Market Overview
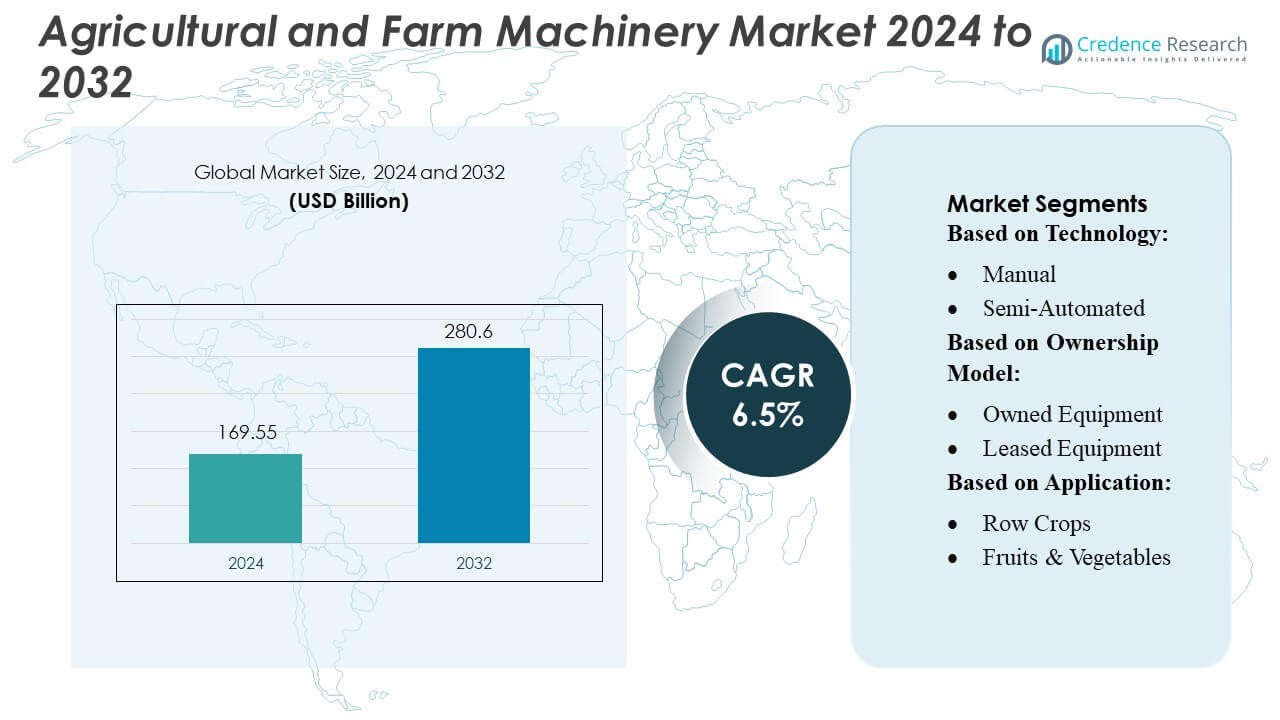
Agricultural and Farm Machinery Market size was valued USD 169.55 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 280.6 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 6.5% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Agricultural and Farm Machinery Market Size 2024 |
USD 169.55 Billion |
| Agricultural and Farm Machinery Market, CAGR |
6.5% |
| Agricultural and Farm Machinery Market Size 2032 |
USD 280.6 Billion |
The Agricultural and Farm Machinery Market remains highly competitive, with global manufacturers expanding their portfolios across tractors, harvesters, precision implements, and automated field systems. Market leadership is shaped by continuous innovation in telematics, GPS-guided controls, robotics, and energy-efficient machinery that enhance productivity and reduce operating costs for farmers. Companies strengthen their positions through digital service platforms, fleet optimization tools, and Equipment-as-a-Service offerings that improve lifecycle value. Asia-Pacific emerges as the leading region, holding an exact market share of 44%, driven by large-scale mechanization programs, rapid adoption of precision technologies, and strong government support for agricultural modernization.
Market Insights
- The Agricultural and Farm Machinery Market reached USD 169.55 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit USD 280.6 billion by 2032 at a 5% CAGR, supported by rising mechanization, precision technologies, and demand for high-efficiency equipment.
- Strong market drivers include rapid adoption of telematics, GPS-guided controls, energy-efficient engines, and automated field systems that boost yield performance and reduce input costs.
- Key market trends involve expansion of robotics, connected machinery, and Equipment-as-a-Service models, enabling predictive maintenance, optimized fleet usage, and lower capital burdens for farmers.
- Market restraints include high equipment acquisition costs, limited digital infrastructure in developing regions, and skill gaps that hinder adoption of advanced precision tools.
- Asia-Pacific leads with 44% regional share, followed by North America and Europe, while tractors and harvesting equipment remain top-performing segments, collectively accounting for over 55% of total machinery demand.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Technology
The agricultural and farm machinery market remains dominated by semi-automated technologies, accounting for over 55% of global revenue, driven by strong adoption across medium-scale farms seeking productivity gains without the high capital cost of full automation. Semi-automated tractors, harvesters, and sprayers benefit from integrated GPS guidance, assisted steering, and variable-rate application controls that improve operational precision. Manual equipment continues to serve smallholders but is losing share, while fully automated machinery grows rapidly in advanced markets due to AI-based perception systems, autonomous navigation, and labor-shortage pressures.
- For instance, APV GmbH’s pneumatic seeders such as the PS 300 M1 feature a 300-liter hopper, 8–16 electric metering outlets, and a working width of up to 12 meters, enabling highly precise semi-automated seeding operations across diverse field conditions.
By Ownership Model
Owned equipment represents the dominant ownership model, holding approximately 48–50% market share, supported by long-term ROI advantages for large farms and government subsidy programs for machinery purchases. However, leasing and rental services are expanding as farmers seek flexible, low-capex access to advanced machinery during peak seasons. The emerging Equipment-as-a-Service (EaaS) model is gaining traction in precision agriculture applications, propelled by telematics-enabled pay-per-use models and performance-based service contracts that reduce maintenance burdens and allow farms to adopt high-tech automation without upfront investment.
- For instance, Farmtrac 6055 PowerMaxx is a 60 HP tractor by Escorts (now Escorts Kubota Limited). It is equipped with the Escorts Smart Assist telematics system, which includes features such as real-time GPS tracking and remote diagnostics.
By Application
Row crop farming leads the market with over 40% share, driven by extensive mechanization requirements in crops such as wheat, rice, soybeans, and corn. High-volume operations rely on tractors, combine harvesters, planters, and sprayers equipped with precision farming technologies that optimize input use and enhance yield predictability. Fruits & vegetables and vineyards increasingly adopt robotics for picking and canopy management, while livestock farming expands demand for feeding, milking, and waste-handling machinery. Forestry and aquaculture remain smaller but fast-growing segments due to rising investments in mechanized harvesting and environmental monitoring systems.
Key Growth Drivers
1. Rising Mechanization to Improve Farm Productivity
Mechanization remains a primary growth catalyst as farmers shift from labor-intensive processes toward high-efficiency equipment to meet yield and quality targets. Growing labor shortages, especially in developing regions, accelerate adoption of tractors, harvesters, and precision sprayers. Governments further stimulate demand through subsidies, financing programs, and mechanization assistance schemes. Advanced machines equipped with GPS guidance, variable-rate control, and yield monitoring enhance operational efficiency, reduce input waste, and improve profitability, encouraging sustained investment in modern farm machinery across small, medium, and large-scale farms.
- For instance, CLAAS KGaA mbH has advanced mechanization through technologies like the LEXION 7700 combine, which integrates the APS SYNFLOW HYBRID threshing system delivering up to 1,790 rpm, a 790-mm pre-acceleration drum, and a CEMOS Automatic optimization system capable of adjusting over 30 machine parameters in real time—significantly boosting throughput with consistently high grain quality.
2. Expansion of Precision Agriculture Technologies
Precision agriculture drives rapid modernization of farm machinery through integration of IoT, GNSS, telematics, and AI-based sensors. Farmers increasingly adopt data-driven machinery to optimize planting, fertilization, and harvesting decisions, reducing costs and improving yield consistency. Automated steering, real-time equipment diagnostics, and variable-rate application systems enhance accuracy while minimizing input usage. The growing ecosystem of digital platforms and cloud-based analytics further boosts adoption, enabling predictive maintenance and operational planning. This shift toward intelligent machinery significantly accelerates market growth, particularly in high-value crop and large-acreage operations.
- For instance, HORSCH Maschinen GmbH advances precision farming through its Avatar SD seed drill, which offers tank capacities up to 6,400 liters, metering systems capable of delivering precise seed rates as low as 1 kg/ha, and SectionControl that switches individual rows automatically—supporting centimeter-level GNSS accuracy and significantly reducing seed and fertilizer overlap across large-acreage operations.
3. Growing Demand for Sustainable and Energy-Efficient Equipment
Environmental considerations strongly influence machinery purchasing decisions as farmers aim to reduce emissions, fuel usage, and soil disturbance. Demand grows for energy-efficient tractors, low-emission engines, electric and hybrid equipment, and conservation-focused implements. Regulations promoting cleaner agricultural practices and carbon reduction strategies further support the transition toward sustainable machinery. Equipment such as precision sprayers, autonomous weeders, and reduced-tillage systems not only cut environmental impact but also improve soil health and operational economics, making sustainability-driven innovation a major driver of long-term market expansion.
Key Trends & Opportunities
1. Rapid Adoption of Autonomous and Robotics-Based Machinery
Autonomous tractors, robotic harvesters, and automated spraying systems present significant growth opportunities as farms look for solutions to labor shortages and rising input costs. Advances in machine vision, LiDAR-based navigation, and AI-driven crop detection accelerate commercial deployment. Robotics adoption is expanding in labor-intensive operations such as fruit harvesting, weeding, and nursery management. The transition toward full autonomy enables 24/7 operations, improved safety, and higher precision. Manufacturers increasingly invest in scalable robotic platforms, positioning automation as a transformative trend shaping the next generation of agricultural machinery.
- For instance, ISEKI & Co., Ltd. has made advancements in autonomous technology, such as the development of a human-supervised 123 HP robotic tractor for large-scale farming operations in Japan.
2. Growing Shift Toward Connected Machinery and Telematics
Connected machinery equipped with telematics, remote monitoring, and cloud-integrated control systems is becoming mainstream, creating opportunities in fleet optimization and predictive maintenance. Farmers benefit from real-time performance insights, geofencing, machine health alerts, and usage analytics that enhance operational planning and reduce downtime. OEMs leverage connectivity to offer subscription-based digital services, increasing lifetime equipment value. This trend also supports the rise of Equipment-as-a-Service (EaaS), enabling pay-per-use models. The connected ecosystem strengthens machinery efficiency and drives digital transformation across global agricultural operations.
- For instance, CNH Industrial N.V. has accelerated its shift to sustainable and energy-efficient machinery by commercializing its T6 Methane Power tractor, which uses a 6-cylinder FPT NEF methane engine rated at 180 hp and 740 Nm of torque, matching the performance of its diesel counterpart.
3. Expansion of Electrification and Alternate Energy Machinery
Electrification emerges as a pivotal opportunity as manufacturers introduce battery-powered tractors, electric utility vehicles, and hybrid machinery to reduce fuel dependence. Improvements in battery density, charging infrastructure, and power electronics enable broader field applications. Electric machinery offers lower maintenance, reduced noise, and zero-emission operation, appealing to environmentally conscious farms and regulatory-driven markets. Additionally, hydrogen-powered tractors and renewable-energy-integrated machinery solutions are under development. This shift creates new opportunities for sustainable farming technologies while reshaping future equipment portfolios.
Key Challenges
1. High Capital Costs Limiting Adoption for Smallholders
The high upfront cost of modern tractors, harvesters, robotics, and precision systems remains a major barrier, particularly for small and marginal farmers. Despite long-term productivity gains, limited access to credit, inconsistent subsidy availability, and fluctuating commodity prices restrict purchasing power. Advanced technologies such as autonomous equipment, telemetry systems, and electric machinery further increase capital requirements. As a result, many farmers continue relying on older machinery or manual labor, slowing mechanization rates in developing regions and widening the technology gap between large commercial farms and smallholders.
2. Limited Digital Infrastructure and Technical Skill Gaps
Widespread adoption of connected and automated machinery is hindered by inadequate broadband coverage, weak IoT infrastructure, and low technology familiarity among farmers. Precision agriculture and telematics-based systems require reliable connectivity and skilled operators to configure, calibrate, and interpret data. Training gaps, limited service availability in rural areas, and complex repair requirements increase operational challenges. These constraints reduce the effectiveness of advanced machinery and slow the transition toward data-driven farming in emerging markets, making capability-building and infrastructure development essential for long-term sector growth.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds approximately 22–24% of the agricultural and farm machinery market, supported by large-scale commercial farming, advanced mechanization, and widespread adoption of precision agriculture technologies. The U.S. leads demand for high-horsepower tractors, autonomous guidance systems, and advanced combines, particularly in row-crop operations. Strong integration of telematics, connected machinery, and fleet-management platforms further accelerates digital transformation. Government initiatives promoting sustainable farming and investments in electric and hybrid machinery strengthen market expansion. Replacement demand also remains robust as farmers upgrade older assets with automation-ready and fuel-efficient equipment.
Europe
Europe accounts for roughly 18–20% of global market share, driven by strong mechanization in Germany, France, Italy, and the U.K. The region benefits from strict environmental regulations that encourage adoption of energy-efficient, low-emission tractors and precision systems that minimize chemical and fuel usage. Demand is strong in both arable farming and specialty crops such as vineyards and orchards, where robotics and autonomous implements gain traction. EU-funded digital farming programs, sustainability incentives, and modernization of small and medium farms support continued growth. High technological maturity and strong OEM presence reinforce Europe’s competitive position.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is the largest regional market, holding 42–45% share, primarily driven by China, India, and Japan. Rapid population growth, rising food demand, and government-led mechanization programs accelerate adoption of tractors, harvesters, and power tillers. Subsidies, rural credit expansion, and farm consolidation further stimulate equipment sales. Japan and South Korea lead in robotics and autonomous machinery, while China aggressively expands smart farming and electric tractor development. Growing investments in precision technologies, combined with a shift from manual labor to mechanized farming, position Asia-Pacific as the fastest-growing agricultural machinery hub.
Latin America
Latin America represents around 8–10% of the agricultural machinery market, supported by large-scale crop production in Brazil and Argentina. Expansion of soybean, sugarcane, and maize cultivation drives strong demand for high-capacity tractors, planters, and harvesters. Growing export-oriented agriculture encourages investment in technologically advanced machinery that enhances yield reliability and reduces operational costs. Government credit programs such as Brazil’s Moderfrota support machinery financing and modernization. Precision farming adoption is rising, particularly in GPS-guided seeding and spraying applications. However, demand remains sensitive to commodity price volatility and economic cycles.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region captures 6–8% of market share, driven by increasing mechanization in Turkey, South Africa, Egypt, and Gulf countries. Water scarcity, limited arable land, and climate challenges accelerate adoption of irrigation-linked machinery, precision sprayers, and fuel-efficient tractors. Governments promote agricultural modernization to improve food security, creating opportunities for mechanized planting and harvesting solutions. Sub-Saharan Africa relies heavily on entry-level tractors and affordable implements, while Middle Eastern markets increasingly invest in high-tech greenhouse, horticulture, and controlled-environment farming equipment. Infrastructure gaps remain a key constraint but modernization momentum is rising.
Market Segmentations:
By Technology:
By Ownership Model:
- Owned Equipment
- Leased Equipment
By Application:
- Row Crops
- Fruits & Vegetables
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the Agricultural and Farm Machinery Market features leading players such as APV GmbH, Escorts Limited, CLAAS KGaA mbH, HORSCH Maschinen GmbH, ISEKI & Co., Ltd., AGCO Corporation, CNH Industrial N.V., Fliegl Agro-Center GmbH, Deere & Company, and Bellota Agrisolutions. The Agricultural and Farm Machinery Market is characterized by strong innovation-driven positioning, with manufacturers expanding their portfolios across tractors, harvesters, precision implements, and autonomous field systems. Companies increasingly prioritize digital integration through telematics, GPS-guided controls, and fleet-management platforms to enhance operational efficiency and machine uptime. Competitive strategies focus on sustainability, including low-emission engines, electric and hybrid machinery, and advanced soil-conservation technologies. Partnerships with agri-tech startups, investments in robotics, and the development of subscription-based maintenance and equipment-as-a-service models strengthen market differentiation. Regional expansion, localized manufacturing, and aftersales service optimization further intensify competition in both developed and emerging agricultural markets.
Key Player Analysis
- APV GmbH
- Escorts Limited
- CLAAS KGaA mbH
- HORSCH Maschinen GmbH
- ISEKI & Co., Ltd.
- AGCO Corporation
- CNH Industrial N.V.
- Fliegl Agro-Center GmbH
- Deere & Company
- Bellota Agrisolutions
Recent Developments
- In February 2025, AGCO Corporation signed a supply agreement with SDF to deliver a streamlined portfolio of low- to mid-range horsepower tractors under its renowned Massey Ferguson brand. This strategic partnership enhances Massey Ferguson’s global position in the low- to mid-horsepower tractor market, enabling the brand to offer more farmers reliable, high-quality, and easy-to-use equipment that boosts productivity and maximizes profitability.
- In December 2024, Fliegl and Stapel announced their strategic collaboration aiming to utilise and expand existing synergies in the field of liquid manure. This collaboration is centered on creating innovative solutions that enhance the efficiency of agricultural tractor unit operations while addressing future demands.
- In September 2024, J C Bamford Excavators Ltd expanded its renowned X Series line with the launch of the 370X tracked excavator, a heavy-duty model in the 35-40-ton category designed for industry-leading productivity, durability, and reliability.
- In September 2024, Kubota North America acquired Bloomfield Robotics, a U.S.-based AgTech startup specializing in AI-powered crop monitoring for specialty crops. The acquisition strengthens Kubota’s smart farming portfolio by integrating plant-level imaging, health diagnostics, and yield prediction into its machinery ecosystem.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Technology, Ownership Model, Application and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market will accelerate adoption of autonomous tractors, robotic harvesters, and AI-enabled field systems.
- Electrification will expand as manufacturers introduce battery-powered and hybrid machinery for sustainable farming.
- Precision agriculture tools will become standard, driving wider use of sensors, telematics, and real-time data analytics.
- Equipment-as-a-Service models will gain traction as farmers seek flexible, low-capex access to advanced machinery.
- Connectivity will deepen, with cloud-linked machinery enabling predictive maintenance and optimized fleet performance.
- OEMs will strengthen partnerships with agri-tech providers to integrate digital platforms and automation solutions.
- Demand for compact and multi-purpose machinery will rise in horticulture, specialty crops, and smallholder farming.
- Government-backed mechanization programs will continue to support technology adoption in developing regions.
- Sustainable equipment designs will grow, emphasizing low emissions, reduced soil disturbance, and efficient fuel use.
- Global competition will intensify as companies innovate in robotics, smart implements, and energy-efficient machinery.




