Market Overview
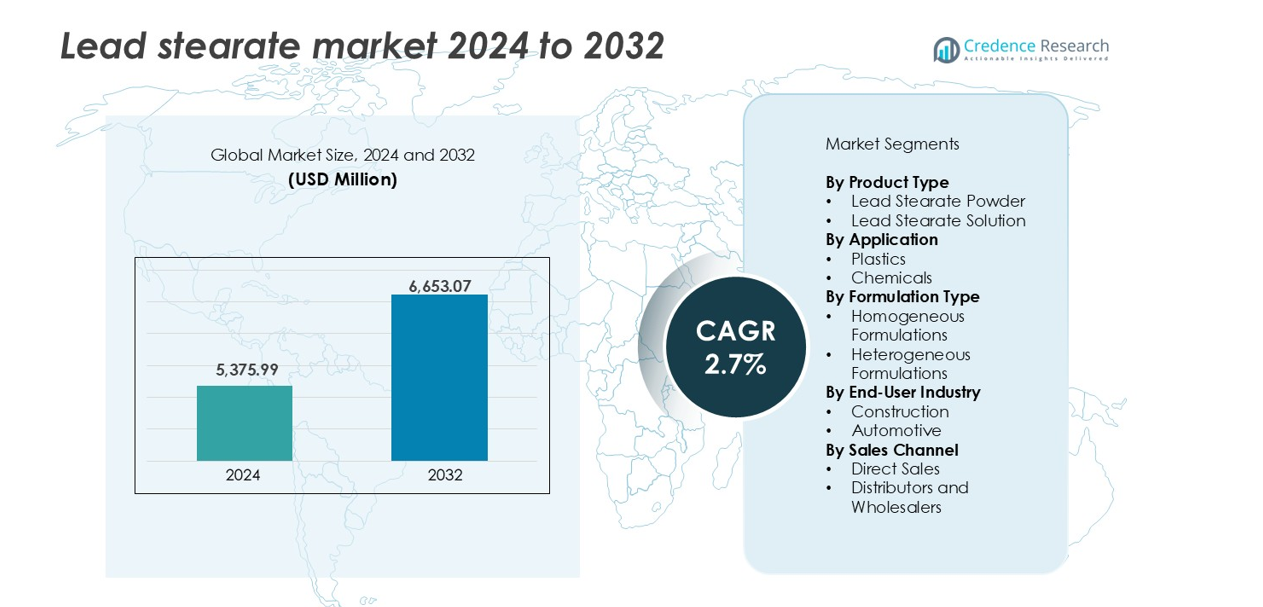
The Lead Stearate Market size was valued at USD 5,375.99 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 6,653.07 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 2.7% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Lead Stearate Market Size 2024 |
USD 5,375.99 million |
| Lead Stearate Market, CAGR |
2.7% |
| Lead Stearate Market Size 2032 |
SD 6,653.07 million |
The lead stearate market is led by a mix of global and regional players, with dominant contributions from companies based in China and India. Key manufacturers include WSD Chemical Limited, American Elements, Triveni Interchem Private Limited, POCL Enterprises Limited, and Xiamen Hisunny Chemical Co., LTD. These companies focus on industrial-grade formulations, serving PVC, plastic, and lubricant sectors across multiple geographies. China holds a strong supply position due to low-cost manufacturing and export capacity, while Indian firms maintain competitive pricing and regional dominance. Asia-Pacific leads the global market with a 45% share in 2024, driven by high plastic consumption, infrastructure projects, and expanding automotive production. Market players continue to strengthen distribution and compliance capabilities to capture both regulated and emerging markets.
Market Insights
- The Lead Stearate Market was valued at USD 5,375.99 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 6,653.07 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 2.7% during the forecast period.
- Rising demand for PVC heat stabilizers in construction and automotive applications is driving market growth, especially in cost-sensitive regions that favor lead-based additives.
- A key trend includes the dual-market strategy where suppliers serve both regulated markets with lead-free alternatives and emerging economies with traditional lead stearate formulations.
- The market remains fragmented with Indian and Chinese players holding strong shares; companies compete on price, supply reliability, and compatibility with legacy compounding systems.
- Asia-Pacific led the market with a 45% share in 2024, followed by North America at 18% and Europe at 14%; plastics held over 70% of the application segment, while lead stearate powder accounted for more than 65% of the product type share.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Product Type
Lead stearate powder holds the dominant share in the product type segment, accounting for over 65% of the market in 2024. Its widespread use in PVC stabilizers and lubricants for plastic manufacturing supports strong demand. The powder form enables easy blending with polymer matrices, making it a preferred choice in extrusion and molding operations. Consistent performance, high thermal stability, and cost-effectiveness drive its selection in industrial applications. In contrast, lead stearate solution is used in niche processes, where liquid formulations are required for uniform dispersion.
- For instance, Baerlocher produces over 40,000 metric tons of metallic stearates annually at individual facilities, but their production focus has shifted toward eco-friendly calcium-zinc stearates for modern rigid PVC processing, in line with current sustainability trends.
By Application
Plastics emerged as the leading application segment, capturing more than 70% of the market in 2024. Lead stearate functions as a heat stabilizer and lubricant in plastic production, especially in rigid PVC compounds used in pipes, cables, and profiles. Its ability to enhance processability and reduce degradation during high-temperature operations drives consistent usage. The chemical segment follows, where lead stearate serves as a catalyst or reaction intermediate. However, regulatory scrutiny limits its expansion compared to the dominant plastics application.
- For instance, Reagens Group, a leader in sustainable PVC additives, supplies calcium-organic systems (COS) and calcium-zinc-based stabilizers for extrusion lines producing a large volume of rigid PVC annually across Europe and Asia, having completely phased out lead-based stabilizers in Europe.
By Formulation Type
Homogeneous formulations lead this segment with a market share exceeding 60% in 2024. These formulations offer consistent performance across production batches, ensuring uniform dispersion and compatibility with base materials. Homogeneous types are favored in automated plastic manufacturing lines where precision and repeatability are critical. Their ease of integration into standard compounding operations further supports demand. Heterogeneous formulations, though used in specialized setups, face limitations due to inconsistent mixing and performance variability under changing processing conditions.
Key Growth Drivers
High Demand in PVC Processing and Stabilization
Lead stearate plays a crucial role in the production of rigid PVC products, acting as a heat stabilizer and internal lubricant. Its ability to improve processability and maintain polymer integrity during high-temperature extrusion and molding supports wide use in pipe, cable, and profile manufacturing. The construction and infrastructure sectors rely heavily on rigid PVC, which boosts lead stearate consumption. Growth in urban development and renovation projects, especially across Asia-Pacific, strengthens this demand. The compound’s effectiveness in stabilizing chlorine degradation during PVC processing gives it a cost-performance advantage over alternatives. Manufacturers in emerging markets continue to prefer lead-based additives for their affordability, reinforcing market expansion despite global regulatory shifts.
- For instance, Finolex Industries operates PVC extrusion lines with a capacity exceeding 495,000 metric tons annually, using lead-free, UV-stabilized materials in pipe production.
Expansion of Automotive and Industrial Manufacturing
Automotive production growth, particularly in Asia and Eastern Europe, supports the lead stearate market through its use in under-the-hood plastic components and wire coatings. The compound’s thermal stability and lubrication properties enhance the durability of PVC parts exposed to high engine temperatures. In industrial manufacturing, lead stearate is valued for its role in greases, coatings, and chemical synthesis. Its compatibility with various polymers allows for flexibility in production setups. Rapid industrialization in developing economies has led to increased demand for high-performance materials, further fueling consumption. The push for localized manufacturing across automotive supply chains also drives the uptake of PVC additives, including lead stearate.
- For instance, Sumitomo Electric utilizes lead-free and halogen-free PVC in wiring harnesses for passenger vehicles to comply with global environmental directives; with a network of over 100 global facilities, the company produces millions of kilometers of cable annually and is currently transitioning to lightweight aluminum harnesses for electric vehicles.
Cost-Effectiveness and Established Supply Chains
Lead stearate remains one of the most cost-effective metal stearates available for industrial use. Its lower price compared to non-lead alternatives, such as calcium-zinc or organic stabilizers, gives it an edge in price-sensitive markets. Established supply chains and mature production processes ensure stable availability and consistent quality. This reliability is important for industries that demand uniform product performance and minimal production downtime. In regions where environmental regulations are less stringent, manufacturers prefer lead-based stabilizers to maintain profitability. The large installed base of PVC compounding equipment compatible with lead stearate formulations further delays the transition to alternative additives, helping sustain its demand.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Shift Toward Lead-Free Alternatives in Regulated Markets
A growing number of countries are enforcing tighter regulations on lead-based additives, pushing industries to explore safer alternatives. This transition, while a challenge for lead stearate, opens opportunities for companies offering hybrid or lead-reduced solutions. Product innovation aimed at replicating the performance of lead stearate without toxicity concerns is gaining traction. Europe and North America are seeing investments in non-lead stabilizer research, but many manufacturers still rely on lead stearate during the transition phase. This scenario creates dual demand traditional use in unregulated regions and replacement demand in regulated ones, allowing manufacturers to serve both markets strategically.
- For instance, Baerlocher has developed calcium-zinc and organic-based stabilizers, now used in over 250,000 metric tons of PVC annually across European processing lines, replacing lead compounds.
Emerging Demand from Developing Economies
Developing countries across Asia, Latin America, and Africa present a major growth opportunity due to increasing investments in construction, power, and industrial infrastructure. These regions prioritize affordability and proven material performance, making lead stearate an ideal solution. Rapid urbanization is driving demand for PVC pipes, fittings, and electrical insulations, all of which rely on heat-stable additives. Limited regulatory enforcement in these areas supports continued use of lead-based compounds. Market players expanding production facilities in proximity to these emerging economies stand to benefit from strong demand growth while offsetting slowing sales in highly regulated markets.
Key Challenges
Stringent Environmental and Health Regulations
Lead stearate faces growing scrutiny due to its toxicological profile and environmental persistence. Regulatory bodies in Europe, North America, and parts of Asia-Pacific are restricting its use in consumer goods and construction materials. Compliance with REACH, RoHS, and other frameworks requires manufacturers to either phase out lead compounds or invest in mitigation systems. These changes increase production costs and limit market access. Companies that fail to adapt face bans or reduced demand. The challenge also lies in finding cost-effective, high-performing alternatives that do not compromise production speed or final product quality.
Growing Pressure from Lead-Free Stabilizer Alternatives
The lead stearate market is increasingly threatened by the rise of non-toxic metal stabilizers like calcium-zinc and organic-based systems. These alternatives offer better environmental profiles and are favored in regions with strict regulatory oversight. As polymer compounders invest in upgrading their processes for lead-free compatibility, the long-term competitiveness of lead stearate declines. Innovation in stabilizer technology is reducing the cost-performance gap, accelerating adoption of alternatives. This transition challenges legacy producers and may lead to demand shifts, particularly in high-value, export-oriented plastic manufacturing.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America accounted for around 18% of the global lead stearate market share in 2024. The region’s demand is driven by the plastics and automotive sectors, particularly in the United States. Despite strict environmental regulations limiting the use of lead-based additives, legacy applications in industrial and construction-grade PVC maintain consistent consumption. Ongoing infrastructure upgrades and replacement demand for piping systems support the use of lead stearate in heat-resistant formulations. However, a gradual shift toward lead-free stabilizers may restrain long-term growth. Market players focus on specialized formulations to comply with evolving health and safety regulations.
Europe
Europe held approximately 14% share in the global lead stearate market in 2024. The region enforces some of the strictest regulations on lead compounds under REACH and RoHS, significantly limiting demand in consumer-facing applications. However, lead stearate remains in use within industrial processes, particularly in Eastern European countries with less stringent enforcement. Substitutes such as calcium-zinc stabilizers are gaining traction, gradually reducing lead-based product demand. Western Europe is witnessing a shift toward sustainable alternatives, but legacy systems and cost-sensitive applications still rely on lead stearate. Market growth in Europe remains slow, shaped by regulatory compliance and reformulation strategies.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific dominates the lead stearate market with over 45% share in 2024, led by strong manufacturing activity in China and India. The region benefits from a large base of PVC processors, construction projects, and plastic product exporters. Cost-effectiveness and performance advantages keep lead stearate as a primary stabilizer across several industrial verticals. Regulatory pressure remains moderate compared to Western countries, allowing widespread use across multiple end-use sectors. Rapid urbanization, infrastructure expansion, and rising automotive production further drive consumption. Domestic manufacturers continue to supply large volumes for local use, supported by established supply chains and relatively lenient environmental regulations.
Latin America
Latin America contributed about 10% to the global lead stearate market in 2024. Brazil and Mexico are the primary demand centers due to their expanding construction and automotive industries. The region favors lead stearate for its affordability and performance in heat-sensitive PVC applications like pipes, conduits, and cable coatings. While awareness of environmental concerns is growing, regulatory enforcement remains uneven, allowing continued use across traditional sectors. Import reliance for finished products and additives poses a challenge, but local compounding activity helps support regional supply. Market growth is stable, though limited by slower regulatory transitions and infrastructure investment cycles.
Middle East & Africa (MEA)
The MEA region held around 8% of the global lead stearate market in 2024. Demand is largely driven by infrastructure and construction activities in the Gulf countries and parts of North Africa. Lead stearate’s cost-efficiency and functional reliability make it a preferred additive in PVC-based building materials. The automotive and chemical sectors in South Africa also contribute to moderate demand. Regulatory control over hazardous substances remains limited across most parts of the region, enabling steady usage. Market penetration is expected to grow slowly, aligned with construction project pipelines and industrial capacity expansions across select urban zones.
Market Segmentations:
By Product Type
- Lead Stearate Powder
- Lead Stearate Solution
By Application
By Formulation Type
- Homogeneous Formulations
- Heterogeneous Formulations
By End-User Industry
By Sales Channel
- Direct Sales
- Distributors and Wholesalers
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The lead stearate market features a mix of global and regional players competing on product quality, price, and distribution reach. China and India dominate the supplier base, with companies like WSD Chemical Limited, Xiamen Hisunny Chemical, and POCL Enterprises Limited serving bulk demand across Asia and emerging markets. U.S.-based American Elements caters to high-purity requirements in niche industrial applications. Indian firms such as Triveni Interchem, Nexus Polychem, and Almstab hold significant presence in domestic and export markets. Most competitors focus on industrial-grade formulations, leveraging established PVC and plastic-processing supply chains. Chinese manufacturers benefit from low-cost production and export strength, while Indian players invest in value-added variants. Market competition is intensifying with the rise of lead-free stabilizer producers, compelling some firms to expand portfolios. Players that maintain consistent quality, cost leadership, and regulatory compliance are best positioned to sustain share in both regulated and developing markets.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Vishal Pharmakem (India)
- Beijing Yunbang Biosciences Co. Ltd. (China)
- Zauba Technologies Pvt Ltd (India)
- American Elements (U.S.)
- POCL Enterprises Limited (India)
- Hunan Shaoyang Tiantang Auxiliaries Chemical, Co., Ltd. (China)
- Stabplastchemo (India)
- WSD Chemical Limited (China)
- Almstab (India)
- Triveni Interchem Private Limited (India)
- Hangzhou Oleochemicals Co., Ltd. (China)
- Nexus Polychem (India)
- aivitchem (India)
- Shristab Pvt. Ltd. (India)
- Qingdao Echemi Technology Co., Ltd. (China)
- Sancheti Polymers (India)
- Pratham Metchem LLP (India)
- Chongqing ChangFeng Chemical Co., Ltd. (China)
- Asian Organo Industries (India)
- Xiamen Hisunny Chemical Co., LTD (China)
- Hengshui Taocheng Chemical Auxiliary Co., Ltd. (China)
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Product Type, Application, Formulation Type, End-User Industry, Sales Channel and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Demand for lead stearate will remain steady in industrial and construction-grade PVC applications.
- Emerging economies will continue to prefer lead-based additives due to cost advantages and availability.
- Regulatory restrictions in Europe and North America will push gradual substitution with safer alternatives.
- Manufacturers will expand operations in Asia and Africa to meet growing infrastructure and plastic demand.
- Investments in hybrid stabilizer technologies may open niche opportunities for modified lead stearate products.
- Automotive and wire coating sectors will support demand for heat-stable and durable PVC compounds.
- Local players in India and China will maintain dominance through competitive pricing and regional supply.
- Innovation in dispersion and blending methods will improve product compatibility and efficiency.
- Export-oriented manufacturers will adapt formulations to meet dual compliance in global and domestic markets.
- Environmental scrutiny will increase pressure on producers to adopt cleaner production and waste disposal methods.




