Market Overview
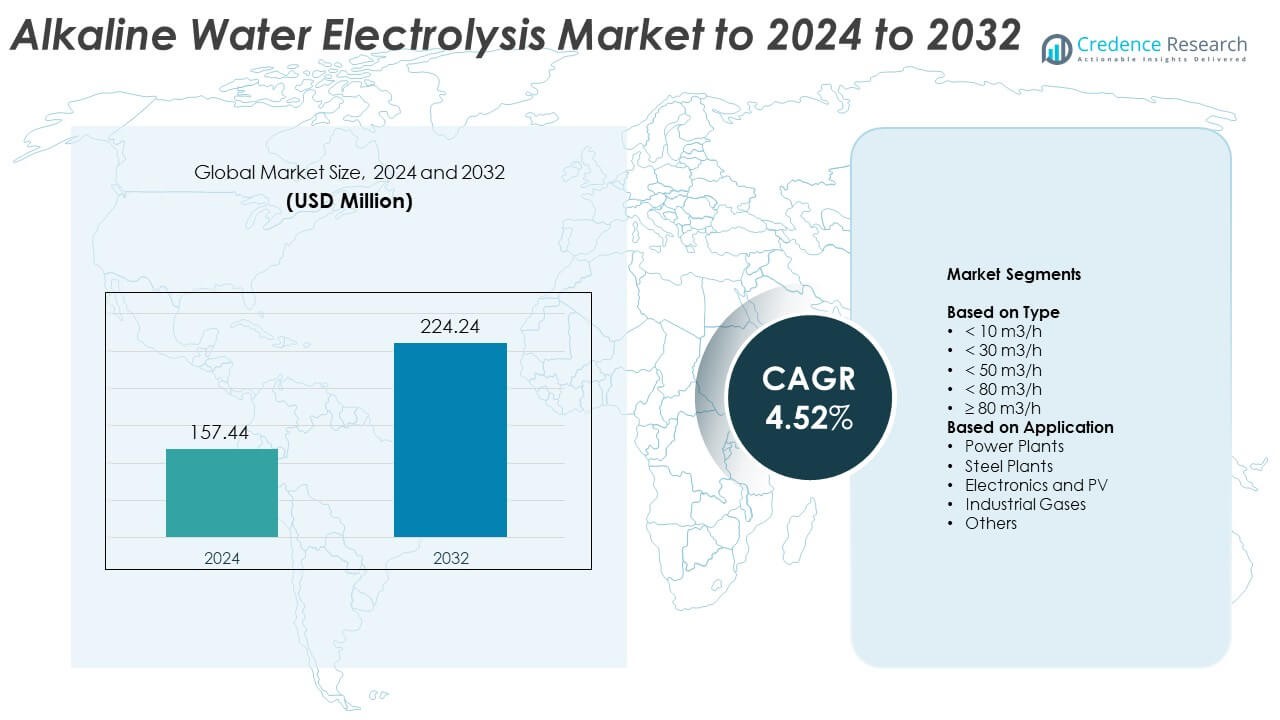
Alkaline Water Electrolysis Market size was valued at USD 157.44 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 224.24 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 4.52% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Alkaline Water Electrolysis Market Size 2024 |
USD 157.44 Million |
| Alkaline Water Electrolysis Market, CAGR |
4.52% |
| Alkaline Water Electrolysis Market Size 2032 |
USD 224.24 Million |
Top players in the alkaline water electrolysis market include ITM Power, NEL Hydrogen, Cummins, McPhy Energy, Thyssenkrupp Uhde Chlorine Engineers, Asahi Kasei, Green Hydrogen Systems, Enaex, SunHydrogen, and Teledyne CARES, each accelerating capacity expansion and advancing high-output electrolyzer technologies for large hydrogen projects. These companies strengthened partnerships with renewable developers and industrial users to support growing demand for clean hydrogen in power, mobility, and heavy industry. Europe led the market in 2024 with about 36% share, supported by strong hydrogen policies and large-scale project pipelines, followed by North America with nearly 32% share driven by major hydrogen hub investments.
Market Insights
- Alkaline water electrolysis market reached USD 157.44 million in 2024 and is projected to hit USD 224.24 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 4.52%.
- Growth is driven by rising green hydrogen demand from power producers, steel plants, and large industrial users, which prefer alkaline systems for high durability and lower operating cost.
- Key trends include expansion of multi-megawatt projects, integration with renewable energy hubs, and rapid scaling of electrolyzer manufacturing capacity across Europe and Asia Pacific.
- Competition intensified as major players increased stack efficiency, improved load-flexibility, and expanded production lines to meet rising orders from utility and industrial customers.
- Europe held about 36% share in 2024, supported by strong hydrogen policies, while North America followed with nearly 32% share; the ≥80 m3/h segment dominated the type category with about 41%, and power plants led applications with roughly 37% share.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Type
The ≥80 m3/h category dominated the type segment in 2024 with about 41% share, supported by rising demand for large-scale green hydrogen projects. Many utility developers selected high-capacity alkaline systems because these units deliver better hydrogen output per stack and lower long-term operating cost. Growth accelerated as countries expanded multi-megawatt installation plans for mobility fuel, ammonia production, and renewable energy storage. The <50 m3/h ranges grew at a steady pace due to wider use in industrial pilot plants, small refineries, and research facilities seeking stable and affordable electrolysis performance.
- For instance, Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions helped deliver the 10 MW Fukushima Hydrogen Energy Research Field plant, which can produce around 1,200 normal cubic meters of hydrogen per hour using alkaline electrolysis.
By Application
Power plants led the application segment in 2024 with nearly 37% share, driven by the adoption of green hydrogen for co-firing, grid balancing, and long-duration storage. Many utilities integrated alkaline units to convert surplus wind and solar power into hydrogen that supports lower emissions and flexible energy use. Steel plants increased adoption as heavy-industry operators tested hydrogen-ready blast furnace and DRI routes. Electronics and PV manufacturers expanded demand for high-purity hydrogen, while industrial gas companies used alkaline systems to strengthen supply security for emerging clean-energy applications.
- For instance, Piel’s small alkaline electrolyzer line includes models with hydrogen flows from 0.4 to 10 normal cubic meters per hour at discharge.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Demand for Green Hydrogen
Global decarbonization programs increased the need for large-scale green hydrogen, which strengthened adoption of alkaline water electrolysis. Many countries expanded renewable-energy-linked hydrogen projects to support heavy industry, mobility, and power storage. This push raised installation of high-capacity alkaline units because they offer long operating life, stable hydrogen purity, and lower system cost than other electrolysis technologies. Growing renewable penetration also created more opportunities to convert excess solar and wind output into hydrogen, reinforcing steady demand across utility and industrial sectors.
- For instance, Nel has expanded its fully automated alkaline electrolyzer factory at Herøya to an annual production capacity of 1 gigawatt, using two 500 megawatt lines dedicated to large green hydrogen projects.
Expansion of Industrial Decarbonization Projects
Steelmaking, ammonia, chemicals, and refineries accelerated hydrogen-based transition plans, which boosted alkaline systems due to their suitability for large continuous output. Heavy industries replaced fossil-fuel-based feedstock with clean hydrogen to meet tightening emission rules and corporate sustainability goals. Many operators adopted multi-megawatt alkaline setups because these units deliver consistent hydrogen flow required in high-temperature and high-volume processes. Supportive policies such as industrial transition funds and carbon-reduction mandates further pushed long-term commitments to alkaline electrolysis.
- For instance, Cepsa’s planned green hydrogen plant at La Rábida in Spain includes a 300 megawatt electrolyzer designed to produce up to 47,000 tonnes of renewable hydrogen per year for use in refining and chemicals.
Government Incentives and Hydrogen Roadmaps
National hydrogen strategies, grants, and tax benefits encouraged wider deployment of alkaline electrolysis in both emerging and mature markets. Governments supported domestic hydrogen production to reduce fossil-fuel imports, stabilize energy supply, and enable new green-industry investments. Public funding also lowered initial capital barriers, helping power producers and industrial users scale up low-carbon hydrogen production. These programs strengthened investor confidence and accelerated project pipelines across Asia, Europe, and North America, making policy support a major growth driver.
Key Trends and Opportunities
Scaling Toward Multi-Gigawatt Manufacturing
Electrolyzer manufacturers expanded capacity to meet the rising number of utility-scale hydrogen projects. Production lines shifted toward automated stack assembly and higher-efficiency membrane technologies. These advances reduced lead times, improved reliability, and opened new supply opportunities for developers planning multi-gigawatt hydrogen hubs. Growing demand for high-volume units also encouraged partnerships between equipment suppliers, EPC firms, and renewable developers, creating strong opportunities across manufacturing and engineering ecosystems.
- For instance, Sunfire reports that its electrolyzer manufacturing capacity is being scaled toward 500 megawatts per year, with plans to reach gigawatt-scale annual output for alkaline and solid oxide systems.
Integration with Renewable Energy Hubs
Alkaline electrolysis gained strong traction in hybrid solar-wind hydrogen plants, where stable hydrogen production allows better use of variable energy. Developers used flexible operating strategies, including partial-load operations, to increase system efficiency and reduce curtailment. This integration created new investment opportunities in storage, mobility fuels, and green ammonia production. Countries with large renewable potential built dedicated hydrogen corridors, ensuring strong long-term prospects for alkaline electrolyzer deployment.
- For instance, NEOM Green Hydrogen Company is developing a complex in Saudi Arabia using around 4 gigawatts of solar and wind capacity to run an electrolyzer system that will produce about 600 tonnes of green hydrogen per day, converted into roughly 1.2 million tonnes of green ammonia per year.
Growth of Hydrogen Use in Mobility and Power
Demand increased from fuel-cell transport, hydrogen refueling corridors, and backup power systems. Many transport and energy players explored hydrogen to meet stricter emission norms and phase-down of diesel fleets. This shift created opportunities for distributed alkaline systems that support refueling stations, microgrids, and remote power units. Mobility-linked hydrogen consumption also encouraged partnerships across infrastructure, transport fleets, and technology providers.
Key Challenges
High Capital Costs and Long Payback Periods
Large alkaline systems require significant upfront investment, which limits adoption in emerging markets and smaller industries. Many project developers face long payback periods due to high installation, stack replacement, and balance-of-plant costs. Although incentives help reduce expenses, financial risks remain for early-stage hydrogen projects. These cost barriers slow commercial scaling and restrict participation from small and medium enterprises, affecting widespread adoption.
Operational Variability with Renewable Inputs
Alkaline electrolyzers perform best under stable power conditions, yet renewable energy often fluctuates. Frequent load changes reduce efficiency, increase wear on stacks, and complicate long-term maintenance planning. Developers need advanced power-management systems and hybrid storage solutions to stabilize operations, raising overall project complexity. These technical constraints challenge deployment in regions with high renewable variability and require better integration strategies to maintain reliable hydrogen output.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America held about 32% share in 2024, supported by strong hydrogen funding programs and rapid expansion of renewable power capacity. The United States advanced several large-scale hydrogen hubs that increased demand for high-capacity alkaline electrolyzers across utilities, steel pilots, and mobility corridors. Canada focused on clean fuel production from hydro and wind resources, creating new deployment opportunities. Industrial decarbonization targets, tax incentives, and strong participation from energy developers helped the region maintain steady leadership. Growing investment in grid storage and hydrogen-based transport reinforced long-term market growth across North America.
Europe
Europe accounted for nearly 36% share in 2024, driven by strong policy support under national hydrogen strategies and strict emission-reduction mandates. Germany, the Netherlands, Spain, and France advanced major green hydrogen projects linked to steelmaking, chemicals, and heavy transport. EU funding programs encouraged large-scale electrolyzer integration with offshore wind and hybrid renewable hubs. Industrial users adopted alkaline systems to meet carbon-neutrality goals, while ports and transport corridors expanded hydrogen infrastructure. Europe’s robust regulatory framework and mature renewable landscape allowed the region to maintain the largest market position.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific captured around 27% share in 2024, supported by rising investment from China, Japan, South Korea, and India. China strengthened large renewable-to-hydrogen projects for industrial gases, mobility, and chemical production, increasing demand for high-output alkaline units. Japan and South Korea pushed hydrogen import and domestic production plans, while India accelerated green hydrogen adoption in refineries and fertilizers. Strong manufacturing capacity, expanding electrolyzer supply chains, and large industrial bases helped the region scale rapidly. Government-backed energy transition programs reinforced Asia Pacific’s growing role in global alkaline electrolysis deployment.
Latin America
Latin America held nearly 3% share in 2024, driven by early-stage but fast-growing interest in hydrogen from countries such as Chile and Brazil. Chile advanced renewable-powered hydrogen projects in the Atacama region, where high solar irradiance supports cost-competitive production. Brazil explored hydrogen integration within industrial clusters and port infrastructure, supported by expanding wind and solar capacity. Many regional developers used pilot-scale alkaline systems to evaluate industrial applications and export potential. Growing foreign investment and favorable natural resources continued to position Latin America as an emerging hydrogen production zone.
Middle East and Africa
Middle East and Africa accounted for about 2% share in 2024, supported by expanding mega-hydrogen projects and strong renewable resources. Countries such as Saudi Arabia, the UAE, Morocco, and South Africa explored large green hydrogen and ammonia ventures that increased interest in high-capacity alkaline electrolyzers. Strong solar and wind conditions supported cost-efficient hydrogen pathways, while partnerships with global energy firms accelerated early deployment. Many national strategies prioritized hydrogen exports to Europe and Asia. Although still in the early phase, large project pipelines strengthened the region’s long-term market potential.
Market Segmentations:
By Type
- < 10 m3/h
- < 30 m3/h
- < 50 m3/h
- < 80 m3/h
- ≥ 80 m3/h
By Application
- Power Plants
- Steel Plants
- Electronics and PV
- Industrial Gases
- Others
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape in the alkaline water electrolysis market includes Green Hydrogen Systems, Teledyne CARES, ITM Power, Cummins, SunHydrogen, Enaex, Asahi Kasei, NEL Hydrogen, McPhy Energy, and Thyssenkrupp Uhde Chlorine Engineers in the first line only. Companies expanded manufacturing capacity to meet rising demand for large-scale hydrogen projects and strengthened supply chains to support multi-megawatt installations. Many players focused on improving electrolyzer durability, enhancing stack efficiency, and reducing system cost through advanced materials and automated production. Strategic partnerships with renewable developers, utilities, and industrial customers accelerated deployment across green hydrogen hubs. Firms also increased investment in R&D to optimize load-flexibility and support integration with variable solar and wind assets. Growing government incentives and national hydrogen roadmaps further intensified competition as manufacturers targeted contracts in emerging and established markets. The combination of technology upgrades, policy support, and expanding project pipelines continued to shape a highly dynamic competitive environment.
Key Player Analysis
- Green Hydrogen Systems
- Teledyne CARES
- ITM Power
- Cummins
- SunHydrogen
- Enaex
- Asahi Kasei
- NEL Hydrogen
- McPhy Energy
- Thyssenkrupp Uhde Chlorine Engineers
Recent Developments
- In 2025, Asahi Kasei announced it would supply an Aqualyzer C3 alkaline-water electrolyzer system of around 1 MW for a hydrogen-powered mobility project in Central Finland, supporting local green hydrogen production for buses and heavy vehicles.
- In 2025, Nel ASA announced a temporary halt of production at its 1 GW alkaline electrolyser factory in Herøya, Norway, following lower-than-expected order intake and project delays, with workforce reductions mainly in the alkaline business segment.
- In 2024, Cummins Commissioned a 10 MW green hydrogen unit at a GAIL plant in India. The project utilized an electrolyzer from Accelera by Cummins.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Type, Application and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market will expand as more countries adopt large-scale green hydrogen projects.
- Developers will increase demand for high-capacity alkaline systems in industrial clusters.
- Manufacturing efficiency will improve through automated stack production and better membranes.
- Government hydrogen policies will continue to accelerate project approvals and investment flows.
- Heavy industries will integrate alkaline units to support deeper decarbonization targets.
- Hybrid solar-wind hydrogen hubs will boost deployment across major renewable regions.
- Technology upgrades will reduce operating cost and improve long-term system reliability.
- Electrolyzer supply chains will expand to support multi-gigawatt manufacturing capacity.
- New opportunities will arise from hydrogen mobility, refueling networks, and power backup systems.
- Long-term growth will strengthen as global energy systems shift toward clean hydrogen adoption.




