Market Overview:
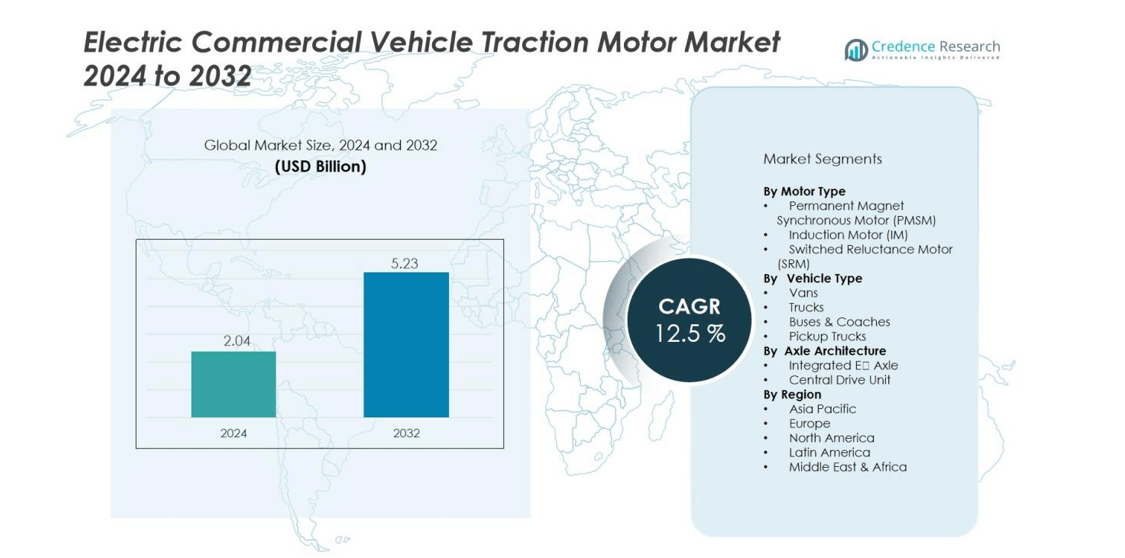
The Electric Commercial Vehicle Traction Motor Market size was valued at USD 2.04 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 5.23 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 12.5 during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Electric Commercial Vehicle Traction Motor Market Size 2024 |
USD 2.04 billion |
| Electric Commercial Vehicle Traction Motor Market, CAGR |
12.5% |
| Electric Commercial Vehicle Traction Motor Market Size 2032 |
USD 5.23 billion |
The growth of the Electric Commercial Vehicle Traction Motor market is fueled by the rising adoption of electric commercial vehicles, including buses, trucks, and vans, as fleets seek to reduce operating costs and comply with stringent emissions regulations. Additionally, improvements in traction motor efficiency, power density, and the use of advanced materials are enhancing the performance of electric vehicles. Government policies and incentives supporting the transition to zero-emission commercial fleets further drive market expansion.
Asia-Pacific dominates the market, particularly driven by China’s extensive electric vehicle initiatives and robust government support. Europe follows closely, where strict emissions regulations and established manufacturers are pushing the market forward. North America is experiencing rapid growth, aided by the expansion of fleet electrification and increasing investments in domestic electric vehicle infrastructure and manufacturing capacity.
Market Insights:
- The Electric Commercial Vehicle Traction Motor Market was valued at USD 2.04 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 5.23 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 12.5% during the forecast period.
- Asia-Pacific dominates the market with over 35% share, driven by China’s leadership in electric vehicle sales and government support for fleet electrification. Europe follows with a 30% share, backed by stringent emissions regulations and established automotive OEMs pushing for zero-emission solutions. North America holds 25%, supported by federal incentives and growing investments in domestic electric vehicle infrastructure.
- The fastest-growing region is North America, with increased demand for fleet electrification, especially in delivery vans and trucks, and strong governmental incentives.
- In terms of vehicle types, trucks account for the largest share, driven by long-haul and heavy-duty logistics fleets transitioning to electric. Buses & coaches also hold a significant share, supported by city and regional transit authorities shifting towards zero-emission vehicles.
- For motor types, Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM) lead the market, driven by their high efficiency and compact size, making them ideal for electric buses and trucks requiring high torque.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Drivers:
Increasing Adoption of Electric Commercial Vehicles (ECVs)
The growing demand for Electric Commercial Vehicles (ECVs) is one of the primary drivers for the Electric Commercial Vehicle Traction Motor Market. Companies and governments are adopting electric vehicles to reduce their carbon footprints and comply with stricter emissions regulations. ECVs, including electric trucks, vans, and buses, offer operational cost savings compared to their internal combustion engine counterparts. As the adoption of electric vehicles expands globally, demand for traction motors to power these vehicles continues to rise.
- For instance, BYD’s commercial vehicle segment has experienced a substantial increase in sales volume in 2025. In the first half of 2025 (H1 2025), BYD’s commercial vehicle sales rose by a significant 459% compared to H1 2024, reaching 32,683 units for that period. In June 2025 alone, commercial vehicle sales were up 333% year-over-year to 4,568 units.
Government Policies and Regulatory Support
Governments worldwide are implementing policies that promote the use of electric vehicles, providing financial incentives and establishing emission reduction targets. These policies accelerate the transition to electric fleets, directly driving the demand for Electric Commercial Vehicle Traction Motors. Regulatory mandates for zero-emission vehicles are becoming stricter, especially in regions like Europe and North America, further encouraging fleet operators to adopt electric solutions. The growing support from authorities is a significant factor in the market’s expansion.
- For instance, under India’s FAME II scheme, over 1.15 million electric vehicles were supported with purchase incentives as of December 2023, and over 1.6 million by the time the scheme ended in March 2024, including significant adoption by various manufacturers like Tata Motors, contributing to lower upfront costs for fleet operators in the e-bus, e-three wheeler, and e-four wheeler commercial segments.
Technological Advancements in Traction Motor Efficiency
Advances in motor technology significantly impact the Electric Commercial Vehicle Traction Motor Market. Traction motors are becoming more efficient, with improvements in power density, material selection, and cooling systems that enhance overall vehicle performance. These innovations lead to better energy efficiency and extended battery life, which are critical factors for fleet operators looking to maximize operational efficiency. The ongoing development of advanced motor technologies strengthens the demand for Electric Commercial Vehicle Traction Motors.
Cost Reduction and Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Benefits
Electric vehicles, powered by efficient traction motors, offer a significant reduction in total cost of ownership compared to traditional diesel-powered vehicles. The lower operating and maintenance costs of electric motors make them an attractive option for fleet operators. Over time, the reduction in fuel costs, coupled with the declining price of electric vehicle components and infrastructure, contributes to the growing appeal of ECVs. This economic advantage drives the increased adoption of electric vehicles, boosting the market for traction motors.
Market Trends:
Integration of High‑Voltage Systems and Compact Drive Units
The Electric Commercial Vehicle Traction Motor Market benefits from the shift towards high‑voltage architectures and compact e‑axle systems. Manufacturers design motors around 800 V systems, which reduce weight and improve power efficiency. It uses smaller, integrated drive units and optimized cooling systems to boost torque density and reduce thermal losses. The move toward water‑cooled and oil‑cooled configurations supports heavy‑duty commercial vehicle demands. This trend supports fleets requiring longer range, higher payloads and lower operational costs.
- For instance, Daimler Truck’s eActros 600 employs an 800 V electric axle architecture with a torque density of 1,700 Nm, enabling a real‐world range of over 500 km on a single charge.
Adoption of Smart Motor Controls and Predictive Maintenance Solutions
Smart motor control systems now shape this market, enabling real‑time monitoring and adaptive torque management. Motor control algorithms exploit artificial intelligence and advanced sensors to optimize motor efficiency and durability. It connects traction motors to vehicle networks, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime for commercial fleets. Manufacturers embed IoT modules in motor units, allowing remote diagnostics and firmware updates. These innovations enhance reliability and lifecycle value for electric commercial vehicles and increase the appeal of electrification among fleet operators.
- For instance, Continental’s high-voltage inverter system for hybrid and electric commercial vehicles achieves >95% efficiency with an approximate 600V to 850V input voltage adaptability (while the system itself is likely compliant with VDA320 electrical requirements, this specific voltage range is standard for high power EV applications).
Market Challenges Analysis:
High Initial Cost and Uncertain Return for Fleet Operators
The Electric Commercial Vehicle Traction Motor Market faces significant pressure from elevated upfront costs of traction motors and associated systems. Manufacturers must invest heavily in advanced materials, precision manufacturing processes and quality control to meet commercial‑vehicle standards. Fleet operators hesitate to adopt electric solutions if projected savings do not offset the capital expense within acceptable timelines. It often results in longer payback periods which dampen demand among cost‑sensitive buyers. Performance expectations and durability concerns further slow uptake, especially where light‑duty cost structures dominate.
Supply‑Chain Limitations, Standardisation Gaps and Thermal Reliability Issues
Manufacturers in the traction‑motor sector contend with supply‑chain bottlenecks for critical raw materials such as rare earth metals and copper, which raise costs and limit scale‑up potential. The market also lacks fully harmonised standards across regions and power ratings, slowing component interoperability and increasing validation time. It reports persistent thermal management challenges, including motor overheating under heavy commercial load, which compromises reliability and deters fleet deployment in demanding duty cycles. This combination of material scarcity, standardisation delays and thermal risk restricts broader penetration of traction‑motor solutions in electric commercial fleets.
Market Opportunities:
Expansion into Last‑Mile Urban Delivery Fleets and Micro‑Logistics
The electric commercial vehicle traction motor market features a strong opportunity in last‑mile urban delivery operations. Urban logistics providers seek compact electric vans and trucks with lower operating costs and zero tailpipe emissions. These fleets require reliable traction motors that support frequent stop‑start cycles and high initial torque. It opens the door for manufacturers to customise motor designs for low‑speed, high‑efficiency duty profiles. Lightweight materials and modular drive‑unit platforms remain in high demand among switchers from internal combustion to electric. Regional regulations that limit city‑centre diesel trucks further accelerate the shift toward electric commercial vehicles.
Retrofit and Aftermarket Service Growth for Commercial Fleet Electrification
The market also offers significant potential in retrofitting existing fleets and servicing aftermarket needs for electric drivetrains. Many fleet operators prefer to convert diesel trucks and vans into electric versions rather than purchase new vehicles. It gives motor suppliers the chance to offer plug‑and‑play traction motor kits and integrated electric drive solutions. Predictive‑maintenance tools tied to these motors allow service providers to sell lifecycle contracts and performance upgrades. Growth in this segment complements new vehicle sales and supports recurring revenue models for manufacturers and suppliers.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Motor Type
The market divides motor types into categories such as permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM), induction motors (IM), and switched reluctance motors (SRM). PMSM currently leads due to its high efficiency and compact size, which appeals to commercial vehicle operators. It finds favour in electric buses and heavy trucks that demand high torque and energy efficiency. Induction motors remain relevant because they offer robustness and lower cost, especially for lighter-duty electric commercial vehicles. SRM is gradually gaining attention thanks to its simpler construction and potential for lower maintenance over the vehicle’s life.
- For Instance, Nidec Corporation is a pioneer in Switched Reluctance Motor (SRM) technology, which offers inherent advantages such as a robust, magnet-free rotor structure and high fault tolerance, making it a promising and reliable candidate for electric vehicle (EV) applications, including commercial vans.
By Vehicle Type
Vehicle segmentation includes vans, trucks, buses & coaches, and pickup trucks. Trucks claim the largest share in the market because long‑haul and heavy‑duty logistics fleets increasingly transition to electric drive systems. Buses and coaches follow closely thanks to city and regional transit authorities shifting toward zero emission vehicles. Vans and pickup trucks grow at a faster rate, supported by the boom in urban delivery and last‑mile logistics where lighter duty electric commercial vehicles dominate.
- For Instance, Miami-Dade County previously secured contracts with Proterra to provide a total of 75 electric buses, with orders placed in 2019 and 2021 to accelerate the county’s zero-emission public transport transition.
By Axle Architecture
The axle architecture segment covers central drive units and integrated e‑axle systems. Integrated e‑axles gain traction because they house the motor, gearbox and inverter in a compact module, simplifying installation in commercial vehicle platforms. It supports cleaner vehicle layouts and allows manufacturers to tailor drive units by axle for both front and rear wheel applications. Central drive units remain relevant for retrofit applications and where legacy transmission systems persist in commercial fleets. Manufacturers focus on this segment to push adoption of full electric commercial vehicles through modular drive architectures.
Segmentations:
By Motor Type
- Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM)
- Induction Motor (IM)
- Switched Reluctance Motor (SRM)
By Vehicle Type
- Vans
- Trucks
- Buses & Coaches
- Pickup Trucks
By Axle Architecture
- Integrated E‑Axle
- Central Drive Unit
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Regional Analysis:
Asia‑Pacific Regional Outlook
Asia‑Pacific holds a market share of over 35% in the Electric Commercial Vehicle Traction Motor Market in 2024. It capitalises on China’s leadership in electric commercial‑vehicle sales, prolific traction‑motor manufacturing capacity and supportive policy frameworks. China, India and Japan invest heavily in fleet electrification for buses, trucks and delivery vans. It benefits from large‑scale domestic production of motors and robust supply of raw materials. Urbanisation trends and rising logistics demand further reinforce market strength in this region. Manufacturers exploit regional cost advantages and localised R&D to tailor traction‑motor solutions to demand profiles.
Europe Regional Outlook
Europe commands a market share of around 30% in the Electric Commercial Vehicle Traction Motor Market. It leans on stringent emissions targets, progressive fleet‑electrification mandates and established automotive OEM ecosystems. Germany, Netherlands and Scandinavian countries drive demand for zero‑emission buses and heavy‑duty trucks. It experiences rising investment in charging infrastructure and high‑voltage drive systems, which stimulate traction‑motor uptake. Localised manufacturing and innovation hubs help integrate advanced motor technologies into commercial‑vehicle platforms. Regulatory momentum and sustainability goals combine to accelerate deployment of electric commercial‑vehicle traction motors.
North America Regional Outlook
North America attracts a market share near 25% for the Electric Commercial Vehicle Traction Motor Market. U.S. federal and state incentives support fleet electrification, especially in delivery vans, medium‑duty trucks and public transport. It sees expansion in domestic traction‑motor production and supply‑chain localisation to reduce import dependency. Commercial‑fleet operators adopt electric models to cut lifecycle costs and meet climate commitments. It faces challenges in infrastructure rollout and component sourcing, but growth remains strong. Motor manufacturers and vehicle OEMs coordinate to scale solutions for class‑8 trucks and urban delivery fleets.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis:
- ABB
- BorgWarner
- Bosch
- Dana
- Delta
- Hitachi Automotive
- Magna
- Nidec
- ZF
Competitive Analysis:
The competitive landscape of the Electric Commercial Vehicle Traction Motor Market presents intense rivalry among leading global suppliers. Key players such as ABB, BorgWarner, Bosch, Dana and Delta Electronics pursue differentiated motor technologies to gain an edge. ABB leverages its long‑standing expertise in heavy‑vehicle drivetrains and global service network to broaden its traction‑motor portfolio. Bosch offers compact, high‑efficiency motors tailored for commercial vehicles with power ratings up to 240 kW. BorgWarner develops rugged electric motors for on‑ and off‑highway use, with focus on high power density and service life. Dana delivers integrated motor and inverter systems specifically for medium‑ and heavy‑duty commercial vehicle platforms. Delta advances in traction motor modules with high‑efficiency designs suited for fleet electrification. Competition revolves around maximizing torque density, reducing system weight and lowering total cost of ownership. Companies strive to secure long‑term supply agreements with commercial‑vehicle OEMs and fleet operators, while extending their manufacturing footprints globally. It leads to ongoing vertical integration and expansion of aftermarket services to support performance and reliability across vehicle duty‑cycles.
Recent Developments:
- In October 2025, ABB announced the sale of its Robotics division to SoftBank Group for $5.375 billion as a strategic move to sharpen its focus on electrification and automation sectors.
- In October 2025, BorgWarner enhanced its collaboration with Great Wall Motor to provide electrified propulsion technologies for passenger cars and light trucks.
Report Coverage:
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Motor Type, Vehicle Type, Axle Architecture and Region. It details leading Market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current Market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven Market expansion in recent years. The report also explores Market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on Market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the Market.
Future Outlook:
- Traction motors will increasingly pair with 800 V vehicle architectures to boost efficiency and reduce system weight.
- Motor manufacturers will push integration of inverter and gearbox into compact e‑axle modules to simplify vehicle platforms and reduce cost.
- Smart motor control systems will connect to vehicle telematics for predictive maintenance and improved fleet uptime.
- Suppliers will target retrofit programmes for existing diesel fleets, creating aftermarket traction‑motor kits and conversion services.
- Materials innovation will drive use of high‑strength rare‑earth free magnets and advanced cooling systems to improve durability and reduce dependency.
- Regional manufacturing hubs will expand, especially in Asia‑Pacific, to serve local fleet electrification programmes and reduce logistics bottlenecks.
- Fleet operators will demand motors that deliver high initial torque with frequent stop‑start cycles in urban logistics and last‑mile delivery applications.
- Standards bodies will develop uniform traction‑motor interface specifications, enabling interoperability across axles, inverters and vehicle platforms.
- Partnerships between motor OEMs and commercial‑vehicle manufacturers will deepen, aligning motor design early in vehicle development to optimise packaging and performance.
- Circular‑economy models will emerge, with motor remanufacturing, component reuse and lifecycle‑service contracts becoming a differentiator in the traction‑motor business.




