Market Overview
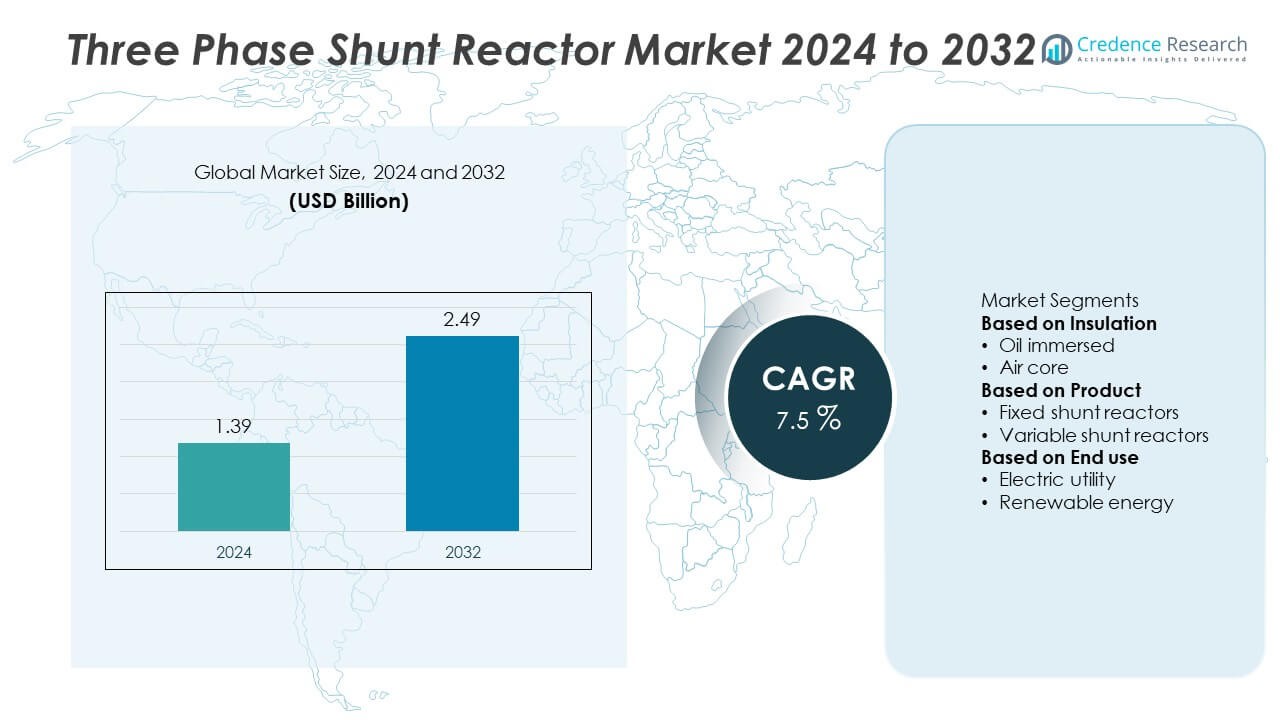
The Three-Phase Shunt Reactor Market was valued at USD 1.39 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 2.49 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 7.5% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Three-Phase Shunt Reactor Market Size 2024 |
USD 1.39 Billion |
| Three-Phase Shunt Reactor Market, CAGR |
7.5% |
| Three-Phase Shunt Reactor Market Size 2032 |
USD 2.49 Billion |
The Three-Phase Shunt Reactor Market is led by key players including Hitachi Energy, GBE, Hyosung Heavy Industries, Nissin Electric, GE, GETRA, Fuji Electric, SGB SMIT, HICO America, and CG Power & Industrial Solutions. These companies dominate through advanced technologies, efficient designs, and strong relationships with utility providers worldwide. Asia-Pacific emerged as the leading region with a 39.7% market share in 2024, supported by rapid grid expansion and renewable energy integration in China and India. Europe followed with a 27.4% share, driven by modernization of transmission systems and offshore wind projects, while North America accounted for 22.6%, supported by grid upgrades and smart substation investments.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The Three-Phase Shunt Reactor Market was valued at USD 1.39 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 2.49 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 7.5% during the forecast period.
- Rising demand for voltage stability, power loss reduction, and reactive power compensation drives adoption, with the oil-immersed segment holding a 69.3% share in 2024 due to superior reliability in high-voltage applications.
- Key market trends include growing integration of renewable energy, expansion of smart grids, and increasing use of digital monitoring and eco-friendly insulation technologies.
- Leading players such as Hitachi Energy, Hyosung Heavy Industries, GE, and Fuji Electric focus on product innovation, global partnerships, and R&D investment to enhance energy efficiency and performance.
- Asia-Pacific led the market with a 39.7% share, followed by Europe (27.4%) and North America (22.6%), driven by grid modernization, renewable integration, and infrastructure expansion.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Insulation
The oil-immersed segment dominated the three-phase shunt reactor market in 2024 with a 69.3% share, driven by its superior cooling efficiency, long service life, and reliability in high-voltage applications. Oil-immersed reactors are widely adopted in transmission and distribution systems to stabilize voltage and compensate for reactive power. Their compact design and ability to handle fluctuating loads make them ideal for grid infrastructure and renewable integration projects. The air-core segment is growing steadily due to its lightweight structure and suitability for indoor and offshore installations where oil-based systems are restricted.
- For instance, Hitachi Energy supplied a 500 kV variable oil-immersed shunt reactor for a wind-power integration project in Uzbekistan, ensuring continuous reactive power compensation and improving system stability during high wind variability
By Product
The fixed shunt reactor segment held the largest market share of 63.8% in 2024, owing to its wide use in transmission networks for continuous voltage regulation and power factor correction. Fixed reactors are preferred for their low maintenance needs, cost efficiency, and stable performance under varying load conditions. Growing electricity demand and grid expansion in developing economies further enhance their deployment. The variable shunt reactor segment is gaining traction in smart grid systems as utilities seek flexible voltage control solutions that adapt to renewable generation variability.
- For instance, GE Vernova has received orders from the Power Grid Corporation of India (PGCIL) for over 70 units of 765 kV class shunt reactors and transformers to be used in transmission projects within India’s renewable energy corridors
By End Use
The electric utility segment accounted for the largest share of 72.1% in 2024, supported by large-scale investments in power transmission and distribution networks. Utilities deploy three-phase shunt reactors to mitigate line charging currents, reduce energy losses, and ensure grid stability under dynamic load conditions. The renewable energy segment is also expanding rapidly, driven by increased wind and solar integration into national grids. As fluctuating renewable outputs create reactive power imbalances, demand for adjustable and efficient shunt reactors continues to rise across solar farms and wind power substations.
Key Growth Drivers
Expansion of Power Transmission Networks
Rising demand for electricity and expanding high-voltage transmission infrastructure drive the adoption of three-phase shunt reactors. Utilities use these reactors to stabilize voltage, improve reactive power compensation, and minimize transmission losses across long-distance lines. Ongoing grid modernization and the construction of new substations further strengthen market growth. Government initiatives to enhance grid reliability and reduce power fluctuations are fueling global investments in advanced shunt reactor technologies.
- For instance, Hyosung Heavy Industries provided 400 kV 100 MVAr shunt reactors for the Energinet grid expansion project at Denmark’s Kasso substation. These reactors are intended to improve voltage regulation in high-voltage transmission networks by balancing reactive power from line capacitance.
Integration of Renewable Energy Sources
The rapid integration of renewable energy, particularly wind and solar, is boosting demand for three-phase shunt reactors. These reactors help maintain voltage stability in power networks affected by fluctuating renewable output. Countries expanding their renewable capacity are deploying shunt reactors to ensure efficient grid synchronization and energy flow control. As renewable projects connect to long transmission lines, the need for voltage regulation equipment continues to rise, enhancing market adoption.
- For instance, Hitachi developed a 275 kV air-core shunt reactor installed at the Nishi-Kameda Switching Station in Hokkaido as part of the Hokkaido–Tohoku interconnection line reinforcement project.
Modernization of Aging Electrical Infrastructure
Aging transmission and distribution networks are being upgraded to improve efficiency and reliability, creating opportunities for three-phase shunt reactor installations. Many countries are investing in replacing outdated grid components with advanced, energy-efficient solutions. Shunt reactors are essential for minimizing reactive power and improving power factor in modern systems. Continuous upgrades in smart grid and substation automation technologies are further supporting the deployment of digital and compact reactor systems.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Adoption of Smart and Digitally Controlled Reactors
Utilities are adopting intelligent shunt reactors integrated with IoT sensors and automated control systems. These digital solutions enable real-time performance monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimized voltage regulation. Growing investment in smart grid technology and demand for remote operation capabilities are driving this trend. Manufacturers focusing on digital twin technology and AI-based grid control solutions are expected to gain a competitive edge.
- For instance, SGB SMIT introduced a 420 kV digitally controlled shunt reactor equipped with Siemens Sensformer 2.0 sensors capable of transmitting load, temperature, and oil moisture data every 60 seconds. The system integrates with SCADA platforms to predict insulation degradation 20 days in advance, significantly reducing maintenance downtime and enhancing operational reliability.
Rising Investments in HVDC and UHV Transmission Lines
The expansion of high-voltage direct current (HVDC) and ultra-high-voltage (UHV) transmission projects is creating major opportunities for the three-phase shunt reactor market. These reactors play a key role in managing reactive power in long-distance and cross-border power transmission. Rapid development of intercontinental grid connections and offshore wind power networks further supports their deployment. The trend is particularly strong in Asia-Pacific, Europe, and the Middle East.
- For instance, Fuji Electric has manufactured numerous shunt reactors for use in Japan’s 500 kV transmission networks and other high-voltage systems to compensate for reactive power on long transmission lines and cable systems.
Key Challenges
High Installation and Maintenance Costs
The complex design and installation requirements of three-phase shunt reactors result in significant initial investment. Additional costs arise from maintenance, insulation testing, and oil management in high-voltage environments. These financial barriers often delay project implementation in developing countries. Manufacturers face pressure to deliver cost-efficient, compact, and low-loss reactor systems to ensure better economic feasibility for utilities.
Technical Limitations in High-Voltage Applications
Three-phase shunt reactors face performance challenges such as insulation failures, thermal stress, and magnetic losses under fluctuating grid loads. Ensuring stable performance in extreme voltage and environmental conditions remains a technical hurdle. These limitations affect system reliability and operational efficiency. Ongoing R&D efforts focus on enhancing insulation materials, improving cooling mechanisms, and developing advanced core designs to mitigate these issues and extend product lifespan.
Regional Analysis
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific dominated the three-phase shunt reactor market in 2024 with a 39.7% share, driven by large-scale investments in grid modernization and renewable energy integration. China and India lead the region with extensive power transmission expansion projects and high-voltage installations. Government initiatives promoting smart grid infrastructure and long-distance HVDC networks further boost adoption. Growing electricity demand and renewable energy capacity additions, particularly from wind and solar, are reinforcing the need for voltage stabilization and reactive power management solutions across the region.
Europe
Europe accounted for a 27.4% share of the three-phase shunt reactor market in 2024, supported by strong focus on grid reliability and renewable integration. Countries such as Germany, France, and the United Kingdom are upgrading existing transmission infrastructure to handle fluctuating renewable energy inputs. The increasing deployment of offshore wind projects and cross-border electricity links has elevated demand for shunt reactors in high-voltage systems. Additionally, the European Union’s decarbonization policies and ongoing investments in smart grids are driving steady market growth.
North America
North America captured a 22.6% share of the three-phase shunt reactor market in 2024, fueled by expanding renewable energy projects and power grid reinforcement programs. The United States leads adoption with substantial investments in upgrading transmission networks to support clean energy integration and reduce power losses. Shunt reactors are increasingly used to manage reactive power in long-distance and inter-regional power lines. The region also benefits from technological innovations and strong participation of key market players focusing on efficient, low-loss, and digitally enabled reactor systems.
Latin America
Latin America held a 6.1% share of the three-phase shunt reactor market in 2024, driven by growing electricity demand and infrastructure expansion in Brazil, Mexico, and Chile. Ongoing rural electrification projects and renewable energy development are key contributors to regional growth. Governments are investing in grid stability solutions to address fluctuating power supply from wind and solar installations. The region’s rising focus on reducing transmission losses and improving energy efficiency is expected to support long-term adoption of advanced reactor technologies.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region accounted for a 4.2% share of the three-phase shunt reactor market in 2024. Market growth is supported by rapid industrialization, expansion of high-voltage networks, and integration of renewable energy sources, particularly in Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and South Africa. Investments in grid interconnections and smart substations are increasing to ensure stable power transmission across large distances. Rising demand for efficient reactive power compensation and voltage control in utility and industrial sectors continues to drive adoption in the region.
Market Segmentations:
By Insulation
By Product
- Fixed shunt reactors
- Variable shunt reactors
By End use
- Electric utility
- Renewable energy
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the Three-Phase Shunt Reactor Market is shaped by leading companies such as Hitachi Energy, GBE, Hyosung Heavy Industries, Nissin Electric, GE, GETRA, Fuji Electric, SGB SMIT, HICO America, and CG Power & Industrial Solutions. These players compete through technological innovation, product customization, and strong global distribution networks. Market leaders are focusing on developing energy-efficient and compact shunt reactors to meet the rising demand for grid reliability and renewable integration. Strategic partnerships with utility providers and EPC contractors are enhancing their market presence. Companies are also investing heavily in digital monitoring systems, smart grid-compatible designs, and eco-friendly insulation technologies to improve operational efficiency and sustainability. Continuous R&D initiatives, along with expansion into emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and the Middle East, remain key strategies to strengthen their competitive position in the global power transmission and distribution industry.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
Recent Developments
- In September 2025, GBE S.p.A. announced supplies of 17 oil-immersed and/or ester-insulated shunt reactors and 8 air-insulated units to European transmission systems.
- In May 2025, GE Vernova announced an order from an Indian renewable-energy transmission corridor to supply extra-high-voltage transformers and three-phase shunt reactors.
- In October 2024, Hitachi Energy scaled its variable shunt reactor to 500 kV specifically for a wind-power application in Uzbekistan.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Insulation, Product, End use and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market will continue growing steadily with rising global electricity demand and grid expansion.
- Utilities will increasingly adopt reactors to enhance voltage stability and reduce transmission losses.
- Renewable energy integration will create strong demand for voltage regulation and reactive power control.
- Manufacturers will focus on developing compact, energy-efficient, and digitally controlled reactor designs.
- Smart grid projects will accelerate adoption of intelligent monitoring and control-enabled shunt reactors.
- Asia-Pacific will remain the leading region, supported by large-scale transmission and renewable projects.
- Europe will see sustained growth due to offshore wind and cross-border power network expansion.
- North America will advance with modernization of high-voltage transmission and substation infrastructure.
- Cost optimization and eco-friendly insulation technologies will become key competitive priorities.
- Strategic collaborations between utilities and manufacturers will drive innovation and long-term market expansion.




