Market Overview
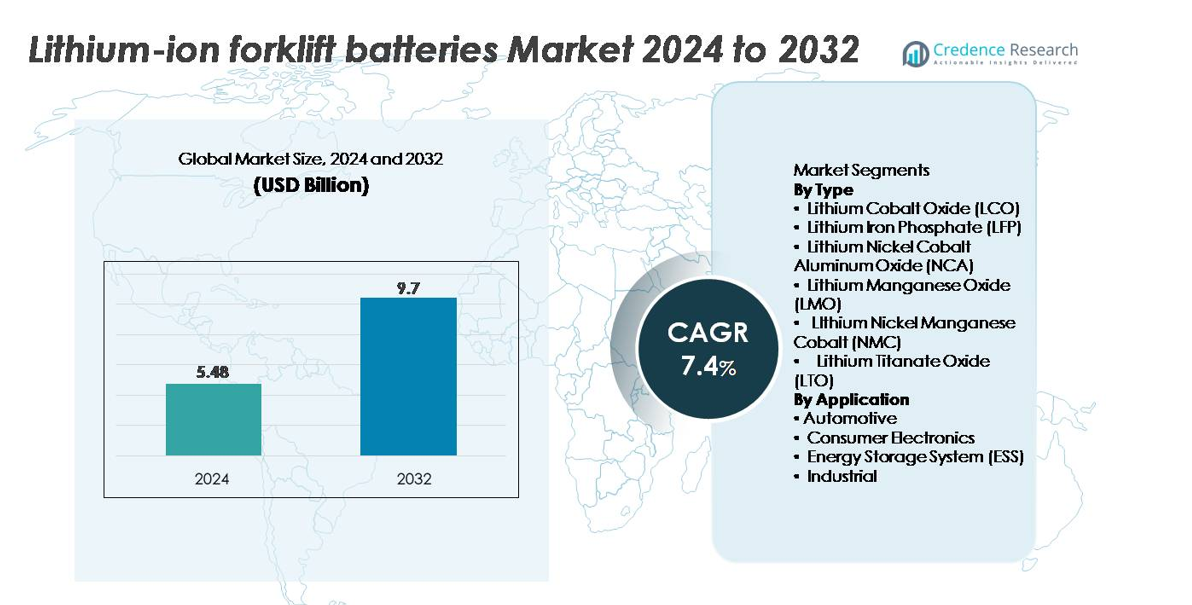
The lithium-ion forklift batteries market was valued at USD 5.48 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 9.7 billion by 2032, reflecting a CAGR of 7.4% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Lithium-Ion Forklift Batteries Market Size 2024 |
USD 5.48 billion |
| Lithium-Ion Forklift Batteries Market, CAGR |
7.4% |
| Lithium-Ion Forklift Batteries Market Size 2032 |
USD 9.7 billion |
Asia Pacific dominates the lithium-ion forklift batteries market, holding approximately 48% of global share due to its strong battery manufacturing base and rapid industrial electrification. The competitive landscape is led by major cell and pack producers such as CATL, BYD Company, LG Chem, Samsung SDI, Panasonic Corporation, BAK Power, Toshiba Corporation, Hitachi, Clarios, and Automotive Energy Supply Corporation. These companies compete on energy density, safety systems, cycle life, and cost-efficient production. Their strategic partnerships with forklift OEMs, expansion of LFP-based solutions, and investments in high-volume manufacturing reinforce their leadership across rapidly growing logistics and warehousing ecosystems.
Market Insights
- The lithium-ion forklift batteries market reached USD 5.48 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit USD 9.7 billion by 2032 at a 7.4% CAGR, supported by strong global electrification of material-handling fleets.
- Market growth is driven by rapid warehouse automation, multi-shift operations, and the shift from lead-acid to fast-charging, maintenance-free lithium-ion chemistries especially LFP, which holds the largest segment share due to long cycle life and thermal stability.
- Key trends include adoption of smart batteries with BMS analytics, opportunity charging, and integration of lithium-ion systems into next-generation Class I–III forklifts.
- Competitive intensity increases as CATL, BYD, LG Chem, Samsung SDI, and Panasonic expand LFP and NMC production, while OEM partnerships and vertically integrated supply chains strengthen market leadership.
- Regionally, Asia Pacific leads with ~48% share, followed by North America (~22%) and Europe (~20%), driven by logistics growth, e-commerce expansion, and strong industrial electrification policies.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Type
Lithium-ion forklift batteries show strong differentiation across chemistries, with Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) emerging as the dominant sub-segment, holding the largest share due to its long cycle life, high thermal stability, and lower maintenance requirements. LFP packs support fast charging and deep-discharge performance, making them ideal for intensive warehouse fleets and multi-shift operations. Meanwhile, NMC and NCA variants gain traction where higher energy density is required, particularly in compact forklift models. LTO and LMO chemistries remain niche options, used mainly in ultra-fast-charging or low-temperature industrial environments.
- For instance, CATL’s LFP cell platform delivers up to 12,000 charge cycles and maintains structural stability through its cell-to-pack (CTP) 3.0 architecture with a 160 Wh/kg LFP energy density benchmark making it highly suitable for multi-shift warehouse operations.
By Application
By application, the Industrial segment accounts for the largest market share, driven by extensive adoption of electric forklifts across logistics centers, e-commerce warehouses, retail distribution hubs, and manufacturing plants. These facilities prioritize lithium-ion systems to eliminate maintenance downtime and achieve predictable, high-throughput operations. Automotive and ESS applications are expanding but remain secondary in forklift-specific demand, while consumer electronics plays a minimal role. Continuous warehouse automation, strict emission regulations, and the shift toward 24/7 material-handling operations solidify the industrial segment’s dominance in lithium-ion forklift battery deployment.
- For instance, BYD’s iron-phosphate industrial battery platform provides over 4,000 full charge–discharge cycles and supports fast charging to 100% in about 60 minutes, enabling uninterrupted multi-shift use. Automotive and ESS applications are growing but remain secondary within forklift-specific deployments.
Key Growth Drivers:
Accelerating Electrification of Material-Handling Equipment
The rapid shift from internal combustion forklifts to electric variants is a major growth catalyst for lithium-ion forklift batteries. Warehousing, logistics, and e-commerce companies increasingly implement fully electric fleets to reduce emissions, improve air quality, and comply with sustainability targets. Lithium-ion systems outperform lead-acid batteries by offering longer cycle life, high energy efficiency, and fast charging without the need for battery swapping rooms. Multi-shift industrial facilities benefit from minimal downtime, enabling continuous operation and improved throughput. The rising cost of labor and the need for automation-friendly power solutions further reinforce adoption. Forklift OEMs are integrating factory-fitted lithium-ion options across Class I, II, and III models, while fleet operators standardize on lithium-ion to optimize total cost of ownership. Collectively, these factors make electrification one of the strongest long-term drivers for lithium-ion forklift battery demand.
- For instance, BYD’s lithium-iron-phosphate forklift batteries deliver over 4,000 full cycles and support full charging in about 60 minutes, eliminating the need for battery-swap rooms.
Expansion of High-Density Warehousing and E-Commerce Fulfillment
The boom in e-commerce, retail distribution, and last-mile delivery has created strong demand for high-throughput warehouse operations, directly expanding the market for lithium-ion forklift batteries. Fulfillment centers rely on electric forklifts, pallet trucks, and order pickers operating continuously across multiple shifts, requiring energy solutions that support fast opportunity charging and consistent power output. Lithium-ion batteries deliver superior charge acceptance, reduced heat generation, and the ability to maintain voltage under heavy loads, making them ideal for high-speed inventory movement. Automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) also depend on stable power platforms compatible with automated workflows. As companies adopt robotics, automated conveyors, and real-time inventory systems, reliable energy storage becomes critical. Lithium-ion technology meets these performance and durability requirements, positioning it as the preferred choice for modern warehouses that prioritize uptime, efficiency, and long-term reliability.
- For instance, a large, custom-engineered Panasonic industrial lithium-ion battery system (comprising numerous cells in parallel) might be capable of providing high stability under loads drawing up to several hundred amps, enabling rapid inventory movement in heavy-duty electric vehicles or large robotics.”
Rising Preference for Maintenance-Free and Long-Lifespan Batteries
Industrial fleet operators increasingly favor lithium-ion forklift batteries because they eliminate the burdensome maintenance associated with lead-acid systems such as watering, equalization, ventilation, and periodic replacements. Lithium-ion batteries deliver long service life with 2,000–5,000 charge cycles depending on chemistry and operating conditions, significantly reducing lifecycle operating costs. Their sealed design enhances safety by preventing acid spills, corrosion, or harmful gas emissions. Fast-charging capability enables opportunity charging during breaks, eliminating the need for spare batteries and storage rooms. Businesses focused on operational efficiency find these advantages especially compelling, particularly in fast-moving sectors like automotive manufacturing, food processing, and pharmaceuticals. Reduced downtime, enhanced energy efficiency, and improved power density create substantial long-term cost benefits, reinforcing lithium-ion systems as the preferred energy solution for modern material-handling equipment.
Key Trends & Opportunities:
Growth of Smart Lithium-Ion Batteries with Telemetry and Fleet Analytics
A major trend is the integration of smart battery management features that provide real-time health monitoring, usage analytics, and predictive maintenance alerts. Connected lithium-ion forklift batteries equipped with IoT sensors enable fleet managers to track charge cycles, temperature fluctuations, depth of discharge, and energy consumption patterns. This data-driven visibility improves battery lifespan and reduces unexpected failures. Predictive diagnostics optimize charging behavior and load balancing, leading to extended operational uptime. Warehouse automation platforms increasingly integrate battery telemetry into fleet management dashboards, enabling users to allocate forklifts more effectively. As logistics centers shift toward digitization and Industry 4.0 principles, smart lithium-ion batteries create new opportunities for efficiency optimization, cost reduction, and fully automated charging ecosystems. This convergence of energy storage and digital intelligence becomes a critical differentiator for advanced industrial operations.
- For instance, BYD’s integrated smart BMS continuously logs numerous key operational parameters per battery, including cell-level temperatures, voltage, current, and charge rates. This data-driven insight extends lifespan and reduces unexpected failures by enabling state of charge (SoC) and state of health (SoH) estimations, as well as thermal management and cell balancing.
Growing Adoption of Fast-Charging and Opportunity Charging Infrastructure
The market is experiencing a strong push toward fast-charging technologies that support 24/7 warehouse operations without traditional battery-swapping requirements. Opportunity charging where forklifts recharge during short breaks has become central to high-volume facilities, reducing the need for backup batteries. Advancements in high-power chargers, thermal control systems, and stable lithium-ion chemistries such as LFP and LTO improve charge acceptance and reduce heat-related degradation. Facilities redesign their energy infrastructure to incorporate rapid chargers at strategic points, enabling seamless workflows and uninterrupted equipment availability. As companies prioritize space optimization, eliminating battery rooms and reducing spare battery inventory lowers operational costs. This trend opens significant opportunities for charging system manufacturers and forklift OEMs offering integrated charging ecosystems compatible with fleet automation strategies.
- For instance, Toshiba’s SCiB LTO cells can charge to 80% in approximately 6 minutes, enabling true opportunity-charging cycles.
Key Challenges:
High Upfront Cost and Capital Investment Barriers
Despite strong long-term benefits, the high initial cost of lithium-ion forklift batteries remains a top challenge for many industrial buyers. Lithium-ion packs are significantly more expensive than lead-acid alternatives, often requiring substantial capital investment, especially for large fleets. Small and medium-sized enterprises with limited budgets face difficulty transitioning to lithium-ion systems, even when lifecycle savings are compelling. Additional expenses related to compatible chargers, electrical upgrades, and safety compliance increase the financial burden. Although leasing and battery-as-a-service models are emerging, adoption remains slower in cost-sensitive markets. These financial constraints continue to hinder wider deployment, particularly in developing regions with price-driven purchasing behavior.
Thermal Management and Safety Concerns in Intensive Industrial Operations
While lithium-ion batteries offer strong performance advantages, thermal management, overheating risks, and concerns around thermal runaway present key challenges in demanding industrial environments. Forklifts operating in high-temperature warehouses, cold storage, or heavy-duty cycles require robust cooling systems and advanced battery management technologies to ensure safe operation. Inadequate thermal control can accelerate cell degradation, reduce cycle life, or increase safety hazards. Meeting stringent industrial safety standards requires sophisticated BMS algorithms, insulation materials, and protective enclosures, which raise system complexity and cost. Ensuring long-term reliability in extreme operating conditions remains a major engineering priority for manufacturers, creating ongoing challenges in design, testing, and certification.
Regional Analysis:
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific holds the largest market share of approximately 48%, driven by massive forklift deployment across manufacturing, automotive, electronics, and e-commerce distribution hubs in China, Japan, South Korea, and Southeast Asia. The region benefits from strong domestic lithium-ion battery manufacturing capacity and rapid adoption of electric forklifts in export-oriented industries. China leads installations due to aggressive electrification mandates and dense warehouse expansion. Growing investments in automated logistics and high-volume industrial operations further reinforce the region’s dominance, supported by cost-effective battery production and strong supply-chain integration.
North America
North America commands an estimated 22% market share, supported by the rapid shift toward electrified material-handling equipment across e-commerce fulfillment centers, retail distribution hubs, and automotive manufacturing plants. The United States drives most demand as companies adopt multi-shift warehouse operations that rely heavily on fast-charging lithium-ion systems. Strict sustainability commitments and OSHA-driven workplace safety improvements accelerate replacement of lead-acid fleets. Expansion of cold storage infrastructure, food logistics, and advanced manufacturing also strengthens the region’s adoption rate, making North America one of the fastest-growing markets for high-efficiency lithium-ion forklift batteries.
Europe
Europe accounts for roughly 20% market share, driven by stringent EU emission standards, automation-focused industrial strategies, and strong electrification uptake across Germany, France, the UK, Italy, and the Nordics. The region’s warehousing ecosystem increasingly prefers lithium-ion systems to support energy efficiency targets and reduce operational downtime. Automotive OEMs, food processing plants, and 3PL providers adopt lithium-ion forklift fleets to align with sustainability programs and reduce total lifecycle costs. European manufacturers also integrate advanced safety and battery-management technologies, reinforcing regional technological leadership and accelerating penetration across indoor and outdoor material-handling applications.
Latin America
Latin America captures approximately 7% market share, with growth led by Brazil, Mexico, and Chile as industrial modernization accelerates. Increasing adoption of electric forklifts in automotive assembly, mining logistics, and consumer goods distribution strengthens the shift from diesel and lead-acid systems to lithium-ion alternatives. Improvements in supply-chain automation and rising investments from multinational manufacturers boost demand for high-cycle, maintenance-free batteries. However, higher upfront costs and limited local charging infrastructure continue to restrain broader adoption, keeping market penetration lower compared with North America and Europe, though growth momentum remains positive.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region represents an estimated 3% market share, driven by expanding logistics, retail warehousing, and industrial operations in the UAE, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, and Nigeria. Growing investment in smart warehouses, free-trade zones, and port automation supports increased deployment of lithium-ion forklift fleets. The technology’s low maintenance and resilience in high-temperature environments make it increasingly attractive. However, reliance on imported batteries, slower electrification adoption, and cost constraints limit large-scale penetration. Despite these challenges, rising infrastructure development and regional industrial diversification are expected to support steady uptake.
Market Segmentations:
By Type
- Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LCO)
- Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP)
- Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide (NCA)
- Lithium Manganese Oxide (LMO)
- Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC)
- Lithium Titanate Oxide (LTO)
By Application
- Automotive
- Consumer Electronics
- Energy Storage System (ESS)
- Industrial
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape:
The competitive landscape of the lithium-ion forklift batteries market is shaped by a mix of global battery manufacturers, forklift OEMs, and specialized industrial energy-storage providers competing on performance, safety, and lifecycle value. Leading players focus on expanding high-energy-density chemistries such as LFP and NMC while integrating advanced battery-management systems that enhance thermal control, charge efficiency, and predictive maintenance. Companies increasingly partner with forklift manufacturers to offer factory-fitted lithium-ion solutions optimized for Class I–III vehicles, reducing integration complexity for end users. Strategic investments in fast-charging infrastructure, modular pack design, and telematics-enabled battery platforms strengthen product differentiation. Major vendors also pursue capacity expansions, recycling programs, and localized manufacturing to address supply-chain stability concerns. As warehouse automation, e-commerce logistics, and sustainability mandates intensify, competition centers on delivering longer cycle life, higher operational uptime, and lower total cost of ownership. This technology-driven environment positions innovation and vertical integration as the primary competitive advantages.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis:
- Samsung SDI (South Korea)
- Hitachi (Japan)
- Clarios (Germany)
- BAK Power (China)
- Panasonic Corporation (Japan)
- Automotive Energy Supply Corporation (Japan)
- Toshiba Corporation (Japan)
- LG Chem (South Korea)
- BYD Company (China)
- Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Ltd (CATL) (China)
Recent Developments:
- In November 2025,Samsung SDI won the “CES Innovation Award – Best of Innovation” for a high-power cylindrical lithium-ion battery design that delivers ultra-fast charging and long life signaling its push toward more robust, high-output battery platforms.
- In September 2025, Samsung SDI unveiled its next-generation “Battery Box 1.7” and an LFP-applied “SBB 2.0” at the global RE+ 2025 energy expo, showcasing high-capacity, safety-enhanced prismatic battery solutions optimized for energy-storage and commercial use.
- In 2025, (Meadowbrook plant anniversary), Clarios celebrated 15 years of operation at its Meadowbrook facility, marking production of over 6 million LTO cells and delivering more than 1 million lithium-ion battery units highlighting its long-term manufacturing scale and capacity.
Report Coverage:
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Type, Application and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook:
- Demand for lithium-ion forklift batteries will rise as warehouses transition fully to electric and automation-ready material-handling fleets.
- LFP chemistries will continue to dominate due to superior safety, long cycle life, and stable thermal performance in multi-shift operations.
- Fast-charging and opportunity-charging solutions will become standard, eliminating spare battery rooms and reducing operational downtime.
- Smart BMS technologies with real-time diagnostics and predictive maintenance will enhance fleet efficiency and extend battery lifespan.
- OEM-integrated lithium-ion forklift models will gain traction, reducing retrofit demand and simplifying fleet electrification.
- Battery-as-a-service and leasing models will expand adoption among cost-sensitive industrial users.
- Recycling and second-life applications will strengthen sustainability and reduce supply-chain risks tied to raw material availability.
- Modular and swappable pack designs will improve flexibility for diverse warehouse layouts and operating intensities.
- Regional manufacturing expansion will reduce dependence on imports and stabilize battery availability.
- Growth of cold chain logistics and high-density warehousing will accelerate adoption of robust lithium-ion systems optimized for extreme environments.




