Market Overview
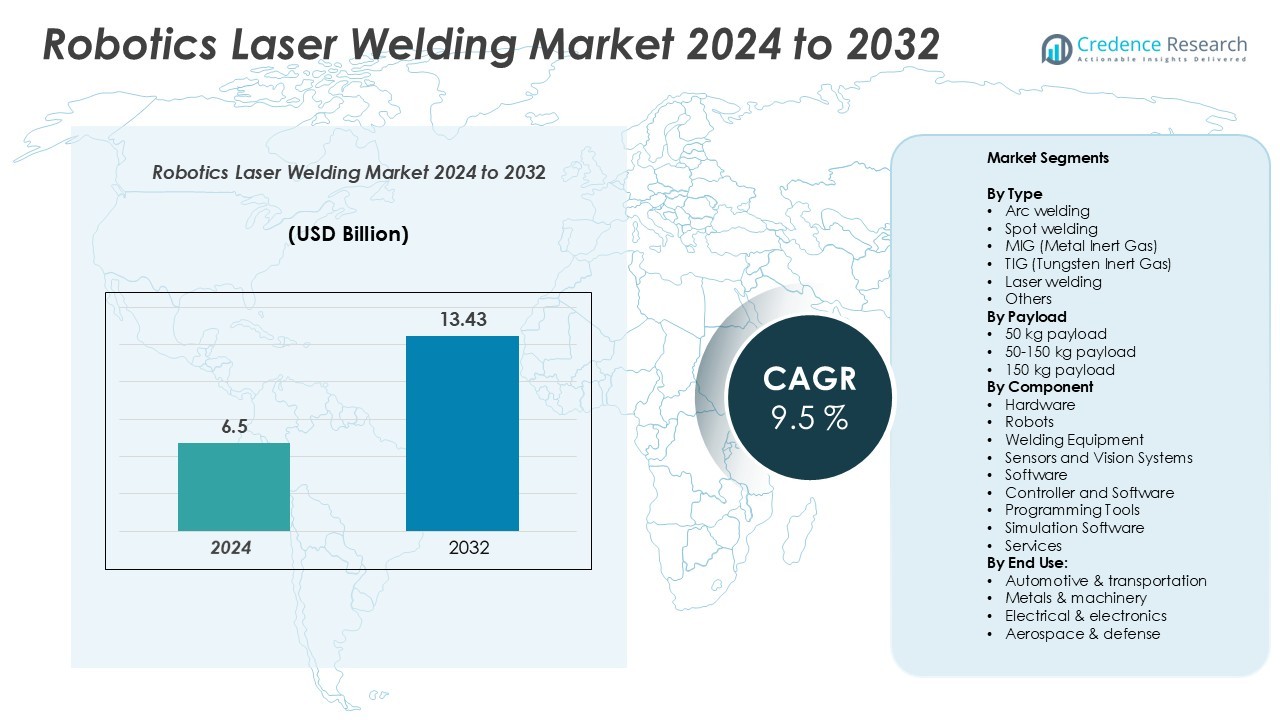
Robotics Laser Welding Market size was valued at USD 6.5 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 13.43 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 9.5% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Robotics Laser Welding Market Size 2024 |
USD 6.5 Billion |
| Robotics Laser Welding Market, CAGR |
9.5% |
| Robotics Laser Welding Market Size 2032 |
USD 13.43 Billion |
The robotics laser welding market is dominated by top players including ABB Ltd., FANUC Corporation, Yaskawa Electric Corporation, KUKA AG, Panasonic Corporation, Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd., and Daihen Corporation. These companies lead through continuous innovation, strategic partnerships, and global operational presence. ABB and KUKA focus on precision engineering and automation technologies, while FANUC and Yaskawa deliver advanced robotic systems for automotive and electronics industries. Panasonic and Kawasaki emphasize integrated robotics-laser welding solutions to enhance efficiency and quality. North America leads the market with a 35% share, followed by Europe at 28% and Asia-Pacific at 25%, reflecting strong adoption of automated and high-precision manufacturing solutions in these regions. Emerging markets in Latin America and the Middle East & Africa contribute smaller shares but offer growth opportunities.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The Robotics Laser Welding Market size was valued at USD 6.5 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 13.43 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 9.5% during the forecast period, with laser welding as the dominant type and 50–150 kg payload robots holding the largest segment share.
- Growth is driven by increasing automation in automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries, rising demand for high-precision welding, and technological advancements in laser and robotic systems improving efficiency and reducing labor dependency.
- Key trends include the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, collaborative robots (cobots) for flexible manufacturing, and expansion in emerging markets such as China, India, and Brazil. Companies focus on R&D, partnerships, and advanced system integration to enhance competitiveness.
- High initial investments, operational costs, and the need for skilled workforce for system operation and maintenance act as restraints, limiting adoption among small and medium enterprises.
- North America leads with 35% market share, Europe holds 28%, Asia-Pacific 25%, Latin America 7%, and Middle East & Africa 5%, reflecting regional adoption trends and industrialization levels.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Type
The Robotics Laser Welding market by type is led by Laser welding, which holds the dominant share due to its precision, speed, and minimal heat-affected zone. Arc welding and MIG welding remain widely used for heavy-duty applications, while TIG and spot welding serve niche industries requiring high-quality seams. Laser welding’s adoption is driven by rising demand in automotive and electronics sectors, where accuracy and repeatability are critical. Advanced fiber laser technology allows integration with robotic arms, improving throughput and reducing cycle times, making it the preferred choice for manufacturers aiming to enhance productivity and reduce operational costs.
- For instance, FANUC’s fiber laser welding systems integrate with various ARC Mate series robots, including the ARC Mate 100iD, to perform high-speed, precision welding for applications like automotive body frames.
By Payload
In the payload segment, 50-150 kg payload robots dominate, balancing flexibility and load capacity for medium-scale welding operations. Robots under 50 kg are increasingly adopted for compact and precision applications, while >150 kg payload units are limited to large-scale industrial processes. The 50-150 kg range is favored due to its compatibility with automotive assembly lines, metal fabrication, and electronics manufacturing. Drivers include enhanced maneuverability, reduced installation costs, and adaptability across various welding types. Manufacturers prefer these robots for their ability to handle moderate components while maintaining high accuracy and speed, supporting diverse production requirements.
- For instance, the ABB IRB 6700 family includes variants that support payloads ranging from 150 kg to 300 kg and reaches from 2.6 m to 3.2 m. One model, the IRB 6700-150/3.20, features a 150 kg payload with a 3.2 m reach. This family of robots is used in welding lines and other applications in automotive manufacturing to improve productivity.
By Component
The component segment is led by Robots, accounting for the largest market share, supported by demand for fully automated welding solutions. Welding equipment and sensors/vision systems complement robotic operations by ensuring precision and quality control, while software, controllers, and simulation tools improve programming and process optimization. Drivers include rising automation adoption in automotive and aerospace industries, integration of AI and vision-based monitoring, and increasing focus on reducing labor dependency. Services also contribute by offering maintenance, retrofitting, and technical support, ensuring operational efficiency and minimizing downtime for manufacturers implementing robotic laser welding systems.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Demand for Precision and Efficiency in Manufacturing
Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics are increasingly adopting robotics laser welding to meet the growing need for high-precision and efficient manufacturing processes. Laser welding offers advantages like minimal thermal distortion, deep penetration, and high-speed processing, which are essential for producing lightweight and complex components. This trend is particularly evident in the automotive sector, where manufacturers seek to enhance vehicle performance and reduce emissions through advanced welding techniques. Integration with robotic arms improves throughput and reduces cycle times, making laser welding the preferred choice for manufacturers aiming to enhance productivity and reduce operational costs.
- For instance, A Panasonic-integrated system for automotive panel assembly would likely combine a high-power diode laser with a purpose-built robotic arm and optical seam-tracking technology. For instance, a system built around the LAPRISS series can feature a 4 kW direct diode laser oscillator. The system would incorporate real-time seam tracking using an optical sensor and software to maintain high-quality welding during high-speed applications on automotive body panels.
Advancements in Laser Technology and Robotics Integration
Continuous innovations in laser sources, control systems, and robotic platforms are driving adoption. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into robotic systems enables real-time monitoring and adaptive control, improving weld quality and consistency. Collaborative robots (cobots) allow safer human-robot interaction and flexible deployment in various manufacturing environments. These technological improvements increase process reliability, reduce error rates, and enable manufacturers to meet rising production demands efficiently while maintaining consistent quality across applications.
- For instance, Yaskawa’s MOTOMAN GP Series industrial robots, such as the GP25, are known for high-speed operation and outstanding repeatability of up to $\pm$0.02 mm. Some Yaskawa systems, like the AR series designed for arc welding, can be equipped with advanced software and potentially AI-driven functionalities to optimize weld quality. The increased processing speed of modern GP robots, which can be up to 39% faster than previous generations, is primarily achieved through advanced servo control.
Labor Shortages and the Need for Automation
The welding industry faces a shortage of skilled labor, prompting manufacturers to invest in automated solutions. Robotics laser welding addresses challenges such as high labor costs, skill gaps, and the need for consistent quality. By implementing robotic systems, companies can maintain high productivity levels while mitigating the impact of labor shortages. Automated solutions also reduce human error and improve workplace safety, further motivating industries to adopt robotic laser welding for long-term operational stability.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Integration with Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing
The shift towards Industry 4.0 is influencing the market, with manufacturers integrating IoT, big data analytics, and cloud computing into operations. This enables predictive maintenance, real-time process optimization, and enhanced traceability, leading to improved efficiency and reduced downtime. Advanced data monitoring helps companies identify defects early and optimize welding parameters, supporting higher throughput and quality. Such integration opens opportunities for smart factories where robotic laser welding systems are fully connected within automated production lines.
- For instance, ABB’s digital service offering, which monitors the health and performance of its robots, enables real-time performance tracking and predictive maintenance through cloud-based diagnostics. While the exact number of robots connected and the specific downtime reduction percentage varies, ABB has reported that its Connected Services have resulted in up to 25% fewer incidents and a 60% faster response time. The company has also stated that its digital solutions help ensure maximum performance and avoid unplanned downtime for customers.
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Emerging economies, particularly in Asia-Pacific, are witnessing rapid industrialization and urbanization, increasing demand for advanced manufacturing technologies. Countries like China, India, and Vietnam are investing heavily in automation to boost production capabilities and meet global supply chain demands. Robotics laser welding providers can capitalize on this growth by establishing localized production and service facilities. Expanding into these regions allows manufacturers to serve automotive, electronics, and machinery sectors, creating new revenue streams and driving market expansion.
- For instance, SENFENG Laser Technology Co., Ltd. holds over 700 technical patents and offers robotic laser welders that combine 6-axis robots with specialized heads for 3D-component welding in China.
Development of Collaborative and Portable Robotic Systems
Collaborative and portable robotic systems are opening new avenues for laser welding applications. These systems offer flexibility in deployment, allowing manufacturers to adapt to changing production requirements and space constraints. The ability to easily reconfigure and relocate welding stations enhances scalability and cost-effectiveness. These trends encourage adoption among small and medium-sized enterprises that require automation solutions without extensive infrastructure modifications.
Key Challenges
High Initial Investment and Operational Costs
Adoption of robotics laser welding systems requires significant capital investment in equipment, software, and infrastructure. Ongoing operational costs, including maintenance, training, and system integration, can be substantial. These financial barriers may deter small and medium-sized enterprises from adopting advanced welding technologies, limiting market growth potential. Companies must carefully evaluate ROI and production scale before implementing these solutions.
Complexity in System Integration and Workforce Training
Integrating robotics laser welding systems into existing manufacturing processes can be complex, requiring compatibility with legacy equipment and software. Specialized skills are necessary to operate and maintain these systems, and a shortage of skilled technicians poses a challenge. Investment in workforce training is essential to ensure effective utilization and maximize benefits from automation, which can otherwise slow down adoption and efficiency gains.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America leads the robotics laser welding market, accounting for approximately 35% of the global share. The region’s dominance is driven by advanced manufacturing infrastructure, strong adoption of automation in automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries, and continuous technological advancements in robotic systems. Major players have established production and R&D facilities here, further supporting growth. Government incentives for industrial automation and strict quality standards in manufacturing also accelerate adoption. The United States remains the primary contributor, leveraging innovations in high-precision laser welding to improve productivity and efficiency, positioning North America as the most mature and competitive regional market.
Europe
Europe holds around 28% of the global robotics laser welding market, led by Germany, France, and Italy. The region benefits from a strong focus on precision engineering, automotive and aerospace sectors, and implementation of Industry 4.0 practices. High demand for quality and efficient production drives adoption of robotic laser welding systems. Collaboration between industrial manufacturers and technology providers, combined with supportive regulatory frameworks, encourages innovation in laser welding technologies. European manufacturers increasingly adopt automated welding to reduce labor dependency, improve product consistency, and meet strict environmental and quality regulations, maintaining Europe’s strong position in the global market.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific captures roughly 25% of the robotics laser welding market, with China, Japan, and South Korea as major contributors. Rapid industrialization, expanding automotive, electronics, and metal fabrication industries, and government support for smart manufacturing fuel growth. Adoption of cost-effective automation solutions, combined with large-scale production capabilities, strengthens the region’s competitiveness. Investments in advanced laser and robotic technologies, along with initiatives to improve production efficiency and product quality, further enhance market share. Asia-Pacific is emerging as a critical hub for global robotics laser welding adoption due to its balance of labor efficiency, technological innovation, and growing industrial demand.
Latin America
Latin America represents about 7% of the global robotics laser welding market, led by Brazil and Mexico. The market is driven by automotive and manufacturing sectors aiming to increase production efficiency and product quality. Investment in smart manufacturing, automation technologies, and partnerships with international technology providers supports gradual adoption. While infrastructure and skilled workforce limitations pose challenges, government initiatives promoting industrial modernization contribute to market growth. The region presents opportunities for expansion, particularly in small- and medium-sized enterprises seeking cost-effective and flexible robotic welding solutions to enhance competitiveness in both domestic and export markets.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region accounts for approximately 5% of the global robotics laser welding market. Adoption is led by countries like Saudi Arabia and the UAE, focusing on oil & gas, automotive, and construction sectors. Market growth is supported by infrastructure development, industrial diversification plans, and collaborations with global technology providers. Although current penetration is limited, strategic investments, government initiatives, and the push for industrial modernization are expected to expand the market. Advanced welding solutions help companies improve efficiency, reduce labor dependency, and meet international standards, positioning the region for steady growth in robotics laser welding adoption.
Market Segmentations:
By Type
- Arc welding
- Spot welding
- MIG (Metal Inert Gas)
- TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas)
- Laser welding
- Others
By Payload
- 50 kg payload
- 50-150 kg payload
- 150 kg payload
By Component
- Hardware
- Robots
- Welding Equipment
- Sensors and Vision Systems
- Software
- Controller and Software
- Programming Tools
- Simulation Software
- Services
By End Use:
- Automotive & transportation
- Metals & machinery
- Electrical & electronics
- Aerospace & defense
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The robotics laser welding market is moderately consolidated, with key players such as FANUC Corporation, Yaskawa Electric Corporation, KUKA AG, ABB Ltd., Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd., Panasonic Corporation, and Daihen Corporation leading the industry. These companies dominate the market through continuous innovation, strategic partnerships, and a strong global presence. FANUC and Yaskawa Electric Corporation are recognized for their advanced robotic systems and automation solutions, catering to various industries, including automotive and electronics. KUKA AG and ABB Ltd. focus on precision engineering and automation technologies, providing tailored solutions to meet the specific needs of their clients. Panasonic Corporation and Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd. emphasize the integration of robotics with laser welding technologies, enhancing efficiency and quality in manufacturing processes. Daihen Corporation is known for its expertise in welding equipment and automation systems. The competitive dynamics are further influenced by factors such as technological advancements, cost efficiency, and the ability to offer scalable solutions to meet the diverse requirements of end-users across various industries.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
Recent Developments
- In August 2024, Gauge Capital announced a strategic growth investment in AGT Robotics, a leading provider of robotic welding solutions for the structural steel and heavy metal fabrication industry. This partnership aims to provide growth capital and recapitalize AGT, supporting the company’s mission to deliver world-class products to its clients.
- In March 2024, Kane Robotics introduced the GRIT Vision System, an AI-powered visual sensor designed to replicate human vision. This system enhances robotic welding by assessing uneven surfaces and enabling collaborative robots (cobots) to make real-time adjustments during grinding tasks.
- In October 2023, Miller UK, a manufacturer of buckets and couplers, upgraded its suite of welding robots to enhance production capabilities. The company invested in five new robots developed by CLOOS, including three QRC 410-2.0 models for welding attachments for machines up to 45 tonnes, and two QRC 350-E models capable of handling attachments for machines up to 100 tonnes.
- In September 2023, ABB Group announced a $280 million investment to establish a new robotics hub in Västerås, Sweden. This initiative aims to expand ABB’s European manufacturing capacity by 50%, enhancing their ability to meet the growing demand for automation and robotics solutions in the region.
- In August 2023, Novarc Technologies, a Vancouver-based provider of advanced robotics solutions, completed a Series A fundraising round with Caterpillar Venture Capital Inc., a subsidiary of Caterpillar Inc. This investment aims to accelerate the development of Novarc’s AI-powered robotic welding solutions, enhancing manufacturing automation.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Type, Payload, Component, End-User and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The robotics laser welding market is projected to experience significant growth, driven by increasing demand for automation in manufacturing processes.
- Advancements in laser technology, such as fiber lasers, are enhancing precision and efficiency in welding applications.
- The automotive industry remains a key driver, with rising demand for electric vehicles necessitating advanced welding solutions.
- Collaborative robots (cobots) are gaining traction, offering flexible and cost-effective automation options for small and medium-sized enterprises.
- Integration with Industry 4.0 technologies enables real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, improving operational efficiency.
- Asia-Pacific is anticipated to lead the market, with countries like China and Japan investing heavily in automation and robotics.
- North America and Europe are also significant markets, focusing on high-precision applications in aerospace and electronics.
- The adoption of laser welding technology is expanding into new sectors, including medical device manufacturing and consumer electronics.
- Challenges such as high initial investment costs and the need for skilled operators may impact market growth.
- Ongoing research and development efforts are expected to lead to more affordable and user-friendly robotic welding solutions.




