Market Overview
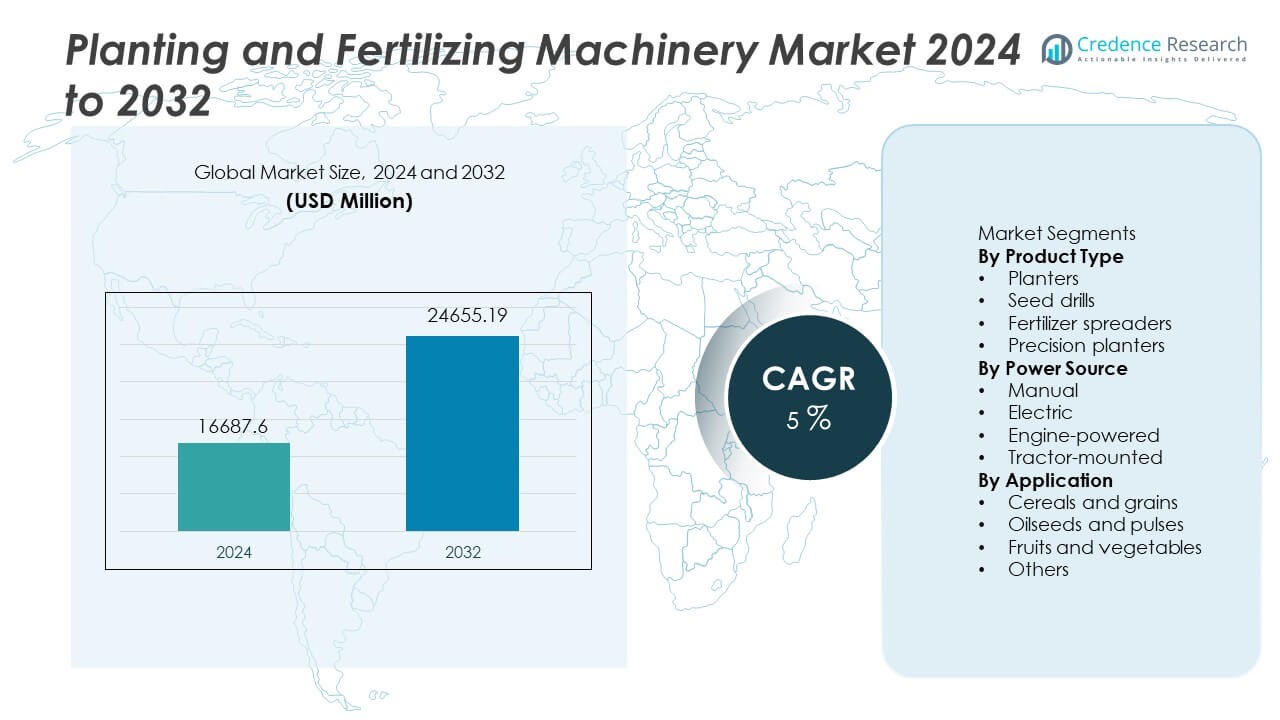
The Planting and Fertilizing Machinery Market was valued at USD 16,687.6 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 24,655.19 million by 2032, registering a CAGR of 5% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Planting and Fertilizing Machinery Market Size 2024 |
USD 16,687.6 Million |
| Planting and Fertilizing Machinery Market, CAGR |
5% |
| Planting and Fertilizing Machinery Market Size 2032 |
USD 24,655.19 Million |
John Deere, CNH Industrial, AGCO Corporation, Kubota Corporation, CLAAS, Amazone, Mahindra & Mahindra, Great Plains Manufacturing, Kverneland Group, and Yanmar lead the Planting and Fertilizing Machinery market with strong portfolios across planters, fertilizer spreaders, and precision farming tools. These companies invest in GPS-enabled systems, variable rate technologies, and automated planting platforms that support high productivity across large agricultural zones. Asia Pacific remains the leading region with a 33% share due to extensive cereal and grain cultivation, government mechanization programs, and growing adoption of tractor-mounted machinery across major agricultural economies.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The Planting and Fertilizing Machinery market reached USD 16,687.6 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 24,655.19 million by 2032 at a CAGR of 5.
- Rising need for higher productivity and reduced labour drives adoption of planters, while planters hold a 39% share due to large-scale cereal cultivation across major farming regions.
- Key trends include GPS-enabled machinery, variable rate fertilization, sustainability-focused features, and digital platforms that improve seed spacing and soil nutrient management.
- Competition intensifies as John Deere, CNH Industrial, AGCO, Kubota, and other manufacturers introduce precision systems, automated spreaders, and remote monitoring to increase field efficiency and reduce downtime.
- Asia Pacific leads with a 33% share, followed by North America at 29% and Europe at 27%, while tractor-mounted platforms hold a 52% share due to strong integration in modern farming operations and high field coverage in commercial farms.
 Market Segmentation Analysis:
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Product Type
Planters hold a 39% share of the product segment and remain the most used machinery due to large-scale planting of cereals and row crops in commercial farms. Planters increase planting accuracy, reduce manual labour, and support higher seed placement efficiency. Seed drills also expand adoption in emerging markets due to crop diversification and the need for uniform seed distribution. Fertilizer spreaders grow through rising nutrient-management practices and higher fertiliser application in intensive farming. Precision planters see strong interest due to digital metering and reduced seed wastage, especially in high-value crops. Planters maintain dominance due to broad field suitability and high productivity across regions.
- For instance, John Deere’s ExactEmerge planter places seeds at speeds up to 10 miles per hour with brush belt delivery and active downforce. The system uses brush-type meters that keep seed spacing uniform at high travel speeds.
By Power Source
Tractor-mounted machinery accounts for a 52% share of the power source segment and leads due to strong usage in medium and large farms. Tractor-mounted systems offer higher field coverage and greater operational efficiency, especially for row crops that require precise planting. Engine-powered equipment remains relevant for smaller farms needing portable machines. Electric systems grow through sustainability goals and reduced maintenance cost, particularly in greenhouse or controlled farming. Manual tools persist in smallholder agriculture across developing regions. Tractor-mounted platforms remain dominant since they integrate easily with modern tractors and support high-capacity field operations during peak planting seasons.
- For instance, CNH Industrial’s Magnum tractors deliver substantial torque that supports high-capacity planter attachments under heavy soil load, with some models offering best-in-class pulling power and a generous torque reserve.
By Application
Cereals and grains command a 57% share of the application segment and remain the major user group because global production of wheat, rice, and corn requires large-area planting and timely fertilisation cycles. Rising population and food-security programs support continuous demand in Asia and Africa. Oilseeds and pulses show expansion through global demand for soybeans and protein crops. Fruits and vegetables adopt advanced planters for precision placement in high-value farming. Other crops gain traction through diversified farm income strategies. Cereals maintain leadership due to wide cultivation area, government support for staple crops, and continuous mechanisation across developing agricultural economies.
Key Growth Drivers
Increasing Farm Mechanization Across Developing Regions
Developing markets increase spending on agricultural machinery to reduce labour dependence and improve planting efficiency. Governments encourage farm upgrades through subsidies and credit programs. Rapid population growth increases demand for staple crops, making mechanization necessary for timely planting. Rising rural wages and scarcity of skilled labour drive adoption of planters and fertilizer spreaders. Commercial farms expand operations to meet rising crop demand. Sustainable farming models further support machinery investment, especially for large acreage crops in Asia and Africa.
- For instance, Mahindra & Mahindra reported delivery of a significant volume of tractors in India during that period, which supported the ongoing mechanization in northern and central states.
Rising Demand for Higher Crop Productivity
Farmers use mechanized planters and spreaders to reduce seed wastage and improve nutrient absorption. Increasing adoption of precision fertilizer placement enhances crop yield and soil performance. Mechanized planting reduces planting time and supports large-scale harvesting cycles. Agribusinesses focus on technology to meet global food demand and improve farm profitability. Adoption of enhanced seed technologies encourages corresponding machinery investments. Continuous yield improvement remains a central priority in global farming.
- For instance, AGCO’s Precision Planting vApplyHD liquid control manages a wide range of flow rates per row unit for accurate nutrient dosing based on soil conditions. The system is designed to handle everything from very low in-furrow starter rates to much higher sidedressing rates across the full range of operating speeds, ensuring precise application without the need for manual adjustments or orifices.
Government Incentives for Modern Agriculture
Several countries run subsidy programs for agricultural machinery and promote mechanization of cereal and oilseed farming. Tax benefits, low-interest loans, and agricultural modernization policies encourage purchase of new machinery. Import duty reductions support access to advanced planting equipment. National food security programs also drive adoption of efficient planting systems for large farmlands. Policy support improves technology penetration in rural regions.
Key Trends and Opportunities
Adoption of Precision Farming and Digital Equipment
Farmers use GPS-enabled planters and variable rate fertilizing systems to control seed depth, spacing, and fertilizer placement. Digital meters improve field accuracy and reduce resource waste. Smart monitoring platforms help track soil health and plant growth. Demand for connected machinery grows across large farms focused on efficiency and sustainability goals. Precision farming supports long-term yield and promotes selective fertilizer use.
- For instance, Trimble’s Autopilot steering technology delivers 1.2 centimeter repeatable accuracy during contour planting with RTK corrections.
Growing Integration of Sustainable Fertilizing Practices
Manufacturers introduce machinery that supports nutrient-use efficiency and balanced soil fertility. Controlled fertilizer placement helps reduce environmental risks and improve plant absorption. Farmers adopt sustainable fertilizing equipment to support regenerative agriculture, water conservation, and reduced input reliance. Food companies encourage sustainable farming through chain-of-supply partnerships.
- For instance, Amazone’s ZG-TX fertiliser spreader supports section control while reducing overlap in field trials from the DLG Test Center.
Key Challenges
High Initial Investment and Ownership Costs
Planting and fertilizing machinery requires high upfront investment, limiting adoption for small farmers. Maintenance cost, spare parts, and fuel usage increase ownership burden. Financial barriers remain common in developing markets without strong credit access. These costs slow technology penetration in rural regions.
Limited Technical Skills for Advanced Equipment
Modern planters and precision fertilizer systems require operational skills that smallholder farmers often lack. Limited training resources restrict wider adoption, especially in remote areas. Lack of skilled operators reduces efficiency, increasing breakdown risks and reducing return on investment. Training and service networks remain a key requirement for sustained growth.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds a 29% share of the Planting and Fertilizing Machinery market supported by modern mechanization, precision farming adoption, and strong commercial agriculture across the United States and Canada. Large farms invest in advanced seed drills, planters, and fertilizing tools for row crops including corn and soybean. Rising demand for higher crop yields and reduced nutrient wastage supports the use of precision fertilizer systems. Growing awareness of soil health and regulated fertilizer application strengthens equipment adoption. Agricultural technology companies expand partnerships with farmers for connected machinery and digital services across regional farms.
Europe
Europe accounts for a 27% share driven by sustainability regulations and increased demand for precision fertilizer placement to reduce emission impact. Countries such as Germany, France, and Italy support agricultural modernization through subsidies and technology grants. Precision planters and fertilizer spreaders gain adoption due to focus on soil management and water-efficient farming. EU policies encourage lower chemical discharge and precision nutrient control. Farmers adopt GPS-guided systems and connected machinery to meet production standards. Continuous investment in agricultural machinery manufacturing supports long-term use of automated equipment across European farmlands.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific holds a 33% share due to large-scale agricultural production across China, India, and Southeast Asia, supported by mechanization programs promoting planters and fertilizer spreaders in staple crop farming. Rice, wheat, and corn cultivation demand larger planting capacity and timely field operations. Governments implement farm mechanization subsidies to improve productivity and reduce labour costs. Commercial farming expands through high-yield seed programs and precision spreading tools. Rising food security priorities encourage sustainable fertilizing practices. Strong local manufacturing and supply chains strengthen machinery adoption across rural regions.
Latin America
Latin America holds a 6% share with rising mechanization across Brazil, Argentina, and Mexico supported by expanding soybean, corn, and sugarcane cultivation. Large farms integrate tractor-mounted planters and fertilizer spreaders for field coverage and planting efficiency. Export-oriented agriculture drives investment in high-capacity machinery. Precision farming tools increase yield potential and fertilizer use efficiency. Governments offer credit lines for agricultural modernization programs. Rising focus on soil management and input optimization influences machinery choice in major producing zones.
Middle East and Africa
The Middle East and Africa represent a 5% share driven by gradual farm modernization and rising food security programs targeting cereal and grain farming. Investments increase in tractor-mounted machinery to support mechanized planting in arid and semi-arid environments. International partnerships introduce modern spreaders and planters into regional markets. Limited skilled labour encourages automated machinery adoption. Water-scarce regions focus on precision fertilizer placement to minimize resource loss. Governments encourage agricultural imports and localized manufacturing to support future mechanization needs.
Market Segmentations:
By Product Type
- Planters
- Seed drills
- Fertilizer spreaders
- Precision planters
By Power Source
- Manual
- Electric
- Engine-powered
- Tractor-mounted
By Application
- Cereals and grains
- Oilseeds and pulses
- Fruits and vegetables
- Others
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
Competitive landscape or analysis in the market is John Deere, CNH Industrial, AGCO Corporation, Kubota Corporation, CLAAS, Amazone, Mahindra & Mahindra, Great Plains Manufacturing, Kverneland Group, and Yanmar dominate the competitive landscape of the Planting and Fertilizing Machinery market. These companies invest in precision planting systems, variable rate fertilizer spreaders, and digital guidance solutions that improve seed placement accuracy and minimize input costs for farmers. Leading players focus on connected machinery equipped with GPS, sensors, and remote monitoring, enabling real-time control of planting and nutrient application. Manufacturers expand regional presence through localized production and dealership networks to support after-sales service and spare parts availability. Companies also integrate sustainability features that support nutrient-efficient farming, soil health, and reduced emissions in line with global agricultural regulations. Rising demand for high-capacity machines encourages continuous innovation in tractor-mounted planters designed for large farmlands.
Key Player Analysis
- John Deere
- CNH Industrial
- AGCO Corporation
- Kubota Corporation
- CLAAS
- Amazone
- Mahindra & Mahindra
- Great Plains Manufacturing
- Kverneland Group
- Yanmar
Recent Developments
- In September 2025, Kubota Corporation introduced its new “Grand L70 Series” compact tractors (at Kubota Connect), signalling expansion of their small-farm planting/utility offerings.
- In February 2025, Kinze announced a new dual-product liquid fertilizer system for their existing 5900 series front-fold planters.
- In 2025, AGCO (via its PTx/Trimble-linked division) displayed a new autonomous fertilizer-application solution – pointing to growing use of automation in fertilizing.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Product Type, Power Source, Application and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Precision planting systems will expand through GPS and sensor integration.
- Automated fertilizer spreaders will support nutrient efficiency and soil protection.
- Demand will rise for tractor-mounted platforms in large commercial farms.
- Electric machinery will gain interest due to lower emissions and maintenance.
- Digital monitoring tools will assist in real-time planting and field mapping.
- Sustainable fertilizing practices will push controlled application technologies.
- Farmers will adopt variable rate systems to reduce waste and input costs.
- Government subsidy programs will continue supporting mechanization upgrades.
- Local manufacturing will increase machinery availability in developing regions.
- Robotics and autonomous planters will emerge in advanced agriculture markets.

 Market Segmentation Analysis:
Market Segmentation Analysis:

