Market Overview
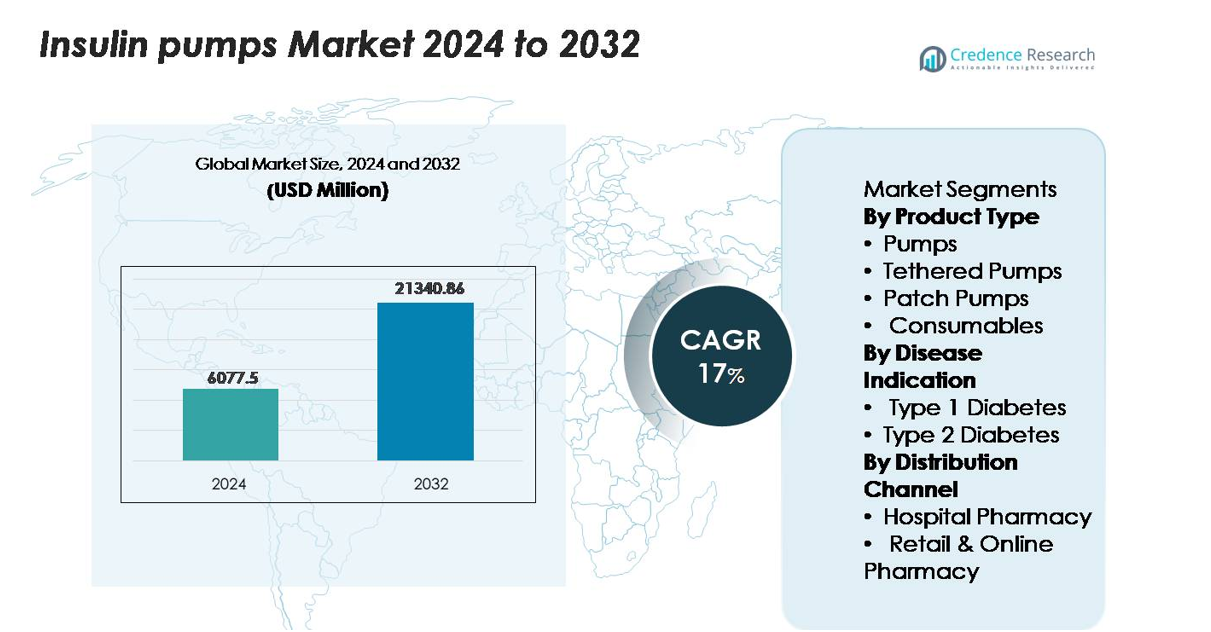
The insulin pumps market size was valued at USD 6,077.5 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 21,340.86 million by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 17% during the forecast period (2025–2032).
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Insulin Pumps Market Size 2024 |
USD 6,077.5 million |
| Insulin Pumps Market, CAGR |
17% |
| Insulin Pumps Market Size 2032 |
USD 21,340.86 million |
The insulin pumps market is dominated by technologically advanced manufacturers including Medtronic, Insulet Corporation, Tandem Diabetes Care, Roche Diabetes Care, and Ypsomed, each leveraging strong portfolios in automated insulin delivery, patch-pump systems, and integrated CGM-pump platforms. Medtronic maintains a leading position with broad clinical adoption of hybrid closed-loop systems, while Insulet drives rapid growth in the tubeless patch-pump segment. Tandem strengthens its presence through algorithm-driven adaptive dosing technologies. Regionally, North America leads the global market with an exact share of 45.5%, supported by high technology uptake, robust reimbursement, and strong endocrinology infrastructure, reinforcing its position as the primary hub for pump innovation and commercialization.
Market Insights
- The insulin pumps market reached USD 6,077.5 million in 2024 and is projected to hit USD 21,340.86 million by 2032, advancing at a 17% CAGR during the forecast period.
- Demand continues to rise as automated insulin delivery systems gain widespread adoption, with tethered pumps holding the largest product share due to strong clinical reliability and broad reimbursement support.
- Key trends include rapid expansion of tubeless patch pumps, integration of smart connectivity with real-time monitoring, and increasing adoption among insulin-dependent Type 2 patients in emerging economies.
- The competitive landscape is led by Medtronic, Insulet, Tandem Diabetes Care, Roche, and Ypsomed, each strengthening portfolios through algorithm-driven dosing, CGM integration, and next-generation wearable designs.
- Regionally, North America leads with 45.5% share, followed by Europe at 20–25% and Asia-Pacific at 15–20%, while Latin America and the Middle East & Africa collectively hold under 15%, reflecting varied access and reimbursement levels.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Product Type
Tethered pumps hold the dominant market share within the product category due to their high dosing accuracy, programmable basal profiles, and strong integration with glucose sensors, which collectively support superior glycemic management for intensive therapy users. Their widespread clinical adoption is reinforced by robust reimbursement frameworks and long-standing physician familiarity. Patch pumps continue expanding as a preferred choice among users seeking tubeless, discreet, and low-maintenance systems, while consumables generate consistent recurring demand through infusion sets, cartridges, and reservoirs. Innovation in automated insulin delivery and closed-loop features further strengthens the leadership of tethered pumps.
- For instance, Tandem’s t:slim X2 tethered pump delivers insulin in precise bolus increments of 0.01 units (at volumes greater than 0.05 units) and supports a reservoir capacity of 300 units, providing the dosing stability and endurance required for intensive daily therapy.
By Disease Indication
Type 1 diabetes represents the dominant segment, as patients with absolute insulin dependence rely heavily on pump therapy to maintain tight glucose control and reduce hypoglycemia risk. Strong clinical validation, early initiation in pediatric care, and increasing use of advanced hybrid closed-loop systems contribute to sustained market leadership. Type 2 diabetes adoption is rising, driven by the growing insulin-dependent population and increasing physician preference for pumps in cases of poor glycemic stability; however, its market share remains comparatively smaller due to cost considerations and variability in treatment progression.
- For instance, Medtronic’s MiniMed 780G system can deliver automatic correction boluses every 5 minutes and supports insulin delivery adjustments as small as 0.025 units—capabilities that are especially critical for Type 1 users requiring tight and continuous glucose regulation.
By Distribution Channel
Hospital pharmacies lead the distribution channel segment, supported by their central role in initiating insulin pump therapy, conducting device onboarding, and ensuring clinician-led training for new users. Hospitals also manage the majority of advanced system prescriptions, which strengthens their share in the supply chain. Retail and online pharmacies are gaining traction, particularly for repeat purchases of consumables and replacement accessories, driven by expanding digital platforms and patient preference for home delivery. Nonetheless, the clinical requirement for supervised initiation ensures hospital pharmacies maintain their dominant position in the distribution ecosystem.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Adoption of Automated Insulin Delivery Systems
Automated insulin delivery (AID) systems are accelerating market growth by offering closed-loop glucose regulation that significantly reduces manual dosing burden. These systems integrate continuous glucose monitoring with algorithm-driven pump control to maintain real-time insulin adjustments, enabling improved glycemic stability. Patients with high variability in glucose levels and those prone to nocturnal hypoglycemia increasingly adopt AID platforms for their proven clinical outcomes. Manufacturers continue enhancing interoperability, device miniaturization, and algorithm precision to expand usability across broader age groups. Additionally, growing acceptance of hybrid closed-loop technologies among endocrinologists and expanding insurance reimbursement for advanced pump systems support rising adoption. As healthcare providers prioritize digital diabetes management and personalized therapy models, AID systems strengthen their position as a preferred therapeutic solution for intensive insulin users, shaping long-term demand for pumps equipped with integrated sensing and automated decision-making capability.
- For instance, Insulet’s Omnipod 5 AID system adjusts insulin delivery automatically using glucose values transmitted every 5 minutes from the Dexcom G6 sensor, and its pod contains a 200-unit reservoir, enabling three days of continuous closed-loop operation.
Expanding Insulin-Dependent Population and Disease Burden
The global rise in diabetes prevalence, particularly among younger Type 1 patients and insulin-dependent Type 2 adults, drives consistent demand for insulin pumps. Increasing diagnoses at earlier ages extend the duration of insulin therapy, creating a sizable lifetime user base. Clinical guidelines increasingly recommend pumps for individuals unable to achieve stable control through injections, accelerating transitions to pump-based therapy. The growing burden of obesity, sedentary lifestyle patterns, and hereditary risk factors contribute to a higher proportion of patients s patients to shift from multiple daily injections. As digital health ecosystems evolve, more patients qualify for pump therapy due to structured monitoring and remote clinician feedback, strengthenirequiring basal-bolus insulin regimens. At the same time, heightened awareness of pump benefits—such as reduced hypoglycemia, fewer glycemic excursions, and improved HbA1c outcomes—encourageng long-term market expansion.
- For instance, Roche’s Accu-Chek Insight pump supports basal rate adjustments as small as 0.02 units per hour and offers cartridge options of 160 units, enabling precise dosing for patients with long-term insulin requirements.
Favorable Reimbursement Environment and Healthcare Infrastructure Support
Improving reimbursement frameworks for advanced diabetes technologies significantly influence pump adoption, particularly in developed markets. Insurers increasingly recognize the cost-efficiency of pumps by reducing emergency visits, hospitalizations, and long-term complications associated with poorly controlled diabetes. Coverage expansion for consumables, automated systems, and sensor-integrated pumps further accelerates penetration. Hospitals and diabetes care centers actively promote structured pump onboarding programs, improving patient confidence and therapy outcomes. Many countries now include pump therapy in national diabetes management guidelines, while public health initiatives focus on early technology adoption among high-risk groups. Meanwhile, the proliferation of specialized endocrinology clinics and telehealth services strengthens access to pump education and follow-up care, particularly for pediatric and rural populations. Collectively, these policies and infrastructure investments create a supportive environment that drives sustained uptake of pump technologies.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Integration of Smart Connectivity and Remote Monitoring Ecosystems
The integration of Bluetooth-enabled pumps, cloud platforms, and real-time data sharing presents one of the most significant opportunities in the market. Connected systems allow patients and clinicians to monitor glucose trends, insulin delivery patterns, and behavioral insights remotely, enabling personalized adjustments without frequent clinic visits. These capabilities are especially transformative for pediatric, elderly, and high-risk patients requiring continuous supervision. Manufacturers are shifting toward predictive analytics and machine-learning algorithms that provide insights into insulin sensitivity, meal patterns, and activity levels. At the same time, interoperability with digital therapeutic platforms and mobile applications enhances patient engagement and therapy adherence. As healthcare providers increasingly leverage telemedicine, connected insulin pumps create a scalable model for continuous diabetes management, positioning digital ecosystems as a substantial future growth catalyst.
- For instance, the Tandem t:connect mobile app transmits pump and glucose data automatically and wirelessly to the cloud, enabling continuous real-time oversight. When paired with a compatible t:slim X2 pump, the app supports remote bolus delivery directly from a smartphone, with the maximum bolus amount being a user-configurable safety limit set in the pump’s Personal Profile, typically ranging from 1 to 25 units.
Expansion of Patch Pumps and Tubeless Wearable Technologies
Tubeless and wearable patch pumps continue gaining momentum as patients prioritize comfort, discretion, and simplified therapy workflows. These pumps eliminate tubing-related inconveniences, offering flexible placement, lightweight design, and reduced device visibility. Manufacturers are investing in modular, disposable, or semi-reusable configurations to lower replacement costs and broaden appeal among Type 2 diabetic users. The integration of automated dosing features in patch pumps and enhanced compatibility with smartphone apps further strengthens adoption. As demand grows among younger, active, and tech-savvy populations, patch pumps present a strong opportunity to penetrate segments previously dependent on injections. Their potential for large-scale cost reduction also positions them as a key enabler for pump expansion in emerging markets.
- For instance, Insulet’s Omnipod DASH pod weighs only 23 grams and holds a 200-unit insulin reservoir, delivering bolus increments as low as 0.05 units, enabling high-precision dosing in a fully tubeless format.
Transition Toward Personalized and Adaptive Insulin Therapy
Personalized therapy solutions represent an emerging trend, fueled by advancements in biosensors, adaptive dosing algorithms, and user-specific insulin profiles. Modern insulin pumps now incorporate customizable basal rates, carbohydrate sensitivity calculations, and automated correction boluses tailored to individual metabolic responses. Emerging developments in multi-hormone pumps, integrating glucagon or amylin analogs, further support tailored glucose regulation strategies. As precision medicine gains prominence in endocrinology, manufacturers increasingly explore AI-driven predictive dosing systems that self-adjust based on historical data, circadian cycles, and lifestyle patterns. This shift toward adaptive therapy models enhances user outcomes and establishes a strong competitive differentiator for next-generation pumps.
Key Challenges
High Upfront Cost and Affordability Constraints
Despite strong technological progress, the high cost of insulin pumps remains a major barrier to widespread adoption, particularly in low- and middle-income markets. Initial device prices, combined with ongoing expenses for infusion sets, reservoirs, and sensors, create substantial financial burdens for uninsured or underinsured patients. Even in developed regions, reimbursement gaps for advanced automated systems limit access for many diabetes sufferers. Price sensitivity is especially pronounced among Type 2 diabetic adults who may not require intensive management, reducing pump penetration in this demographic. Healthcare systems with limited funding often prioritize essential treatments over advanced devices, further restricting accessibility. As manufacturers introduce more sophisticated technologies, balancing innovation with affordability remains a persistent challenge for long-term market expansion.
Device Complexity, Training Needs, and Risk of Technical Failures
Insulin pumps, despite their benefits, demand significant user training, ongoing maintenance, and adherence to operational protocols. New users often face challenges related to device setup, infusion site selection, troubleshooting alarms, and understanding algorithm-driven dosing recommendations. Inconsistent user proficiency can lead to dosing errors, hyperglycemia, or device misuse. Technical malfunctions—including occlusions, battery failures, or connectivity issues—pose safety risks and create reluctance among risk-averse patients. Healthcare providers also face training burdens due to increasing device complexity, requiring additional time and resources to ensure patient readiness. These operational challenges can discourage adoption, particularly in regions with limited diabetes education support or inadequate clinical follow-up systems.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America commands a dominant position, capturing approximately 45.5% of the global insulin-pumps market in 2024. The region benefits from high diabetes prevalence, robust adoption of advanced closed-loop pump systems, and strong reimbursement frameworks. The U.S. leads market penetration, driven by major device manufacturers and rapid approval of next-generation automated delivery systems. High treatment costs are offset by widespread insurance coverage, while infrastructure supports patient training and pump initiation. As a result, North America remains the largest regional contributor and sets global benchmarks for technology and care models.
Europe
Europe holds a significant share, estimated at around 20–25% of the global insulin-pumps market in 2024. The market is supported by advanced healthcare infrastructure, national diabetes management programmes, and strong physician acceptance of pump therapy—especially in Germany, the U.K., France and the Nordics. Reimbursement policies in many countries cover pump initiation for intensive insulin users, pediatric Type 1 patients and high-risk Type 2 cohorts. While growth is steady, cost pressures and heterogeneous reimbursement across countries moderate expansion. Europe remains a key secondary region with upward potential through sensor-pump integration and tele-health expansion.
Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific region accounts for roughly 15–20% of the global insulin-pumps market in 2024, and stands out as the fastest-growing region. Demand is driven by rising diabetes incidence—especially insulin-dependent cases—improving healthcare infrastructure in China, Japan, Australia and Southeast Asia, and increasing private insurance coverage. Patch and tubeless pump formats are gaining traction among younger, active populations. However, adoption rates remain lower than in Western markets due to cost and access constraints. With expanding digital health ecosystems and local manufacturing partnerships, Asia-Pacific offers the next wave of growth for the insulin-pumps market.
Latin America
Latin America represents approximately 6–8% of the global insulin-pumps market in 2024. Growth is influenced by increasing insulin-dependent Type 2 prevalence, urbanization, and improving access to diabetes care in Brazil, Mexico and Argentina. Yet market penetration remains modest due to high device costs, limited reimbursement, and disparities in access between urban and rural settings. Private healthcare uptake and digital pharmacy channels are gradually improving reach. While Latin America presents meaningful opportunity, its contribution to global volume remains modest relative to developed regions.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region currently holds around 3–5% of the global insulin-pumps market in 2024. Leading adoption is concentrated in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries, where high investment in medical technology and favorable insurance frameworks accelerate uptake. Nonetheless, broader regional penetration is limited by inconsistent reimbursement, lower patient awareness, and fewer structured pump-training programmes. Healthcare infrastructure in many African markets remains underdeveloped for advanced device deployment. The region offers long-term opportunity as governments prioritize diabetes programmes, but near-term share gains will be incremental.
Market Segmentations:
By Product Type
- Pumps
- Tethered Pumps
- Patch Pumps
- Consumables
By Disease Indication
- Type 1 Diabetes
- Type 2 Diabetes
By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacy
- Retail & Online Pharmacy
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the insulin pumps market is defined by strong technological differentiation, continuous innovation, and expanding integration with digital diabetes-management ecosystems. Leading players such as Medtronic, Insulet Corporation, Tandem Diabetes Care, Roche Diabetes Care, and Ypsomed dominate through advanced delivery algorithms, hybrid closed-loop systems, and user-centric device designs. Medtronic maintains a broad global footprint with extensive clinical validation for its automated insulin delivery platforms, while Insulet accelerates market disruption with its tubeless patch-pump technology. Tandem strengthens its position through adaptive dosing algorithms and interoperable pump-CGM solutions. Increasing competition also emerges from smaller innovators developing miniaturized pumps, disposable patch systems, and Bluetooth-enabled smart controllers. Companies prioritize strategic collaborations, digital-health partnerships, and AI-driven software enhancements to improve therapy outcomes and expand patient adherence. As pricing pressure intensifies and reimbursement frameworks evolve, manufacturers focus on scalable, cost-efficient designs to capture growing demand across both developed and emerging regions.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- EOFLOW CO., LTD. (Korea)
- ViCentra B.V. (Netherlands)
- Tandem Diabetes Care, Inc. (U.S.)
- Ypsomed AG (Switzerland)
- Microtec Medical Ltd (U.K.)
- Insulet Corporation (U.S.)
- SOOIL Developments Co., Ltd (Korea)
- CeQur Simplicity (Switzerland)
- Medtronic (Ireland)
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd (Switzerland)
Recent Developments
- In May 2025, Ypsomed reported that its mylife YpsoPump achieved CHF 175.3 million in revenue in FY 2024/25 (an 80.8% increase year-over-year), driven by the mylife Loop system and growth in Germany, France, UK, Spain and Australia.
- In October 2024, ViCentra announced CE-mark certification for its next-generation “Kaleido” insulin patch pump under the EU Medical Device Regulation.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Product type, Disease indication, Distribution channel and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Adoption of automated and fully closed-loop insulin delivery systems will accelerate as algorithms become more precise and adaptive.
- Patch pumps and tubeless wearable formats will gain stronger traction due to rising demand for discreet, flexible, and low-maintenance insulin delivery.
- Integration of pumps with continuous glucose monitoring and cloud-based platforms will expand remote diabetes management.
- AI-driven predictive dosing and personalized therapy models will enhance treatment accuracy and patient adherence.
- Emerging markets will experience increasing pump penetration as awareness, insurance coverage, and digital-health infrastructure expand.
- Manufacturers will prioritize miniaturization, longer-wear infusion sets, and simplified onboarding to improve user experience.
- Competition will intensify as new entrants introduce cost-efficient pumps and interoperable device ecosystems.
- Regulatory pathways will evolve to support innovative hybrid and multi-hormone pump technologies.
- Hospitals and diabetes clinics will adopt structured training programs to increase safe initiation for first-time pump users.
- Sustainability-driven designs, including recyclable components and low-waste consumables, will influence next-generation product development.




