Market Overview:
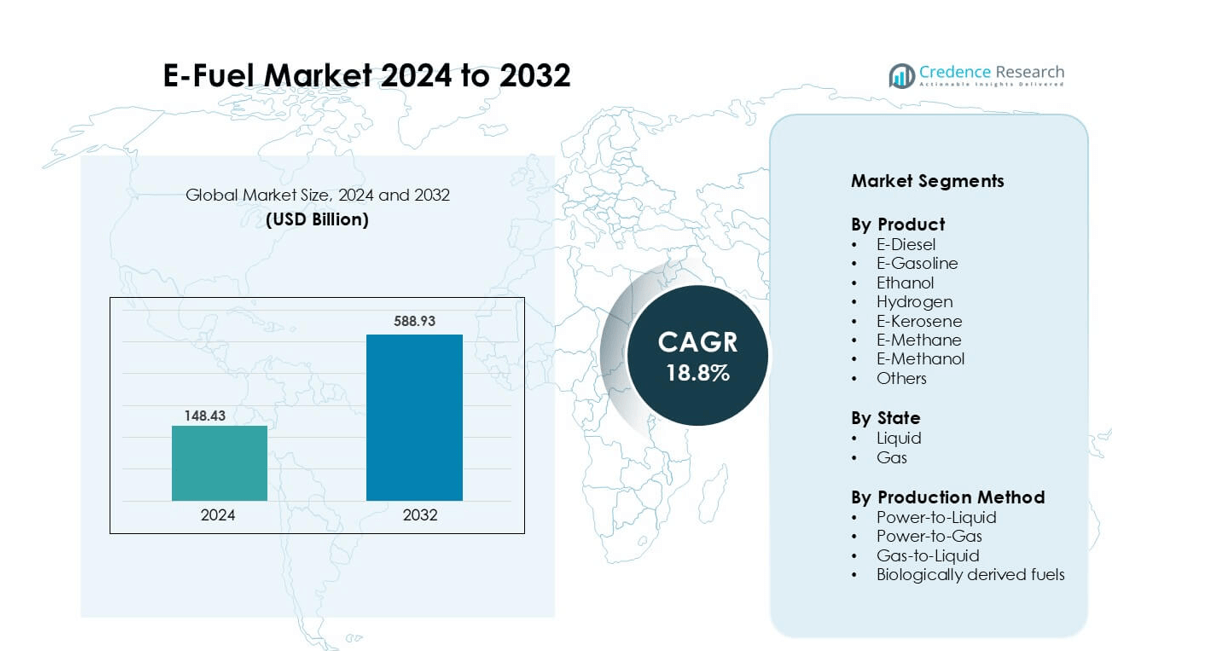
E-Fuel Market was valued at USD 148.43 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 588.93 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 18.8 % during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| E-Fuel Market Size 2024 |
USD 148.43 billion |
| E-Fuel Market, CAGR |
18.8% |
| E-Fuel Market Size 2032 |
USD 588.93 billion |
The E-Fuel market includes key players such as Archer Daniels Midland Co., E-Fuel Corporation, Neste, Ceres Power Holding Plc, Ballard Power Systems, Inc., Norsk e-Fuel AS, Hexagon Agility, Clean Fuels Alliance America, eFuel Pacific Limited, and Climeworks AG. These companies focus on large-scale Power-to-Liquid projects, renewable hydrogen integration, carbon capture, and synthetic fuel production for aviation, marine, and heavy-duty transport. Strategic partnerships, technology advancements, and long-term supply agreements strengthen competitiveness. Europe leads the market with a 41% share, supported by strict emission regulations, strong renewable infrastructure, and government-backed investment in Power-to-X facilities and sustainable aviation fuel supply.
Market Insights
- The E-Fuel market was valued at USD 148.43 billion in 2024 and is expected to grow at a 18.8% CAGR during the forecast period.
- Government decarbonization policies, aviation fuel mandates, and demand for drop-in alternatives to fossil fuels drive strong adoption across transport and industrial sectors.
- Synthetic kerosene and e-diesel lead product adoption due to engine compatibility, while the liquid state segment holds a dominant 67% share because it supports existing fuel logistics and storage systems.
- The market is competitive, with companies such as Neste, Archer Daniels Midland Co., Norsk e-Fuel AS, and Climeworks AG expanding Power-to-Liquid capacity, carbon capture, and hydrogen technology to reduce production cost and scale commercial supply.
- Europe accounts for 41% of the global share, supported by strict carbon policies and large renewable capacity, while North America and Asia Pacific increase investment in aviation-grade synthetic fuels and hydrogen-based production.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Product
E-Diesel leads this segment with a 32% market share due to strong demand from commercial fleets seeking low-carbon drop-in fuels. Logistics operators prefer E-Diesel because it works with existing diesel engines and infrastructure, avoiding costly hardware changes. Growing adoption in freight transport, mining trucks, and marine vessels strengthens its position. Government incentives for renewable diesel blending and lower lifecycle emissions also support growth. Other products like E-Gasoline and E-Kerosene gain traction in mobility and aviation, but E-Diesel remains dominant because of scalability, compatibility, and rapid decarbonization benefits for heavy transport.
- For instance, Diamond Green Diesel LLC (a joint venture between Valero Energy Corporation and Darling Ingredients Inc.) has expanded its renewable diesel production capacity to approximately 1.2 billion gallons per year.
By State
The liquid segment dominates with a 67% market share, driven by ease of storage, transport, and blending with traditional fuels. Liquid e-fuels integrate with current fuel supply chains and refueling systems, enabling quick deployment across road, marine, and aviation sectors. Refiners and producers prioritize liquid formats to meet emission targets without replacing engines or distribution networks. Gas-state fuels are expanding in power generation and industrial heating, but their reliance on pressurized systems slows adoption. Strong uptake of e-diesel, e-gasoline, and e-kerosene ensures that liquids remain the preferred state across global markets.
- For instance, HIF Global’s demonstration facility in Chile (Haru Oni) started with a capacity of 0.13 million litres per year of e-gasoline.
By Production Method
Power-to-Liquid holds the largest share at 48%, supported by expanding renewable electricity capacity and large-scale carbon capture systems. This method converts green hydrogen and captured CO₂ into synthetic liquid fuels that replicate fossil fuel performance. The aviation and marine sectors rely on Power-to-Liquid technologies to cut emissions without redesigning engines or logistics assets. Investments from fuel producers and energy companies drive higher output, while stricter decarbonization targets accelerate demand. Other methods such as Power-to-Gas and biologically derived fuels are increasing, but Power-to-Liquid remains the most scalable pathway for commercial mobility and aviation fuel supply.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Decarbonization Targets Across Transportation
Global emission reduction mandates are accelerating the need for clean fuels, pushing governments and industries to transition toward low-carbon energy sources. Aviation, maritime, trucking, and heavy-duty vehicles face limited electrification feasibility because of long-range requirements and high energy density needs. E-fuels provide a drop-in alternative that works with current engines, reducing carbon emissions without replacing fleets or infrastructure. Policies such as carbon taxes, renewable fuel quotas, and international aviation frameworks support adoption. Corporations also commit to net-zero goals, driving demand for sustainable liquid fuels. Infrastructure compatibility, long lifecycle emissions reduction, and global policy alignment make e-fuels a practical route for large industries seeking fast decarbonization.
- For instance, Neste Corporation’s “Veturi” e‑fuel research project produced hundreds of kilograms of synthetic hydrocarbons, refined into drop‑in e‑diesel and tested in a tractor in Finland in late 2023.
Expanding Renewable Energy and Power-to-X Investments
Increasing deployment of solar and wind power creates surplus clean electricity, which producers convert into e-fuels through Power-to-X technology. This pathway enables storage of renewable energy in fuel form, supporting energy security and grid balancing. Hydrogen electrolysis, captured CO₂ utilization, and synthetic fuel production benefit from falling renewable energy costs. Large energy companies and fuel refiners invest in industrial-scale plants to produce e-diesel, e-kerosene, and e-methanol. Government funding and private partnerships accelerate commercialization, especially in regions with strong renewable capacity such as Europe and North America. As renewable infrastructure expands, e-fuel output increases, improving cost efficiency and global supply reliability.
- For instance, Norsk e-Fuel AS is developing a Power-to-Liquid plant in Mosjøen, Norway, designed to produce 50 million liters of e-Crude annually, of which up to 40 million liters will be upgraded to synthetic aviation fuel (SAF) using renewable electricity and captured CO₂.
Aviation and Marine Sector Adoption
Airlines and shipping companies face strict decarbonization rules and limited alternatives to fossil fuels. Battery technology lacks required energy density for long-haul flights and ocean transport, making e-fuels a strategic choice. Synthetic aviation fuels blend seamlessly with existing jet engines and refueling systems, helping carriers meet emission goals without changing hardware. Marine operators use e-diesel, e-methanol, and e-gas as cleaner propulsion solutions. International Maritime Organization and aviation fuel standards push adoption, supported by pilot projects and commercial agreements between airlines, ports, and e-fuel producers. These sectors create steady, long-term demand, accelerating market growth.
Key Trend & Opportunity
Carbon Capture Integration and Circular Carbon Pathways
Producers increasingly combine direct air capture and industrial CO₂ recovery with renewable power to manufacture synthetic fuels. This creates a circular pathway that reuses emissions instead of releasing them, supporting low lifecycle carbon intensity. Governments and energy companies invest in carbon capture clusters near industrial hubs, enabling large-scale feedstock availability for e-fuel production. This trend presents major opportunities in aviation and shipping, where fuel-embedded carbon footprints play a key role in regulatory compliance. As carbon accounting frameworks mature, synthetic fuels with verified carbon reuse gain competitive advantage over traditional fossil options.
- For instance, Climeworks AG operates a direct air capture plant in Iceland that captures 4,000 metric tons of CO₂ per year, which is then mineralized or supplied for synthetic fuel projects.
Commercialization of Power-to-Liquid Plants
Demonstration plants are scaling into commercial production facilities, enabling thousands of tons of annual synthetic fuel output. Producers leverage modular electrolyzers, advanced catalysts, and efficient CO₂-to-fuel conversion routes to lower costs. Countries with strong renewable capacity partner with oil companies and technology developers to build new synthetic kerosene, methanol, and gasoline plants. Commercial aviation biofuel programs expand to include synthetic alternatives, attracting long-term supply contracts. Increasing output reduces price gaps and enhances market confidence, creating new opportunities for global trade and refinery integration.
- For instance, Norsk e-Fuel is indeed planning a plant in Herøya, Porsgrunn, which is engineered to eventually produce 100 million liters per year of renewable (synthetic) e-Fuel using renewable electricity and captured CO₂.
Key Challenge
High Production Costs and Limited Scale
E-fuel production remains more expensive than conventional fuels because of capital-intensive electrolyzers, renewable power requirements, and carbon capture infrastructure. Limited commercial-scale plants restrict output and lead to higher per-unit fuel prices. Competing low-carbon options, such as biofuels and electric mobility, increase cost pressure. Subsidies, carbon credits, and long-term supply agreements are helping improve economics, but widespread price competitiveness remains many years away. Producers must expand capacity, improve conversion efficiency, and reduce equipment cost to reach commercial scale.
Energy Consumption and Efficiency Losses
Synthetic fuels require large amounts of clean electricity and face energy losses during conversion from power to liquid fuel. In regions without high renewable availability, producers risk relying on grid electricity, weakening carbon reduction benefits. Storage, transport, and distribution add further energy requirements. To solve this, manufacturers focus on improving electrolyzer efficiency, catalyst performance, and integrated renewable supply. While technological advancements continue, energy intensity remains one of the most difficult barriers to large-scale global adoption
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds a 27% market share, supported by strong growth in renewable electricity and decarbonization mandates across aviation and marine sectors. The United States leads with federal clean fuel standards, tax incentives, and large-scale Power-to-Liquid projects backed by energy companies and aircraft operators. Airlines sign long-term offtake agreements for synthetic aviation fuel, while ports adopt e-diesel and e-methanol for cleaner maritime operations. Canada expands investment in hydrogen and carbon capture, strengthening cross-border collaboration. The region benefits from advanced infrastructure, mature refiners, and strong technology partnerships, driving commercialization and domestic production capacity.
Europe
Europe dominates the global e-fuel market with a 41% market share, driven by strict carbon neutrality targets and heavy investment in Power-to-X infrastructure. Germany, the UK, and Nordic countries support industrial plants for e-kerosene, e-diesel, and hydrogen-based fuels. EU policies such as Fit for 55 and Sustainable Aviation Fuel mandates create stable demand, especially across long-haul air transport. Major airlines and shipping companies commit to synthetic fuel adoption, supported by government subsidies and carbon pricing frameworks. Strong renewable energy generation and large carbon capture clusters further boost fuel production and export potential.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific accounts for 22% of the market, led by Japan, South Korea, China, and Australia. Japan and South Korea invest in hydrogen and synthetic kerosene programs to decarbonize aviation and heavy industries. China leverages large renewable capacity and carbon capture sites to scale methanol and synthetic gasoline production. Australia focuses on exporting renewable-based e-fuels to Asia and Europe, supported by large solar-to-hydrogen infrastructure. Growing air traffic, industrial energy demand, and net-zero strategies create strong long-term opportunities. Regional partnerships with global fuel producers accelerate technology deployment and plant development.
Latin America
Latin America holds a 6% share, with early adoption driven by Brazil, Chile, and Argentina. Chile leads with renewable hydrogen projects and Power-to-Liquid investments supported by large solar and wind resources. Brazil leverages existing biofuel expertise to transition into synthetic fuel blending, particularly for aviation and road transport. Regional governments promote export-driven production capacity to supply Europe and North America. However, infrastructure gaps and limited scale keep adoption moderate. As international trade routes expand and investment increases, the region becomes a strategic supplier of renewable-based synthetic fuels.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region captures a 4% market share, driven by growing diversification away from fossil fuel dependency. Saudi Arabia and the UAE invest in green hydrogen and synthetic fuel projects linked to renewable mega-farms and industrial zones. E-methanol and e-diesel gain interest for shipping and logistics operations across major ports. Africa’s potential lies in renewable-rich countries like Morocco and South Africa, attracting foreign partnerships and pilot Power-to-X ventures. Limited commercialization and technology costs slow adoption, but strategic investments position the region as a future exporter of low-carbon synthetic fuels.
Market Segmentations:
By Product
- E-Diesel
- E-Gasoline
- Ethanol
- Hydrogen
- E-Kerosene
- E-Methane
- E-Methanol
- Others
By State
By Production Method
- Power-to-Liquid
- Power-to-Gas
- Gas-to-Liquid
- Biologically derived fuels
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The E-Fuel market features a mix of fuel producers, technology developers, renewable energy firms, and carbon capture specialists competing to scale commercial production. Major companies such asNeste, Norsk e-Fuel AS, and E-Fuel Corporation focus on Power-to-Liquid development for aviation and heavy transport. Climeworks AG and Ceres Power Holding Plc strengthen the value chain through direct air capture and electrolyzer innovations. Ballard Power Systems, Inc. and Hexagon Agility supply hydrogen and storage solutions that enable fuel distribution. Traditional energy players form partnerships with governments and aircraft operators to secure long-term offtake agreements. Most companies prioritize reducing production costs, expanding pilot plants into industrial-scale facilities, and forming international supply networks. The competitive environment is shaped by carbon mandates, technological efficiency, renewable energy availability, and financing access. Firms with strong renewable portfolios, efficient conversion technologies, and certified low-carbon fuel options hold a strategic advantage as global regulations tighten.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
Recent Developments
- In September 2025, Hexagon Agility Announces receipt of new orders in North America for natural-gas fuel systems supporting heavy-duty truck fleets transitioning from diesel.
- In February 2025, Partnered with RES Group and Prime Capital AG to develop Project Alby in Ånge, Sweden, targeting annual output of ~80,000 tons e-SAF
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Product, State, Production Method and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Demand for synthetic aviation fuels will rise as airlines meet stricter emission targets.
- Power-to-Liquid plants will expand, shifting from pilot operations to commercial-scale production.
- Falling renewable electricity costs will improve e-fuel price competitiveness.
- Carbon capture integration will help producers lower lifecycle emissions and gain certification advantages.
- Maritime operators will increase use of e-diesel, e-methanol, and e-gas for clean shipping.
- Governments will introduce additional fuel blending mandates and carbon-based penalties.
- Technology partnerships between energy firms and aircraft manufacturers will strengthen supply security.
- Hydrogen and methanol-based e-fuels will gain adoption in heavy industry and long-distance transport.
- New trade routes will develop as renewable-rich regions export e-fuel to global markets.
- Advances in electrolyzers and catalysts will improve conversion efficiency and reduce production losses.




