Market Overview
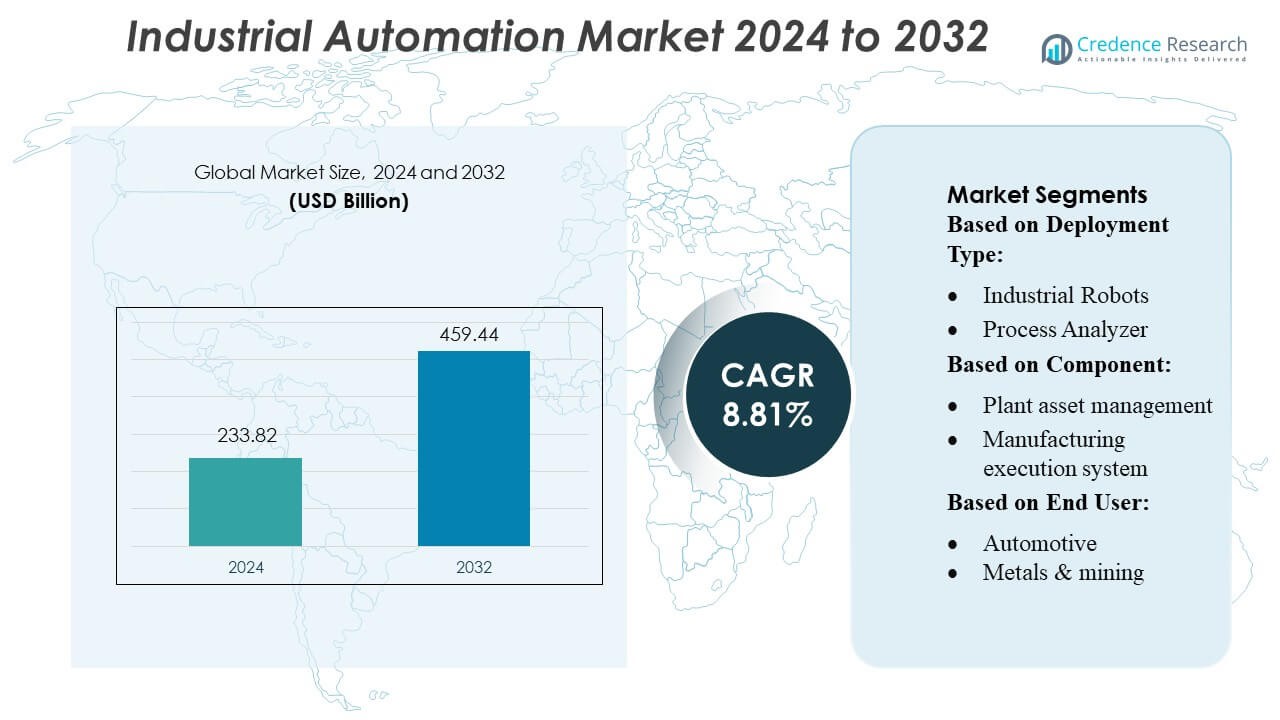
Industrial Automation Market size was valued USD 233.82 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 459.44 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 8.81% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Industrial Automation Market Size 2024 |
USD 233.82 Billion |
| Industrial Automation Market, CAGR |
8.81% |
| Industrial Automation Market Size 2032 |
USD 459.44 Billion |
The industrial automation market—such as ABB Ltd., Siemens AG, Rockwell Automation, Schneider Electric, and Mitsubishi Electric Corporation—lead the development and deployment of advanced robotics, control systems, and IIoT-enabled platforms. These firms drive innovation through strategic investments in R&D, digital service offerings, and scalable automation architectures. Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region commands the largest share of the market, accounting for approximately 39 % of global revenue, propelled by rapid industrialization, high robot installations, and strong demand for smart manufacturing across China, Japan, and South Korea.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The Industrial Automation Market reached USD 233.82 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit USD 459.44 billion by 2032 at 81% CAGR, driven by rising adoption of smart manufacturing and connected industrial systems.
- Strong market drivers include accelerated deployment of robotics, IIoT devices, and AI-powered control systems as industries prioritize productivity gains, reduced downtime, and real-time operational visibility.
- Major trends involve rapid adoption of cloud-based automation platforms, predictive maintenance, and scalable modular systems, with industrial robots holding the largest segment share at about 30%.
- Competitive intensity remains high as global leaders focus on digital service ecosystems, automation software, and strategic partnerships to expand technology integration across manufacturing, energy, and process industries.
- Asia-Pacific leads regional performance with around 39% market share, followed by North America and Europe, supported by expanding industrial bases, high robot installation density, and government-backed smart factory initiatives.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Deployment Type
The industrial automation market shows strong traction across deployment types, with industrial robots holding the dominant position, accounting for an estimated 28–30% of segment share due to widespread adoption in automotive, electronics, and precision manufacturing. Growth is driven by rising robotic density, improved payload capacities, and advancements in collaborative robots enabling safer human–machine interaction. Machine vision systems and industrial sensors follow closely as factories accelerate digitalization and quality control automation. Increasing demand for real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and higher production accuracy continues to push manufacturers toward integrated robotic and sensor-driven automation platforms.
- For instance, Kawasaki Heavy Industries offers its MG15HL robot with a payload capacity of 1,500 kg and a reach of 4,005 mm, enabling heavy-duty applications like riveting and machining with high repeatability.
By Component
Within components, the manufacturing execution system (MES) segment leads the market, representing approximately 25–27% of the share, driven by its ability to unify production planning, real-time operations tracking, and quality management in complex industrial environments. MES adoption accelerates as manufacturers pursue higher production visibility and reduced downtime. Programmable logic controllers and distributed control systems also remain critical as industries modernize legacy infrastructure. Industrial safety solutions are expanding steadily, supported by stricter global compliance norms. Overall, the component landscape grows as enterprises shift toward connected, data-centric control architectures for end-to-end manufacturing optimization.
- For instance, Rockwell’s PharmaSuite v8.4 provides workflow flexibility by enabling operators to re-run or skip steps, automatically logging each change for quality audits, while its FactoryTalk Quality v4.0 includes built-in statistical process control charts to continuously monitor process stability.
By End-User
The automotive sector dominates the end-user landscape, contributing about 22–24% of total demand, driven by high deployment of robots, vision systems, and automation software for welding, assembly, paint processes, and precision inspection. Electronics and semiconductor manufacturers follow due to the need for micron-level accuracy in fabrication and packaging. Food & beverages and pharmaceuticals also show rising adoption as companies automate to enhance hygiene, traceability, and compliance. Industries such as oil & gas and chemicals rely on automation for safety-critical monitoring and process efficiency. Broadly, rising labor costs, quality requirements, and Industry 4.0 adoption continue to accelerate automation across all verticals.
Key Growth Drivers
- Rising Adoption of Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing
The rapid shift toward Industry 4.0 strongly accelerates industrial automation adoption as manufacturers integrate advanced robotics, IoT-enabled sensors, and connected control systems to streamline workflows. Companies prioritize digital twins, automated process orchestration, and seamless data exchange across machinery to enhance operational visibility and minimize downtime. Increased investment in cyber-physical systems, predictive analytics, and cloud-based supervisory control strengthens automation penetration. This transition enables faster decision-making, higher production flexibility, and substantial long-term cost savings, making intelligent automation a central driver of industrial modernization.
- For instance, Emerson also highlighted its PACSystems RX3i CPL410 controller, which supports modular I/O and predictive analytics for proactive maintenance, and its Movicon Pro.Lean SCADA suite, which aggregates real-time production data from thousands of connected devices to optimize throughput.
- Increasing Demand for Operational Efficiency and Cost Reduction
Automation adoption grows as industries face pressure to reduce operational costs, enhance throughput, and improve quality consistency. Automated production lines minimize human error, optimize cycle times, and support 24/7 operations, enabling higher output at lower labor dependency. The rising need for energy-efficient manufacturing and predictive maintenance further strengthens automation’s value proposition. Companies increasingly deploy robots, advanced controllers, and AI-enabled monitoring systems to reduce equipment failures, extend asset life cycles, and ensure streamlined production. These efficiency-focused initiatives continue to be a major driver of automation investments globally.
- For instance, OMRON’s Matsusaka Factory reduced downtime by 40% and boosted productivity by 40% by visualizing equipment status and energy consumption, and optimizing board-feeding logic.
- Expansion of Robotics and AI-Driven Manufacturing Applications
Industrial robots, collaborative robots (cobots), and AI-powered vision systems significantly boost automation adoption across automotive, electronics, and precision manufacturing sectors. Advances in robotic dexterity, safety-certified cobots, and autonomous inspection tools enhance productivity and support complex, repetitive, or hazardous tasks. AI integration improves adaptability in tasks such as real-time quality inspection, anomaly detection, and autonomous process adjustments. Reduced robot costs and modular automation platforms broaden accessibility for mid-sized manufacturers. The convergence of robotics and AI thus serves as a critical growth catalyst for next-generation automated factories.
Key Trends & Opportunities
- Rapid Growth of IIoT and Edge Computing Integration
A major industry trend involves deploying IIoT devices and edge-based analytics to enable real-time decision-making and faster process control. Manufacturers leverage sensor networks, edge gateways, and decentralized computing to reduce latency in critical operations. This shift creates opportunities for advanced condition monitoring, near-instant anomaly detection, and autonomous process adjustments. Vendors increasingly develop scalable, cybersecure edge platforms tailored for high-volume industrial data. As enterprises digitize brownfield sites, IIoT-edge ecosystems offer major commercial opportunities in connectivity hardware, predictive analytics, and software integrations across production lines.
- For instance, Honeywell’s ECG100-CE Edge Data Gateway features a dual-core Arm Cortex-A9 processor, 1 GB RAM and 4 GB flash memory, and can process up to 1,500 digital points per second, enabling real-time computation at the edge.
- Expansion of Modular, Flexible, and Scalable Automation Systems
Growing demand for production flexibility drives adoption of modular robots, reconfigurable assembly lines, and plug-and-play automation components. Manufacturers seek systems that support rapid product changeovers, small-batch customization, and adaptive workflows. This trend creates strong opportunities for vendors offering scalable automation platforms, cobots with easy programming interfaces, and interoperable machine-module systems. The rise of low-code configuration tools and wireless industrial connectivity further accelerates modular automation uptake. As companies diversify product portfolios, flexible automation becomes essential to maintain agility and reduce retooling costs.
- For instance, ABB introduced the IRB 7710 and IRB 7720 robots, which are part of a wider portfolio of 46 variants handling payloads from 70 kg to 620 kg, enabling users to choose precisely the right robot for their use case.
- Increased Focus on Sustainability and Energy-Efficient Automation
Sustainability requirements push industries to adopt automation technologies that minimize energy consumption, reduce waste, and improve resource utilization. Energy-efficient motors, optimized drive systems, and intelligent power management solutions gain traction as manufacturers align with global ESG and carbon-reduction targets. Green automation initiatives create new opportunities for vendors offering eco-designed robotics, optimized HVAC automation, and AI-led efficiency management platforms. Automated tracking of emissions, water usage, and waste streams further supports sustainability compliance. This trend positions automation as a key enabler of clean and responsible manufacturing.
Key Challenges
- High Capital Investment and Integration Complexity
A major challenge for automation adoption lies in the substantial upfront investment required for advanced robotics, control systems, and integration services. Small and mid-sized enterprises often find it difficult to justify costs related to system redesign, training, and long implementation cycles. Integration with legacy equipment increases complexity and prolongs deployment timelines. Inadequate digital readiness and limited interoperability between old and new systems further hinder modernization efforts. These financial and technical barriers slow automation adoption, especially in cost-sensitive regions and traditional manufacturing environments.
- Cybersecurity Risks and Vulnerability of Connected Systems
As factories become increasingly digitized, cybersecurity threats pose a critical challenge to industrial automation deployment. Connected robots, sensors, and control systems present entry points for malware, ransomware, and operational disruptions. The integration of IIoT devices and cloud-based control platforms expands the attack surface. Many industrial facilities also operate older systems with limited built-in security, increasing vulnerability. Ensuring secure communication protocols, real-time threat monitoring, and robust identity management significantly raises overall implementation complexity and cost. Cyber risk concerns thus remain a major barrier to large-scale automation adoption.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America accounts for around 30–32% of the global industrial automation market, driven by strong adoption across automotive, aerospace, and advanced manufacturing sectors. The U.S. leads regional demand with high investment in robotics, AI-driven automation, and industrial software for operational optimization. Growth accelerates due to increased adoption of IIoT platforms, edge computing, and predictive maintenance solutions across large-scale manufacturing plants. A mature technology ecosystem, strong R&D capabilities, and rapid modernization of legacy production assets further strengthen the region’s position. Government incentives supporting smart factories and digital transformation continue to sustain the region’s dominant share.
Europe
Europe holds approximately 25–27% of the industrial automation market, supported by well-established manufacturing hubs in Germany, Italy, and France. The region benefits from rapid adoption of advanced robotics, machine vision, and energy-efficient automation systems driven by stringent regulatory requirements and Industry 4.0 initiatives. Germany remains the center of innovation, particularly in automotive and machinery manufacturing. The EU’s focus on sustainability, carbon reduction, and green automation technologies also drives demand for eco-efficient industrial systems. Investments in digital twins, advanced analytics, and flexible automation platforms further position Europe as a leading automation adopter.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific represents the largest and fastest-growing share, estimated at 38–40%, fueled by large-scale automation in China, Japan, South Korea, and emerging economies like India and Vietnam. China leads the region due to rapid industrialization and strong government support for smart manufacturing under initiatives such as “Made in China 2025.” High robot installation rates, expanding electronics manufacturing, and rising labor costs accelerate automation adoption. Japan and South Korea contribute significantly due to leadership in robotics innovation. The region’s large manufacturing base, expanding semiconductor production, and strong investment inflows make APAC the global growth engine for industrial automation.
Latin America
Latin America accounts for around 6–7% of the industrial automation market, with growth driven by increasing automation adoption in automotive, food & beverage, and oil & gas sectors. Brazil and Mexico lead the regional market due to expanding manufacturing activities and rising investments in plant modernization. Companies are gradually adopting robotics, PLCs, and SCADA systems to enhance productivity and reduce operational risks. Economic diversification efforts, improved digital infrastructure, and the push for energy efficiency support regional expansion. Despite slower adoption compared to developed markets, automation penetration continues to rise as industries focus on reducing production costs.
Middle East & Africa (MEA)
The MEA region holds around 4–5% of the global industrial automation market, driven primarily by demand from oil & gas, chemicals, energy, and utility sectors. Gulf countries invest heavily in automation to improve operational safety, reduce downtime, and enhance productivity in critical infrastructure. Smart city megaprojects, digital transformation programs, and increasing industrial diversification support automation uptake. South Africa contributes to regional growth through modernization in mining and manufacturing. Although the market is smaller, high-value automation investments and government-led industrial initiatives position MEA as an emerging growth area for advanced control systems and industrial software.
Market Segmentations:
By Deployment Type:
- Industrial Robots
- Process Analyzer
By Component:
- Plant asset management
- Manufacturing execution system
By End User:
- Automotive
- Metals & mining
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the industrial automation market features leading global players—including Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd., Rockwell Automation, Inc., Siemens AG, Emerson Electric Co., OMRON Corporation, Honeywell International, Inc., ABB Ltd., Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Yokogawa Electric Corporation, and Schneider Electric. The industrial automation market remains highly competitive, shaped by continuous technological innovation, rapid digital transformation, and rising demand for integrated, data-driven manufacturing systems. Companies compete by expanding their portfolios across robotics, advanced control systems, industrial software, and IIoT-enabled platforms that enhance productivity, safety, and real-time decision-making. Market leadership increasingly depends on the ability to deliver scalable, interoperable solutions that support predictive maintenance, autonomous operations, and flexible production. Vendors strengthen their positions through strategic acquisitions, partnerships with digital technology providers, and expansion into high-growth sectors such as electronics, pharmaceuticals, and renewable energy. The push toward smart factories, energy efficiency, and AI-driven automation further intensifies competition, prompting continuous investment in R&D and service-based business models that enhance long-term customer value.
Key Player Analysis
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- Rockwell Automation, Inc.
- Siemens AG
- Emerson Electric Co.
- OMRON Corporation
- Honeywell International, Inc.
- ABB Ltd.
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Yokogawa Electric Corporation
- Schneider Electric
Recent Developments
- In March 2025, Oxa tapped NVIDIA to enhance industrial mobility automation. A Self-driving vehicle software provider Oxa has made further inroads into industry, with plans to use Nvidia Cosmos generative world foundation models (WFMs). This can be attained with the support of physical AI, creating photoreal virtual real-world states to escalate its training tools.
- In September 2024, ABB India launched the wireless ABB-free@home smart home automation system for the residential market, focusing on enhancing comfort, security, and energy efficiency.
- In July 2024, Nozomi Networks Inc. announced Arc Embedded, the first security sensor for OT and IoT that can be embedded directly into Mitsubishi Electric programmable logic controllers (PLCs). This allows for real-time visibility and threat detection at the process level within industrial control systems, enhancing security without disrupting operations.
- In January 2024, Ares Management Corporation launched Automated Industrial Robotics Inc. (AIR), a new company aimed at meeting the global demand for manufacturing automation solutions. AIR will focus on acquiring and growing leading industrial automation companies to provide innovative, cost-competitive solutions to a wide range of businesses.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Deployment Type, Component, End-User and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The market will accelerate as manufacturers adopt advanced robotics, AI-driven analytics, and autonomous systems to enhance productivity.
- Industrial IoT and edge computing will drive real-time decision-making and expand connected factory ecosystems.
- Demand for flexible, modular automation solutions will rise to support rapid product customization and shorter production cycles.
- Cloud-based industrial platforms will gain wider adoption for centralized monitoring, asset management, and predictive maintenance.
- Sustainability initiatives will push industries toward energy-efficient automation and low-emission manufacturing practices.
- Collaborative robots will see increased deployment as small and mid-sized enterprises adopt cost-effective automation.
- Cybersecurity solutions will become a key investment priority due to expanding digital connectivity in factories.
- AI-enabled quality inspection and machine vision systems will become standard across high-precision industries.
- Workforce transformation will advance as companies invest in upskilling to support digital and automated operations.
- Emerging markets will expand their automation footprint as governments promote industrial modernization and smart manufacturing.




