| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Indonesia Cardiovascular Devices Market Size 2024 |
USD440.59 million |
| Indonesia Cardiovascular Devices Market, CGR |
6.5% |
| Indonesia Cardiovascular Devices Market Size 2032 |
USD778.13 million |
Market Overview
The Indonesia Cardiovascular Devices Market is projected to grow from USD440.59 million in 2024 to an estimated USD778.13 million based on 2032, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) 6.5% from 2025 to 2032. This growth trajectory reflects increasing healthcare expenditures, the rising prevalence of cardiovascular diseases, and the government’s continued efforts to strengthen medical infrastructure across the country.
Key drivers influencing the market include the growing burden of non-communicable diseases, especially heart-related ailments, largely driven by lifestyle changes, tobacco use, and dietary habits. Additionally, the adoption of minimally invasive procedures, rising awareness about early diagnosis, and technological innovations in cardiovascular devices are reshaping treatment protocols. Trends such as digital health integration, wearable cardiac monitoring devices, and smart implants are gaining traction in urban healthcare settings, further bolstering market growth.
Geographically, major urban centers such as Jakarta, Surabaya, and Bandung dominate market demand due to better hospital infrastructure and higher patient volumes. The public and private sector hospitals in these regions are actively adopting advanced cardiovascular solutions to improve clinical outcomes. Key players contributing to the competitive landscape include Medtronic plc, Abbott Laboratories, Boston Scientific Corporation, GE HealthCare, and Philips Healthcare, all of which continue to expand their regional footprint through distribution partnerships and localized innovation.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The Indonesia Cardiovascular Devices Market is projected to grow from USD 440.59 million in 2024 to USD 778.13 million by 2032, registering a CAGR of 6.5% from 2025 to 2032.
- The global cardiovascular devices market is projected to grow from USD 72,115.60 million in 2024 to USD 133,700.94 million by 2032, with a CAGR of 7.1% from 2025 to 2032, driven by increasing cardiovascular diseases and advancements in medical technology.
- Rising cases of cardiovascular diseases, driven by aging, sedentary lifestyles, and poor dietary habits, are significantly increasing the demand for diagnostic and interventional devices.
- Adoption of minimally invasive procedures, wearable heart monitors, and AI-integrated diagnostic tools is transforming cardiovascular care across urban hospitals.
- Government investments in health infrastructure and the expansion of private specialty clinics are enhancing accessibility to advanced cardiac treatments.
- Heavy reliance on imported medical devices and complex regulatory procedures continue to pose challenges for timely and affordable product availability.
- Regions like Jakarta, Surabaya, and Bandung dominate the market due to superior hospital infrastructure and high patient volumes.
- The growing use of telemedicine, mobile diagnostics, and remote monitoring systems presents new growth avenues, especially in rural and underserved regions.
Report Scope
This report segments the Indonesia Cardiovascular Devices Market as follows:
Market Drivers
Rising Prevalence of Cardiovascular Diseases and Lifestyle Shifts
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) have emerged as a leading cause of mortality in Indonesia, accounting for a significant share of the national disease burden. The shift in lifestyle behaviors, particularly in urban areas, has resulted in increased incidences of hypertension, obesity, diabetes, and high cholesterol levels—all of which are risk factors for heart-related conditions. According to the World Heart Federation, Indonesia recorded 651,481 deaths due to cardiovascular diseases in 2019. The age-standardized cardiovascular disease mortality rate was 383 per 100,000 population, while the incidence rate stood at 635 per 100,000 population. Urbanization has introduced sedentary work cultures, dietary transitions favoring high-fat and processed foods, and decreased physical activity, collectively contributing to a surge in cardiovascular ailments. This epidemiological shift has heightened the need for early detection, accurate diagnosis, and effective treatment modalities—thereby driving demand for a wide range of cardiovascular devices such as electrocardiographs, defibrillators, stents, pacemakers, and cardiac imaging systems. As patients and healthcare providers seek to manage CVDs more efficiently, the role of technologically advanced devices becomes increasingly vital to clinical outcomes.
Expansion of Healthcare Infrastructure and Government Initiatives
Indonesia’s government has made significant strides in expanding and modernizing its healthcare infrastructure to cater to the growing needs of its 270+ million population. Under the universal health coverage scheme, Jaminan Kesehatan Nasional (JKN), efforts have been made to improve access to medical services across both urban and rural areas. Substantial investments in hospital upgrades, procurement of advanced medical equipment, and training of healthcare professionals are enabling broader adoption of cardiovascular diagnostic and treatment tools. The government’s increased healthcare spending—aimed at achieving Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and improving cardiac health indicators—continues to create favorable conditions for medical device manufacturers. Indonesia has seen advancements in AI-driven cardiac imaging, wearable ECG monitors, and remote patient monitoring devices, which are improving early detection and personalized treatment strategies. The adoption of minimally invasive cardiovascular procedures, including drug-eluting stents and transcatheter heart valves, is reducing recovery times and improving patient outcomes. In addition, Indonesia’s Ministry of Health has been collaborating with private players to set up specialized cardiac care centers and improve referral systems in secondary and tertiary hospitals. These initiatives enhance patient access to timely diagnosis and intervention, encouraging hospitals to invest in modern cardiovascular devices that offer precision, minimally invasive procedures, and reduced recovery times.
Technological Advancements and Adoption of Minimally Invasive Procedures
Technological progress in cardiovascular devices has significantly influenced their adoption in Indonesia’s healthcare landscape. Manufacturers are increasingly introducing next-generation devices that integrate digital capabilities, artificial intelligence, remote monitoring, and real-time diagnostics. These innovations enable more accurate assessments, early detection of anomalies, and better post-operative care. For instance, portable ECG monitors and wearable cardiac devices are gaining traction not only among physicians but also health-conscious individuals. Moreover, the preference for minimally invasive surgical interventions — such as angioplasty and transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) — is growing due to their reduced procedural risks, faster recovery periods, and decreased hospitalization costs. Surgeons and interventional cardiologists are more inclined toward advanced catheter-based solutions and real-time imaging technologies that improve surgical precision. The increasing acceptance of these technologies, combined with patient demand for low-risk treatment options, is fueling the demand for sophisticated cardiovascular devices in the Indonesian market.
Growing Private Sector Participation and Foreign Investment
The role of private healthcare providers and foreign investors in shaping Indonesia’s cardiovascular device landscape is becoming increasingly prominent. With rising disposable income and greater health awareness, a segment of the population is actively seeking premium care options in private hospitals, which are better equipped and more likely to adopt the latest cardiovascular technologies. International medical device companies view Indonesia as a high-potential market due to its large population, unmet medical needs, and regulatory improvements aimed at streamlining import and distribution processes. Collaborations between global manufacturers and local distributors or healthcare institutions are helping bridge the technological gap and improve device accessibility. Foreign direct investment (FDI) in the healthcare sector, alongside strategic partnerships and joint ventures, has accelerated the introduction of advanced cardiac care technologies. Moreover, medical device companies are increasingly localizing their operations — including assembly, servicing, and training — to meet national standards and build long-term relationships with healthcare providers. This active participation from both local and international stakeholders plays a crucial role in expanding the cardiovascular devices market in Indonesia.
Market Trends
Integration of Digital Health Technologies in Cardiac Monitoring
One of the most significant trends reshaping the Indonesia Cardiovascular Devices Market is the integration of digital health technologies in cardiac care. The growing adoption of wearable heart monitors, remote patient monitoring (RPM) devices, and mobile ECG applications is revolutionizing how cardiovascular health is tracked and managed. These innovations enable continuous monitoring of heart rhythms, blood pressure, and arrhythmias in real-time, empowering both patients and healthcare providers with actionable data. For instance, Indonesia has around 53 million digital health users, benefiting from improved access to healthcare through telemedicine and wearable monitoring solutions. Urban patients, in particular, are showing increased interest in wearable tech, driven by rising health awareness and easier access to smartphones and internet connectivity. Furthermore, healthcare institutions are increasingly incorporating cloud-based platforms and artificial intelligence (AI) tools to analyze cardiac data, detect anomalies, and facilitate early interventions. These solutions are especially valuable in Indonesia’s geographically dispersed regions, where access to specialists is limited. The Indonesian government’s digital health agenda, including the expansion of telemedicine platforms and electronic health records (EHRs), is further supporting the growth of this trend. As the population becomes more tech-savvy and the healthcare system undergoes digital transformation, the market for smart cardiovascular devices is expected to experience robust growth, enhancing both clinical outcomes and patient engagement across the care continuum.
Rising Preference for Minimally Invasive and Catheter-Based Interventions
Minimally invasive cardiovascular procedures are gaining substantial momentum across Indonesian hospitals and specialty clinics. Increasing demand for reduced-risk procedures with shorter recovery times has encouraged cardiologists to adopt catheter-based interventions such as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), angioplasty, and electrophysiology studies. These techniques allow for accurate diagnosis and treatment of heart conditions with minimal surgical trauma, making them ideal for elderly and high-risk patients. Indonesian hospitals, particularly in major cities like Jakarta, Surabaya, and Medan, are investing in advanced catheterization labs and fluoroscopy systems to support this growing trend.Additionally, innovations such as drug-eluting stents, bioresorbable vascular scaffolds, and steerable catheters are being introduced to improve procedural success rates and reduce long-term complications. For instance, Indonesia has seen a steady increase in demand for minimally invasive cardiovascular surgery devices, driven by advancements in surgical techniques and patient preference for less invasive options. Healthcare professionals are also receiving specialized training in interventional cardiology, supported by partnerships with global device manufacturers. Patients are increasingly aware of the benefits of these less invasive approaches, driving demand for procedures that minimize hospital stays and enhance post-operative quality of life. As private hospitals expand their specialty offerings and public facilities receive funding upgrades, the adoption of minimally invasive cardiovascular treatments is expected to accelerate, reinforcing a long-term shift in treatment protocols across the country.
Growing Focus on Local Manufacturing and Import Substitution
The Indonesian cardiovascular devices market is witnessing a gradual but important shift toward local manufacturing and reduced reliance on imported medical equipment. Historically, the majority of cardiovascular devices used in the country were imported, particularly from the U.S., Europe, and Japan. However, increasing import costs, currency fluctuations, and long lead times have prompted the government and private sector to support domestic production. Regulatory reforms, including streamlined licensing and incentives for medical device manufacturers, are encouraging local firms to enter the space. Companies are exploring collaborations with global manufacturers for technology transfer and joint ventures to establish assembly units in Indonesia. This not only enhances cost-effectiveness but also ensures faster supply chain responsiveness to meet local demand. The Ministry of Industry has identified medical devices as a priority sector under its “Making Indonesia 4.0” initiative, supporting automation, quality control, and innovation in local production. As demand for affordable cardiovascular care rises, especially in underserved provinces, the availability of cost-efficient, locally produced stents, monitors, and diagnostic tools is becoming essential. This trend is expected to build long-term resilience in the domestic medical device ecosystem and reduce barriers to access across different socioeconomic groups.
Expansion of Private Cardiac Care Facilities and Specialty Clinics
The expansion of private hospitals and specialty cardiac care clinics across Indonesia is transforming the landscape of cardiovascular healthcare delivery. Driven by rising incomes, greater health awareness, and a growing middle class, many Indonesians are opting for private healthcare services that offer shorter wait times, personalized care, and access to advanced medical technologies. Private hospitals are actively investing in state-of-the-art cardiovascular imaging systems, hybrid operating rooms, and robotic-assisted surgery capabilities. In metropolitan areas, multi-specialty cardiac centers are offering comprehensive services including diagnostics, interventional procedures, rehabilitation, and post-treatment monitoring. These facilities are also forming alliances with international healthcare groups to bring best practices and clinical expertise into the Indonesian market. Furthermore, the presence of specialized cardiology clinics in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities is gradually improving regional access to quality care. These developments are particularly significant in addressing non-communicable disease burdens outside major urban centers. Insurance penetration and corporate wellness programs are also contributing to the affordability of private care, encouraging patients to seek timely diagnosis and intervention. As the demand for premium, patient-centric cardiovascular care continues to grow, the private sector’s role in shaping the overall market trajectory is becoming increasingly influential.
Market Challenges
Inadequate Access to Advanced Healthcare in Rural and Remote Areas
One of the most pressing challenges in the Indonesia Cardiovascular Devices Market is the limited access to advanced healthcare infrastructure in rural and remote regions. Despite ongoing government initiatives aimed at improving healthcare equity, significant disparities persist between urban centers and less-developed areas. A large portion of the population resides outside major cities like Jakarta, Surabaya, and Bandung, where modern hospitals and specialized cardiac care facilities are concentrated. In remote areas, hospitals often lack essential diagnostic equipment such as ECG machines, echocardiography systems, and catheterization labs. The shortage of trained cardiologists and interventional specialists further exacerbates this access gap, leaving many cardiovascular conditions undiagnosed or untreated until advanced stages.Transportation barriers, limited health literacy, and the absence of robust referral systems compound the problem, particularly for elderly patients and those with chronic conditions. For instance, Indonesia has been witnessing a steady increase in healthcare expenditure, driven by economic growth, expanding middle-class population, and increasing health insurance coverage, which supports the adoption of advanced medical technologies, including cardiovascular devices. Additionally, public hospitals in these areas often operate with budget constraints that hinder the procurement of advanced cardiovascular devices.As a result, early detection, preventive screenings, and timely interventions are compromised, leading to higher morbidity and mortality rates. Bridging this urban-rural healthcare divide requires strategic investments in medical infrastructure, workforce training, and telecardiology solutions. Until such systemic improvements are realized, access limitations will remain a major barrier to market growth and equitable cardiovascular care in Indonesia.
High Dependence on Imports and Regulatory Hurdles
Indonesia’s cardiovascular devices market is heavily reliant on imported products, which presents multiple challenges including cost inflation, long supply chains, and vulnerability to global market fluctuations. More than 90% of advanced cardiovascular devices—such as implantable defibrillators, cardiac monitors, and vascular stents—are sourced from international suppliers. As a result, the prices of these devices are subject to currency volatility, tariffs, and logistics-related delays, affecting their affordability and availability within the domestic market. Hospitals, particularly those in the public sector, often face procurement challenges and delayed device adoption due to limited budgets and administrative bottlenecks. Moreover, regulatory procedures for importing and registering medical devices in Indonesia are complex and time-consuming. Manufacturers must comply with strict labeling, certification, and local testing requirements, which often lead to delays in market entry for newer technologies. These regulatory hurdles discourage small and mid-sized foreign firms from entering the market, limiting product variety and innovation. Additionally, local distributors may lack the technical training and after-sales support necessary to ensure proper installation and maintenance of sophisticated cardiovascular systems. The absence of a robust domestic manufacturing base further compounds the problem, as local production capabilities remain underdeveloped. Addressing these issues will require regulatory reforms, incentivized local production, and capacity-building initiatives to reduce import dependency and streamline the flow of life-saving cardiovascular technologies into the Indonesian healthcare system.
Market Opportunities
Expanding Middle-Class Population and Rising Health Consciousness
Indonesia’s expanding middle-class population, coupled with increasing health awareness, presents a strong opportunity for the cardiovascular devices market. As disposable incomes rise, more individuals are prioritizing preventive healthcare, early diagnosis, and access to specialized cardiac care. This demographic shift is driving demand for advanced diagnostic and therapeutic devices, including portable ECGs, wearable heart monitors, and minimally invasive surgical tools. Urban consumers are becoming more health-conscious, actively participating in wellness programs and seeking routine screenings for cardiovascular risks. This behavioral shift is encouraging private hospitals and clinics to invest in modern cardiovascular technologies to meet growing patient expectations. Furthermore, the growing penetration of private health insurance and corporate wellness initiatives is making premium cardiovascular treatments more accessible, expanding the addressable market for device manufacturers.
Growth of Telemedicine and Digital Health Ecosystems
The rapid development of telemedicine and digital health infrastructure in Indonesia offers a substantial opportunity for expanding access to cardiovascular care, especially in remote and underserved regions. With government support for digital transformation in healthcare, telecardiology platforms are emerging as effective tools for real-time consultations, remote monitoring, and diagnostics. These systems allow specialists in urban centers to interpret data and guide treatment for patients in distant locations, reducing the burden on physical infrastructure. The integration of AI-driven analytics, cloud-based data sharing, and mobile health applications enhances the functionality of cardiovascular devices and promotes continuous patient engagement. As digital health adoption accelerates, manufacturers that align their product strategies with smart, connected solutions stand to gain a competitive advantage in the evolving Indonesian healthcare landscape.
Market Segmentation Analysis
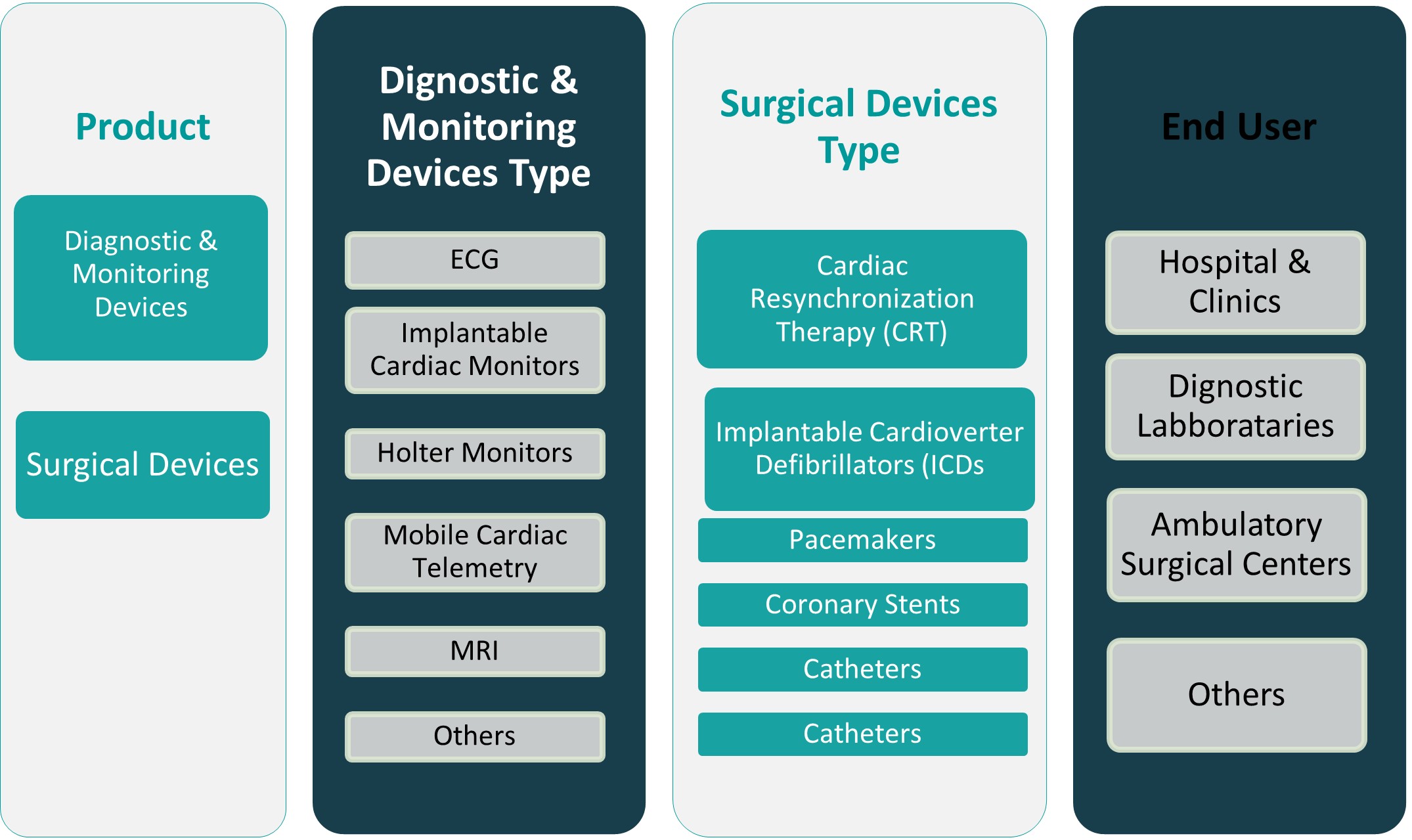
By Product
The Indonesia Cardiovascular Devices Market is segmented into Diagnostic & Monitoring Devices and Surgical Devices. Diagnostic and monitoring devices, including electrocardiograms (ECG), Holter monitors, and cardiac imaging systems, constitute a significant portion of the market due to their essential role in early detection and disease management. These devices are increasingly adopted in both urban and semi-urban healthcare settings, driven by the rising incidence of heart-related ailments and the growing emphasis on preventive care. Technological advancements such as portable and wearable ECGs have further enhanced market penetration. On the other hand, surgical devices, including stents, pacemakers, and defibrillators, are gaining traction with the expansion of interventional cardiology services. Hospitals and specialized cardiac centers are investing in advanced surgical tools to support minimally invasive procedures, thus driving the growth of this segment.
By End User
In terms of end users, hospitals and clinics dominate the market, accounting for the largest share. These facilities possess the necessary infrastructure and skilled personnel required to conduct complex cardiac procedures and manage acute cardiovascular conditions. As both public and private hospitals continue to expand their cardiac care departments, the demand for both diagnostic and surgical cardiovascular devices is expected to rise. Diagnostic laboratories are another critical segment, driven by the need for timely and accurate cardiac assessments. These labs increasingly rely on advanced imaging and monitoring tools to deliver comprehensive diagnostic solutions. Ambulatory surgical centers are gradually gaining prominence due to their cost-effective and patient-friendly approach to minor cardiac procedures. These centers offer reduced hospital stays and faster recovery, attracting patients seeking efficient treatment alternatives. The “Others” segment includes home care settings and research institutes, where portable and smart cardiac devices are being utilized for continuous monitoring and academic purposes.
Segments
Based on Product
- Diagnostic & Monitoring Devices
- Surgical Devices
Based on End User
- Hospitals & Clinics
- Diagnostic Laboratories
- Ambulatory Surgical Centers
- Others
Based on Diagnostic & Monitoring Devices Type
- ECG
- Implantable Cardiac Monitors
- Holter Monitors
- Mobile Cardiac Telemetry
- MRI
- Others
Based on Surgical Devices Type
- Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT)
- Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (ICDs
- Pacemakers
- Coronary Stents
- Catheters
Based on Region
- Java
- Sumatra
- Kalimantan
- Sulawesi
Regional Analysis
Java (62%)
Java dominates the national market, accounting for approximately 62% of the total cardiovascular devices market share. The island’s high population density, urbanization, and presence of major healthcare institutions—particularly in cities like Jakarta, Surabaya, and Bandung—drive strong demand for both diagnostic and surgical cardiovascular devices. These urban centers are equipped with advanced hospitals, specialist cardiology units, and private medical centers that actively invest in the latest medical technologies, contributing to higher device uptake.
Sumatra (18%)
Sumatra holds the second-largest share in the market, representing nearly 18% of the national total. Key cities such as Medan and Palembang have seen notable improvements in healthcare services, including the expansion of diagnostic laboratories and cardiac care units. Government efforts to upgrade regional hospitals and attract private sector participation have contributed to the gradual development of cardiovascular care infrastructure across the island.
Key players
- Abbott
- GE HealthCare
- Siemens Healthcare GmbH
- Canon Medical Systems Asia Pte. Ltd.
- Kalbe Farma
- Medion
- Medtronic
- Boston Scientific Corporation
- Sumber Daya Rekayasa
- Biotronik Indonesi
Competitive Analysis
The Indonesia Cardiovascular Devices Market features a competitive mix of global and domestic players, each contributing uniquely to market dynamics. Global leaders such as Abbott, Medtronic, Boston Scientific Corporation, and GE HealthCare dominate in terms of advanced technology offerings and robust distribution networks. These companies leverage strong R\&D capabilities and a wide portfolio of minimally invasive devices and diagnostic tools to maintain their competitive edge. Siemens Healthcare GmbH and Canon Medical Systems provide high-end imaging and diagnostic solutions, supporting early cardiac diagnosis. On the local front, Kalbe Farma, PT. Medion, and PT. Sumber Daya Rekayasa are strengthening their presence by offering cost-effective solutions and partnering with international brands. Biotronik Indonesia focuses on specialized cardiovascular implants and has gradually built a strong regional foothold. Competitive advantage in this market increasingly hinges on localization strategies, regulatory adaptability, after-sales service, and partnerships with healthcare providers to expand market reach and device accessibility.
Recent Developments
- In February 2025, Abbott issued a safety notification for certain Assurity and Endurity pacemakers due to potential epoxy mixing issues during manufacturing, which could lead to device malfunction.
- In April 2025, GE HealthCare launched the Revolution™ Vibe CT system featuring Unlimited One-Beat Cardiac imaging and AI solutions, enhancing cardiac imaging capabilities.
- In April 2025, Medtronic reported promising evidence for its Affera™ pulsed field ablation technologies in treating atrial fibrillation patients
- In May 2024, Siemens Healthineers announced new cardiology applications with artificial intelligence for the Acuson Sequoia ultrasound system, including a new 4D transesophageal (TEE) transducer for cardiology exams.
- In February 2025, Philips developed a miniaturized intracardiac transducer, enabling higher-resolution views of cardiac structures and functions, benefiting structural heart disease and electrophysiology procedures.
- In March 2025, Boston Scientific announced the acquisition of SoniVie Ltd. to expand its interventional cardiology therapies offerings with ultrasound-based renal denervation technology.
- In June 2024, Biovac Institute entered a partnership with Sanofi to locally manufacture inactivated polio vaccines in Africa, aiming to serve the potential needs of over 40 African countries.
Market Concentration and Characteristics
The Indonesia Cardiovascular Devices Market exhibits a moderately concentrated structure, characterized by the dominance of a few global medical technology giants such as Abbott, Medtronic, and Boston Scientific Corporation, alongside a growing presence of regional players like Kalbe Farma and PT. Medion. The market is defined by a high reliance on imported advanced devices, particularly for surgical and interventional procedures, while local manufacturers primarily focus on basic diagnostic tools and distribution partnerships. Technological innovation, regulatory compliance, and strong distribution networks are key competitive factors. The market is also shaped by increasing urban demand, government healthcare reforms, and a shift toward minimally invasive treatments. Despite infrastructure limitations in rural areas, rising awareness and healthcare investments are gradually expanding market access. Overall, the market reflects a blend of advanced clinical demand and emerging local manufacturing potential, with strategic collaborations and localization expected to shape future competitive dynamics.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Product, End User, Diagnostic & Monitoring Devices Type, Surgical Devices Type and Region. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The Indonesia Cardiovascular Devices Market is expected to witness sustained growth driven by rising cardiovascular disease prevalence and expanding healthcare awareness across urban and semi-urban regions. Continued demand for early diagnosis and intervention will fuel adoption of both monitoring and surgical devices in hospitals and clinics.
- Increasing government healthcare expenditure and support for infrastructure development will improve accessibility to advanced cardiovascular technologies. Public sector initiatives, especially under universal health coverage (JKN), are likely to drive equitable distribution of cardiac care services.
- The adoption of digital health tools, including remote monitoring and wearable cardiac devices, will gain momentum. These technologies will support real-time diagnostics and chronic disease management, particularly in underserved areas.
- Growth in private healthcare facilities and specialty cardiac centers will accelerate demand for premium cardiovascular devices. Urban populations will continue to seek high-quality, patient-centric treatment options, promoting advanced device utilization.
- The market will benefit from an increase in local manufacturing and import substitution initiatives. Policy incentives and public-private collaborations will encourage domestic production of essential cardiovascular tools.
- Technological advancements in minimally invasive procedures will further transform treatment protocols. New-generation stents, catheters, and real-time imaging systems will become more widely adopted across tertiary care centers.
- Strategic partnerships between global medtech firms and local distributors will strengthen market penetration and after-sales service. These collaborations will enable faster market entry and localized product offerings tailored to Indonesian needs.
- Medical tourism may contribute marginally to growth as Indonesia upgrades its cardiac care facilities to regional standards. Enhanced infrastructure and affordability could attract patients from neighboring Southeast Asian countries in the future.
- Regulatory reforms aimed at streamlining device approvals and ensuring product quality will create a more conducive business environment. Simplified procedures and transparent guidelines will improve foreign investment and innovation flow into the market.
- Education and training programs for healthcare professionals in interventional cardiology will support optimal device utilization. As procedural expertise improves, advanced cardiovascular devices will achieve deeper integration into routine clinical practice.




