Market Overview
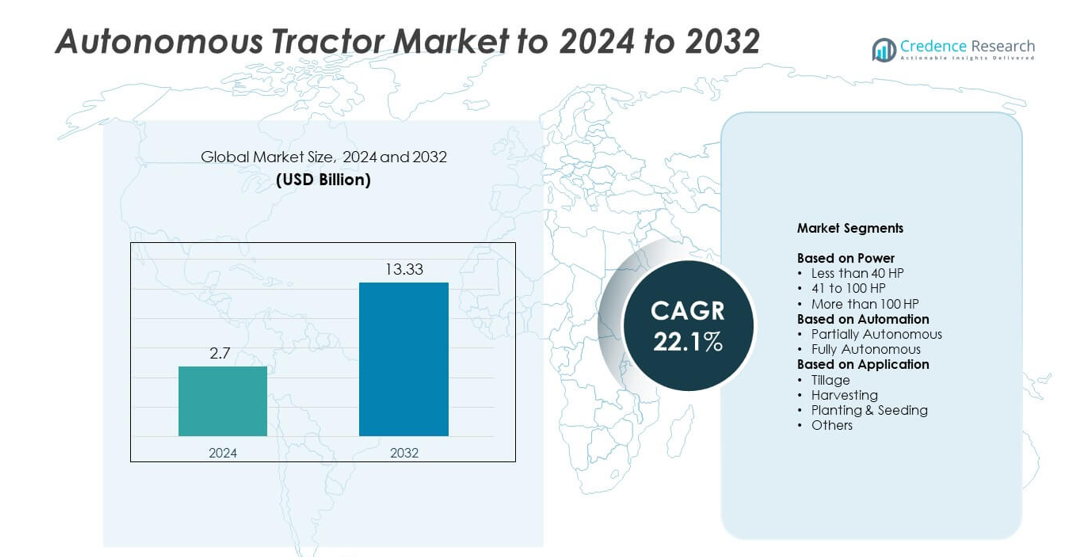
Autonomous Tractor Market size was valued at USD 2.7 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 13.33 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 22.1% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Autonomous Tractor Market Size 2024 |
USD 2.7 billion |
| Autonomous Tractor Market, CAGR |
22.1% |
| Autonomous Tractor Market Size 2032 |
USD 13.33 billion |
The Autonomous Tractor Market is led by major players including Kubota Corporation, TYM Corporation, Monarch Tractor, AGCO Corporation, Claas KGaA mbH, Yanmar Co., Ltd., Mahindra & Mahindra, CNH Industrial, John Deere (Deere & Company), and SDF Group. These companies strengthen the market through advanced automation platforms, AI-based navigation, and precision farming technologies. North America emerged as the leading region in 2024 with about 38% market share, supported by strong digital infrastructure and high adoption of precision agriculture. Europe followed with nearly 29% share, driven by sustainability policies and rapid mechanization, while Asia Pacific accounted for around 24% due to expanding smart-farming investments.
Market Insights
- The Autonomous Tractor Market was valued at USD 2.7 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 13.33 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 22.1%.
- Strong market growth is driven by rising labor shortages, expanding precision farming adoption, and increasing demand for higher farm productivity across major agricultural economies.
- Key trends include rapid integration of AI, growth of fully autonomous prototypes, and rising interest in electrified tractor designs that support sustainability goals.
- The competitive landscape features established global manufacturers advancing automation platforms, remote fleet control, and sensor-driven navigation systems to strengthen market positioning.
- North America led the market with about 38% share in 2024, followed by Europe at nearly 29% and Asia Pacific at around 24%, while the 41 to 100 HP segment held the dominant share of approximately 46% across power categories.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Power
The 41 to 100 HP category held the dominant share in 2024, accounting for about 46% of the Autonomous Tractor Market. Mid-range power tractors remained the preferred choice due to strong suitability for diverse farm sizes and cost-efficient field operations. Farmers adopted these tractors widely because they balance fuel use, automation capability, and operational control. Their compatibility with guidance systems, automated steering, and remote monitoring tools supported rapid deployment across global farms. Strong demand from row-crop farming and mixed-crop operations further reinforced segment leadership.
- For instance, Fendt’s 200 Vario tractors span from 79 hp to 124 hp.
By Automation
Partially autonomous tractors dominated this segment in 2024 with nearly 58% share. Farmers selected these systems because they offer lower upfront cost compared with fully autonomous models while still improving accuracy and labor efficiency. The segment grew as operators used features such as GPS-based steering, path planning, and automated turning to reduce operator fatigue. Wider availability from leading manufacturers also supported faster adoption. Strong performance across medium and large farms positioned partially autonomous tractors as a practical entry point into automation.
- For instance, Sabanto reports that its autonomous retrofit system seeded 872 acres in 113.5 hours with a single tractor, showing how partially autonomous machines can handle long operations with minimal on-board labor.
By Application
Tillage led the application segment in 2024 with around 40% share of the Autonomous Tractor Market. Strong demand came from farms seeking higher precision in soil preparation, reduced labor dependency, and consistent field depth. Autonomous systems provided improved control during repetitive tillage tasks, helping farmers cut fuel waste and time. The segment expanded further as large commercial farms adopted autonomous tractors for continuous, long-duration operations. Strong integration with mapping tools and real-time field data also helped growers boost operational efficiency in the tillage process.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Labor Shortages in Agriculture
Farm labor shortages pushed farmers to adopt autonomous tractors to maintain productivity. Many regions faced reduced seasonal labor availability, forcing growers to rely on automation for critical tasks. Autonomous tractors helped sustain large-scale operations through consistent output and reduced downtime. Farmers preferred these systems because they lowered labor costs and improved field precision. This steady shift strengthened long-term adoption across small and large farms.
- For instance, Sabanto retrofits 5100E utility tractors for unattended fieldwork using autonomy kits.
Advancements in Precision Farming Technologies
Rapid growth in precision farming tools boosted demand for autonomous tractors. Technologies such as GPS guidance, machine vision, and advanced sensors improved field accuracy and reduced input waste. Farmers used these tractors to achieve better soil management and optimized resource use. Strong integration with mapping platforms allowed operators to monitor conditions in real time. These improvements increased operational efficiency and encouraged broader adoption across crop types.
- For instance, CNH’s tillage automation can hold working depth to one-tenth-inch accuracy.
Strong Push for Higher Farm Productivity
Farmers adopted autonomous tractors to increase productivity and reduce delays during peak seasons. Automated operations supported round-the-clock working cycles, which helped finish tasks faster and with higher consistency. These systems reduced human error and delivered uniform performance across large fields. Growers used them to control fuel use, improve soil health, and boost crop yields. This productivity advantage remained a key motivator for growth in advanced farming regions.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Expansion of Fully Autonomous Tractor Prototypes
Manufacturers accelerated testing of fully autonomous tractors, creating new opportunities for future deployment. These models attracted interest due to complete hands-free operation and better integration with digital farm platforms. Trials focused on navigation accuracy, safety features, and remote fleet control. As reliability increased, demand shifted toward full automation for labor-intensive tasks. This trend encouraged development of new business models, including subscription-based autonomous tractor services.
- For instance, Monarch’s MK-V electric tractor delivers up to 14 operating hours per charge.
Rising Integration of AI and Data Analytics
AI-enabled systems created major opportunities by improving field decision-making and operational accuracy. Advanced algorithms analyzed soil patterns, weather changes, and machinery behavior to optimize tractor performance. Farmers used these insights to reduce input costs and predict field needs more effectively. Data-driven automation also improved route planning and minimized equipment wear. The growing role of digital intelligence positioned autonomous tractors as a core part of smart-farm ecosystems.
- For instance, NVIDIA’s Jetson AGX Xavier offers 32 TOPS while running at 10–30 watts.
Growth of Electrified and Sustainable Tractor Designs
Sustainability trends encouraged manufacturers to develop electric and hybrid autonomous tractors. These models supported lower emissions, reduced noise, and improved long-term operating costs. Farmers with environmental goals adopted cleaner propulsion systems to meet regulatory expectations. As battery technology advanced, electrified tractors delivered better power efficiency and longer run times. This shift opened significant opportunities in regions promoting low-carbon farming solutions.
Key Challenges
High Initial Capital Investment
High purchase costs limited adoption, especially among small and medium-scale farmers. The need for advanced sensors, AI hardware, and autonomous platforms increased equipment prices. Many growers struggled to justify large upfront spending despite long-term benefits. Limited financing options further slowed deployment in developing regions. This challenge remained a major barrier for widespread adoption of autonomous tractors.
Lack of Rural Connectivity and Digital Infrastructure
Autonomous tractors relied heavily on stable connectivity for navigation and real-time monitoring. Rural areas with weak network coverage faced disruptions that affected operational accuracy. Many farms lacked the digital infrastructure needed for seamless communication between machines and control systems. This gap slowed automation adoption and reduced efficiency in remote locations. Improving connectivity became essential for unlocking full autonomous potential.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America held the largest share of the Autonomous Tractor Market in 2024 with about 38%. Demand increased as large farms invested in automation to counter labor shortages and rising operational costs. Strong adoption of precision farming tools and supportive digital infrastructure encouraged faster deployment across the United States and Canada. Manufacturers expanded field trials and introduced advanced semi-autonomous and fully autonomous models suited for large-scale operations. The region benefited from high awareness, strong technology readiness, and early integration of sensors, GPS guidance, and AI-driven systems across key crop-producing states.
Europe
Europe accounted for nearly 29% of the market in 2024, supported by strong mechanization and sustainability-driven farming policies. Countries such as Germany, France, and the United Kingdom adopted autonomous tractors to address labor gaps and improve resource efficiency. Growth accelerated as farms embraced digital platforms, remote monitoring, and low-emission machinery. The region saw rising interest in electric and hybrid autonomous tractors due to environmental regulations. Strong support programs and innovation centers helped expand automation across medium and large farms. Wider use of precision technologies strengthened the region’s long-term market position.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific captured around 24% of the Autonomous Tractor Market in 2024 as large agricultural economies increased mechanization efforts. Demand grew quickly in China, India, Japan, and Australia, driven by expanding farm sizes and rising investment in smart farming. Government programs promoting automation and precision agriculture accelerated technology adoption. Local manufacturers introduced cost-effective autonomous tractor models suited for regional farming conditions. Strong digital expansion and rising awareness improved farmer readiness. The region’s rapid shift toward efficient and high-yield processes positioned Asia Pacific as one of the fastest-growing markets.
Latin America
Latin America held nearly 6% share in 2024, supported by growing interest in advanced mechanization across major farming countries such as Brazil and Argentina. Large-scale soybean, corn, and sugarcane producers invested in autonomous tractors to manage vast field areas with fewer manual workers. Adoption increased as farms focused on improving efficiency, reducing fuel waste, and enhancing crop consistency. The region benefited from expanding precision farming programs and partnerships between global manufacturers and local distributors. Rising digital adoption and higher production demands created steady opportunities for long-term growth.
Middle East & Africa
Middle East & Africa accounted for about 3% of the market in 2024, driven by gradual modernization of farming practices. Countries in the Gulf region adopted autonomous tractors to address extreme climate conditions and labor constraints. Parts of Africa showed early interest as governments supported mechanization to improve food security. Limited connectivity and budget constraints slowed widespread adoption, but pilot projects highlighted strong long-term potential. Improving digital infrastructure and rising investment in controlled-environment farming encouraged slow but steady adoption of autonomous tractor technologies across the region.
Market Segmentations:
By Power
- Less than 40 HP
- 41 to 100 HP
- More than 100 HP
By Automation
- Partially Autonomous
- Fully Autonomous
By Application
- Tillage
- Harvesting
- Planting & Seeding
- Others
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The Autonomous Tractor Market is shaped by leading players such as Kubota Corporation, TYM Corporation, Monarch Tractor, AGCO Corporation, Claas KGaA mbH, Yanmar Co., Ltd., Mahindra & Mahindra, CNH Industrial, John Deere (Deere & Company), and SDF Group. The competitive environment continues to strengthen as manufacturers invest heavily in automation technologies, AI-enabled navigation, and precision farming platforms. Companies focus on developing tractors with advanced sensors, autonomous steering, and improved safety features to support long working hours with minimal human involvement. Strong emphasis on software integration, remote fleet control, and electrified models drives differentiation across the market. Strategic partnerships with agritech firms, digital platform providers, and research institutions help expand product capabilities. Vendors also compete by offering scalable automation solutions that suit both large commercial farms and medium-size operators. Growing demand for sustainable machinery and government support for smart farming further intensify competition, pushing continuous innovation across global markets.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Kubota Corporation
- TYM Corporation
- Monarch Tractor
- AGCO Corporation
- Claas KGaA mbH
- Yanmar Co., Ltd.
- Mahindra & Mahindra
- CNH Industrial
- John Deere (Deere & Company)
- SDF Group
Recent Developments
- In 2025, John Deere unveiled its second-generation autonomy kit and four new autonomous machines, including the Autonomous 9RX Tractor for large-scale agriculture and the Autonomous 5ML Orchard Tractor, at CES 2025
- In 2025, Kubota North America announced a strategic collaboration with Agtonomy to commercialize autonomous operations on Kubota diesel tractors, including the M5N series.
- In 2025, Mahindra showcased alternate fuel tractors including CNG/CBG, ethanol flex-fuel, and electric models at Agrovision 2025.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Power, Automation, Application and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market will expand as farmers adopt automation to handle labor shortages.
- Fully autonomous tractor models will gain momentum with better reliability.
- AI-driven decision tools will enhance field accuracy and reduce input waste.
- Electrified autonomous tractors will grow as sustainability pressures increase.
- Remote fleet management will become a standard feature across large farms.
- Sensor integration will improve soil mapping, route planning, and real-time control.
- Subscription and leasing models will rise as farmers seek lower upfront costs.
- Government support for smart farming will accelerate adoption in emerging regions.
- Connectivity upgrades in rural areas will improve autonomous tractor performance.
- Partnerships between tech firms and OEMs will speed up product innovation.




