Market Overview
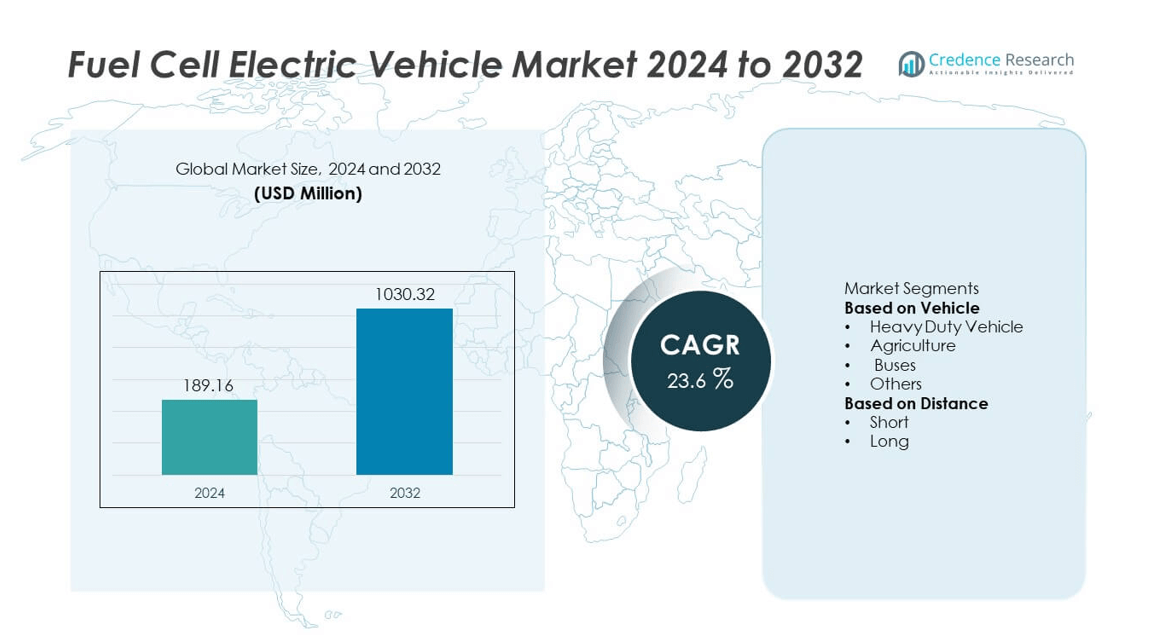
The Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV) market was valued at USD 189.16 million in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 1,030.32 million by 2032, registering a CAGR of 23.6% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle Market Size 2024 |
USD 189.16 million |
| Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle Market, CAGR |
23.6% |
| Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle Market Size 2032 |
USD 1,030.32 million |
The Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle market includes major companies such as Hydrogenics, Honda Motor Co., Ltd., US Hybrid, Audi AG, Anhui Heli, Ballard Power Systems, Toyota Motor Corporation, Dana Limited, Hyundai Motor Co., Ltd., and Hyster-Yale Materials Handling. These players focus on fuel cell stack efficiency, extended driving range, and partnerships for hydrogen supply and refueling networks. Asia Pacific leads the global market with a 45% market share, supported by strong hydrogen mobility programs, large-scale commercial fleet deployment, and expanding refueling infrastructure in China, Japan, and South Korea. North America and Europe follow, driven by clean transportation mandates and investment in long-haul hydrogen freight solutions.
Market Insights
- The Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle market reached USD 189.16 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 1,030.32 million by 2032, registering a CAGR of 23.6%.
- Market growth is driven by rising demand for zero-emission mobility, strong government hydrogen mobility programs, and expansion of fuel cell truck and bus fleets across long-distance transport. Heavy-duty vehicles lead the market with a 42% share, supported by logistics and commercial fleet adoption.
- Key trends include growth in hydrogen-powered commercial fleets, increased investments in green hydrogen production, and fuel cell stack advancements that lower operating costs and extend vehicle range.
- Competitive dynamics feature companies including Hydrogenics, Honda, US Hybrid, Audi, Anhui Heli, Ballard Power Systems, Toyota, Dana, Hyundai, and Hyster-Yale, focusing on partnerships for refueling infrastructure and cost-efficient fuel cell systems.
- Asia Pacific leads with a 45% regional share, followed by North America at 37% and Europe at 32%, supported by refueling corridor development and clean mobility incentives.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Vehicle Segment
The heavy-duty vehicle segment holds the dominant position with a market share of 42% in the Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle market. Strong demand for zero-emission freight transport, longer driving range, and short refueling time support adoption in logistics and long-haul operations. Fuel cell trucks and heavy commercial fleets reduce dependency on diesel and help fleet owners meet emission compliance targets. The bus segment accounts for 31% share, driven by municipal clean mobility programs and hydrogen transit investments. Agriculture and other vehicle categories represent the remaining 27% share, supported by interest in off-highway and specialized hydrogen-powered machinery.
- For instance, Toyota SORA fuel cell buses operate in Tokyo, with 100 units placed ahead of global sporting events to support public transportation.
By Distance Segment
The long-distance segment leads the market with a market share of 58%, driven by the need for extended driving range and fewer refueling breaks for commercial fleets. Hydrogen fuel cells enable efficient long-haul travel, making them suitable for interstate trucking, cargo movement, and intercity passenger transport. Increasing deployment of long-route fuel cell buses and logistics vehicles further strengthens segment growth. The short-distance segment accounts for the remaining 42% share, supported by urban delivery vehicles, regional passenger transport, and small fleet applications. Short refueling cycles, quiet operation, and favorable total cost of ownership boost adoption in city-based hydrogen mobility programs.
- For instance, Hyzon Motors delivered its first hydrogen-powered heavy-duty milk truck in the Netherlands, which was expected to have a range of up to 520 km. The company also joined a program with a goal to deploy 1,000 hydrogen trucks in Europe by 2025, and had received an order for up to 20 hydrogen trucks from Dutch transport companies.
KEY GROWTH DRIVERS
Growing Demand for Zero-Emission Transportation
Governments and fleet operators focus on clean mobility to cut greenhouse gas emissions. Fuel cell electric vehicles support zero tailpipe emissions and enable longer driving ranges with fast refueling, making them suitable for heavy-duty and long-haul applications. Public and private fleet decarbonization programs strengthen adoption across logistics, public transit, and corporate transportation. Companies also align with sustainability commitments, which increases interest in hydrogen-based mobility. This momentum encourages innovation in vehicle platforms and hydrogen storage systems, supporting wider FCEV deployment.
- For instance, Ballard Power Systems delivered 120 kW fuel cell modules for heavy-duty trucks, enabling range capability above 600 km on a single refueling.
Expansion of Hydrogen Refueling Infrastructure
Hydrogen refueling stations continue to expand across major transport corridors, supporting commercial and passenger mobility. Energy suppliers, automakers, and infrastructure developers collaborate to deploy stations with improved dispensing capacity and higher reliability. New hydrogen hubs and regional fueling networks help reduce range anxiety for fleet managers. Short refueling cycles and operational efficiency support adoption in freight and transit operations. As infrastructure becomes more accessible and strategically placed, fuel cell vehicles gain stronger market appeal.
- For instance, Air Liquide operates more than 120 hydrogen stations worldwide, including sites capable of dispensing 700 bar compressed hydrogen for trucks and buses.
Advancements in Fuel Cell System Efficiency
Fuel cell propulsion systems benefit from improved stack durability, higher power density, and better cold-start performance. Material improvements reduce reliance on costly catalysts, lowering long-term production expenses. Automakers integrate compact and lightweight systems that enhance energy conversion and vehicle performance. Fleet operators appreciate reduced maintenance requirements and longer system life, making hydrogen vehicles more competitive with diesel and battery electric alternatives. Continued R&D and scaling of manufacturing processes strengthen cost efficiency and industry confidence.
KEY TRENDS & OPPORTUNITIES
Hydrogen-Powered Fleets and Commercial Adoption
Fleet operators adopt hydrogen-powered trucks and buses for reliable long-range operation and minimal downtime. Municipal authorities introduce hydrogen buses within clean public transit plans, supporting large-scale fleet commitments. Logistics companies explore hydrogen fuel cell platforms to meet sustainability targets and reduce diesel dependency. Fleet leasing and hydrogen-as-a-service models help reduce upfront barriers and support market adoption. This creates opportunities for suppliers of stacks, storage tanks, powertrains, and fleet charging platforms.
- For instance, Amazon tested fuel cell yard tractors from Plug Power at distribution centers handling over 300 trailer moves per day. Fleet leasing and hydrogen-as-a-service models lower upfront cost barriers.
Acceleration of Green Hydrogen Production
Growing investment in solar and wind-based hydrogen production strengthens the long-term cost competitiveness of FCEVs. Green hydrogen helps reduce lifecycle emissions across transport and industrial sectors. Energy developers plan large-scale electrolyzer installations and hydrogen supply hubs to support heavy mobility applications. National hydrogen roadmaps prioritize transportation, creating pilot fleet and infrastructure projects. As greener hydrogen becomes widely available, adoption of FCEVs increases across highway freight, agriculture, and public mobility segments.
- For instance, Iberdrola has commissioned the green hydrogen plant in Puertollano, Spain, which is operational and uses a 100 MW photovoltaic generation capacity and produces 3,000 metric tons per year.
KEY CHALLENGES
Limited Refueling Coverage and Infrastructure Costs
Hydrogen station networks remain uneven across regions, creating availability gaps for long-distance travel and fleet planning. Refueling infrastructure requires high capital expenditure, along with advanced safety and regulatory approvals. Stakeholders face challenges standardizing fueling protocols and optimizing station economics. Limited fueling options discourage private and commercial buyers, delaying deployment of FCEV fleets. Overcoming this challenge requires coordinated investment, policy support, and scalable infrastructure models.
High Production and Fuel Supply Costs
Fuel cell systems rely on advanced membranes and catalysts, leading to higher vehicle manufacturing costs. Limited production volumes and specialized components make cost reduction gradual. Hydrogen production, storage, and transport expenses also affect the total cost of ownership, especially in regions without local supply. These cost barriers slow adoption among price-sensitive fleet segments and emerging markets. Broader production scaling, material innovation, and expanded green hydrogen supply are critical to resolving these constraints.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds a market share of 37% driven by strong investments in hydrogen mobility and clean transportation policies. The United States supports deployment of hydrogen trucks and transit buses through state-level incentives and funding for corridor-based refueling networks. Canada promotes hydrogen adoption in heavy transport and port operations, strengthening commercial fleet interest. Major automakers and energy companies collaborate to expand the supply chain for fuel cell systems and green hydrogen production. Growing interest in zero-emission logistics and long-haul freight continues to enhance regional market growth and infrastructure readiness.
Europe
Europe accounts for a market share of 32% supported by strict emissions regulations, carbon-neutrality targets, and hydrogen-transition strategies. Germany, France, the United Kingdom, and the Netherlands invest in hydrogen transport corridors, scalable electrolyzer capacity, and fuel cell-powered public transit. The region encourages deployment of hydrogen trucks and intercity buses to reduce diesel reliance in commercial fleets. Public-private partnerships promote research in stack efficiency, lightweight materials, and storage technologies. EU-wide hydrogen funding platforms and cross-border mobility programs further strengthen adoption among logistics, municipal transportation, and industrial fleet operators.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific leads with a market share of 45% supported by strong government-backed hydrogen roadmaps and large-scale commercial FCEV deployments. China expands hydrogen refueling networks and local manufacturing of fuel cell trucks and buses to support clean freight and urban transit. Japan and South Korea advance national hydrogen strategies, promoting passenger FCEVs and heavy-duty mobility for long-distance transport. Regional supply chains strengthen through partnerships in fuel cell stack manufacturing, green hydrogen production, and storage solutions. Rapid industrialization and urban emission reduction targets reinforce market leadership across the region.
Latin America
Latin America holds a market share of 9% driven by early-stage hydrogen mobility programs and pilot deployment of fuel cell buses. Chile, Brazil, and Argentina explore hydrogen production from renewable resources to support sustainable transportation. Public transit authorities introduce fuel cell buses in selected urban routes to reduce emissions and diesel consumption. Partnerships with global automakers and energy developers support feasibility studies and small-scale commercial fleet trials. Although infrastructure and cost barriers remain, growing interest in low-carbon transport and abundant renewable power potential create future expansion opportunities.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region represents a market share of 6% supported by increasing investments in green hydrogen production and export-oriented hydrogen projects. The United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia explore hydrogen-powered mobility for logistics and industrial transport linked to smart city initiatives. South Africa leverages platinum resources for fuel cell stack development, encouraging domestic value creation in hydrogen technologies. Limited refueling infrastructure slows broad adoption, yet pilot FCEV fleets and renewable hydrogen hubs strengthen long-term prospects. Government-backed diversification strategies and clean energy goals support gradual market advancement across the region.
Market Segmentations:
By Vehicle
- Heavy Duty Vehicle
- Agriculture
- Buses
- Others
By Distance
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
Competitive landscape or analysis in the Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle market features key players including Hydrogenics, Honda Motor Co., Ltd., US Hybrid, Audi AG, Anhui Heli, Ballard Power Systems, Toyota Motor Corporation, Dana Limited, Hyundai Motor Co., Ltd., and Hyster-Yale Materials Handling. Market competition intensifies as automakers and technology providers invest in fuel cell stack durability, hydrogen storage systems, and scalable mobility platforms. Companies prioritize partnerships with hydrogen producers and infrastructure developers to secure fuel supply and accelerate refueling network expansion. Heavy-duty and commercial fleet applications remain a strategic focus, prompting collaborations with logistics companies and public transit authorities. Technology advancement efforts emphasize reduced catalyst costs, longer operating life, and higher power density to strengthen total cost of ownership benefits. Several players also build localized production capabilities to support regional hydrogen initiatives and shorten supply chains. As hydrogen adoption expands across freight, public mobility, and industrial fleets, competition shifts toward long-term cost reduction and integrated mobility solutions.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Hydrogenics
- Honda Motor Co., Ltd.
- US Hybrid
- Audi AG
- Anhui Heli
- Ballard Power Systems
- Toyota Motor Corporation
- Dana Limited
- Hyundai Motor Co., Ltd.
- Hyster-Yale Materials Handling
Recent Developments
- In June 2025, Honda changed plans for its new production plant in Japan dedicated to the next-generation fuel-cell module.
- In April 2025, Hyundai Motor Co., Ltd. introduced the all-new NEXO FCEV at the Seoul Mobility Show, featuring enhanced fuel-cell technology and bold new design.
- In February 2025, Toyota Motor Corporation announced its new 3rd-generation fuel-cell system designed for commercial vehicles, offering diesel-level durability and improved efficiency.
- In February 2025, Honda Motor Co., Ltd. unveiled details of its Next Generation Fuel Cell Module featuring 150 kW output, half the cost of the current model and triple volumetric power density
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Vehicle, Distance and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Fuel cell vehicles will gain wider adoption in long-haul and heavy-duty transport fleets.
- Green hydrogen production will expand and support cost-effective fuel supply for mobility.
- Hydrogen refueling corridors will grow across major highways and logistics routes.
- Fuel cell system efficiency will improve with longer operating life and lower maintenance needs.
- Partnerships between automakers and energy companies will accelerate ecosystem development.
- More countries will include hydrogen mobility targets in national clean transport policies.
- Bus and commercial fleet deployments will rise in public transit and freight operations.
- Material innovations will reduce fuel cell stack cost and improve power density.
- Battery–fuel cell hybrid architectures will increase range and performance in larger vehicles.
- Regional value chains for fuel cell components and hydrogen storage will strengthen market competitiveness.




