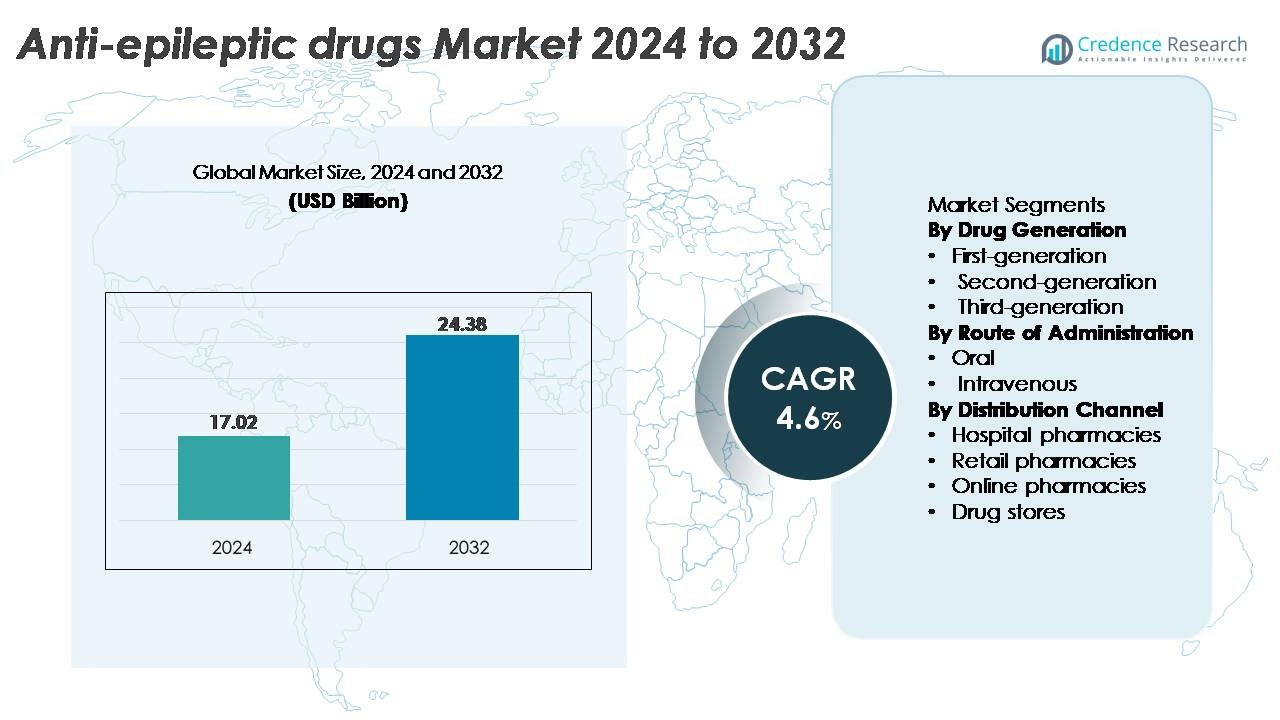
The global Anti-Epileptic Drugs (AED) Market was valued at USD 17.02 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 24.38 billion by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 4.6% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Anti-Epileptic Drugs (AED) Market Size 2024 |
USD 17.02 Billion |
| Anti-Epileptic Drugs (AED) Market, CAGR |
4.6% |
| Anti-Epileptic Drugs (AED) Market Size 2032 |
USD 24.38 Billion |
Major players in the anti-epileptic drugs market include Pfizer Inc., Novartis AG, Sanofi, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc., GlaxoSmithKline plc, AstraZeneca, Abbott, Eisai Co., Ltd., and Merck KGaA. These companies compete through diversified neurology portfolios, strong global distribution, and continued investment in next-generation therapies targeting refractory and genetic epilepsies. Eisai and UCB remain influential in specialty epilepsy care, while Teva and other generics manufacturers expand access in cost-sensitive regions. North America leads the global market with approximately 38% share, supported by advanced diagnostic infrastructure, high awareness, and strong adoption of both branded and generic anti-epileptic drugs.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The anti-epileptic drugs market was valued at USD 17.02 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 24.38 billion by 2032, registering a 4.6% CAGR over the forecast period.
- Demand strengthens as second-generation drugs remain the dominant segment, driven by better tolerability and broad clinical adoption, while expanding diagnosis rates and increased awareness accelerate treatment uptake across all age groups.
- Emerging trends include the rise of precision neurology, digital seizure-monitoring tools, and expanding pipelines targeting refractory and rare epilepsies, encouraging adoption of next-generation therapies.
- Competitive intensity increases as Pfizer, Novartis, Sanofi, Eisai, Teva, and GSK advance specialty formulations while generics manufacturers improve affordability, though challenges persist due to adverse-effect profiles and treatment gaps in low-resource regions.
- Regionally, North America leads with ~38% share, followed by Europe at ~28%, Asia Pacific at ~22%, Latin America at ~7%, and Middle East & Africa at ~5%, reflecting varying diagnostic access, reimbursement strength, and treatment penetration.
 Market Segmentation Analysis:
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Drug Generation
First-, second-, and third-generation anti-epileptic drugs form a tiered treatment landscape, with second-generation AEDs holding the dominant market share due to their improved safety profiles, fewer drug–drug interactions, and broader therapeutic windows. Agents such as lamotrigine, levetiracetam, and topiramate remain core options in both monotherapy and adjunctive therapy, enabling strong clinician preference. Growing adoption is further encouraged by extensive pediatric indications, favorable tolerability, and expanding generic availability. Meanwhile, third-generation molecules gain traction in refractory epilepsy, while first-generation drugs remain relevant in cost-sensitive settings.
- For instance, UCB’s levetiracetam (Keppra®) demonstrated a median seizure-frequency reduction of 49.8% in a pooled analysis of 904 patients across three randomized trials, establishing strong evidence for its broad utility in focal seizures.
By Route of Administration
The market is divided into oral and intravenous formulations, with the oral segment commanding the largest share as it supports long-term outpatient management, simplified dosing schedules, and wide patient accessibility. Oral AEDs dominate maintenance therapy across pediatric, adult, and geriatric populations, driving consistent prescription volume. Their strong market position is reinforced by extensive generic penetration, chronic treatment requirements, and high adherence supported by extended-release versions. Intravenous formulations remain essential in hospital environments for acute seizure control and status epilepticus, but their use is comparatively limited to emergency and inpatient care.
- For instance, Eisai’s oral formulation of perampanel (Fycompa®) demonstrated a median percentagereduction of 5% in seizure episodes per 28 days at the 8 mg/day dose in a Phase III trial (Study 305) of 386 patients with refractory partial-onset seizures, underscoring the clinical effectiveness of oral agents in daily management.
By Distribution Channel
Hospital pharmacies, retail pharmacies, online pharmacies, and drug stores constitute the distribution ecosystem, with retail pharmacies emerging as the leading channel due to steady prescription refills and strong community-level access for chronic epilepsy management. High patient reliance on monthly or quarterly dispensing cycles sustains the segment’s dominance. Hospital pharmacies play a critical role in acute care and severe seizure episodes, while online pharmacies gain momentum through home-delivery convenience and competitive pricing. Drug stores maintain modest participation, mainly supporting OTC adjuncts rather than prescription AEDs. Retail remains strongest due to scale, accessibility, and established dispensing infrastructure.
Market Overview
KEY GROWTH DRIVERS
Rising Global Epilepsy Prevalence and Expanding Diagnostic Capabilities
The growing global burden of epilepsy continues to be a primary driver for anti-epileptic drug demand, supported by expanding diagnostic capabilities in both developed and emerging healthcare systems. Improved access to EEG monitoring, neuroimaging, and genetic screening allows clinicians to detect epilepsy earlier and classify seizure types more accurately, resulting in more targeted pharmacological interventions. The expansion of specialty neurology clinics and tele-neurology platforms further broadens patient reach, enabling consistent follow-up and optimized medication titration. Increasing awareness campaigns by medical associations and patient advocacy groups also enhance treatment-seeking behavior, reducing the number of untreated cases. As diagnostic precision improves, healthcare providers can shift toward personalized therapy regimens that reduce seizure frequency, improve quality of life, and sustain adherence ultimately strengthening long-term utilization of anti-epileptic medications across demographics.
- For instance, Ceribell’s FDA-cleared Rapid Response EEG system features a 10-electrode headband that can be applied in under 5 minutes and delivers real-time seizure detection with a 500 Hz sampling rate and an automated seizure-burden algorithm validated across more than 6,000 ICU recordings, enabling clinicians to identify non-convulsive seizures far faster than traditional EEG setups that typically require 30–60 minutes for deployment.
Advancements in Novel Mechanisms and Next-Generation Therapeutics
The industry benefits significantly from continued innovation in drug development, with next-generation anti-epileptic therapies targeting multiple mechanisms to improve efficacy, tolerability, and resistance profiles. Pharmaceutical pipelines increasingly focus on treatments for refractory and genetic epilepsies, incorporating sodium-channel modulators, SV2A-binding agents, and GABAergic enhancers with superior pharmacokinetics. These advancements offer differentiated seizure control with fewer side effects, strengthening clinical adoption. Precision-medicine-based approaches, including therapies tailored for Dravet syndrome, Lennox–Gastaut syndrome, and tuberous sclerosis complex, expand opportunities for high-value specialty drugs. Additionally, extended-release formulations and optimized dosing profiles enhance adherence and reduce breakthrough seizures. The combined impact of innovative mechanisms, regulatory support for orphan indications, and strong clinical evidence positions next-generation AEDs as a major driver of market expansion.
· For instance, UCB’s cenobamate has shown exceptional long-term efficacy, with post-hoc analyses from the C021 open-label study reporting ≥90% seizure reduction in roughly one-third of adults with uncontrolled focal seizures. In the same dataset, about 13% of patients maintained complete seizure freedom during the long-term maintenance phase, which had a median duration of nearly 30 months.
Growing Availability of Generics and Improved Treatment Accessibility
A robust influx of generic anti-epileptic drugs continues to make treatment more accessible globally, driving strong market penetration, particularly in cost-sensitive regions. Generic versions of widely used agents such as levetiracetam, lamotrigine, valproate, and carbamazepine provide clinically equivalent efficacy at substantially lower cost, facilitating long-term adherence among chronic epilepsy patients. Healthcare payers, insurance providers, and government reimbursement programs increasingly encourage generic substitution, improving affordability and enabling wider coverage across public health systems. This trend is especially impactful in low- and middle-income countries, where out-of-pocket expenses historically limited epilepsy treatment uptake. As distribution networks expand and regulatory frameworks strengthen bioequivalence standards, generic AEDs continue to support high-volume prescriptions, reduce treatment gaps, and enhance patient continuity of care collectively reinforcing market growth.
KEY TRENDS & OPPORTUNITIES
Expansion of Personalized and Precision Neurology Treatment Models
The anti-epileptic drugs market is witnessing rapid adoption of personalized treatment models, supported by advances in neurogenetics, biomarker research, and AI-driven clinical decision tools. Genetic sequencing allows clinicians to identify mutation-specific epilepsies and tailor treatment plans based on drug responsiveness and metabolic profiles, reducing adverse reactions and improving seizure outcomes. Precision neurology accelerates the development of condition-specific drugs, such as those targeted at SCN1A-related syndromes. Additionally, AI-enabled platforms assist in predicting treatment response, optimizing dose titration, and identifying early signs of drug resistance. As research collaborations strengthen between pharmaceutical companies, universities, and digital-health innovators, personalized epilepsy care becomes more mainstream, creating substantial opportunities for premium therapies, companion diagnostics, and long-term patient management ecosystems.
· For instance, Invitae’s Epilepsy Panel analyzes more than 300 epilepsy-related genes such as SCN1A, SCN2A, and KCNQ2 using next-generation sequencing. The test provides a typical diagnostic turnaround of about 10–21 days and reports >99% analytical sensitivity for single-nucleotide variant detection. This level of accuracy helps clinicians select therapies based on confirmed genetic drivers of epilepsy.
Increasing Integration of Digital Therapeutics and Remote Monitoring Solutions
Digital health tools are transforming epilepsy management by enabling continuous monitoring, remote consultations, and improved adherence tracking. Wearable seizure detection devices, smartphone-based seizure diaries, and connected EEG systems support real-time data capture and early intervention, reducing emergency episodes and optimizing medication adjustments. Digital therapeutics platforms complement pharmacological therapy by providing cognitive support, behavioral tracking, and medication reminders, improving overall patient outcomes. Healthcare providers and payers increasingly integrate these tools into chronic disease management programs, creating opportunities for hybrid treatment frameworks that combine AEDs with digital solutions. As regulatory bodies streamline pathways for software-as-a-medical-device (SaMD) approvals, the market experiences stronger innovation momentum and expanded value-added service opportunities.
- For instance, Empatica’s FDA-cleared Embrace2 wearable uses electrodermal activity and accelerometry to detect generalized tonic–clonic seizures, achieving a validated sensitivity of 98% across 6,530 monitored hours in clinical studies, enabling rapid caregiver alerts through mobile networks.
Rising Focus on Therapies for Drug-Resistant and Rare Epilepsies
Drug-resistant epilepsy affects nearly one-third of diagnosed patients, creating significant unmet clinical needs and fostering targeted innovation. Pharmaceutical pipelines increasingly prioritize molecules designed to address refractory seizures and rare syndromes, supported by favorable orphan-drug incentives and accelerated approval pathways. Enhanced research in synaptic modulation, neuroinflammation pathways, and gene therapy expands therapeutic possibilities beyond conventional AEDs. Specialty formulations with improved blood–brain barrier penetration and novel receptor interactions strengthen efficacy in previously underserved patient groups. As multidisciplinary care centers grow and clinical trial networks expand globally, the market gains new opportunities for high-value treatments specifically designed for complex and severe epilepsies.
KEY CHALLENGES
High Incidence of Adverse Effects and Treatment Tolerability Issues
Despite therapeutic advances, anti-epileptic drugs continue to pose significant tolerability challenges, including cognitive impairment, weight fluctuations, mood disturbances, and organ toxicity depending on the molecule. These adverse events often require dose modification or medication switching, affecting long-term adherence and treatment outcomes. Polytherapy in complex epilepsies further increases the cumulative side-effect burden, complicating patient management. Differences in metabolism across age groups especially in pediatric and geriatric populations add additional risks and dosing complexities. Limited availability of personalized titration tools and inter-patient variation in drug response also contribute to inconsistent outcomes. These tolerability concerns represent a major barrier to market growth, particularly in chronic therapy environments where adherence is essential.
Persistent Treatment Gaps, Limited Specialist Access, and Diagnostic Delays
Global disparities in neurologist availability, diagnostic infrastructure, and treatment accessibility continue to constrain optimal epilepsy management. Many regions face prolonged delays in EEG testing, limited availability of MRI imaging, and shortages of trained epilepsy specialists, resulting in underdiagnosis and misclassification of seizure disorders. These systemic limitations delay treatment initiation and hinder the adoption of advanced AEDs. In low-resource settings, inadequate supply chains, inconsistent medication availability, and high out-of-pocket costs further restrict continuity of care. Even in developed markets, fragmented care pathways and low patient awareness contribute to treatment gaps. These challenges collectively limit the full therapeutic potential of anti-epileptic drugs and impede uniform market expansion.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds the largest share of approximately 38% due to strong clinical adoption of advanced anti-epileptic drugs, high diagnostic capability, and a well-established neurologist network. The U.S. leads treatment uptake with widespread EEG access, structured epilepsy care pathways, and strong reimbursement support for both branded and generic AEDs. Rising prevalence of drug-resistant epilepsy and expanding specialty centers further reinforce demand for next-generation therapies. Strong R&D pipelines, frequent FDA approvals for rare epilepsies, and growing tele-neurology adoption continue to strengthen the region’s market dominance and drive consistent long-term growth.
Europe
Europe accounts for roughly 28% of the market, driven by robust public health coverage, strong neurology infrastructure, and high adoption of guideline-based epilepsy management. Western European countries particularly Germany, France, Italy, and the U.K. demonstrate strong utilization of second- and third-generation AEDs supported by standardized care protocols. Increasing clinical focus on pediatric and genetic epilepsies, along with expanded reimbursement for newer therapies, strengthens market momentum. The region also benefits from active pharmaceutical research collaborations and growing access to digital epilepsy-monitoring tools that improve treatment outcomes and broaden long-term patient engagement.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific captures nearly 22% of the global market, supported by a rising epilepsy patient pool, improving awareness programs, and expanding access to neurology services across China, Japan, India, and South Korea. Growing availability of generic AEDs significantly boosts affordability in middle-income economies. Japan continues to lead adoption of innovative formulations due to its strong healthcare infrastructure. Meanwhile, China’s expanding hospital networks and government-led neurological disease initiatives improve diagnostic rates. Increasing urbanization, widening access to EEG and MRI diagnostics, and investment in specialty care centers are accelerating market growth across the region.
Latin America
Latin America represents around 7% of the market, with growth supported by gradual improvements in neurology care and increasing availability of cost-effective generic AEDs. Brazil and Mexico dominate regional demand due to stronger healthcare access and broader distribution networks. Despite rising diagnosis rates, many patients still face treatment gaps due to uneven specialist availability and inconsistent medication supply. Government programs aimed at improving chronic disease management and expanding essential drug lists help enhance AED accessibility. Continued private-sector investment in hospital infrastructure is expected to improve long-term adoption of modern anti-epileptic therapies.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region holds approximately 5% of the market, characterized by growing healthcare investments and a rising focus on neurological disorder management. Gulf countries, including Saudi Arabia and the UAE, drive regional adoption with improving diagnostic capabilities and increasing access to branded and generic AEDs. In Africa, substantial treatment gaps persist due to limited neurology specialists and constrained pharmaceutical distribution networks. International health organizations are strengthening epilepsy awareness and medication supply programs, gradually improving treatment penetration. Expanding hospital infrastructure and national health reforms support moderate but steady market growth.
Market Segmentations:
By Drug Generation
- First-generation
- Second-generation
- Third-generation
By Route of Administration
By Distribution Channel
- Hospital pharmacies
- Retail pharmacies
- Online pharmacies
- Drug stores
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The anti-epileptic drugs market features a competitive mix of multinational pharmaceutical companies and specialty neurology-focused developers, each advancing portfolios across first-, second-, and third-generation therapies. Leading players such as UCB, Pfizer, Novartis, Eisai, and GlaxoSmithKline maintain strong commercial presence supported by extensive clinical data, broad global distribution, and long-established neurology expertise. UCB continues to strengthen its position through innovations addressing drug-resistant epilepsy, while Eisai expands its footprint with differentiated mechanisms targeting both pediatric and adult segments. Several companies focus on lifecycle management strategies, including extended-release formulations and new indications to sustain product longevity. Meanwhile, generics manufacturers such as Teva, Sun Pharma, and Cipla intensify price competition by offering cost-effective versions of widely used AEDs, improving accessibility in emerging markets. Pipeline activity remains robust, with firms pursuing novel mechanisms, orphan-drug designations, and precision medicine approaches for rare epilepsies, intensifying innovation-driven competition across global markets.
Key Player Analysis
- Pfizer Inc.
- Novartis AG
- Sanofi
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
- Eisai Co., Ltd.
- GlaxoSmithKline plc (GSK)
- UCB Pharma SA
- Lundbeck A/S
- Jazz Pharmaceuticals plc
- Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Recent Developments
- In December 2025, a global biopharmaceutical company, UCB, revealed 29 studies, including four late breakers, at the AES Annual Meeting 2025, highlighting commitment to transforming epilepsy care outcomes and partnering with patients and the scientific community.
- In April 2024, Stanford Medicine researchers discovered a previously overlooked region of the hippocampus, the fasciola cinerea, is involved in instigating and propagating seizures, potentially aiding patients who lack relief after surgery.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Drug generation, Route of administration, Distribution channel and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market will see expanding adoption of next-generation therapies targeting refractory and rare epilepsies.
- Precision neurology and genetic profiling will increasingly guide individualized treatment strategies.
- Digital seizure-monitoring tools and remote neurology platforms will strengthen long-term patient management.
- Pharmaceutical pipelines will prioritize multi-mechanism molecules with improved safety and tolerability.
- Generic penetration will continue to rise, enhancing affordability and treatment continuity in emerging regions.
- Extended-release and optimized-dosing formulations will support better adherence and reduce breakthrough seizures.
- Regulatory incentives for orphan and pediatric epilepsy therapies will accelerate innovation.
- AI-assisted decision-support tools will improve dosing accuracy and therapy adjustments.
- Expansion of neurology specialty centers will increase diagnosis rates and elevate treatment standards.
- Integration of combination therapy approaches will become more common to address complex and drug-resistant epilepsies.

 Market Segmentation Analysis:
Market Segmentation Analysis:

