine, Inc. will launch the FoundationOne® Germline and FoundationOne® Germline More NGS tests (50 genes associated with hereditary cancers) in the United States via a partnership.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on DiseaseType, Sample Type, Technology and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Demand for hereditary testing will rise as more hospitals integrate multi-gene panels into routine care.
- Adoption of AI-driven variant interpretation will improve accuracy and reduce reporting time.
- At-home genetic testing kits will gain stronger traction due to convenience and higher consumer awareness.
- Molecular testing will remain the dominant technology as sequencing becomes faster and more affordable.
- Clinical guidelines will expand to include broader hereditary cancer and cardiovascular risk screening.
- Partnerships between diagnostic labs and oncology centers will strengthen global testing accessibility.
- Genetic counseling services will grow as countries invest in specialized training programs.
- Precision medicine programs will increase testing uptake across oncology, cardiology, and rare disease management.
- Emerging markets in Asia Pacific and Latin America will adopt hereditary testing at a faster pace.
- Regulatory frameworks will evolve to support standardized reporting and improved test reliability.




