Market Overview:
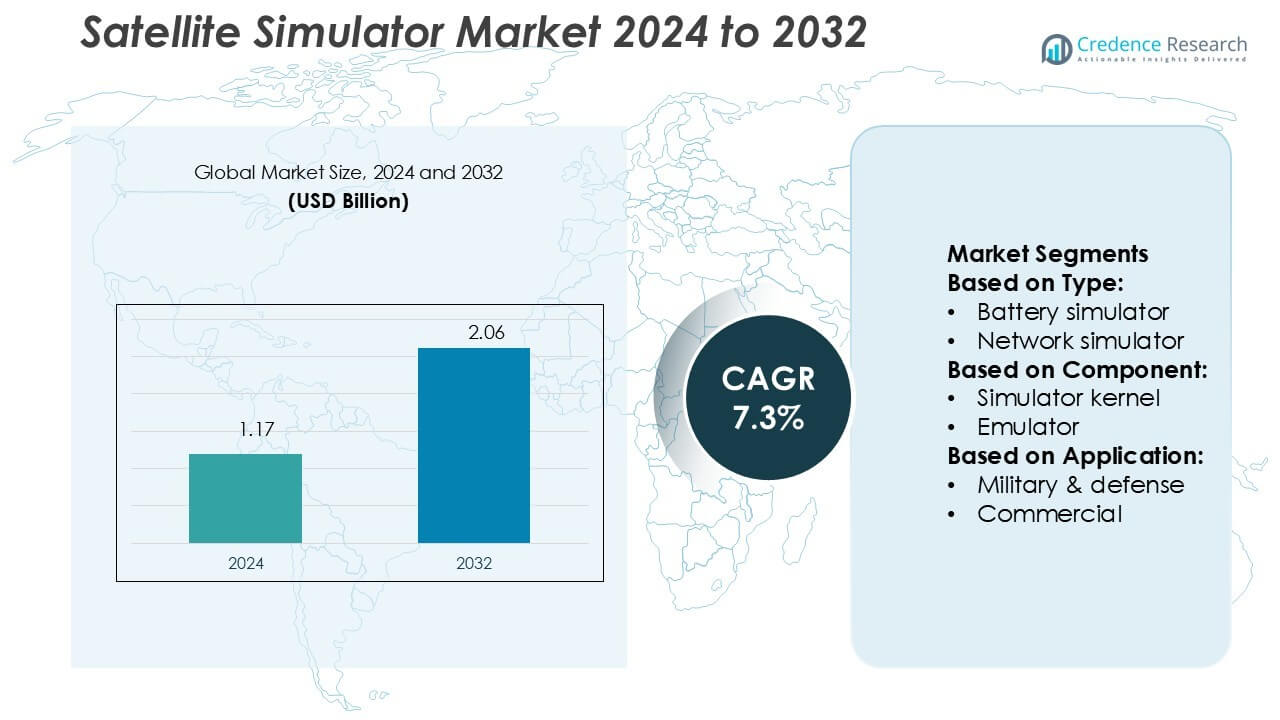
Satellite Simulator Market size was valued USD 1.17 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 2.06 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 7.3% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Satellite Simulator Market Size 2024 |
USD 1.17 billion |
| Satellite Simulator Market, CAGR |
7.3% |
| Satellite Simulator Market Size 2032 |
USD 2.06 billion |
The satellite simulator market features strong competition among key players such as Indra, Hollis Electronics, GMV, Mitre, NGC Aerospace, Keysight Technologies, Kratos, IFEN GmbH, Anritsu, and Atlantic Microwave. These companies focus on delivering advanced simulation platforms that support communication testing, spacecraft dynamics, and mission readiness for both defense and commercial sectors. Product innovation, integration of digital twin technology, and cloud-based solutions are central to their strategies. North America leads the global market with a 38% share in 2024, driven by significant investments in defense modernization, space exploration programs, and the rapid expansion of commercial satellite networks.
Market Insights
- The Satellite Simulator Market size was valued at USD 1.17 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 2.06 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 7.3%.
- Growing demand for satellite constellations, defense modernization, and secure communication systems are key drivers fueling the market’s expansion.
- The market is witnessing trends such as the integration of digital twin technology, AI-based modeling, and cloud-enabled simulators, improving accuracy and reducing operational costs.
- Competitive dynamics remain strong with players like Indra, Hollis Electronics, GMV, Mitre, NGC Aerospace, Keysight Technologies, Kratos, IFEN GmbH, Anritsu, and Atlantic Microwave focusing on innovation and partnerships; however, high development and maintenance costs act as restraints.
- North America dominates with a 38% share in 2024, followed by Europe at 27% and Asia-Pacific at 22%, while the military and defense application segment holds the largest share at 41%, reflecting its central role in driving simulator demand.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Type
The satellite simulator market by type is led by network simulators, holding a 32% share in 2024. Their dominance stems from rising demand for advanced communication testing, ensuring seamless connectivity across satellite constellations and ground stations. Network simulators allow real-time evaluation of link performance, latency, and bandwidth, which is critical for low-earth orbit satellite operations. Growing adoption of LEO networks for broadband services and defense communications continues to drive this segment’s expansion, making it the preferred choice for manufacturers and service providers seeking reliable performance validation.
- For instance, Hollis offers its HSDS-140/HSDS-70 satellite simulators, which support a wide range of configurable delays for simulating satellite orbits and links. The simulators provide an Eb/No accuracy of ±0.1 dB and use dual internal digital power meters along with built-in noise generators to ensure accurate and repeatable testing.
By Component
Among components, the simulator kernel dominates with a 35% share in 2024. This segment leads as it forms the foundation of all simulation processes, enabling accurate replication of orbital dynamics, signal behavior, and environmental effects. Demand is rising due to increased complexity of satellite missions, requiring scalable kernels that support modular integration with spacecraft, ground, and environment modules. Defense organizations and commercial operators increasingly rely on simulator kernels to validate mission-critical scenarios, reduce development costs, and improve system readiness, reinforcing its leadership in the component landscape.
- For instance, ESA BIOMASS mission, which has a planned 5-year operational life, underwent an extensive simulation campaign as part of its development and launch preparation ensured the successful integration and operation of its advanced technology, such as the 7.5-meter radar antenna.
By Application
The military and defense segment commands the largest share at 41% in 2024. Its leadership is fueled by the growing requirement for secure communications, radar testing, and space-based surveillance systems. Defense agencies invest heavily in simulation platforms to enhance mission training, assess resilience under cyber and electronic warfare conditions, and validate satellite interoperability. Rising geopolitical tensions and government-funded space programs further accelerate adoption. The commercial segment is expanding as private operators adopt simulators for broadband services, but defense remains the largest revenue driver due to strategic and security priorities.
Market Overview
Rising Demand for Satellite Constellations
The expansion of low-earth orbit (LEO) constellations is a key growth driver for the satellite simulator market. Companies and governments are deploying large fleets of satellites for global connectivity, navigation, and earth observation. These projects require advanced simulators to validate communication protocols, orbital dynamics, and inter-satellite links. The surge in broadband satellite networks such as Starlink and OneWeb accelerates simulator adoption. By reducing risks and ensuring mission readiness, satellite simulators play a vital role in the successful deployment of these expanding constellations.
- For instance, NGC has delivered GNC software for several ESA spacecraft, including PROBA-1 (which remained active over 20 years beyond its 2-year design life) and PROBA-2, demonstrating long-term runtime reliability.
Increased Defense and Security Investments
Military and defense applications represent a major force driving market growth. Governments are allocating larger budgets to space-based surveillance, secure communications, and radar testing. Satellite simulators provide a cost-effective way to conduct realistic training, evaluate resilience against cyber and electronic warfare, and test mission-critical satellite interoperability. The growing emphasis on national security and space dominance encourages higher demand for advanced simulation platforms. This rising focus positions defense agencies as dominant end-users, ensuring consistent investments in simulator technologies across global markets.
- For instance, Keysight’s S8825A Satellite and Aerospace Channel Emulation Toolset supports testing of Non-Terrestrial Network (NTN) links. When integrated with specific high-performance hardware, the toolset can achieve channel models of up to 54 GHz and modulation bandwidths of 2.5 GHz per channel.
Advancement in Simulation Technologies
Technological progress is significantly boosting the adoption of satellite simulators. The integration of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and high-fidelity modeling enhances simulation accuracy and scalability. These innovations allow simulators to replicate complex orbital conditions, multi-satellite interactions, and dynamic environments with greater precision. Additionally, cloud-based simulation platforms reduce infrastructure costs while enabling remote accessibility for global teams. These technological improvements support diverse applications, from commercial broadband services to scientific missions, making simulators a vital component in modern satellite program lifecycles.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Shift Toward Digital Twin Integration
The adoption of digital twin technology is emerging as a significant trend in the satellite simulator market. Digital twins replicate satellites in virtual environments, enabling continuous monitoring, predictive maintenance, and performance optimization. This integration allows operators to identify potential system failures before deployment, reducing risks and costs. The growing use of digital twins in space missions creates opportunities for simulator providers to design platforms that seamlessly align with digital engineering frameworks, making satellite operations more efficient and sustainable.
- For instance, Keysight’s MP4300A mainframe can accommodate up to six modular solar array simulator (SAS) modules in a compact 2U rack space. Using 1 kW modules, a 6 kW configuration is possible, while using higher-power 1.4 kW modules allows for an 8.4 kW configuration. Keysight also offers a 10 kW mainframe version in the MP4300 series.
Commercial Space Expansion
The rapid growth of private space ventures opens substantial opportunities for simulator adoption. Start-ups and commercial operators entering the satellite sector require affordable, flexible simulation platforms to support varied applications, including broadband connectivity, IoT, and earth imaging. These companies often lack the extensive resources of government agencies, driving demand for scalable cloud-based simulators that minimize upfront investments. As commercial space activity accelerates, simulator vendors benefit from serving a broader customer base, diversifying revenue sources, and fostering innovation tailored to private sector requirements.
- For instance, their NRP67SN-V power sensor measures from 50 MHz to 67 GHz and spans dynamic range up to 93 dB, enabling both output and reflected signal monitoring even inside thermal vacuum chambers.
Key Challenges
High Development and Maintenance Costs
The satellite simulator market faces a challenge of high development and lifecycle costs. Building advanced simulators requires complex hardware, precise software modeling, and continuous updates to reflect evolving mission requirements. Smaller organizations, especially in emerging economies, find it difficult to afford such investments. Maintenance also adds to operational expenses, as simulators must remain compatible with new technologies and mission designs. These financial barriers limit wider adoption, particularly in the commercial sector, where budget constraints often delay or restrict simulator procurement.
Complexity of Multi-Satellite Simulations
Another challenge lies in the increasing complexity of simulating large satellite constellations and multi-orbit systems. Accurately modeling interactions, communication delays, and environmental conditions across hundreds of satellites demands significant computational power and expertise. Inadequate modeling can lead to errors in mission planning and performance validation. As satellite networks grow in scale, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in simulations becomes harder to achieve. This complexity creates operational risks and pushes organizations to continually seek more advanced solutions, straining resources and development timelines.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America leads the satellite simulator market with a 38% share in 2024. The region benefits from strong investments in space exploration, defense modernization, and commercial satellite networks. NASA, SpaceX, and defense agencies drive demand for advanced simulators to test communication systems, orbital dynamics, and mission readiness. The U.S. government’s focus on space dominance and cybersecurity strengthens adoption, while Canada contributes through earth observation and satellite-based research. With robust funding, technological leadership, and active private players, North America maintains its position as the largest regional market, fostering steady innovation and long-term growth.
Europe
Europe holds a 27% share in the global satellite simulator market, supported by strong institutional and industrial participation. The European Space Agency (ESA) and leading aerospace companies drive simulator adoption to support navigation, communication, and environmental monitoring programs. Countries like France, Germany, and the UK spearhead investments in simulation technologies to enhance competitiveness and mission success. The region also emphasizes sustainability and space situational awareness, creating demand for high-fidelity modeling tools. Europe’s growing focus on collaborative missions and digital engineering ensures continued expansion of simulator adoption across defense and commercial applications.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific accounts for 22% of the satellite simulator market in 2024, fueled by rapid space expansion in China, India, and Japan. Governments are investing heavily in national satellite programs for communication, navigation, and defense. China’s ambitious satellite constellations, India’s ISRO missions, and Japan’s commercial partnerships drive demand for simulation platforms. Growing commercial space activity and regional security challenges further support adoption. Affordable simulation solutions tailored for emerging operators are also gaining traction. With its increasing satellite launch frequency and rising private investments, Asia-Pacific is positioned as the fastest-growing regional market.
Latin America
Latin America captures a 6% share of the global satellite simulator market, with Brazil and Mexico leading adoption. Brazil’s investments in earth observation, environmental monitoring, and defense satellites drive regional demand. Mexico supports communication and navigation projects that rely on simulation platforms for testing and validation. Despite budgetary constraints, the region benefits from collaborations with international agencies and private players. Growing interest in digital infrastructure and climate monitoring further supports simulator use. Latin America’s market remains smaller compared to others but demonstrates consistent growth opportunities through government-backed programs and increasing commercial sector participation.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region holds a 7% share in the satellite simulator market. Countries such as the UAE and Saudi Arabia are expanding space research and defense programs, creating niche opportunities for simulator adoption. National space agencies focus on building capabilities for communication, navigation, and surveillance satellites. Africa is gradually adopting simulators for telecommunication and earth observation needs, though limited budgets constrain large-scale use. Strategic partnerships with global providers and investments in local training centers are helping the region strengthen its simulation infrastructure, with growth prospects centered on defense and commercial satellite initiatives.
Market Segmentations:
By Type:
- Battery simulator
- Network simulator
By Component:
- Simulator kernel
- Emulator
By Application:
- Military & defense
- Commercial
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- UK
- France
- Germany
- Italy
- Spain
- Russia
- Belgium
- Netherlands
- Austria
- Sweden
- Poland
- Denmark
- Switzerland
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Thailand
- Indonesia
- Vietnam
- Malaysia
- Philippines
- Taiwan
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Peru
- Chile
- Colombia
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East
- UAE
- KSA
- Israel
- Turkey
- Iran
- Rest of Middle East
- Africa
- Egypt
- Nigeria
- Algeria
- Morocco
- Rest of Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the satellite simulator market features prominent players including Indra, Hollis Electronics, GMV, Mitre, NGC Aerospace, Keysight Technologies, Kratos, IFEN GmbH, Anritsu, and Atlantic Microwave. The satellite simulator market is highly competitive, driven by continuous innovation and rising demand across defense and commercial sectors. Companies are focusing on developing advanced platforms that integrate artificial intelligence, digital twin technology, and cloud-based solutions to enhance accuracy, scalability, and cost efficiency. The market is shaped by the need to support complex missions, including satellite constellations, secure communications, and earth observation programs. Competition also revolves around providing customizable modules for spacecraft, ground, and environmental simulations, ensuring flexibility for diverse applications. Strategic partnerships, investments in R&D, and expansion into emerging markets further define the competitive landscape.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
Recent Developments
- In May 2025, Safaricom announced plans to collaborate with satellite internet firms to boost broadband in underserved Kenyan regions. This move responds to Starlink’s rapid growth, which doubled its market share in three months, prompting Safaricom to urge regulators to require satellite providers to partner with local operators.
- In April 2025, Amazon’s Project Kuiper successfully launched its KA-01 mission, deploying 27 LEO satellites as part of a 3,200-satellite constellation plan. This marks the beginning of full-scale operations, with service expected to begin later this year, enhancing global broadband coverage and competition.
- In November 2024, BSNL, in collaboration with Viasat, launched India’s first satellite-to-device service using L-band geostationary satellites. This two-way communication system enables connectivity in remote areas without cellular or Wi-Fi. It supports emergency calls, messaging, and digital payments, advancing India’s non-terrestrial network capabilities.
- In July 2024, Orbex broadcasted during the Orlando Space Commerce Conference that they would employ Altair’s HyperWorks software to automatically enhance their robotic systems design, simulation, and composites manufacturing
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Type, Component, Application and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The satellite simulator market will expand with growing satellite constellation deployments.
- Defense agencies will continue to drive demand for mission-critical simulation platforms.
- Commercial operators will adopt cost-effective cloud-based simulation solutions.
- Integration of AI and machine learning will enhance simulation accuracy and efficiency.
- Digital twin technology will become a standard feature in advanced simulators.
- Rising private space investments will broaden the customer base for simulation providers.
- Training and education programs will increasingly rely on high-fidelity satellite simulators.
- Emerging economies will create opportunities through new space research initiatives.
- Cybersecurity and resilience testing will gain greater importance in simulation frameworks.
- Strategic collaborations will shape innovation and strengthen market competitiveness.




