Market Overview
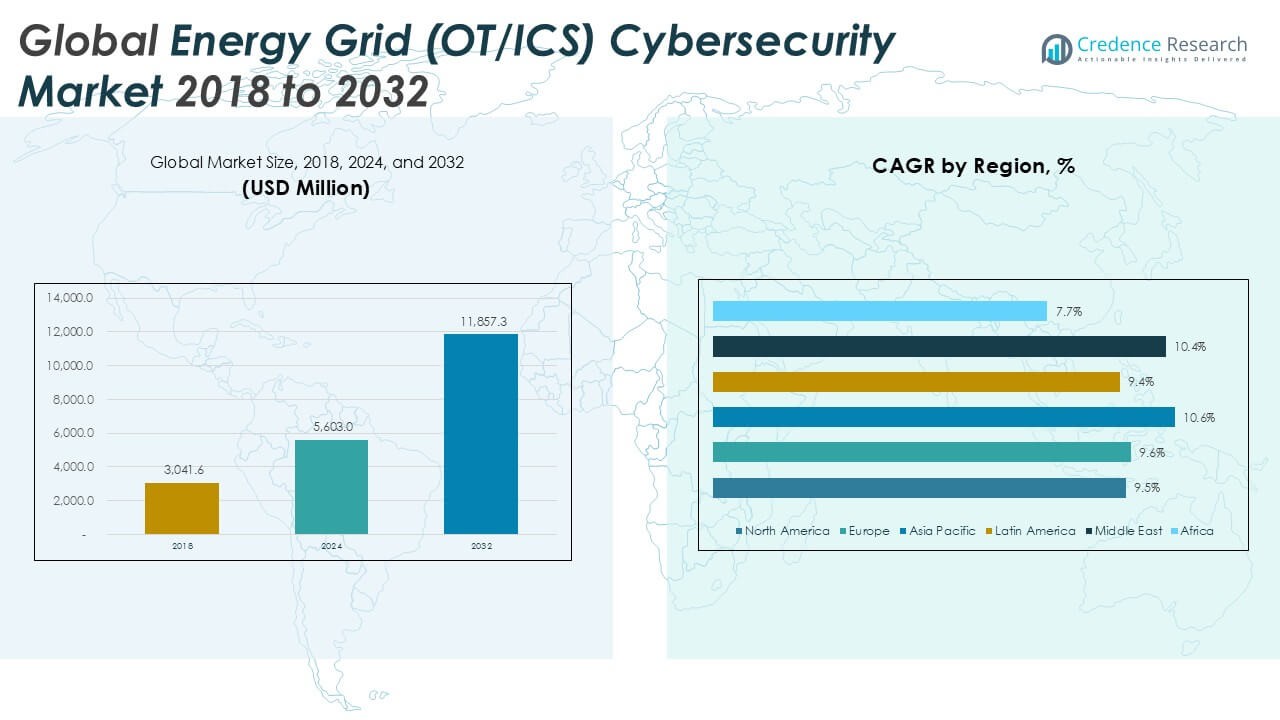
The Global Energy Grid (OTICS) Cybersecurity market size was valued at USD 3,041.6 million in 2018 and grew to USD 5,603.0 million in 2024. It is anticipated to reach USD 11,857.3 million by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 9.85% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Energy Grid (OTICS) Cybersecurity Market Size 2024 |
USD 5,603.0 Million |
| Energy Grid (OTICS) Cybersecurity Market, CAGR |
9.85% |
| Energy Grid (OTICS) Cybersecurity Market Size 2032 |
USD 11,857.3 Million |
The Global Energy Grid (OTICS) Cybersecurity market is driven by a mix of industrial leaders and specialized cybersecurity firms. Top players such as Siemens, ABB, Hitachi Energy Ltd., GE Vernova, and OMICRON Cybersecurity dominate through integrated grid security solutions, while Dragos, Claroty, Nozomi Networks, Cisco Systems, Palo Alto Networks, and HCL Technologies strengthen the market with advanced monitoring, detection, and AI-driven threat intelligence platforms. Regionally, Europe led the market in 2024 with a 30% share, supported by stringent EU directives and strong adoption of renewable grids. North America followed with 27%, driven by NERC CIP regulations and rising smart grid deployment. Asia Pacific accounted for 22%, marking the fastest growth due to rapid digitalization and renewable integration.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The Global Energy Grid (OTICS) Cybersecurity market was valued at USD 3,041.6 million in 2018 and is expected to reach USD 11,857.3 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 9.85% during the forecast period.
- Growing regulatory mandates such as NERC CIP in North America and NIS2 Directive in Europe are driving adoption, with risk and compliance management services holding over 35% share in 2024.
- Key trends include rapid digitalization of grids, AI-driven monitoring, and increasing reliance on hybrid and private cloud deployments, with hybrid models emerging as the fastest-growing deployment segment.
- The market is highly competitive, with players like Siemens, ABB, Hitachi Energy, GE Vernova, Dragos, and Cisco Systems investing in partnerships, acquisitions, and AI-based solutions to strengthen cybersecurity portfolios.
- Europe led with 30% share in 2024, followed by North America at 27% and Asia Pacific at 22%, with Asia Pacific projected as the fastest-growing region.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Services
Risk & Compliance Management dominated the services segment in 2024 with over 35% market share, driven by strict global regulations such as NERC CIP in North America and the EU Cybersecurity Act. Utilities prioritize compliance frameworks to protect sensitive operational data and avoid costly penalties, fueling adoption of advanced governance tools. Identity & Access Management and Monitoring & Detection are growing rapidly as utilities expand digital systems. Managed Infrastructure Security Services also gain traction, supported by outsourcing trends to reduce costs and ensure 24/7 operational resilience.
- For instance, IBM Security helped a major U.S. utility meet NERC CIP compliance in 2023 by deploying QRadar SIEM across 12 control centers, monitoring more than 5,000 endpoints in real time.
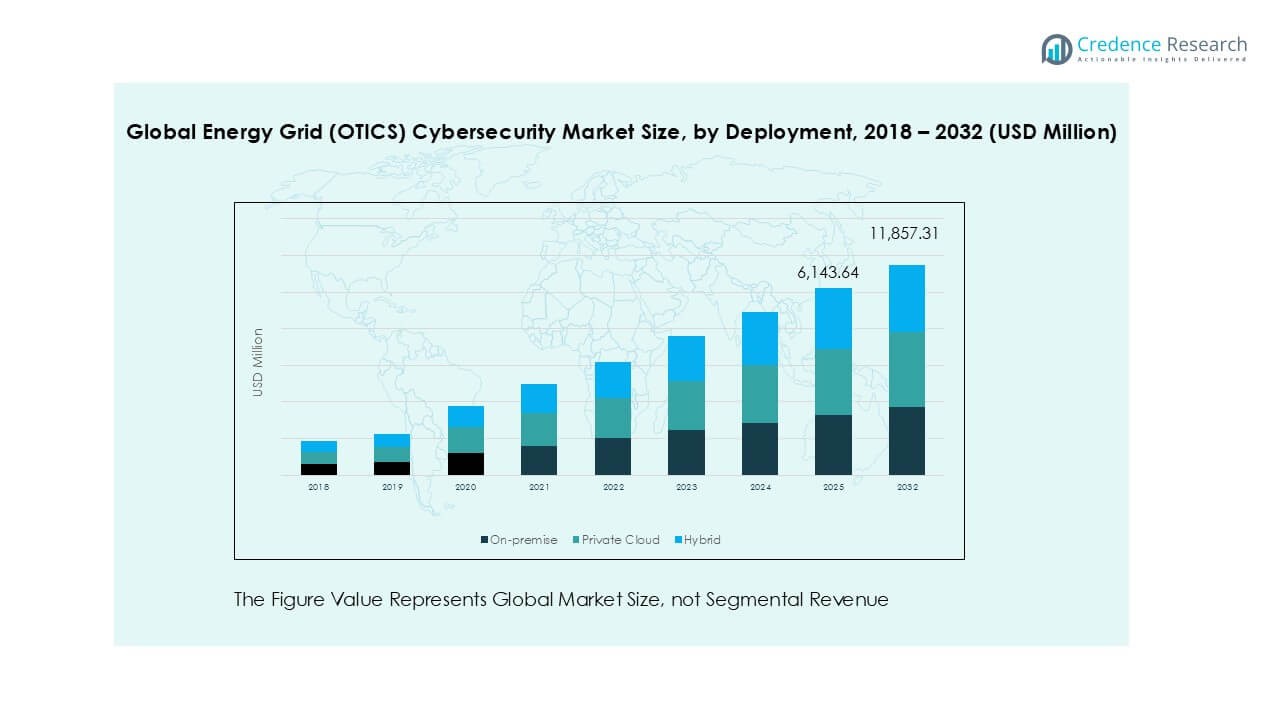
By Deployment
On-premises solutions held the largest share of nearly 45% in 2024, reflecting the need for utilities to maintain direct control over critical operational data and infrastructure. Power companies adopt on-premises deployments for reliability, regulatory compliance, and reduced exposure to external threats. However, Private Cloud and Hybrid models are expanding quickly, driven by their flexibility, cost efficiency, and scalability. Hybrid adoption is particularly strong in large grid operators seeking to balance control with cloud-enabled analytics, positioning it as the fastest-growing deployment model.
- For instance, Schneider Electric partnered with Enel in 2023 to deploy a hybrid cloud architecture for grid operations, enabling real-time analytics on 60 million smart meters while retaining core SCADA functions on-premises.
By Substation Class
Transmission (EHV/HV) substations accounted for the dominant share of about 40% in 2024, as high-voltage substations are critical nodes in national and cross-border electricity networks. Securing these assets is vital to prevent cascading failures and grid-wide disruptions. Primary Distribution (MV/HV) substations also contribute significantly, supported by rising demand for secure mid-scale networks in urban areas. Secondary Distribution (LV/MV) substations are growing steadily due to smart grid expansion and the integration of distributed energy resources, which increase exposure to cyber threats at lower-voltage levels.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Regulatory Mandates and Compliance Requirements
Governments and regulatory bodies are tightening cybersecurity standards for critical infrastructure, making compliance a top priority for utilities. Frameworks like the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) Critical Infrastructure Protection (CIP) standards, the European Union Network and Information Security (NIS2) Directive, and similar mandates in Asia-Pacific are compelling energy companies to invest in advanced OTICS cybersecurity systems. These requirements cover risk assessment, access control, and continuous monitoring of grid operations. Non-compliance leads to severe penalties, financial losses, and reputational damage. As utilities upgrade their networks with smart grid technologies, ensuring adherence to regulatory frameworks has become a fundamental growth driver for the market. This regulatory push directly increases demand for compliance-driven security solutions, driving steady adoption across global energy grids.
- For instance, as part of its broader cybersecurity efforts for European utility customers, Siemens Energy offers OT security solutions to help transmission operators address the requirements of the NIS2 directive. The company actively provides solutions and consultancy to help grid operators prepare for and meet the NIS2 deadline, which was set for October 2024.
Growing Adoption of Smart Grids and Digital Technologies
The increasing digitization of power grids is a major driver for cybersecurity investment. Smart grid technologies, IoT-enabled sensors, advanced SCADA systems, and distributed energy resources (DERs) are transforming grid operations but also expanding the attack surface for cyber threats. Utilities worldwide are deploying real-time monitoring and analytics platforms to optimize energy distribution and improve resilience. However, these connected assets are vulnerable to malware, ransomware, and nation-state cyberattacks. Cybersecurity solutions for OTICS environments are now seen as essential for ensuring uninterrupted energy supply and protecting sensitive operational data. As countries accelerate smart city initiatives and renewable energy integration, the reliance on digital grid infrastructure will further intensify, creating a strong growth pathway for advanced cybersecurity measures within the energy sector.
- For instance, in February 2023, GE Digital announced its new GridOS software portfolio, designed for grid orchestration and to help utilities manage a more complex, modern grid.
Rising Incidents of Cyberattacks on Energy Infrastructure
The energy sector has become a prime target for sophisticated cyberattacks, with utilities frequently reporting ransomware, phishing, and advanced persistent threats (APTs). High-profile incidents, such as grid disruptions in Ukraine and ransomware attacks on major pipelines, underscore the vulnerabilities of critical infrastructure. These attacks can cause large-scale blackouts, economic losses, and national security risks. As adversaries employ more complex tactics, utilities are compelled to adopt proactive security measures including anomaly detection, threat intelligence, and automated response systems. The growing frequency and scale of these attacks are accelerating investments in OTICS cybersecurity to protect high-voltage substations, control systems, and distribution networks. This rising threat landscape ensures cybersecurity remains a strategic priority for governments and grid operators, fueling sustained market demand.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML technologies are reshaping energy grid cybersecurity by enabling predictive and adaptive defense systems. Utilities are increasingly deploying AI-powered solutions to detect anomalies in real time, identify suspicious traffic patterns, and automate incident responses. Machine learning models can analyze vast datasets generated by OT and IT systems, reducing false positives and enhancing accuracy in identifying threats. This trend not only strengthens resilience against evolving attacks but also reduces operational burdens on security teams. Vendors offering AI-driven cybersecurity platforms are gaining traction, creating opportunities for innovation and partnerships between energy companies and technology providers.
- For instance, Darktrace deployed its AI-powered Cyber AI Analyst across a North American utility in 2023, analyzing more than 2.2 million OT/IT events daily and cutting incident response times by 92%.
Cloud-Based Cybersecurity and Hybrid Deployment Models
The growing shift toward cloud-enabled services is opening new opportunities for cybersecurity in energy grids. While on-premises solutions remain dominant for sensitive operations, utilities are increasingly adopting hybrid and private cloud deployments to enhance scalability and cost-efficiency. Cloud-based platforms support remote monitoring, centralized control, and faster updates, making them attractive for large-scale utilities. Cybersecurity providers are developing specialized cloud-native solutions that ensure compliance and secure integration with operational technology systems. This trend positions cloud adoption as both a driver of modernization and a major opportunity for vendors to expand their service portfolios.
Expansion of Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) and Decentralized Grids
The rapid growth of distributed energy resources, including solar farms, wind turbines, and energy storage systems, is creating new cybersecurity needs. These decentralized assets increase the number of access points and demand robust endpoint protection and secure communication channels. As more DERs are integrated into smart grids, utilities face heightened risks of cyber intrusions that could disrupt local and regional energy distribution. This expansion provides significant opportunities for cybersecurity vendors to offer tailored solutions for DER protection, from secure gateways to real-time intrusion detection systems, ensuring reliable and safe integration of renewable energy sources.
Key Challenges
Complexity of Securing Legacy Infrastructure
Many energy grids still rely on decades-old operational technology systems that were not designed with cybersecurity in mind. These legacy assets often lack basic security features such as encryption or access control, making them highly vulnerable to cyberattacks. Integrating modern cybersecurity solutions into these outdated systems is both costly and technically challenging. Utilities must balance modernization with uninterrupted operations, creating delays in large-scale deployments. This complexity hinders rapid adoption of advanced OTICS cybersecurity measures, particularly in developing economies where infrastructure upgrades face budget constraints.
High Implementation Costs and Limited Skilled Workforce
Deploying comprehensive OTICS cybersecurity frameworks requires significant financial investment in hardware, software, and continuous monitoring services. Smaller utilities and operators in emerging markets often face budgetary restrictions that limit their ability to adopt advanced solutions. Additionally, there is a global shortage of skilled cybersecurity professionals with expertise in both IT and OT systems. This talent gap delays effective deployment, increases reliance on third-party services, and raises overall operational costs. The combination of high expenses and limited skilled resources remains a key challenge for the widespread adoption of energy grid cybersecurity solutions.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America held a significant position in the global Energy Grid (OTICS) Cybersecurity market, valued at USD 848.29 million in 2018, rising to USD 1,536.02 million in 2024. The region is projected to reach USD 3,175.39 million by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 9.5%. North America accounted for nearly 27% of the global share in 2024, supported by strict regulatory frameworks such as NERC CIP and large-scale adoption of smart grids in the U.S. and Canada. Investments in modernizing legacy systems and rising cyber incidents continue to drive sustained demand.
Europe
Europe captured the largest share in 2024, with revenues growing from USD 1,040.52 million in 2018 to USD 1,895.41 million in 2024, representing around 30% of the global market. The region is forecasted to reach USD 3,950.85 million by 2032 at a CAGR of 9.6%. Strong regulatory frameworks under the EU NIS2 Directive and rapid renewable integration are fueling cybersecurity investments. Countries such as Germany, France, and the U.K. are leading deployments, with utilities focusing on compliance-driven solutions and securing high-voltage transmission substations across interconnected grids.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region, expanding at a CAGR of 10.6%. Market size grew from USD 713.25 million in 2018 to USD 1,375.86 million in 2024, and is projected to reach USD 3,086.46 million by 2032, accounting for nearly 22% of the global share. The region’s growth is fueled by rising investments in smart grids, expansion of distributed renewable energy resources, and government-led digital infrastructure programs in China, India, and Japan. Increasing cyber threats targeting regional utilities are prompting investments in monitoring, detection, and identity management solutions across grid operators.
Latin America
Latin America contributed a smaller but steadily expanding share, valued at USD 226.60 million in 2018 and rising to USD 407.34 million in 2024. By 2032, the market is expected to reach USD 833.57 million, advancing at a CAGR of 9.4%. The region represented around 6% of the global market in 2024, with growth driven by modernization of distribution networks and increasing reliance on renewable energy sources in Brazil, Mexico, and Chile. Government initiatives to improve grid reliability and mitigate operational risks are creating opportunities for cybersecurity vendors in the region.
Middle East
The Middle East showcased strong growth potential, expanding from USD 142.04 million in 2018 to USD 270.54 million in 2024, and expected to reach USD 597.61 million by 2032. The region is projected to grow at a CAGR of 10.4%, contributing about 4% of the global market in 2024. Rising investments in smart grid development, particularly in Saudi Arabia, UAE, and Qatar, are driving adoption of OTICS cybersecurity. The region’s increasing integration of renewable energy, coupled with growing exposure to state-sponsored cyberattacks, is compelling utilities to invest heavily in advanced grid security solutions.
Africa
Africa remains the smallest market but shows steady progress, growing from USD 70.87 million in 2018 to USD 117.82 million in 2024, with expectations to reach USD 213.43 million by 2032. The region recorded a CAGR of 7.7%, holding nearly 2% of the global market in 2024. Growth is supported by electrification programs, investments in renewable projects, and international funding for smart grid initiatives across South Africa, Kenya, and Nigeria. However, limited budgets and legacy infrastructure challenges slow adoption rates, although cybersecurity remains critical as grids modernize and expand to meet rising electricity demand.
Market Segmentations:
By Services
- Risk & Compliance Management
- Identity & Access Management
- Monitoring & Detection
- Managed Infrastructure Security Services
By Deployment
- On-premises
- Private Cloud
- Hybrid
By Substation Class
- Transmission (EHV/HV)
- Primary Distribution (MV/HV)
- Secondary Distribution (LV/MV)
By End User
- Power Generation Plants
- Transmission Substations
- Distribution Substations
- Others
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the Global Energy Grid (OTICS) Cybersecurity market is characterized by the presence of established industrial technology firms and specialized cybersecurity providers. Leading players such as Siemens, ABB, Hitachi Energy Ltd., and GE Vernova leverage their strong positions in grid infrastructure to integrate cybersecurity solutions directly into operational technology systems. Meanwhile, cybersecurity-focused firms including Dragos, Inc., Claroty, and Nozomi Networks specialize in threat detection, monitoring, and incident response tailored to OT environments. Global IT and security giants like Cisco Systems, Palo Alto Networks, and HCL Technologies are expanding their portfolios to address critical infrastructure needs, offering scalable, AI-driven platforms for grid operators. OMICRON Cybersecurity also plays a key role with advanced testing and monitoring tools for energy systems. Strategic collaborations, acquisitions, and continuous innovation define the market, as companies compete to address growing cyber threats, regulatory requirements, and the increasing digitalization of global energy grids.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- OMICRON Cybersecurity
- Siemens
- ABB
- Hitachi Energy Ltd.
- GE Vernova
- DRAGOS, INC
- HCL Technologies Limited
- Palo Alto Networks
- Cisco Systems
- Claroty
- Nozomi Networks
- Other Key Players
Recent Developments
- In June 2025, a bipartisan bill was introduced in the Senate, proposing a USD50 Mn cyber threat analysis program aimed at enhancing cybersecurity in the U.S. energy sector. The proposed legislation, which spans fiscal years 2025 to 2029, seeks to improve information sharing on cyber threats across the sector. Experts suggest that the private sector is likely to welcome this new initiative, as it is expected to bolster collaboration and fortify defenses against growing cyber risks.
- In June 2025, a new cybersecurity tool, V-INT: Automated Vulnerability Intelligence and Risk Assessment, was launched with funding from the DOE CESER. Developed in collaboration with Bastazo, Network Perception, and the University of Arkansas, the tool helps energy utilities assess and address security vulnerabilities, particularly in understanding complex firewall policies. The solution aims to enhance cybersecurity and resilience in critical energy systems, addressing key risks in the face of evolving cyber threats.
- In April 2025, the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) released two Industrial Control Systems (ICS) advisories, ICSA-25-091-01 and ICSA-24-331-04, highlighting critical vulnerabilities in Rockwell Automation and Hitachi Energy products. These advisories provide key details on security flaws that, if exploited, could jeopardize industrial operations, emphasizing the need for immediate attention to mitigate potential risks.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Services, Deployment, Substation Class, End User and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market will expand steadily as utilities modernize grids with digital technologies.
- Regulatory compliance will remain a core driver of cybersecurity investments worldwide.
- Adoption of hybrid deployment models will accelerate due to scalability and flexibility benefits.
- AI and machine learning will play a larger role in predictive threat detection.
- Cloud-based platforms will gain traction as utilities seek remote monitoring and cost efficiency.
- Growth of distributed energy resources will increase demand for endpoint protection solutions.
- Vendors will strengthen collaborations with utilities to provide tailored cybersecurity frameworks.
- Legacy infrastructure upgrades will open opportunities for advanced integration services.
- Regional growth will be strongest in Asia Pacific, supported by rapid smart grid adoption.
- The competitive landscape will intensify as industrial giants and cybersecurity firms expand portfolios.






