Market Overview
Early Production Facility Market was valued at USD 15.03 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 19.19 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 3.1% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Early Production Facility Market Size 2024 |
USD 15.03 billion |
| Early Production Facility Market, CAGR |
3.1% |
| Early Production Facility MarketSize 2032 |
USD 169.91 million |
The Early Production Facility market features key players such as Huichuan International, Expro, Penspen, CPPE, PETECS, OilSERV, Halliburton, CECO Environmental, Global Process Systems, and EN-FAB. These companies provide modular separation units, gas treatment systems, flare packages, and mobile processing facilities that support fast field monetization and reservoir appraisal. Many suppliers focus on skid-mounted designs, rental models, and digital monitoring platforms to reduce installation time and operating costs in remote wells. The Middle East & Africa remains the leading region with 38% market share, supported by large exploration programs, high-capacity production, and strong investment from national oil companies seeking rapid commercialization of new discoveries.
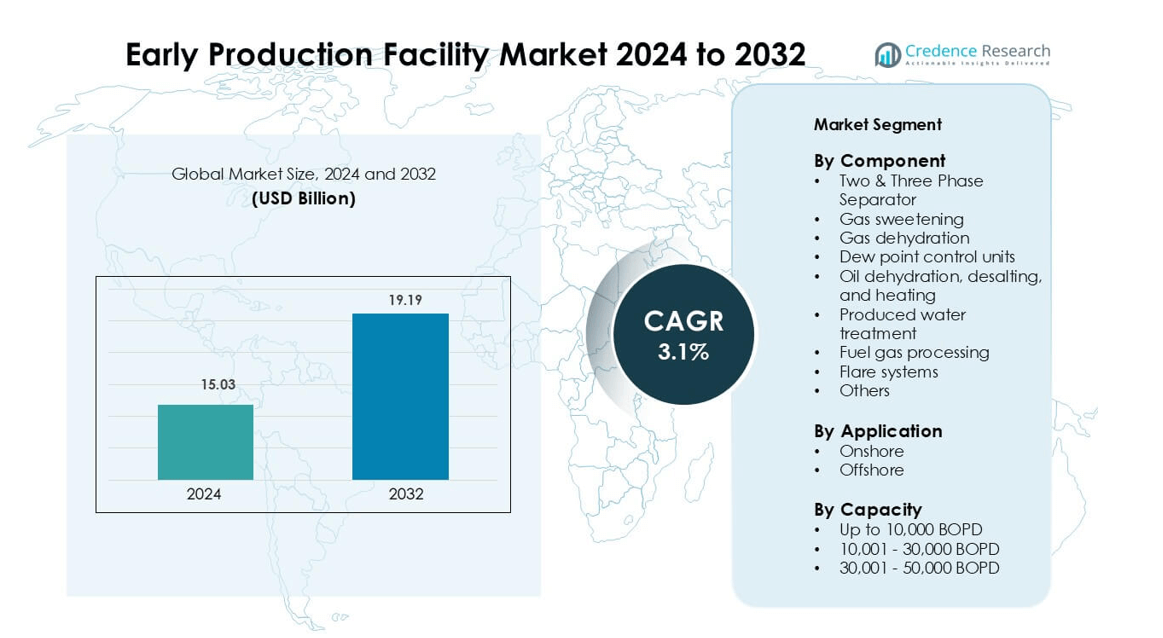
Market Insights
- The Early Production Facility market is valued at USD 15.03 Billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 19.19 Billion by 2032 at a 3.1% CAGR.
- Rapid monetization of new oil discoveries drives investment in modular EPFs that support fast installation, lower capital spending, and early revenue generation for marginal and remote fields.
- Key trends include adoption of skid-mounted systems, produced water treatment, digital monitoring, and low-emission flare units, improving operational uptime and environmental compliance.
- The Middle East & Africa leads the market with 38% share, while North America follows with 28%, driven by shale and tight-oil projects that rely on mobile EPFs.
- Two & Three Phase Separators hold the largest segment share at 32%, but smaller operators face restraints from high maintenance costs, skilled workforce shortages, and strict environmental approvals for water discharge and flare emissions.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Component
Two & Three Phase Separator holds the largest share of the Early Production Facility market, capturing 32% due to its vital role in separating oil, gas, and water at the wellhead for faster commercialization. Gas sweetening and dehydration units also see wide adoption in sour gas fields where hydrogen sulfide and moisture removal improve downstream efficiency. Produced water treatment solutions gain traction as operators aim to meet discharge regulations and improve water reuse. Rising demand for mobile EPF units in remote blocks supports growth of flare systems, fuel gas processing, and dew point control units for safe and continuous flow assurance.
- For instance, Expro has deployed modular solutions in the North Sea for specific projects, including a modular flow-back package for an operator that ensured timely first oil and enhanced efficiency.
By Application
Onshore operations dominate the market with 61% share, supported by expanding exploration across marginal, stranded, and shale reservoirs. Onshore EPF units offer faster setup, low capital cost, and higher mobility, making them suitable for appraisal and early cashflow generation. Offshore application continues to grow as operators deploy modular EPF systems for deep-water tiebacks and short-life reservoirs. EPFs reduce shutdown risk, enable early monetization, and optimize process stabilization before full production platforms are installed.
- For instance, Halliburton delivered an offshore EPF package for a West African deep-water operator that processed 18,000 barrels per day with a compact three-phase separator, gas dehydration skid, and produced-water treatment system, allowing continuous flowback and testing while full topside facilities were still under construction.
By Capacity
Facilities with capacity Up to 10,000 BOPD hold 46% share because small and mid-size explorers prefer low-cost, skid-mounted units that accelerate field appraisal and minimize infrastructure needs. The 10,001–30,000 BOPD range gains traction in brownfield redevelopment where operators seek higher throughput without building permanent processing plants. Higher-capacity EPFs above 30,000 BOPD support offshore and mature basin projects needing faster hydrocarbon separation at scale. Growing investment in modular units and short-cycle development continues to push demand across all capacity ranges.
Key Growth Drivers
Rapid Monetization of New Oil Discoveries
Early Production Facilities help operators generate revenue within months, instead of waiting years for a full permanent plant. This faster monetization makes EPFs a preferred choice for marginal fields, unconventional blocks, and remote discoveries. Companies reduce financial risk by validating the reservoir early, improving well-testing accuracy, and optimizing long-term facility planning. Modular EPFs support phased development, allowing producers to expand capacity once reservoir performance stabilizes. Lower upfront investment improves return on capital, which attracts private operators and national oil firms. Many nations with untapped reserves use EPFs to boost local production and reduce crude imports. These economic advantages make rapid field development a critical growth driver.
- For instance, Expro deployed a modular EPF in Kurdistan capable of processing 25,000 barrels per day with integrated metering, gas compression, and water handling, allowing the operator to begin oil sales in September 2015.
Rising Focus on Portable and Modular Oilfield Processing
Operators now demand flexible surface facilities that can move from one field to another. Modular EPFs use skid-mounted designs that reduce setup time and transportation costs. Contractors can install separation, sweetening, heating, dehydration, and flare systems without heavy infrastructure. This flexibility fits short-life wells, appraisal campaigns, and pilot development. Many shale and tight-oil producers use EPFs to handle fast well hookups and frequent changes in production rates. EPC companies offer rental models that avoid high capital spending. Modular deployment also improves compliance with flaring limits and water disposal rules. The growing shift toward portable facilities strongly drives global demand.
- For instance, Expro supplied a relocatable EPF package for a Middle East operator that included a three-phase separator, gas treating skid, and a produced-water unit capable of processing 15,000 barrels per day, while the entire system remained transportable on standard trucks for redeployment between remote well pads.
Expansion of Oil and Gas Projects in Emerging Regions
Countries in Africa, the Middle East, Latin America, and Asia are opening new blocks to global investors. Many fields in these regions lack processing pipelines, storage networks, or gathering systems. EPFs solve this gap by delivering oil that meets export quality standards without full infrastructure. National oil companies use EPFs to accelerate field appraisal and avoid delays caused by logistics or regulatory approvals. Offshore exploration also supports demand, as operators prefer temporary processing units for tiebacks and pilot wells. Growth in unconventional resources, enhanced oil recovery plans, and marginal field redevelopment further drives EPF adoption across developing markets.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Growth of Digital Monitoring and Automated Process Control
Digital EPFs now use smart sensors, remote control, cloud dashboards, and predictive maintenance software. This reduces downtime, improves safety, and helps operators manage sour gas, heavy crude, and unstable flow conditions. Real-time monitoring lowers flaring, improves water reinjection quality, and optimizes separation efficiency. Automated chemical dosing and emission tracking help meet stricter safety and environmental rules. Investment in digitalization creates strong opportunities for technology vendors and EPC contractors offering integrated smart-EPF packages.
- For instance, The Leucipa solution is currently running on over 70,000 wells globally across 20 countries, a much larger number than 2,000.
Increased Demand for Water Treatment and Emission-Controlled EPFs
Produced water volumes are rising in many basins, driving demand for efficient desalting, filtration, and disposal units. New designs support oil-water separation, reinjection, and reuse to meet environmental limits. Emission-controlled flare systems gain traction as governments tighten methane and VOC restrictions. Energy-efficient heaters and low-NOC burners reduce processing costs. This trend opens commercial opportunities for companies with advanced separation media, chemical additives, and compact treatment units.
- For instance, CECO Environmental specializes in environmental solutions, including produced water treatment and oily water separators.
Key Challenges
High Operational Complexity in Harsh Environments
EPFs operate in remote deserts, jungles, offshore zones, and high-temperature fields. Corrosion, sand production, high-pressure fluids, and sour hydrocarbons require advanced metallurgy and frequent maintenance. Any equipment failure stops production and reduces cash flow. Logistics and spare-parts supply add complexity in landlocked countries. Skilled workforce shortages increase safety risks and downtime. These challenges limit adoption among small operators.
Stringent Environmental and Regulatory Compliance
Governments are tightening rules on gas flaring, water discharge, emissions, and chemical use. Many aging EPFs require upgrades to meet new emission standards, adding cost. Delays in environmental approvals slow project timelines. Offshore regions have stricter limits on spills, flare emissions, and produced water discharge, which demands high investment in treatment units. Operators without strong compliance systems face penalties or shutdowns.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds 28% of the Early Production Facility market, driven by shale and tight-oil activity in the United States and Canada. Operators rely on modular EPFs to speed up production from short-life wells, avoid pipeline delays, and reduce upfront capital spending. Mobile skid-mounted systems support fast hook-ups in unconventional basins such as the Permian, Bakken, and Montney. Stricter flaring and water disposal rules increase demand for advanced separation, dehydration, and produced water treatment units. Rental-based EPF models and digital monitoring platforms help mid-sized companies manage costs while improving field testing and reservoir evaluation.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region leads the market with 38% share, supported by large-scale exploration campaigns and low-cost field development. National oil companies use EPFs to monetize newly drilled wells, manage sour gas fields, and handle high production rates in remote deserts and offshore zones. Strong activity in Saudi Arabia, UAE, Oman, Nigeria, and Angola drives adoption of large-capacity systems, including three-phase separators, sweetening, desalting, and flare packages. Governments support EPFs to boost exports and reduce project delays caused by permanent infrastructure approvals. Rising offshore tiebacks in West Africa strengthen demand for temporary processing units.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific accounts for 21% of the market, fueled by onshore development in China, India, Indonesia, and Australia. Many fields lack pipeline networks, making EPFs essential for fast commercialization. Small and mid-sized operators prefer compact modular packages with produced water treatment, dehydration, and fuel gas processing units. Growing interest in marginal fields and enhanced oil recovery projects increases adoption. Offshore EPFs also gain traction in deep-water assets in Malaysia and Indonesia. Regional investments in digital monitoring and low-emission flare systems support continued growth.
Europe
Europe holds 9% share, with demand centered on offshore projects in the North Sea and mature field redevelopment. Operators deploy EPFs to extend the life of declining wells and speed tiebacks to existing platforms. Strict environmental rules push adoption of emission-controlled flares, sour gas handling, and advanced water treatment. Countries such as the U.K., Norway, and Denmark use EPFs for rapid field appraisal before installing permanent topside units. Rental models and modular skids allow flexible deployment as production rates change over time.
Latin America
Latin America represents 4% of the market, mainly driven by new exploration in Brazil, Guyana, and Argentina. EPFs help operators handle early flow from deep-water and shale projects while full infrastructure is under construction. National oil companies use EPFs for marginal wells and pilot developments in remote basins. Produced water processing and desalting systems see demand due to strict discharge laws. However, slower project approvals and investment delays limit growth compared to other regions.
Market Segmentations:
By Component
- Two & Three Phase Separator
- Gas sweetening
- Gas dehydration
- Dew point control units
- Oil dehydration, desalting, and heating
- Produced water treatment
- Fuel gas processing
- Flare systems
- Others
By Application
By Capacity
- Up to 10,000 BOPD
- 10,001 – 30,000 BOPD
- 30,001 – 50,000 BOPD
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the Early Production Facility market includes engineering contractors, oilfield service companies, and modular equipment suppliers offering customized processing packages. Key players focus on skid-mounted separation, dehydration, sweetening, and produced water treatment systems designed for rapid deployment in remote fields. Companies expand portfolios through rental models, larger capacity modules, and digital monitoring platforms that improve operational uptime and reservoir evaluation. Many suppliers strengthen partnerships with national oil companies for long-term contracts and integrated field development services. Technology providers continue to upgrade flare control, low-emission burners, and compact oil-water separation units to meet stricter environmental standards. The industry also sees rising demand for modular offshore EPFs used in tiebacks, pilot wells, and short-life assets. Competitive advantage depends on manufacturing quality, fast delivery, engineering support, and proven performance in harsh environments. Players with global fabrication yards and strong after-sales service remain better positioned to secure projects in emerging resource regions.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
Recent Developments
- In October 2025, Penspen announced record-breaking year in Middle East & Africa with over US $400 million in project wins, which includes upstream developments relevant to the EPF market.
- In September 2025, Penspen strengthened leadership team with new European Director of Sales & Marketing, signalling strategic focus that may impact EPF business lines
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Component, Application, Capacity and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Demand for modular and mobile EPFs will rise as operators seek faster field monetization.
- Digital monitoring and automation will improve uptime, reduce flaring, and enhance process control.
- Produced water treatment units will gain wider use due to strict environmental rules and reinjection needs.
- Offshore tieback projects will adopt compact EPFs to handle early flow before permanent platforms start.
- Rental-based business models will expand, helping small and mid-size operators reduce capital spending.
- EPF designs will include low-emission flare systems and energy-efficient heaters to meet emission limits.
- Growing activity in Africa, Latin America, and Southeast Asia will boost demand for large-capacity units.
- Enhanced oil recovery programs will use EPFs for rapid evaluation of reservoir performance.
- Engineering firms will offer integrated packages covering separation, gas treatment, and water handling.
- Service providers with global fabrication yards and fast delivery capability will gain competitive advantage.




