Market Overview
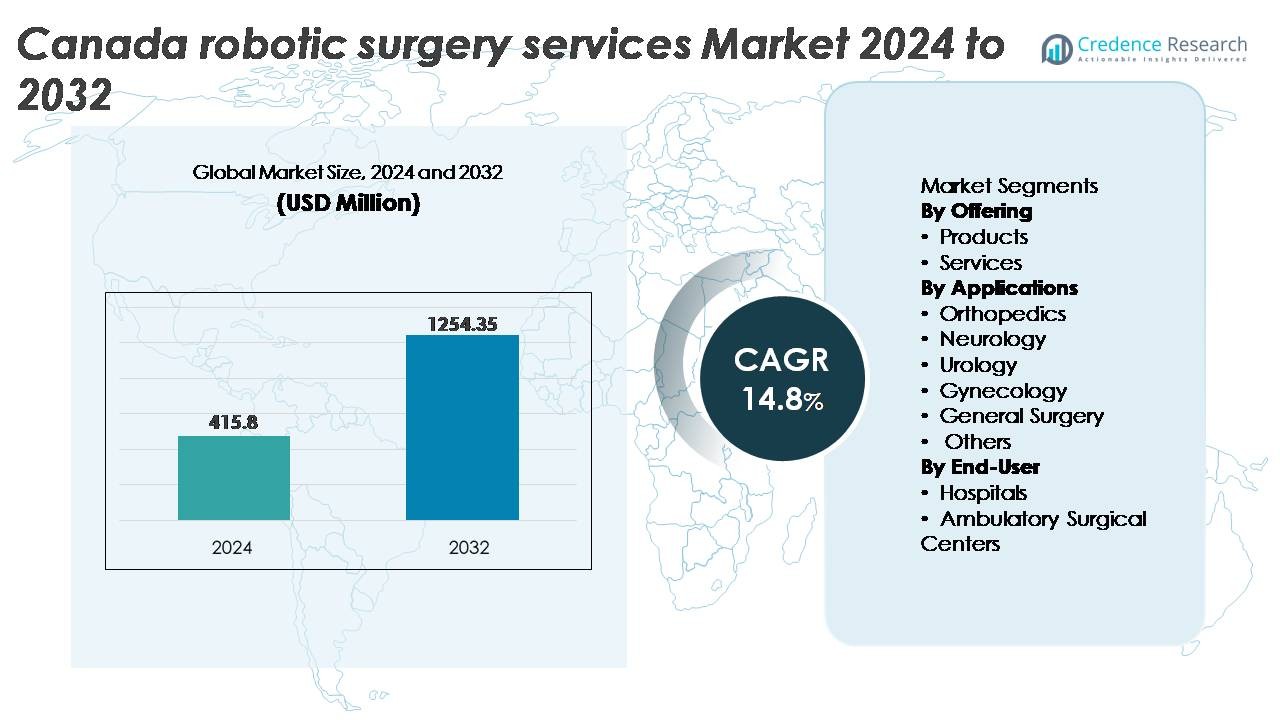
The Canada robotic surgery services market was valued at USD 415.8 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 1,254.35 million by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 14.8% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Canada robotic surgery services market Size 2024 |
USD 415.8 Million |
| Canada robotic surgery services market, CAGR |
14.8% |
| Canada robotic surgery services market Size 2032 |
USD 1,254.35 Million |
The Canada robotic surgery services market is shaped by a strong mix of global technology leaders and domestic innovators, including Medtronic, Intuitive Surgical, THINK Surgical, Inc., Zimmer Biomet, Renishaw plc, Titan Medical Inc (CAN), TransEnterix, Inc (CAN), and HSS Global Technologies Inc (CAN). These players compete through advancements in multi-specialty robotic platforms, AI-enabled surgical navigation, and flexible service-based deployment models that support broader adoption across hospitals and ambulatory centers. Regionally, Ontario represents the largest share at approximately 38%, driven by high surgical volumes, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and early adoption of robotic-assisted procedures, positioning it as the primary growth hub within the national market.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The Canada robotic surgery services market was valued at USD 415.8 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 1,254.35 million by 2032, registering a CAGR of 8% during the forecast period.
- Continued demand for minimally invasive procedures and faster patient recovery drives strong adoption of robotic platforms across urology, gynecology, and general surgery services in hospitals and surgical centers.
- Key trends include AI-enabled surgical guidance, compact robotic systems for outpatient surgeries, and growing service-based models that reduce upfront acquisition costs.
- High capital investment, maintenance expenses, and a shortage of trained robotic surgeons continue to restrain expansion, particularly in smaller healthcare networks.
- Regionally, Ontario leads with approximately 38% market share, followed by Quebec with 22% and British Columbia at 16%; by offering, services account for the dominant share driven by lifecycle maintenance, software upgrades, and procedure-based support contracts.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Offering
The services segment holds the dominant share in the Canada robotic surgery services market, supported by growing implementation of maintenance contracts, training programs, procedure-based service billing, and system lifecycle management. Healthcare providers increasingly prefer service-based models to reduce capital expenditure and maximize system usage efficiency. Service partnerships enable hospitals to optimize uptime, address component failures quickly, and access continuous software updates. Meanwhile, the demand for robotic surgery products continues to grow, driven by technological advancements in multi-arm systems, 3D visualization, haptic controls, and enhanced instrument compatibility across surgical departments.
- For instance, Intuitive Surgical reported more than 2.2 millionrobotic-assisted procedures performed globally in 2023, supported by ongoing service, instrumentation supply, and software upgrades tied to the da Vinci platform. The cumulative total of procedures performed with da Vinci systems since their introduction now exceeds 14 million”.
By Applications
Urology represents the leading application segment, accounting for the largest share due to the high adoption of robotic systems for prostatectomy, partial nephrectomy, and bladder oncology procedures. The precision required in organ-preserving surgeries, reduced blood loss, and lower complication rates reinforce the dominance of robotics in urologic care. Gynecology and general surgery are emerging as high-growth segments as minimally invasive hysterectomies, hernia repairs, and bariatric interventions increasingly transition to robotic platforms. Orthopedics and neurology display steady adoption, supported by robotic navigation systems for joint replacements and cranial procedures requiring micro-level accuracy.
- For instance, Zimmer Biomet’s ROSA Knee system is FDA-cleared for total knee arthroplasty and has demonstrated improved mechanical alignment accuracy in peer-reviewed studies, with several trials reporting reductions in alignment deviation compared to manual techniques. These findings support wider adoption of robotic navigation in orthopedic procedures.
By End-User
Hospitals dominate the end-user landscape, holding the majority share as tertiary and multi-specialty hospitals remain primary adopters of advanced surgical technologies. The presence of skilled surgeons, larger patient volumes, and reimbursement support drive hospital-based robotic deployments. These institutions benefit from improved clinical outcomes, reduced inpatient days, and enhanced surgical portfolios that boost competitive positioning. Ambulatory surgical centers are gaining traction with the rise of outpatient robotic procedures, particularly in general surgery and orthopedics. Their growth is propelled by shorter recovery times, bundled payments, and the advancement of compact robotic platforms suitable for day-care environments.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Demand for Minimally Invasive Surgeries
The growing preference for minimally invasive procedures is a major force driving robotic surgery adoption in Canada. Patients increasingly seek surgical pathways that reduce postoperative pain, shorten recovery timelines, and minimize hospital stays. Robotic platforms provide enhanced dexterity, tremor filtration, and 3D visualization, enabling surgeons to perform complex procedures with precision that surpasses conventional laparoscopy. Healthcare providers benefit from greater procedure volume capacity and lower readmission rates, improving overall care efficiency. Improved patient satisfaction, reduced scarring, and faster rehabilitation contribute to strong preference for robotic-assisted surgical outcomes. Combined with an aging population and increasing chronic disease burden, the clinical advantages of MIS continue to accelerate adoption across specialty departments, reinforcing demand within hospitals and surgical centers.
· For instance, Intuitive Surgical’s da Vinci system provides surgeons with high-definition 3D vision offering up to 10× optical magnification. Its EndoWrist instruments deliver seven degrees of motion, which supports precise articulation and controlled movement in tight anatomical spaces.
Expansion of Surgical Applications Across Specialties
Robotic surgery services are scaling rapidly as new clinical applications emerge across urology, gynecology, orthopedics, thoracic surgery, and gastrointestinal procedures. System manufacturers are developing domain-specific instruments and navigation tools to support complex interventions such as nerve-sparing prostatectomies, bariatric operations, and robotic-assisted joint replacements. Greater procedural versatility improves return on investment for healthcare institutions by allowing multi-specialty use of robotic systems. Additionally, the ability to standardize surgical precision supports improved patient outcomes and enhances training efficiency for surgeons. As clinical evidence grows and regulatory pathways support expanded indications, Canadian healthcare networks increasingly integrate robotics into routine surgical practice, lowering barriers to adoption.
Government and Private Investment in Digital and Surgical Infrastructure
Federal and provincial initiatives aimed at healthcare modernization are accelerating investment in robotic surgical technologies. Funding programs for medical innovation, digital operating theaters, and advanced imaging integration support the deployment of robotic platforms across Canada’s hospital networks. Private healthcare providers are also investing in robotic capabilities to differentiate patient services and reduce long-term operating costs associated with inpatient care. Robotics fit strategically within Canada’s digital health roadmap, where data analytics, AI-powered surgical assistance, and interoperable platforms enable smarter procedure planning and outcome tracking. As investment expands, ecosystem growth encourages robotics training programs, engineering collaboration, and public-private partnerships that strengthen the country’s surgical innovation capacity.
- For instance, Medtronic’s Hugo™ RAS system received Health Canada licensing in 2021, allowing Canadian hospitals to integrate modular robotic towers and 3D visualization into digital OR programs supported by provincial innovation funds.
Key Trends & Opportunities
AI-Enabled Surgical Automation and Decision Support
Artificial intelligence is emerging as a transformative technology in the robotic surgery services market, creating new opportunities for predictive analytics, intraoperative guidance, and semi-autonomous procedures. AI-powered software assists surgeons with feature recognition, risk evaluation, and instrument positioning. Machine learning models trained on thousands of surgical cases are enabling real-time decision support and error reduction. Opportunities arise for remote collaboration, where surgeons can receive expert assistance during complex procedures without geographic constraints. As 5G connectivity improves, Canada is positioned to advance tele-robotic surgery platforms, which may expand access to remote and under-served populations through digitally supported operating workflows.
· For instance, Auris Health’s Monarch® Platform, now part of Johnson & Johnson MedTech, uses robotic control with real-time computer-assisted navigation to reach peripheral lung nodules during bronchoscopy. Clinical studies have shown that Monarch improves airway access and enables stable visualization during lesion targeting, supporting more accurate diagnosis of small pulmonary nodules.
Growth of Outpatient and Day-Care Robotic Procedures
The shift toward outpatient care and bundled payment models presents an opportunity for robotic systems optimized for same-day discharge procedures. Smaller and cost-efficient robotic platforms allow ambulatory surgical centers to perform general surgery, gynecologic, and orthopedic procedures in day-care settings. Reduced hospitalization benefits patients and alleviates pressure on public health capacity. Emerging business models such as device leasing and pay-per-use services are enabling wider adoption among private clinics. As recovery times shorten and patient preference for outpatient care grows, robotics-integrated day-care services represent a scalable and profitable opportunity for healthcare providers across Canada.
- For instance, THINK Surgical’s TMINI Miniature Robotic System features a wireless handheld robot with an average setup time of approximately 6 minutes, enabling rapid turnaround between same-day orthopedic procedures.
Key Challenges
High Capital and Maintenance Costs
One of the most significant challenges facing the Canada robotic surgery services market is the substantial capital investment required for procurement, installation, maintenance, and training. Robotic platforms carry high acquisition costs, and yearly service contracts further increase financial burdens for hospitals with limited budgets or lower surgical volumes. While services-based billing models alleviate expenses, cost justification remains difficult in smaller care settings. Financial barriers also affect equitable access, creating geographic disparities between large hospital networks and community-based providers. Without innovative pricing models and public funding expansion, cost constraints will continue to impede widespread adoption, particularly outside major metropolitan centers.
Skill Shortage and Training Requirements
Robotic surgery demands specialized training and learning curves that challenge surgeons and operating staff transitioning from conventional procedures. Training timelines, certification requirements, and simulation access increase operational pressures for healthcare providers. A shortage of surgeons trained in robotics restricts procedure availability, prolongs patient wait times, and limits hospital utilization rates. Ongoing competency maintenance and technology upgrades require continuous professional development, adding to institutional training workloads. The uneven distribution of experienced robotic surgeons across provinces creates access gaps for rural and remote populations. Addressing these challenges requires investment in robotics-focused education programs, simulation labs, and standardized national training pathways to build a scalable workforce.
Regional Analysis
Ontario
Ontario holds the dominant share of the Canada robotic surgery services market, accounting for approximately 38% of the national revenue. The province benefits from a dense concentration of multi-specialty hospitals, academic medical centers, and research-driven institutions implementing robotics for urology, gynecology, and oncology procedures. Government-supported innovation programs and partnerships with medical technology developers enable early adoption of advanced platforms. High patient volumes, greater reimbursement accessibility, and strong surgical workforce capacity further reinforce demand. Growth continues to accelerate as hospitals expand robotic operating suites and integrate AI-based surgical analytics, strengthening Ontario’s position as the primary hub for robotic-assisted care delivery.
Quebec
Quebec represents around 22% of the market share, driven by rising investments by public healthcare networks and university-affiliated teaching hospitals adopting robotic systems for minimally invasive surgery. The province is witnessing notable traction in general surgery and gynecological robotic applications, supported by clinical outcome improvements and reduced inpatient stays. Provincial healthcare modernization initiatives focused on digital surgical ecosystems also fuel robotic adoption. Despite increasing utilization, the pace of expansion is moderated by budgetary constraints and regional disparities in surgical infrastructure. However, ongoing pilot robotic projects in secondary care facilities signal strong future potential for broader implementation beyond metropolitan areas.
British Columbia
British Columbia accounts for nearly 16% of the market, supported by growing adoption of robotic procedures in urology, thoracic surgery, and bariatric interventions. The province’s investment in advanced operating theaters and focus on improving patient throughput are key growth drivers. Robotic surgery plays a strategic role in supporting reduced wait times and enhancing surgical efficiencies for complex procedures. A strong culture of clinical research and collaboration between healthcare providers and medical technology vendors contributes to faster procedural expansion. While concentrated primarily in major cities, increasing demand for outpatient robotic capabilities is encouraging private surgical centers to consider adoption.
Alberta
Alberta represents approximately 14% market share, sustained by specialized surgical centers and tertiary hospitals equipped with robotic platforms for oncology, colorectal, and orthopedic procedures. The province’s investment in digitized hospital infrastructure supports integration of robotics with preoperative imaging and postoperative monitoring systems. Rising patient preference for minimally invasive interventions and improved surgical precision enhance adoption momentum. However, economic fluctuations and public healthcare budget allocation create periodic variation in procurement cycles. Adoption is further supported by training partnerships and surgeon exchange programs with leading facilities across Canada, helping expand the skilled workforce necessary for robotic surgical growth.
Atlantic Canada
Atlantic Canada and the remaining provinces collectively account for nearly 10% of the market share, with adoption primarily centered around large regional hospitals where patient demand supports robotic program development. Limited access to robotic platforms in smaller communities and lower surgical volumes hinder expansion; however, momentum is building as provinces expand provincial surgical modernization budgets. Increasing interest in tele-mentored robotic surgery presents an opportunity to bridge geographic gaps in specialist availability. The shift toward outpatient robotic procedures may enable adoption by smaller facilities, provided cost optimization models and shared-access frameworks become more widely implemented.
Market Segmentations:
By Offering
By Applications
- Orthopedics
- Neurology
- Urology
- Gynecology
- General Surgery
- Others
By End-User
- Hospitals
- Ambulatory Surgical Centers
By Geography
- Ontario
- Quebec
- British Columbia
- Alberta
- Atlantic Canada
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the Canada robotic surgery services market is characterized by expanding participation from global medical technology companies, domestic healthcare service providers, and specialized surgical training institutions. Leading robotic platform manufacturers continue to strengthen their presence as hospitals invest in multi-specialty surgical systems to support urology, gynecology, general surgery, and thoracic procedures. Competitive differentiation increasingly focuses on system ergonomics, instrument versatility, imaging integration, and AI-assisted workflow automation that enhances preoperative planning and intraoperative precision. Service-based models, including pay-per-use, leasing, and long-term maintenance partnerships, are reshaping procurement dynamics, allowing broader access beyond major academic centers. Meanwhile, collaboration between surgical device developers and Canadian universities accelerates research-driven adoption and skill development. The landscape is also defined by the emergence of compact robotic platforms suited for outpatient facilities, intensifying competition among vendors seeking to serve ambulatory surgical centers. As clinical evidence grows and pricing models evolve, competition will shift from hardware sales to integrated surgical ecosystem solutions.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
Recent Developments
- In October 2025: Zimmer Biomet showcased its expanded robotics portfolio at the 2025 AAHKS meeting, highlighting recent innovations including the newly acquired surgeon-guided system from Monogram Technologies.
- In April 2025, THINK Surgical, Inc. announced the first use of the TMINI Miniature Robotic System with Maxx Orthopedics’ Freedom Total Knee implant marking a key milestone in orthopedic robotic-assisted surgery deployment.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Offering, Application, End-User and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Robotic surgery will become a standard option across major specialties, moving beyond urology into general, thoracic, and orthopedic procedures.
- AI-assisted decision support will enhance surgical precision and reduce intraoperative errors.
- Compact and mobile robotic platforms will expand adoption in outpatient and day-care surgical centers.
- Greater interoperability with imaging, navigation, and digital records will improve workflow integration.
- Training programs and simulation environments will produce a broader skilled robotic surgery workforce.
- Service-based and pay-per-use models will reduce financial barriers for smaller healthcare facilities.
- Remote telesurgery capabilities will support access to specialists across rural and underserved regions.
- Growing patient preference for minimally invasive procedures will sustain demand.
- Partnerships between med-tech firms, hospitals, and research institutions will accelerate innovation.
- Regulatory support and healthcare modernization initiatives will facilitate wider market expansion across Canada.




