Market Overview
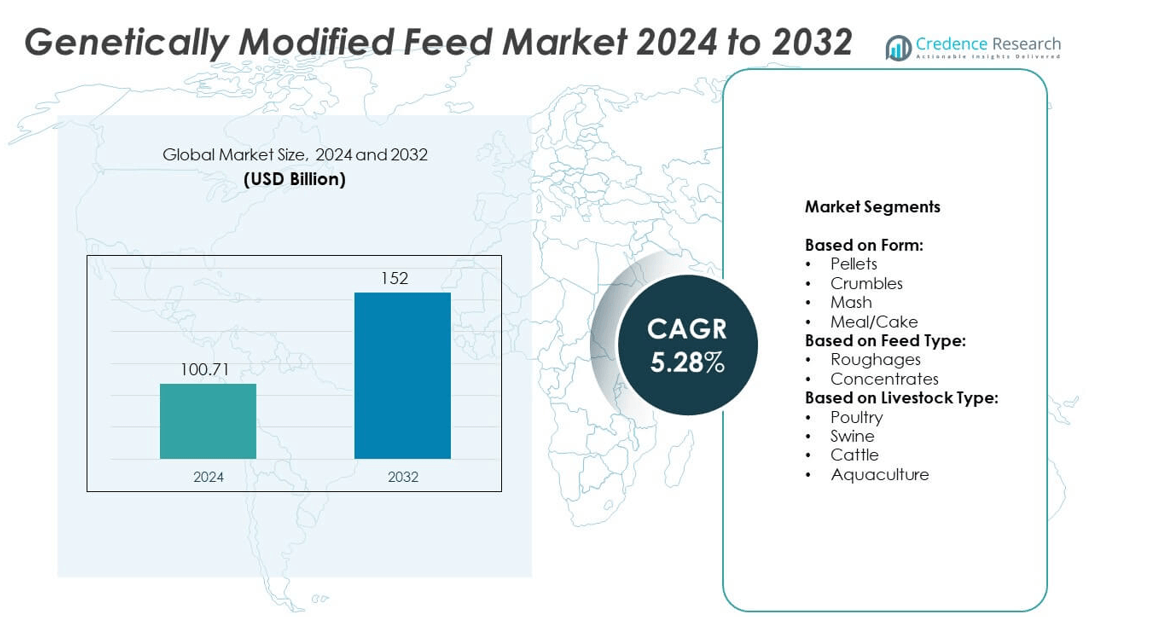
Genetically Modified Feed Market size was valued at USD 100.71 Billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 152 Billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 5.28% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Genetically Modified Feed Market Size 2024 |
USD 100.71 Billion |
| Genetically Modified Feed Market , CAGR |
5.28% |
| Genetically Modified Feed Market Size 2032 |
USD 152 Billion |
The Genetically Modified Feed market grows due to rising livestock production, increasing demand for protein-rich diets, and the need for efficient feed solutions. Farmers adopt genetically modified crops for higher yields, pest resistance, and consistent nutrient content. Biotechnology integration with precision farming improves productivity and sustainability. Expanding global trade networks ensure reliable feed supply across regions. The market benefits from regulatory support in key countries and evolving consumer demand for affordable, high-quality meat, dairy, and aquaculture products.
North America leads the Genetically Modified Feed market with advanced biotechnology adoption and strong livestock demand, while Asia Pacific shows rapid growth driven by expanding poultry and aquaculture industries. Europe relies on imports to meet protein needs under strict regulatory frameworks, whereas Latin America plays a dual role as both a producer and exporter of soybean and maize feed. Key players shaping the market landscape include Bayer AG, BASF SE, Corteva Agriscience, and Syngenta Crop Protection AG.
Market Insights
- The Genetically Modified Feed market was valued at USD 100.71 Billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 152 Billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 5.28%.
- Rising demand for protein-rich diets and increasing livestock production are driving adoption of genetically modified feed worldwide.
- Growing use of herbicide-tolerant and pest-resistant crops reflects a major trend, ensuring stable yields and reliable feed supply.
- Competitive dynamics are shaped by innovation in crop traits, partnerships with feed processors, and global distribution networks.
- Strict regulatory frameworks, public perception issues, and trade restrictions act as restraints limiting faster expansion of genetically modified feed.
- North America leads due to large-scale adoption of modified crops, Europe depends on imports under tight regulations, Asia Pacific shows strong growth from poultry and aquaculture demand, Latin America plays a key role in exports, and the Middle East and Africa rely on trade for supply security.
- Continuous advancements in biotechnology and increasing global trade integration provide long-term opportunities, strengthening feed security across emerging and developed markets.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Drivers
Rising Demand for High-Yield Livestock Production
The Genetically Modified Feed market benefits from growing livestock production to meet global protein needs. Farmers adopt genetically modified feed to enhance animal growth rates and optimize feed conversion. It supports consistent weight gain in poultry, cattle, and swine. Consumers expect stable meat, milk, and egg supplies, driving reliance on high-performance feed. Increasing population in developing nations strengthens demand for efficient feed solutions. Genetic traits in modified crops ensure reliable nutrient content for intensive farming systems.
- For instance, Studies on broiler birds supplemented with Diamond V XPC have shown mixed results regarding feed intake. While a study found a reduction in feed intake and improved feed efficiency with XPC added at 1.25% to 2% of the feed, other research has yielded different conclusions, with some studies finding an increase in feed intake and others reporting no significant impact
Improved Resistance Against Crop Diseases and Pests
The market grows due to genetically modified feed crops offering resistance to pests and diseases. It reduces losses in corn, soybean, and canola production, ensuring stable feed supplies. Lower dependency on chemical pesticides aligns with farm sustainability goals. Farmers achieve higher output per acre, securing long-term feed availability. Improved resistance lowers risks of supply shortages during unfavorable seasons. The consistent quality of modified crops supports large-scale commercial feed operations.
- For instance, field-evolved resistance to the Cry1F protein was documented in ECB populations in Canada as of 2018. A report submitted to the EU in November 2024 detailed the cultivation of MON 810 Bt maize in Europe for the 2023 growing season, covering approximately 48,225 hectares (roughly 119,166 acres) in Spain and Portugal.
Enhanced Nutritional Content for Animal Health
The Genetically Modified Feed market advances through crops engineered with superior nutrient levels. It improves protein, amino acids, and oil content in feed ingredients. Livestock health benefits from balanced nutrition, reducing veterinary costs for farmers. Modified soybean and maize strains deliver optimized energy and digestibility. Consistent nutrient profiles enhance animal productivity and product quality. Nutritionally enriched feed supports commercial farms targeting premium output standards.
Support from Global Regulatory and Trade Policies
The market gains momentum from favorable policies and acceptance of genetically modified feed in global trade. It ensures steady cross-border supply of corn and soymeal. Governments recognize its role in reducing agricultural pressure on land and resources. Trade agreements increasingly include provisions for modified crops. International demand for cost-effective feed imports continues to rise. Regulatory frameworks create a stable foundation for long-term industry adoption.
Market Trends
Growing Adoption of Herbicide-Tolerant and Insect-Resistant Crops
The Genetically Modified Feed market shows strong adoption of herbicide-tolerant and insect-resistant crops. Farmers prefer soybean, maize, and cotton varieties with proven field performance. It reduces input costs by minimizing crop loss from weeds and pests. Stable harvests improve feed supply reliability for intensive livestock farming. Adoption expands in emerging economies with rising agricultural mechanization. These crop traits continue to drive large-scale feed production efficiency.
- For instance, a study on improved maize hybrids with introgressed genes reported lysine content of 0.367% in flour compared to 0.150-0.250% in standard maize.
Integration of Biotechnology with Precision Farming Practices
The market reflects integration of biotechnology with precision agriculture for higher productivity. It enables accurate use of modified seeds with GPS, sensors, and smart irrigation. Farmers achieve higher yield per acre with optimized resource use. Precision tools help measure feed crop output with greater accuracy. It enhances sustainability while reducing environmental impact in commercial farming. The trend accelerates with digital agriculture investments in key producing regions.
- For instance, Brazil is a major global exporter of corn, with exports to Asia, particularly China, significantly increasing since 2022 due to a trade agreement. Brazil’s total corn exports were around 55.35 million metric tons in 2023.
Focus on Sustainable and Low-Input Farming Systems
The Genetically Modified Feed market aligns with sustainability goals in global agriculture. Crops engineered for drought tolerance and low fertilizer needs gain attention. It supports farming practices that conserve water and reduce chemical reliance. Sustainability certifications strengthen acceptance among global buyers. Farmers adapt these systems to meet rising consumer demand for eco-friendly products. Long-term adoption of such crops secures resilient feed supply chains.
Expansion of International Trade in GM Feed Crops
The market expands with strong international trade of genetically modified corn and soybean meal. Exporters secure competitive advantage with large-scale production capabilities. It ensures steady imports for countries with limited agricultural resources. Trade partnerships strengthen supply networks across Asia, Europe, and the Middle East. Regulatory approvals across regions increase acceptance of modified crops. Expanding global trade reinforces growth in feed manufacturing hubs.
Market Challenges Analysis
Regulatory Barriers and Public Perception Issues
The Genetically Modified Feed market faces obstacles from strict regulatory frameworks in several regions. Governments impose rigorous approval processes that delay crop adoption. It creates uncertainty for farmers and feed producers planning large-scale use. Public perception remains divided, with consumer groups opposing genetically modified ingredients. Concerns over food safety and environmental risks limit acceptance in key markets. Such barriers restrict smooth expansion despite technological progress and proven benefits.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Trade Restrictions
The market experiences challenges from global supply chain disruptions and trade restrictions. Weather extremes, transport delays, and geopolitical conflicts interrupt steady feed crop movement. It raises costs for producers reliant on imported soybean and maize. Export bans and regional trade disputes further strain supply availability. Feed manufacturers must balance volatile costs while meeting livestock sector demand. These challenges pressure margins and reduce predictability in long-term feed planning.
Market Opportunities
Rising Demand for Protein-Rich Diets in Emerging Economies
The Genetically Modified Feed market offers opportunities from increasing meat and dairy consumption in developing nations. Expanding middle-class populations in Asia and Latin America drive demand for protein-rich diets. It creates strong need for efficient feed solutions to support livestock growth. Genetically modified crops with higher yields and stable nutrition address this demand effectively. Governments in these regions invest in agricultural modernization to secure food supply. Expanding livestock farming opens new revenue streams for feed producers.
Advancements in Crop Engineering and Trait Development
Opportunities emerge from advancements in crop engineering that improve feed crop efficiency. It allows the development of varieties with drought tolerance, higher nutrient density, and lower resource requirements. These innovations meet sustainability goals while improving farm profitability. Feed producers gain advantage by offering consistent quality inputs for animal health. International trade potential grows with wider acceptance of genetically modified crops. Expanding trait innovations create long-term opportunities for global feed supply networks.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Form:
The Genetically Modified Feed market includes pellets, crumbles, mash, and meal or cake. Pellets dominate due to ease of storage, transportation, and controlled nutrient delivery. Crumbles are widely used in poultry production for young birds requiring smaller feed sizes. Mash remains important in traditional farming setups where low processing costs matter. Meal or cake derived from soybean and canola supports protein-rich diets for livestock. It ensures flexibility for farmers to choose feed formats based on efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- For instance, According to Corteva’s 2023 Sustainability Report, the company’s focus on sustainable innovation includes developing new technologies for genetic gain, such as enhanced seed varieties. The report states that from 2021 to 2023, Corteva supported 4.2 million acres with biodiversity and outcomes aligned with regenerative agriculture
By Feed Type:
The market is divided into roughages and concentrates. Concentrates hold the largest share because of their nutrient density and contribution to faster growth cycles. Roughages are still necessary for ruminants, particularly cattle, where fiber intake is vital. It provides balance in livestock nutrition by complementing high-energy concentrates. Farmers rely on genetically modified crops such as corn and soymeal to produce efficient concentrate feeds. This segment benefits from large-scale production capabilities in major agricultural regions.
- For instance, John Deere manufactures precision planting systems, such as the ExactEmerge planter, which uses electric drives for precise seed placement even at fast planting speeds. The company also offers the ExactShot planting technology, introduced at CES 2023, which reduces starter fertilizer usage by more than 60% by precisely applying fertilizer onto each seed as it is planted
By Livestock Type:
The Genetically Modified Feed market serves poultry, swine, cattle, and aquaculture. Poultry dominates due to rising global consumption of chicken meat and eggs. Swine production relies on energy-dense feed to improve feed-to-meat conversion rates. Cattle segment benefits from protein-rich soybean meal that supports milk and beef productivity. Aquaculture shows rapid growth with genetically modified soybean meal replacing traditional fishmeal. It ensures sustainable alternatives for the seafood industry facing supply constraints. This diverse livestock adoption strengthens demand for genetically modified feed across global markets.
Segments:
Based on Form:
- Pellets
- Crumbles
- Mash
- Meal/Cake
Based on Feed Type:
Based on Livestock Type:
- Poultry
- Swine
- Cattle
- Aquaculture
Based on the Geography:
- North America
- Europe
- UK
- France
- Germany
- Italy
- Spain
- Russia
- Belgium
- Netherlands
- Austria
- Sweden
- Poland
- Denmark
- Switzerland
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Thailand
- Indonesia
- Vietnam
- Malaysia
- Philippines
- Taiwan
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Peru
- Chile
- Colombia
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East
- UAE
- KSA
- Israel
- Turkey
- Iran
- Rest of Middle East
- Africa
- Egypt
- Nigeria
- Algeria
- Morocco
- Rest of Africa
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds the largest share of the Genetically Modified Feed market with 38%. The region leads due to extensive cultivation of genetically modified corn and soybean used in feed formulations. Farmers in the United States and Canada benefit from advanced biotechnology adoption and favorable regulations supporting genetically modified crops. It ensures consistent feed supply for a highly developed livestock and poultry industry. Strong presence of agribusiness giants and established trade networks further reinforces market leadership. The demand for protein-rich meat and dairy products continues to expand, driving long-term feed adoption across commercial farming systems.
Europe
Europe accounts for 22% of the Genetically Modified Feed market, supported by imports of soybean and maize from North and South America. The European Union enforces strict approval processes, but consistent demand for animal protein sustains feed imports. It reflects the region’s reliance on genetically modified raw materials despite cautious regulatory frameworks. Countries like Spain and the Netherlands play a vital role in feed processing and distribution. Rising livestock production in these nations strengthens regional consumption. The feed sector adapts to sustainability goals while balancing consumer concerns about genetically modified inputs.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific represents 28% of the Genetically Modified Feed market, driven by rapid expansion of livestock farming in China, India, and Southeast Asia. Poultry and aquaculture industries experience strong growth due to increasing protein consumption across urban populations. It secures higher feed demand supported by large-scale soybean and maize imports from the Americas. Domestic production of genetically modified crops in countries like China also contributes to regional growth. Farmers adopt feed solutions that enhance efficiency and reduce input costs. Expanding middle-class income levels create steady opportunities for global feed suppliers targeting the region.
Latin America
Latin America contributes 8% to the Genetically Modified Feed market, with Brazil and Argentina leading in soybean and maize production. The region not only consumes but also exports large volumes of feed crops worldwide. It holds competitive advantage due to large-scale cultivation of genetically modified seeds and favorable climatic conditions. Domestic livestock industries in Brazil and Argentina expand rapidly, fueling local feed usage. Trade policies encourage strong international partnerships, boosting exports to Asia and Europe. Rising investments in feed processing facilities strengthen the region’s role in the global supply chain.
Middle East and Africa
Middle East and Africa hold 4% share of the Genetically Modified Feed market, relying heavily on imports to meet feed requirements. Limited arable land and water scarcity restrict large-scale crop cultivation. It increases dependency on global suppliers for soybean meal and maize feed. Poultry and dairy farming sectors grow steadily to meet urban consumer demand for protein. Governments focus on securing food supplies through long-term trade agreements with exporting nations. Investments in aquaculture projects further support gradual expansion of genetically modified feed in the region.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Stine Seed Company
- Bayer AG
- Tyson Foods
- Anderson Exports
- KWS SAAT SE & Co. KGaA
- R. Simplot Company
- BASF SE
- Okanagan Specialty Fruits Inc.
- Groupe Limagrain Holding
- Syngenta Crop Protection AG
- Corteva Agriscience
Competitive Analysis
The leading players in the Genetically Modified Feed market include Stine Seed Company, Bayer AG, Tyson Foods, Anderson Exports, KWS SAAT SE & Co. KGaA, J.R. Simplot Company, BASF SE, Okanagan Specialty Fruits Inc., Groupe Limagrain Holding, Syngenta Crop Protection AG, and Corteva Agriscience. These companies play a central role in shaping the competitive environment through advanced seed technologies, feed innovations, and strong global distribution networks. Their strategies emphasize high-yield crop development, enhanced nutritional value, and sustainable farming practices to meet the rising global protein demand. Competition in the market is defined by continuous investment in biotechnology and trait development. Companies strengthen their portfolios with herbicide-tolerant and pest-resistant crops that improve farm efficiency and feed reliability. Expansion into emerging economies provides further opportunities as livestock production grows rapidly. Strategic partnerships with distributors and feed processors enhance market presence across key regions. Players also prioritize regulatory compliance and sustainability, aligning with government policies and international trade requirements. The market remains highly competitive, with firms leveraging innovation, scale, and supply chain strength to maintain leadership. Continuous improvements in genetically modified crop performance and tailored feed solutions will sustain competitive momentum across global markets.
Recent Developments
- In 2025, BASF signed a trait licensing agreement with Corteva Agriscience and M.S. Technologies, L.L.C. to bring a novel nematode-resistant soybean trait (NRS) combined with Enlist E3® and Conkesta E3® soybeans to market in Brazil
- In 2025, Corteva partnered with BASF and M.S. Technologies to license and commercialize the nematode-resistant soybean trait incorporated into its Enlist E3® and Conkesta E3® soybean technologies for Brazilian markets
- In 2024, Bayer licensed gene-edited mustard greens (CRISPR-developed) from Pairwise for grocery store distribution across the US, targeting consumer-friendly traits with improved taste and nutritio
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Form, Feed Type, Livestock Type and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The Genetically Modified Feed market will expand with rising global protein demand.
- Adoption of high-yield genetically modified crops will strengthen livestock feed supply.
- It will benefit from advances in crop engineering for drought and pest resistance.
- Regulatory approvals in new regions will support broader market acceptance.
- Livestock producers will prefer nutritionally enhanced feed for better productivity.
- International trade of soybean and maize will remain central to feed availability.
- Growing aquaculture industries will drive demand for sustainable feed alternatives.
- It will align with sustainability goals by reducing reliance on chemicals and water.
- Investments in precision agriculture will optimize genetically modified feed production.
- Expansion in emerging economies will create significant long-term growth opportunities.




