Market Overview
Drought Tolerant Seeds Market size was valued USD 8.89 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 16.33 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 7.9% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Drought Tolerant Seeds Market Size 2024 |
USD 8.89 billion |
| Drought Tolerant Seeds Market, CAGR |
7.9% |
| Drought Tolerant Seeds Market Size 2032 |
USD 16.33 billion |
The global drought-tolerant seeds market is primarily driven by major players such as Bayer AG, Corteva Agriscience, Syngenta, BASF SE, and KWS SAAT SE & Co. KGaA. These companies lead in research and development, offering advanced seed varieties tailored for water-scarce regions. In 2024, North America held a significant market share of 39.8%, attributed to its advanced agricultural practices and high adoption of genetically modified crops. Asia Pacific is anticipated to witness the fastest growth, propelled by countries like China and India, which are investing heavily in drought-resistant seed technologies to ensure food security amid climate challenges.
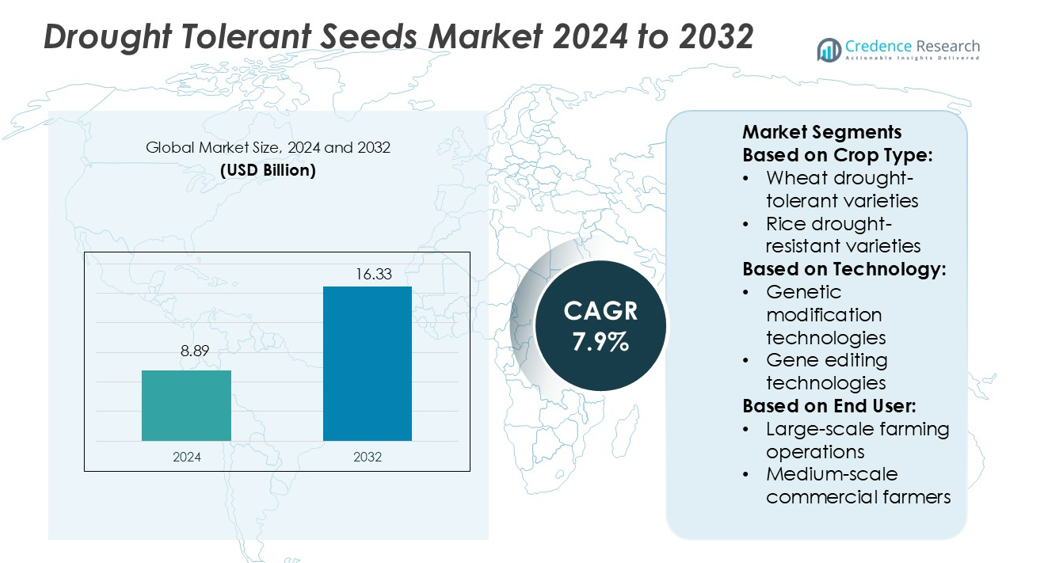
Market Insights
- The drought-tolerant seeds market was valued at USD 8.89 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 16.33 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 7.9%.
- Major players such as Bayer AG, Corteva Agriscience, Syngenta, BASF SE, and KWS SAAT SE & Co. KGaA lead the market through innovation and advanced drought-resistant seed varieties.
- North America held the largest regional share of 39.8% in 2024, driven by high adoption of genetically modified crops and advanced farming practices.
- Asia Pacific is expected to experience the fastest growth due to investments in drought-tolerant seeds in countries like China and India to ensure food security.
- Market growth is supported by rising demand for sustainable agriculture, technological advancements in seed development, and increasing focus on climate-resilient crops, while high costs of advanced seeds may restrain adoption in developing regions.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Crop Type
The cereals and grains segment dominates the drought-tolerant seeds market, driven by maize/corn drought-resistant varieties. Maize holds the largest share due to its global demand and vulnerability to water stress, followed by wheat and rice varieties tailored for arid conditions. Sorghum and millet also show steady growth, especially in semi-arid regions. Key drivers include rising food security concerns, changing rainfall patterns, and government initiatives promoting climate-resilient crops. Farmers increasingly adopt these varieties to maintain yield stability, reduce crop losses, and enhance profitability amid frequent droughts and erratic weather patterns.
- For instance, KUHN’s CCX 9000 cover crop seeder, when mounted on the Excelerator vertical tillage tool, allows operators to seed cover crops across 3.4 m to 10.4 m widths while tilling simultaneously.
By Technology
Genetic modification technologies lead the drought-tolerant seeds market, supported by innovations in gene expression and stress resistance. Conventional breeding remains significant, particularly for maize and wheat, but gene editing technologies are gaining traction for precision improvements. Seed enhancement technologies further complement these approaches, boosting germination and early growth under low-water conditions. Drivers include the need for higher yield stability, climate-resilient agriculture, and supportive regulatory frameworks in key regions. Continuous R&D and public-private collaborations accelerate adoption, enabling farmers to access technologically advanced seeds that perform under extreme environmental stress.
- For instance, Bourgault manufactures seeding equipment, including the 4420 Deep Knife Drill (DKD). This drill uses a deep knife to place fertilizer at depths of 120 to 165 mm, followed by a separate, shallower seed knife to precisely place legume seed, which enhances nitrogen fixation.
By End User
Commercial agriculture is the dominant end-user segment, with large-scale farming operations capturing the highest share. Medium-scale commercial farmers are expanding adoption, particularly for maize, wheat, and soybean drought-resistant varieties. Smallholder and semi-commercial farmers contribute growth in emerging economies, while research institutions and universities drive innovation through breeding programs and experimental trials. Drivers include government subsidies, increasing investment in precision farming, and the need to secure food supply under water scarcity. Adoption is further fueled by rising awareness of climate-resilient practices and technological assistance from international agricultural research centers.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Climate Change and Water Scarcity
Increasing global temperatures and erratic rainfall patterns drive demand for drought-tolerant seeds. Farmers face frequent crop losses in semi-arid and arid regions, pushing adoption of resilient varieties. This trend is especially pronounced in maize, wheat, and soybean cultivation, where water stress severely impacts yields. Government programs and subsidies promoting climate-resilient agriculture further accelerate growth. Additionally, drought-tolerant seeds help maintain food security and stabilize farm incomes, making them a preferred choice for both commercial and smallholder farmers aiming to mitigate climate-induced risks.
- For instance, Bayer’s Seminis® Pennybridge broccoli hybrid requires 31,000–39,000 seeds per acre in warm climates; it has maturity of 80 days; its bead structure is fine-medium, and field trials show tighter florets and improved yield potential compared to variety BC1611.
Expansion of Commercial Agriculture
Large-scale farming operations increasingly adopt drought-tolerant seeds to enhance productivity and profitability. High-value crops such as maize, soybean, and sunflower benefit from stress-resilient varieties, reducing yield losses during dry seasons. Growing investment in mechanized and precision farming supports adoption across commercial farms. Medium-scale farmers are also expanding usage due to better access to seed technologies. The commercial focus on maximizing output under limited water availability ensures sustained demand for drought-tolerant seeds, particularly in regions with intensive farming and government-backed agricultural development programs.
- For instance, Enza Zaden tested its baby spinach varieties ‘Crosstrek’, ‘Traverse’, and ‘Acadia’ under nitrogen levels of 0, 30, 60, 90, 120, and 150 mg/L in soilless substrate. ‘Crosstrek’ achieved a fresh mass of 921.4 g/m² at 120 mg/L, with significantly higher levels of β-carotene and lutein compared to lower nitrogen treatments.
Technological Advancements in Seed Development
Advances in genetic modification, gene editing, and seed enhancement technologies drive market growth. Precision breeding allows development of high-yielding, drought-resistant varieties tailored for specific crops. Innovations reduce germination failure and improve early-stage growth under water stress. Public-private collaborations, research institutions, and international agricultural centers accelerate deployment of new varieties. Farmers increasingly adopt technologically advanced seeds to ensure yield stability and cost-efficiency. These advancements also enable scalability, allowing medium and large commercial farms to integrate resilient seeds into existing cropping systems seamlessly.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Integration of Biotechnology and Gene Editing
The adoption of CRISPR and other gene-editing technologies presents significant growth opportunities. These tools allow precise modifications, enhancing drought tolerance without compromising yield. Biotechnology integration also facilitates faster development of new crop varieties for cereals, pulses, and oilseeds. Emerging markets benefit from access to advanced seeds, while public research institutions collaborate with private players to accelerate innovation. This trend creates opportunities for high-value seed products and strengthens partnerships across agritech companies, universities, and international research centers, driving overall market expansion.
- For instance, at its Nunhems facility in ‘s-Gravenzande, Netherlands, BASF achieved a tomato yield of 121 kilograms per square metre under a hybrid LED+HPS lighting regimen delivering 300 µmol light intensity, showing about 40% higher yield than baseline trials without that regime.
Growing Adoption Among Smallholder Farmers
Smallholders in emerging economies increasingly adopt drought-tolerant seeds to improve food security and income stability. Semi-commercial farmers and subsistence cultivators benefit from government extension programs and seed distribution schemes. This trend encourages localized seed solutions for maize, wheat, and pulses, enhancing resilience in vulnerable regions. Opportunities also exist for micro-finance and agritech platforms to provide affordable access to improved seeds. Expanding awareness about climate-resilient agriculture creates potential for new market penetration, particularly in Asia, Africa, and Latin America.
- For instance, DuPont Pioneer’s Premium Seed Treatment system is tested across over 400 locations and 65,000 plots annually, with treated soybean seeds showing an average yield gain of 4.5 bushels/acre in responsive environments versus untreated seed.
Expansion of Public-Private Partnerships
Collaborations between governments, research institutions, and seed companies drive innovation and adoption. These partnerships facilitate large-scale distribution of drought-tolerant seeds, improve training for farmers, and support regulatory approval for advanced varieties. Joint initiatives enhance R&D efficiency, enabling tailored solutions for diverse crops and regional conditions. Opportunities arise in developing hybrid varieties, seed enhancement programs, and precision farming support. Such collaboration ensures that both commercial and smallholder farmers access resilient seeds, fostering sustainable agriculture and long-term market growth.
Key Challenges
Regulatory and Approval Barriers
Strict regulatory frameworks for genetically modified and gene-edited seeds slow market entry. Approval processes vary by country, delaying commercialization and increasing development costs. Farmers in regions with restrictive policies may face limited access to advanced drought-tolerant varieties. Compliance with biosafety standards, labeling, and testing adds operational complexity for seed companies. Navigating these regulatory hurdles requires collaboration with government agencies and adherence to local agricultural laws, which can limit rapid adoption, particularly for cutting-edge biotechnological solutions.
High Development and Adoption Costs
Developing drought-tolerant seeds requires significant R&D investment in breeding, gene editing, and field trials. High costs of advanced seed varieties can limit adoption among smallholder and semi-commercial farmers. Additionally, farmers may need training and supportive infrastructure to maximize yield potential. Price sensitivity in emerging markets poses a challenge for widespread deployment. Companies must balance innovation with affordability to ensure market penetration. Financing schemes, subsidies, and extension services play a critical role in overcoming cost-related barriers and facilitating broader adoption of resilient seeds.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds a significant share of the drought-tolerant seeds market, led by the United States and Canada. Maize and soybean drought-resistant varieties dominate due to extensive commercial farming and advanced agritech adoption. The region accounts for approximately 30% of the global market, driven by government incentives, research investments, and precision agriculture practices. Large-scale operations and medium-scale commercial farmers increasingly adopt genetically modified and gene-edited seeds to maintain yield stability under frequent droughts. Strong collaboration between public research institutions and private seed companies accelerates innovation, enhancing the development of high-performing, climate-resilient crops across cereals, oilseeds, and pulses.
Europe
Europe captures around 20% of the global drought-tolerant seeds market, with Germany, France, and Spain leading adoption. Wheat and maize drought-tolerant varieties are primary contributors, supported by advanced seed technologies and regulatory frameworks. Gene editing and conventional breeding technologies see strong use in large-scale commercial farms and R&D institutions. Drivers include rising climate variability, government support for sustainable agriculture, and increasing demand for food security. Public-private partnerships foster innovation, enabling the development of high-yielding, stress-resistant seeds. Medium-scale farmers also expand adoption, particularly in Southern Europe, where water scarcity and soil limitations create significant demand for resilient crop varieties.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, accounting for approximately 28% of the market. India, China, and Australia lead adoption due to increasing water scarcity and the need for food security. Maize, rice, and pulses dominate crop segments, while genetic modification and seed enhancement technologies drive growth. Adoption among smallholder and semi-commercial farmers is rising due to government subsidies and extension programs. International agricultural research centers collaborate with local institutions to provide climate-resilient solutions. The region’s diverse climatic conditions and growing population create opportunities for scaling drought-tolerant seeds, particularly in cereals, oilseeds, and legume crops.
Latin America
Latin America represents about 12% of the global drought-tolerant seeds market, with Brazil and Argentina driving adoption. Maize and soybean varieties dominate due to extensive commercial farming. Growth is supported by favorable government policies, seed enhancement technologies, and expanding R&D investments. Large-scale commercial farmers lead adoption, while medium-scale and smallholders increasingly access resilient seeds through cooperative programs. Climate variability, including frequent droughts, encourages use of genetically improved and conventionally bred seeds. Public-private collaborations further enhance market penetration, particularly in regions vulnerable to water scarcity. Rising focus on sustainable agriculture also fuels long-term demand for drought-tolerant crops.
Middle East & Africa
Middle East & Africa holds approximately 10% of the drought-tolerant seeds market, driven by arid and semi-arid conditions. Sorghum, millet, maize, and cowpea varieties are dominant, addressing food security and water scarcity challenges. Adoption spans smallholder farmers to commercial agricultural operations, supported by government programs, international research institutions, and seed enhancement technologies. Growth is fueled by climate-resilient agriculture initiatives and rising awareness of crop productivity optimization. Challenges include limited infrastructure and high adoption costs. Nonetheless, collaborations between seed companies, NGOs, and research centers facilitate deployment of drought-tolerant varieties, particularly in Sub-Saharan Africa and the Gulf region, promoting sustainable farming.
Market Segmentations:
By Crop Type:
- Wheat drought-tolerant varieties
- Rice drought-resistant varieties
By Technology:
- Genetic modification technologies
- Gene editing technologies
By End User:
- Large-scale farming operations
- Medium-scale commercial farmers
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The drought-tolerant seeds market players such as Calyxt Inc., DowDuPont, R. Simplot Co., Monsanto, Stine Seed Farm Inc., Syngenta, BASF SE, Bayer CropScience, Maharashtra Hybrid Seed Company (MAHYCO), and Nuseed Pty Ltd. The drought-tolerant seeds market is highly competitive, driven by continuous innovation in genetic modification, gene editing, and seed enhancement technologies. Companies focus on developing high-yielding, climate-resilient varieties of maize, wheat, soybean, rice, and pulses to address water scarcity and global food security challenges. Adoption spans large-scale commercial farms to smallholder and semi-commercial operations, supported by government programs and international research collaborations. Strategic R&D investments and advanced distribution networks enable rapid market penetration and regional expansion. Ongoing technological advancements and public-private partnerships enhance seed performance, improve germination under drought conditions, and ensure sustainable agricultural practices worldwide.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Calyxt Inc.
- DowDuPont
- Simplot Co.
- Monsanto
- Stine Seed Farm Inc.
- Syngenta
- BASF SE
- Bayer CropScience
- Maharashtra Hybrid Seed Company (MAHYCO)
- Nuseed Pty Ltd.
Recent Developments
- In July 2025, Zambia launched pilot projects for drought-tolerant seed varieties at the Zambia Agriculture Research Institute (ZARI) to enhance food security from severe weather events.
- In March 2025, Moldova with their active partnership with FAO, started drought relief program. The program was set up to support farmers who are heavily affected by crop loss exceeding 70% due to the drought.
- In November 2024, Corteva introduced a proprietary and novel non-GMO hybrid technology for wheat, which is expected to ensure substantial yield improvements to the crop. The new method boosts yield potential by 10% while utilizing the same quantity of land resources.
- In June 2023, Takii unveiled a new advanced seed production facility in Karacabey, Turkey. The plant, situated in the Bursa province, has been established to improve the company’s production process for both flower and vegetable seeds.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Crop Type, Technology, End User and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Adoption of drought-tolerant seeds will expand in semi-arid and arid regions globally.
- Gene editing and biotechnology will drive development of higher-yielding, climate-resilient crops.
- Smallholder and semi-commercial farmers will increasingly access improved seed varieties.
- Public-private collaborations will accelerate R&D and regional deployment of advanced seeds.
- Precision farming and digital agriculture will enhance seed performance and resource efficiency.
- Maize, wheat, rice, and soybean will remain the most widely adopted crop segments.
- Government incentives and subsidies will continue to support adoption in emerging economies.
- International research centers will contribute to developing region-specific drought-resistant varieties.
- Seed enhancement technologies will improve germination rates under water-stressed conditions.
- Market growth will be driven by rising food security concerns and climate change adaptation.




