Market Overview
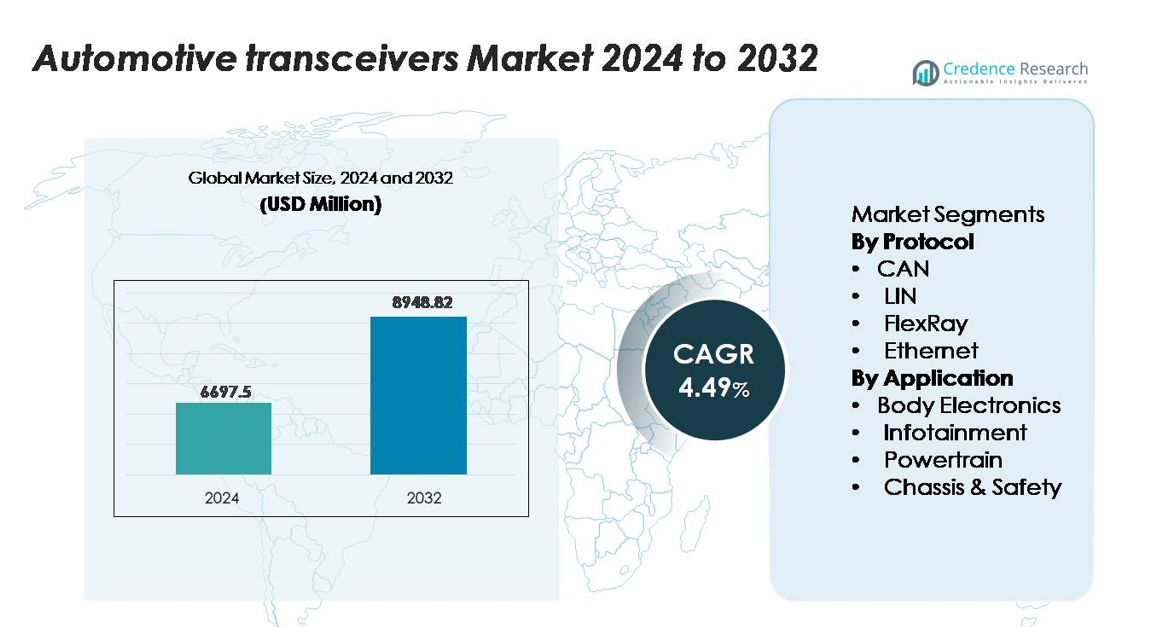
The automotive transceivers market was valued at USD 6,297.5 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 8,948.82 million by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 4.49% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Automotive Transceivers Market Size 2024 |
USD 6,297.5 million |
| Automotive Transceivers Market, CAGR |
4.49% |
| Automotive Transceivers Market Size 2032 |
USD 8,948.82 million |
The automotive transceivers market is led by major players such as NXP Semiconductors, Texas Instruments, Infineon Technologies, Renesas Electronics, STMicroelectronics, and Microchip Technology, each providing high-reliability CAN, LIN, FlexRay, and Ethernet solutions for body electronics, powertrain, ADAS, and infotainment systems. These companies benefit from strong portfolios in automotive-grade mixed-signal ICs and long-term OEM partnerships. Asia-Pacific remains the leading region, holding an exact market share of 48%, driven by large-scale vehicle production, rapid electrification, and expanding semiconductor manufacturing capacity. Europe and North America follow with advanced adoption of high-speed in-vehicle network architectures.
Market Insights
- The automotive transceivers market was valued at USD 6,297.5 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 8,948.82 million by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 4.49% during the forecast period.
- Market growth is driven by rising electronic content per vehicle, increasing ADAS integration, and accelerating electrification, which boosts demand for high-reliability CAN, LIN, FlexRay, and Ethernet transceivers across body, powertrain, and safety domains.
- Trends include rapid migration toward automotive Ethernet, adoption of zonal architectures, and higher data-bandwidth requirements supporting connected infotainment, sensor fusion, and software-defined vehicle platforms.
- The competitive landscape is led by NXP, Infineon, Texas Instruments, Renesas, Microchip, and STMicroelectronics, with CAN holding the largest protocol share and Body Electronics dominating application share due to extensive ECU deployment.
- Asia-Pacific leads with a 48% regional share, followed by Europe at 22% and North America at 27%, supported by vehicle production strengths, electrification initiatives, and advanced in-vehicle network adoption.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Protocol
Within the protocol landscape, CAN remains the dominant sub-segment, holding the largest market share due to its proven robustness, low-cost implementation, and suitability for real-time control across powertrain, body electronics, and chassis applications. Automakers increasingly adopt CAN FD to handle rising data loads from electrification and advanced driver assistance systems, reinforcing its leadership. LIN expands in entry-level comfort functions, while FlexRay retains relevance in deterministic safety architectures. Ethernet experiences the fastest growth as vehicles transition toward high-bandwidth zonal architectures, supporting ADAS, sensor fusion, and rich infotainment data streams.
- For instance, NXP Semiconductors’ TJA146x family of CAN FD transceivers supports data rates up to 8 Mbps and integrates CAN Signal Improvement Capability (SIC) to reduce signal ringing, enabling reliable communication in larger, more complex network architectures.
By Application
Across applications, Body Electronics stands as the dominant sub-segment, accounting for the largest share due to the extensive use of transceivers in body control modules, lighting, HVAC, and digital cockpit systems. Its growth is driven by rising adoption of smart interior features and increased electronic content per vehicle. Infotainment accelerates with demand for connected navigation, multimedia streaming, and telematics, relying on higher-speed protocols such as Ethernet. Powertrain applications remain critical for engine management and transmission systems, while Chassis & Safety segments gain momentum with expanding ADAS and autonomous driving functionalities requiring high-reliability communication.
- For instance, the Marvell 88Q5072 automotive Ethernet switch is an 11-port switch that primarily delivers 100 Mbps per port on its six fixed 100BASE-T1 ports. It also includes a configurable multi-speed SerDes port that can support higher speeds, including 2.5 Gbps (as well as 1 Gbps and 5 Gbps), enabling high-bandwidth multimedia data flow in digital cockpit and ADAS architectures.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Electronic Content Per Vehicle
The continuous expansion of electronic systems in modern vehicles significantly accelerates demand for automotive transceivers. Automakers integrate more sensors, controllers, and actuators into body electronics, infotainment, powertrain, and safety domains, driving the need for reliable in-vehicle communication. Features such as digital cockpits, ambient lighting, advanced HVAC controls, and connected infotainment require transceivers to support real-time data exchange across multiple nodes. Additionally, the shift toward zonal vehicle architecture increases data pathways and necessitates more robust communication protocols, particularly CAN FD and Ethernet. Electrification further amplifies electronic complexity with high-voltage battery management systems, thermal management, and motor control units all relying on accurate, high-speed signal transmission. As vehicles transition from hardware-defined to software-enabled platforms, the density of ECUs, domain controllers, and signal-processing units continues to rise.
- For instance, NXP’s S32K3 MCU platform integrates up to 12 CAN FD interfaces and 8 LIN channels, allowing high-density body electronics networks with deterministic routing across more than 100 distributed sensors and actuators.
Expansion of ADAS and Autonomous Driving Systems
The rapid advancement of ADAS and semi-autonomous driving technologies is a major catalyst for automotive transceiver adoption. Systems such as adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assistance, automated emergency braking, and sensor fusion platforms generate massive volumes of data that must be exchanged with high reliability and minimal latency. Transceivers enable communication between radars, LiDAR units, cameras, ultrasonic sensors, and central controllers responsible for decision-making and actuation. As vehicle automation progresses toward Level 3 and Level 4 capabilities, high-bandwidth, deterministic, and low-latency communication becomes essential, accelerating the migration from traditional CAN to Ethernet-based architectures. Safety regulations worldwide are also mandating increased adoption of ADAS, compelling OEMs to integrate more transceivers into mandatory safety systems. Furthermore, advanced perception and compute platforms require seamless networking across redundant sensor clusters, domain controllers, and actuators, ensuring strong, sustained demand for high-performance automotive transceivers.
- For instance, Aptiv’s Smart Vehicle Architecture uses domain controllers connected by 10 Gbps Ethernet switching fabrics to exchange real-time perception data across more than 40 sensor nodes with deterministic timing budgets below 10 milliseconds.
Shift Toward Electrification and Powertrain Modernization
Electrification of the global automotive fleet significantly boosts the adoption of transceivers across electric powertrain and battery management systems. EV platforms contain a higher number of electronic controllers compared to internal combustion vehicles, including inverters, onboard chargers, DC-DC converters, thermal management units, and high-voltage safety monitoring modules. These systems depend on transceivers to ensure fault-free communication across high-voltage components and real-time status reporting for safety and efficiency. Efficient communication is critical for monitoring cell voltages, temperatures, and state-of-charge across battery modules, making transceivers vital to BMS architecture. Additionally, next-generation e-powertrains require deterministic communication for motor control and inverter synchronization, strengthening the demand for robust CAN FD and Ethernet technologies. As automakers scale dedicated EV platforms and adopt zonal architectures, the number of communication interfaces per vehicle is rising, positioning transceivers as essential components in all electrified mobility ecosystems.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Growing Adoption of High-Speed Automotive Ethernet
A prominent trend shaping the market is the shift toward automotive Ethernet as the backbone for in-vehicle data communication. Ethernet offers substantially higher bandwidth compared to legacy protocols, enabling support for ADAS sensors, high-resolution cameras, infotainment streaming, and centralized compute architectures. As automotive architectures migrate from distributed ECUs to zonal and centralized processing units, Ethernet’s scalability and flexibility create major opportunities for transceiver manufacturers. The rise of software-defined vehicles, over-the-air updates, and cloud-integrated telematics further increases the need for high-speed, secure networking capabilities. Additionally, emerging automotive standards such as 100BASE-T1 and 1000BASE-T1 allow single-pair Ethernet to deliver gigabit-level performance while meeting stringent automotive environmental requirements. Suppliers that innovate in low-power, EMI-resistant, and cybersecurity-hardened Ethernet transceivers are positioned to capture significant growth as OEMs build future-ready communication infrastructures.
- For instance, Broadcom’s BCM8958X family of automotive Ethernet switches supports an aggregate switching capacity of 50 Gbps and integrates up to 16 Ethernet ports, enabling high-bandwidth zonal architectures in next-generation vehicles.
Acceleration of Zonal and Centralized Vehicle Architectures
The transition toward zonal and centralized electronic architectures presents a major long-term opportunity. Traditional wiring harnesses are heavy, complex, and costly; zonal designs consolidate functions into fewer high-capacity domain controllers connected via high-speed communication links. This shift requires more intelligent and efficient transceivers capable of managing multi-protocol communication within each zone. As OEMs aim to reduce wiring by up to 40% and lower vehicle weight, transceivers become central to enabling scalable data routing between sensors, actuators, and compute nodes. The architecture also supports seamless OTA software updates and functional expansion, increasing the role of advanced communication protocols such as Ethernet and upgraded CAN FD. The industry’s move toward centralized computing, particularly for ADAS and infotainment, strengthens the demand for versatile transceivers capable of integrating security, diagnostics, and high data throughput.
- For instance, Aptiv’s Smart Vehicle Architecture (SVA™) replaces legacy distributed ECUs with zonal controllers and has demonstrated wiring mass reductions of up to 74 kg in production vehicle programs by reducing cable lengths through consolidated zonal nodes, each interfacing with up to 40 sensor and actuator endpoints.
Integration of Cybersecurity and Functional Safety Features
As vehicles become more connected and software-intensive, cybersecurity and safety-centric opportunities for transceiver innovation continue to grow. OEMs increasingly require hardware-level protections such as secure communication interfaces, intrusion detection, and fault-tolerant signaling to safeguard critical vehicle networks. Transceivers supporting built-in encryption, error correction, and real-time diagnostics are gaining traction as cyber risks escalate. Additionally, ISO 26262 functional safety compliance is becoming a key differentiator, especially for high-risk domains like powertrain and autonomous driving. Advanced transceivers that combine high bandwidth with safety-critical features enable manufacturers to meet regulatory requirements while enhancing reliability. This trend opens new avenues for suppliers specializing in secure, safety-certified communication ICs tailored for next-generation vehicle networks.
Key Challenges
Increasing Network Complexity and Integration Constraints
Rising electronic density and multi-protocol communication networks create significant integration challenges for OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers. Modern vehicles must accommodate multiple communication standards—including CAN, LIN, FlexRay, and Ethernet—each with unique performance and design requirements. Ensuring compatibility among dozens of ECUs, domain controllers, and sensors demands extensive validation, increasing development time and cost. As software-defined architectures expand, network traffic surges, raising concerns around congestion, signal integrity, and latency. Additionally, packaging constraints in compact EV platforms complicate thermal management and EMI mitigation for high-speed transceivers. Managing these complexities while maintaining reliability, safety, and cost targets poses a major obstacle for manufacturers.
Cost Pressures and Transition to Next-Generation Protocols
The automotive industry faces strong cost pressures as OEMs balance vehicle affordability with the integration of advanced electronics. Upgrading networks from CAN to CAN FD or Ethernet requires new hardware, redesigned architectures, and more advanced transceivers—often increasing system-level costs. Suppliers struggle to optimize high-performance transceivers while maintaining low power consumption, functional safety compliance, and rugged automotive-grade reliability within strict price constraints. Additionally, smaller manufacturers may face challenges adapting to evolving standards and scaling production for newer protocols. This tension between performance demands and cost competitiveness slows the speed of protocol transition, making it a persistent challenge for the market.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America accounts for approximately 25-30% of the global automotive transceivers market, driven by strong OEM investment in advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), high electronic content per vehicle, and robust electric vehicle adoption. U.S. and Canadian manufacturers deploy modern network architectures, increasing demand for high-speed transceivers. The region’s mature automotive ecosystem and focus on connectivity and safety features support sustained growth in body electronics, powertrain, and chassis applications. While growth is somewhat slower than in emerging regions, North America remains a reliable contributor to global volume and value due to premium vehicle production and early adoption of new protocols.
Europe
Europe holds an estimated 20-25% share of the global automotive transceivers market, underpinned by stringent safety regulations, a strong luxury and premium vehicle segment, and widespread electrification efforts. Countries such as Germany, France and the U.K. lead in vehicle electrification and in-vehicle networking upgrades, which increases transceiver integration across body, infotainment, and powertrain applications. The region’s OEMs push for higher data-bandwidth systems and zonal architectures, thus reinforcing demand. While growth rates may moderate due to market maturation, Europe continues to drive technology adoption and supports transceiver suppliers with high specification, high-reliability demand.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific dominates the global automotive transceivers market with an estimated 45-50% share, thanks to massive vehicle production in China, Japan, India and South Korea and accelerated electrification. Strong consumer demand for connected features, growing EV penetration, and large-scale manufacturing capacities fuel high unit volumes of transceivers. Regional semiconductor and component suppliers add further scale. Ongoing shifts to networked architectures and higher content per vehicle in this region make it the primary growth engine for the market. Price competitiveness and localisation of supply chains further enhance Asia-Pacific’s leadership position.
Latin America
Latin America represents around 5-7% of the global automotive transceivers market, supported by growing vehicle production in Brazil and Mexico and increasing adoption of body electronics and comfort features. While premium applications and high-bandwidth systems are less prevalent compared to developed regions, the gradual improvement in vehicle content supports transceiver demand in mid-range and commercial vehicle segments. Cost-sensitive programmes and aftermarket upgrades also help uptake. Growth is steady but constrained by macroeconomic cycles, import dependence, and slower deployment of advanced network architectures.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region holds roughly 3-5% share of the global automotive transceivers market and is characterized by selective uptake of premium features in Gulf countries, alongside more modest growth in other markets. Demand stems primarily from luxury vehicles, growing EV initiatives, and fleets equipped with advanced body and safety electronics. However, limited indigenous vehicle manufacturing and diverse regulatory environments affect penetration of high-speed transceiver technologies. Nevertheless, increasing connected car adoption, urban mobility initiatives, and premium vehicle imports support incremental growth in this region.
Market Segmentations:
By Protocol
By Application
- Body Electronics
- Infotainment
- Powertrain
- Chassis & Safety
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the automotive transceivers market is defined by a concentrated group of semiconductor leaders that consistently innovate to meet rising vehicle communication demands. Companies such as NXP Semiconductors, Infineon Technologies, Texas Instruments, Renesas Electronics, STMicroelectronics, and Microchip Technology dominate the space through extensive portfolios spanning CAN, LIN, FlexRay, and automotive Ethernet transceivers. Their strengths lie in automotive-grade reliability, strong OEM partnerships, and deep integration across powertrain, body electronics, infotainment, and ADAS domains. Competitive strategies focus on developing high-bandwidth, low-latency solutions aligned with zonal architectures, electrification, and software-defined vehicle platforms. Leading players also invest heavily in cybersecurity-enabled transceivers and ISO 26262 functional safety compliance to support advanced vehicle networks. With Asia-Pacific driving high-volume production and Europe and North America pushing high-specification designs, suppliers balance cost efficiency with performance leadership to maintain their market positions.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
Recent Developments
- In November 2025, Microchip Technology, Inc. announced the launch of its LAN866x family of 10BASE-T1S endpoint devices with Remote Control Protocol (RCP) to extend Ethernet connectivity to edge nodes in zonal automotive architectures.
- In 2025, Texas Instruments announced the launch of its TCAN6062-Q1 Transceiver, which supports the ISO 11898‑2:2024 (CAN XL) specification with fast-mode data signalling up to 20 Mbps and SIC mode up to 8 Mbps.
- In 2022, Broadcom, Inc. unveiled its initial 50G automotive Ethernet switch product family, the BCM8958X, designed to meet the growing bandwidth needs for in-vehicle networking applications and facilitate the adoption of software-defined vehicles (SDVs)
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Protocol, Application and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Automotive transceivers will see strong adoption as vehicles transition toward centralized and zonal electronic architectures.
- High-speed automotive Ethernet will expand rapidly to support sensor fusion, ADAS, and infotainment data demands.
- CAN FD will continue replacing traditional CAN in powertrain and body domains for higher data throughput.
- Growth in electric vehicles will increase demand for transceivers in battery management, inverter control, and thermal management systems.
- ADAS and semi-autonomous driving functions will require more deterministic and low-latency communication interfaces.
- Cybersecurity-enhanced transceivers will gain prominence as vehicles become more connected and software-defined.
- Miniaturized, low-power transceiver designs will rise to support compact module integration in EV platforms.
- Integration of diagnostics and functional safety features will become standard across premium and mid-range vehicles.
- Asia-Pacific will remain the major manufacturing hub driving high-volume transceiver deployment.
- Increasing digital cockpit and infotainment complexity will accelerate the shift to multi-protocol, high-bandwidth communication solutions.




