| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market Size 2024 |
USD 25,361.38 Million |
| Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market, CAGR |
9.38% |
| Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market Size 2032 |
USD 54,650.92 Million |
Market Overview
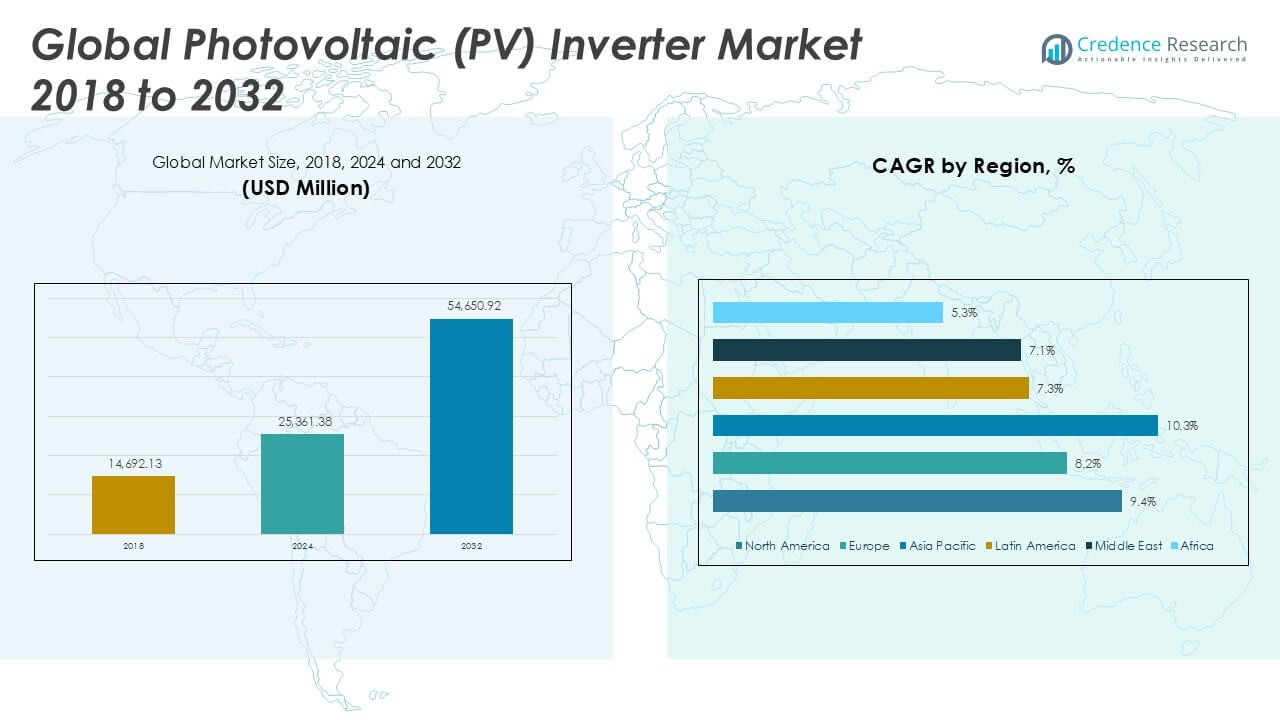
The Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market size was valued at USD 14,692.13 million in 2018, increased to USD 25,361.38 million in 2024, and is anticipated to reach USD 54,650.92 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 9.38% during the forecast period.
The Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market is driven by the growing adoption of solar energy across residential, commercial, and utility sectors due to rising energy demand and supportive government policies. Initiatives such as feed-in tariffs, tax incentives, and renewable energy targets have accelerated PV installations globally. Technological advancements in inverter efficiency, grid integration, and smart monitoring systems enhance energy output and operational reliability, supporting broader deployment. The shift toward decentralized power generation and the integration of energy storage systems further boost demand for advanced inverters. Trends such as digitalization, real-time data analytics, and AI-enabled inverters are reshaping energy management and performance optimization. Increasing investments in microgrid infrastructure and rural electrification projects, particularly in developing economies, also contribute to market expansion. The transition toward zero-emission energy solutions and the declining cost of photovoltaic components continue to support long-term growth, positioning PV inverters as a key enabler in the global shift to sustainable power.
The Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market demonstrates strong geographical diversification, with Asia Pacific leading in terms of installations due to large-scale solar initiatives in China, India, and Japan. North America shows steady expansion driven by residential rooftop projects and policy incentives in the United States and Canada. Europe maintains robust growth through climate-driven policies and grid modernization efforts, particularly in Germany, Italy, and the Netherlands. Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa are witnessing rising demand supported by rural electrification, declining system costs, and increasing solar investments. Key players shaping the global market include SMA Solar Technology AG, known for advanced string inverters and monitoring systems; Delta Electronics, Inc, offering high-efficiency solutions for residential and utility applications; and Fimer Group, recognized for its diverse product range and strong presence across EMEA regions. Omron Corporation also holds a notable position with its focus on compact residential inverter solutions and smart energy integration.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market was valued at USD 25,361.38 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 54,650.92 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 9.38% during the forecast period.
- Growing demand for clean and sustainable energy, coupled with favorable government policies and incentives, drives large-scale solar adoption across residential, commercial, and utility sectors.
- Advancements in inverter technology, including the development of smart, hybrid, and storage-integrated inverters, are reshaping system design and improving energy efficiency.
- Manufacturers like SMA Solar Technology AG, Delta Electronics, Fimer Group, and Omron Corporation lead the market with diversified portfolios and investments in digital integration.
- High pricing pressure and concerns over inverter reliability in extreme weather conditions present challenges, particularly in cost-sensitive and infrastructure-limited regions.
- Asia Pacific leads the market due to strong solar infrastructure in China, India, and Japan, while North America and Europe follow with steady residential and commercial uptake.
- Decentralized energy systems, smart grid expansion, and rural electrification projects in Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa offer long-term growth opportunities.
Market Drivers
Rising Demand for Clean Energy and Supportive Government Policies Stimulate Market Growth
The Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market benefits significantly from the global shift toward renewable energy to reduce carbon emissions and meet climate targets. Countries are enforcing regulations and offering incentives such as feed-in tariffs, investment tax credits, and renewable portfolio standards. These programs directly boost solar energy installations, creating sustained demand for efficient inverters. National energy security concerns and efforts to diversify power sources strengthen the case for solar infrastructure. Emerging economies are expanding solar deployment to support rural electrification and reduce grid dependency. The market leverages this momentum to scale production and innovation across regions.
- For instance, SMA Solar Technology AG shipped inverters totaling over 15.6 GW globally in 2023, meeting demand driven by favorable renewable energy targets.
Technological Advancements in Inverter Design Improve Energy Yield and Reliability
Continuous innovation in inverter technology enhances system performance, contributing to higher energy yields and better grid integration. Manufacturers are developing smart inverters with features like real-time monitoring, remote control, and reactive power support. These upgrades enable better load management, faster fault detection, and minimal energy loss. The Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market is moving toward hybrid inverters that support both solar and storage functions. Advanced cooling systems and compact form factors increase product lifespan and simplify installation. It creates new opportunities for both residential and commercial segments demanding robust and intelligent energy solutions.
- For instance, Delta Electronics’ M125HV inverter offers 125 kVA power output with 98.8% efficiency, contributing to higher yields in utility-scale installations.
Rapid Decline in PV System Costs Expands Adoption Across Sectors
Falling prices of solar panels and related hardware reduce the total cost of ownership, encouraging broader adoption of solar power systems. The Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market gains traction as users across industrial, commercial, and household segments seek cost-effective energy alternatives. Improved manufacturing efficiencies and economies of scale allow inverter producers to offer competitive pricing. It enables greater penetration into low-income and price-sensitive markets. Project developers also benefit from lower installation costs, shortening payback periods and increasing return on investment. This dynamic directly supports market expansion and technology upgrades.
Grid Modernization and Energy Storage Integration Drive Long-Term Demand
The shift toward smart grids and the growing need for two-way energy flow support inverter innovation and deployment. Governments and utilities are upgrading grid infrastructure to accommodate intermittent solar inputs and enhance system stability. The Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market aligns with this trend through grid-supportive technologies like frequency regulation and voltage control. Integrated solutions that connect seamlessly with battery storage systems allow users to optimize energy usage and reduce dependency on the grid. It positions inverters as a critical component in both standalone and hybrid energy systems. Strong policy backing for grid modernization sustains the long-term growth trajectory of the market.
Market Trends
Integration of Smart Features and Digital Monitoring Systems Shapes Product Evolution
Smart inverters equipped with advanced digital monitoring systems are transforming energy management across all segments. These inverters support real-time data tracking, remote diagnostics, and performance analytics, enabling users to optimize solar output and detect system faults quickly. It enhances energy efficiency while reducing operational downtime and maintenance costs. The Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market is witnessing demand for devices compatible with IoT and AI platforms, supporting intelligent grid interaction. Smart features such as reactive power control and anti-islanding help maintain grid stability under variable load conditions. These developments improve the performance and versatility of PV systems in both grid-tied and off-grid environments.
- For instance, Huawei shipped over 20 GW of smart string inverters in 2023, equipped with AI-based arc fault detection and remote monitoring via FusionSolar platform.
Hybrid and Storage-Ready Inverters Gain Popularity in Decentralized Energy Models
Decentralized energy systems are expanding in residential and commercial settings, increasing demand for hybrid and storage-ready inverters. These inverters allow integration with battery storage, enabling users to store excess solar power and manage energy consumption more effectively. It supports energy independence and grid resilience, especially in areas with unreliable power infrastructure. The Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market is moving toward multifunctional devices that support solar, battery, and generator connections in a single unit. Consumers seek flexible systems capable of adapting to future energy needs without requiring major hardware upgrades. This trend reflects growing interest in self-sufficient and sustainable energy solutions.
- For instance, SolarEdge sold over 3.3 GW of inverters with integrated energy storage compatibility in 2023, supporting decentralized solar installations across more than 30 countries.
String and Microinverters Continue to Replace Centralized Systems in Residential Applications
Demand for string and microinverters is increasing due to their scalability, efficiency, and lower installation complexity. These inverters are preferred for small-scale applications, particularly in residential and small commercial projects, due to their modular design and improved shading tolerance. It enables installers to customize configurations based on available rooftop space and orientation. The Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market is shifting away from traditional centralized inverters toward more distributed formats that maximize energy capture. Microinverters offer panel-level monitoring and enhance system reliability, which appeals to homeowners prioritizing long-term performance. The flexibility and simplicity of these systems support widespread market adoption.
Regulatory Trends and Grid Codes Influence Design and Deployment Strategies
Evolving grid codes and regulatory frameworks are shaping inverter design, requiring compliance with specific operational and safety standards. Utilities demand inverters that can provide ancillary services such as voltage support, frequency regulation, and grid communication. It drives manufacturers to innovate and certify products across various international markets. The Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market aligns with these changes by developing compliant solutions that support seamless integration into modern grids. Government mandates related to distributed generation and renewable penetration influence both product functionality and deployment timelines. These regulatory trends ensure sustained product innovation and alignment with national energy goals.
Market Challenges Analysis
High Cost Pressure and Product Reliability Concerns Limit Wider Adoption
The Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market faces challenges related to cost competitiveness and product reliability, especially in price-sensitive regions. Intense competition among manufacturers often drives pricing pressure, making it difficult for smaller players to sustain profitability. Inverter failure remains a critical concern due to harsh environmental conditions, such as heat, dust, and humidity, which can compromise system performance. It raises concerns among consumers about product lifespan and return on investment. Installation quality and lack of standardized maintenance practices further affect long-term reliability. These factors deter broader adoption in regions lacking skilled workforce and support infrastructure.
Complex Regulatory Landscape and Grid Integration Issues Hinder Market Growth
Evolving grid codes and inconsistent regulatory frameworks across countries pose major challenges for inverter manufacturers. Navigating diverse compliance requirements delays product approvals and increases certification costs. The Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market must adapt to shifting technical standards that vary significantly between utility grids, especially in developing economies. It increases engineering complexity and slows product rollout. Poor grid infrastructure in certain regions limits the capability of smart inverters to perform advanced grid-support functions. These integration barriers reduce the operational benefits of high-end inverters and restrict their deployment across fragmented markets.
Market Opportunities
Expansion of Renewable Energy Targets and Rural Electrification Programs Creates New Avenues
Government-backed renewable energy targets and large-scale rural electrification initiatives offer strong growth potential for the Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market. Nations across Asia, Africa, and Latin America are scaling solar deployments to address energy access gaps in off-grid and underserved areas. These efforts increase demand for reliable, standalone, and hybrid inverters tailored to remote conditions. It enables manufacturers to introduce rugged, low-maintenance solutions with scalable output. International development programs and climate finance mechanisms further support solar adoption in emerging economies. These opportunities allow companies to expand their footprint while addressing sustainable energy goals.
Growing Demand for Smart Infrastructure and Decentralized Energy Drives Innovation
The rising demand for smart homes, smart cities, and decentralized energy systems opens up space for advanced inverter technologies. Consumers and utilities seek inverters that integrate with digital platforms, storage systems, and electric vehicle charging networks. The Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market can capitalize on this trend by developing interoperable and software-defined solutions. It supports dynamic energy management and enhances overall grid flexibility. Partnerships with smart technology providers and utility companies can unlock new revenue streams and product offerings. The growing role of inverters in grid stabilization and energy intelligence strengthens their strategic importance in future-ready infrastructure.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Product:
The Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market is segmented by product into string PV inverters, central PV inverters, micro- PV inverters, and others. String PV inverters hold the dominant share due to their suitability for residential and small commercial systems. They offer easy installation, lower maintenance, and efficient performance across varying conditions. Central PV inverters are used in utility-scale projects, where high capacity and centralized control are required. Micro PV inverters are gaining traction in rooftop applications for their ability to optimize performance at the panel level and reduce the impact of shading or panel mismatch. The “others” category includes hybrid and custom-built inverters, catering to niche applications with specialized requirements.
- For instance, Enphase Energy shipped approximately 10.4 million microinverters globally in 2023, driven by growing rooftop PV demand in North America and Europe.
By Connectivity:
The market is divided into standalone and on-grid segments. On-grid systems dominate due to their integration with national power grids and widespread usage in urban and industrial environments. These systems benefit from incentives such as net metering and grid feed-in policies, encouraging higher deployment rates. The standalone segment serves off-grid applications where grid access is limited or absent. It supports rural electrification and remote infrastructure, particularly in emerging markets. The demand for standalone inverters is growing in regions with unstable grids or limited energy access.
- For instance, Schneider Electric’s Access to Energy initiative deployed over 42,000 standalone PV inverter systems in sub-Saharan Africa between 2019 and 2023, targeting communities without reliable grid access.
By End-Use:
The Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market serves commercial & industrial, utilities, and residential sectors. Utilities account for the largest share due to significant investment in large-scale solar farms and national renewable energy goals. Commercial and industrial users deploy inverters to reduce operational energy costs and improve sustainability profiles. The residential segment is expanding steadily due to rooftop solar installations, net-zero building policies, and growing awareness of energy independence. It supports smaller inverters with smart features for real-time energy management and remote monitoring. Each end-use category demands different performance characteristics, driving ongoing product diversification.
Segments:
Based on Product:
- String PV Inverter
- Central PV Inverter
- Micro PV Inverter
- Others
Based on Connectivity:
Based on End Use:
- Commercial & Industrial
- Utilities
- Residential
Based on the Geography:
- North America
- Europe
- UK
- France
- Germany
- Italy
- Spain
- Russia
- Belgium
- Netherlands
- Austria
- Sweden
- Poland
- Denmark
- Switzerland
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Thailand
- Indonesia
- Vietnam
- Malaysia
- Philippines
- Taiwan
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Peru
- Chile
- Colombia
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East
- UAE
- KSA
- Israel
- Turkey
- Iran
- Rest of Middle East
- Africa
- Egypt
- Nigeria
- Algeria
- Morocco
- Rest of Africa
Regional Analysis
North America Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market
North America Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market grew from USD 4,779.94 million in 2018 to USD 8,136.06 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 17,597.87 million by 2032, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.4%. North America is holding a 32% market share. The United States drives the majority of regional demand due to federal solar tax credits, strong net metering policies, and expanding residential solar adoption. Canada supports growth through its clean energy transition strategy, particularly in provinces with favorable solar potential. The region benefits from rising rooftop solar installations and strong adoption of smart inverter technologies. It sees consistent investments from utilities aiming to modernize grids and integrate renewable sources more effectively.
Europe Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market
Europe Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market grew from USD 2,884.73 million in 2018 to USD 4,720.20 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 9,297.09 million by 2032, reflecting a CAGR of 8.2%. Europe holds a 17% market share. Germany, Italy, and Spain remain key contributors due to their mature solar markets and updated renewable energy policies. The European Union’s Green Deal and carbon neutrality targets accelerate regional demand for distributed solar generation. The market benefits from regulatory support for grid-tied inverters and rapid smart grid deployments. It leverages innovations in energy storage integration and digital monitoring systems to align with future-ready energy networks.
Asia Pacific Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market
Asia Pacific Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market grew from USD 5,868.86 million in 2018 to USD 10,539.96 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 24,222.98 million by 2032, reflecting a CAGR of 10.3%. Asia Pacific commands the largest market share at 44%. China dominates the region with extensive utility-scale solar projects, while India and Japan contribute through policy-driven rooftop installations and smart grid investments. Emerging markets such as Vietnam, South Korea, and Australia expand rapidly through favorable feed-in tariffs and supportive solar frameworks. The market benefits from large-scale manufacturing, export capacity, and government-backed solar initiatives. It continues to lead innovation in hybrid inverter technology and microgrid integration.
Latin America Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market
Latin America Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market grew from USD 565.00 million in 2018 to USD 960.40 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 1,776.64 million by 2032, reflecting a CAGR of 7.3%. Latin America holds a 3.3% market share. Brazil leads the region with growing distributed generation and strong net metering programs. Mexico, Chile, and Argentina support development through clean energy auctions and policy frameworks. Falling solar panel costs and favorable climate conditions improve the economics of PV systems. It experiences growing interest from foreign investors and energy developers looking to scale solar capacity. Hybrid and off-grid inverter solutions are gaining ground in rural and isolated areas.
Middle East Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market
Middle East Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market grew from USD 419.61 million in 2018 to USD 663.29 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 1,210.71 million by 2032, reflecting a CAGR of 7.1%. The Middle East holds a 2% market share. The United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia spearhead regional development through mega-scale solar projects and long-term energy transition strategies. National visions and government-led tenders drive adoption of advanced inverter technologies. The region prioritizes energy diversification and seeks to reduce dependence on fossil fuels. It shows potential for off-grid and hybrid inverters to support remote operations and desalination plants. Investment in smart grids enhances compatibility with large solar arrays.
Africa Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market
Africa Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market grew from USD 174.00 million in 2018 to USD 341.47 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 545.64 million by 2032, reflecting a CAGR of 5.3%. Africa holds a 1.0% market share. South Africa leads the continent through renewable procurement programs and distributed solar generation. Nigeria, Kenya, and Egypt are advancing through rural electrification initiatives and international development support. Limited grid infrastructure promotes demand for standalone and hybrid inverters. It offers growth opportunities for cost-efficient and durable inverter models. The need to power remote communities and small businesses positions Africa as a key long-term opportunity for solar inverter deployment.
Key Player Analysis
- Omron Corporation
- Power Electronics S.L.
- Hitachi Hi-Rel Power Electronics Private Limited
- Delta Electronics, Inc
- Eaton
- Emerson Electric Co.
- Fimer Group
- Siemens Energy
- SMA Solar Technology AG
- SunPower Corporation
Competitive Analysis
The Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market is highly competitive, with key players including SMA Solar Technology AG, Delta Electronics, Inc., Fimer Group, Omron Corporation, Emerson Electric Co., Eaton, Siemens Energy, Power Electronics S.L., Hitachi Hi-Rel Power Electronics Private Limited, and SunPower Corporation. These companies maintain a strong global presence through advanced product portfolios, strategic partnerships, and regional expansion. Innovation remains central to market positioning, with a strong focus on smart inverters, hybrid systems, and integration with battery storage. Firms prioritize compatibility with emerging digital platforms to support real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and enhanced energy optimization. Strategic partnerships with solar developers, utilities, and EPC contractors strengthen distribution networks and enhance market penetration. Companies invest in research and development to meet evolving grid codes and deliver high-efficiency products with extended service life. Regional expansion into Asia, Latin America, and Africa continues to gain momentum, with tailored offerings for local infrastructure and climate conditions. Pricing pressure and demand for compact, user-friendly inverters further influence product strategies. The market rewards players that balance technical performance with scalability, after-sales support, and regulatory compliance.
Recent Developments
- In July 2023, LG Energy Solution Ltd., a South Korea-based battery manufacturer, introduced new hybrid inverters tailored for residential applications in the European market. Designed to accommodate both low-voltage and high-voltage configurations, these inverters come equipped with a built-in backup function, specifically crafted to seamlessly integrate with the company’s distinctive line of batteries.
- In July 2023, Enphase Energy reported the start of production of its IQ Microinverters and Flex systems in Colombia. This action aligns with the Enphase corporate cleaner energy policy system strategies regarding industry advanced technology, strategic local manufacturing, and further technological innovation. The move also extends the company’s leadership on the microinverter market while increasing business and benefits the company overall.
- In January 2023, SOFARSOLAR Co., Ltd., a global supplier of photovoltaic (PV) and energy storage solutions, announced the launch of a new inverter SOFAR 100-125KTL-G4. This new inverter features the integration of industry-leading ultra-high current, easy installation, and intelligent protection.
Market Concentration & Characteristics
The Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter Market exhibits moderate to high market concentration, with a handful of established players dominating global revenue through advanced technology, strong distribution networks, and large-scale manufacturing capabilities. It is characterized by rapid innovation cycles, driven by demand for higher efficiency, grid compatibility, and integration with digital and storage systems. The market favors companies that offer product differentiation, regulatory compliance, and strong technical support. Entry barriers remain moderate due to capital-intensive manufacturing, evolving grid standards, and certification requirements across regions. Price sensitivity in emerging markets pushes companies to focus on cost-effective, durable, and scalable solutions. The market shows a growing preference for intelligent inverters that support real-time monitoring and two-way energy flow. It remains dynamic, with characteristics such as increasing demand for hybrid systems, short product lifecycles, and rapid adaptation to grid modernization trends. Regional diversification and policy-driven solar adoption continue to shape competition and strategic positioning.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Product, Connectivity, End-Use and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The demand for photovoltaic inverters will continue to rise due to accelerating global investments in solar energy infrastructure.
- Governments across developed and developing countries will increasingly implement favorable policies and subsidies to promote solar adoption.
- Technological advancements will enhance inverter efficiency, grid compatibility, and remote monitoring capabilities.
- Residential solar installations will grow steadily, driving demand for compact and smart string inverters.
- Large-scale utility projects will boost the deployment of central inverters with higher power ratings.
- Hybrid inverters integrated with energy storage systems will gain significant traction as energy resilience becomes a priority.
- The shift toward decentralized energy systems will create opportunities for microinverters and module-level power electronics.
- Asia-Pacific will remain the leading market, with rapid solar installations in China, India, and Southeast Asia.
- Manufacturers will increasingly focus on digitalization, including AI-driven diagnostics and predictive maintenance.
- Stringent grid regulations and standards will shape product innovations and influence design improvements globally.





