Market Overview
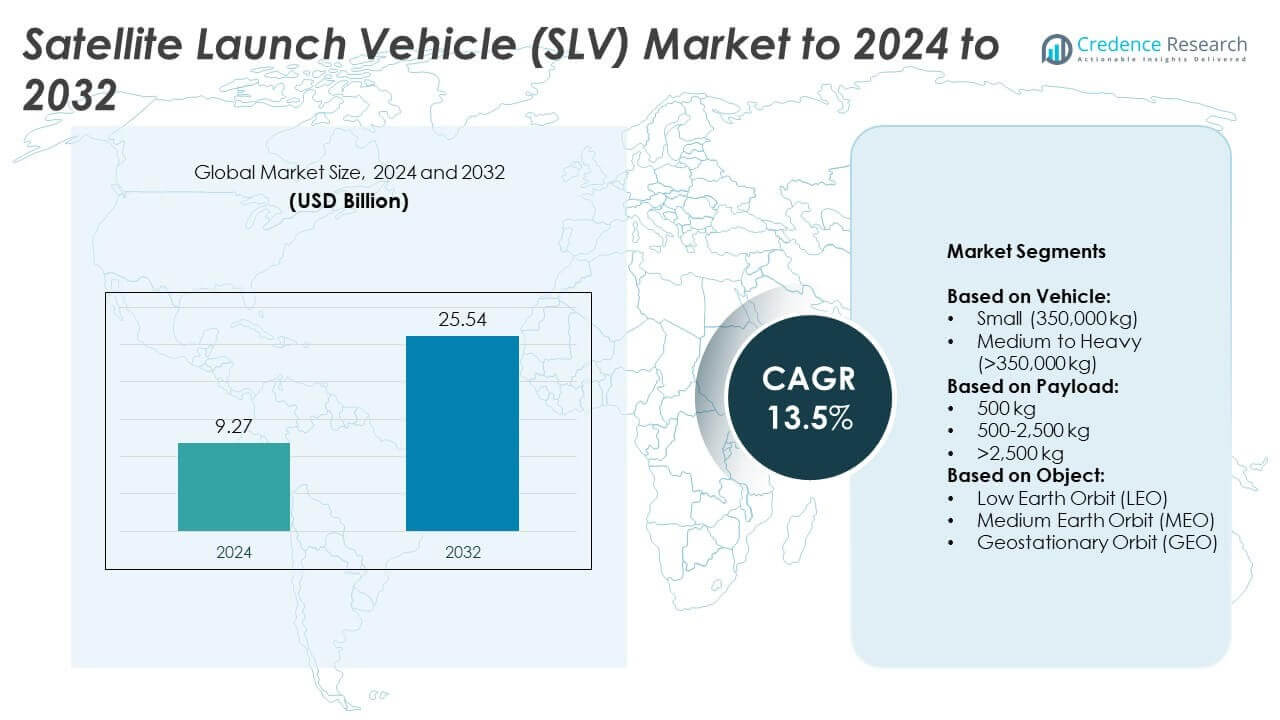
Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV) Market size was valued at USD 9.27 Billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 25.54 Billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 13.5% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV) Market Size 2024 |
USD 9.27 Billion |
| Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV) Market, CAGR |
13.5% |
| Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV) Market Size 2032 |
USD 25.54 Billion |
The Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV) market is driven by prominent players including Relativity Space, SpaceX, Blue Origin, Northrop Grumman Corporation, United Launch Alliance (ULA), ISRO, Arianespace, Rocket Lab USA, Inc., Firefly Aerospace, Boeing Defense, Space & Security, Lockheed Martin Corporation, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Rocket Factory Augsburg (RFA), and Virgin Orbit. These companies compete through advancements in reusable launch technologies, cost-efficient small satellite launch services, and strategic collaborations. Regionally, North America held the largest share with 40% in 2024, supported by strong government programs and private investments. Asia Pacific followed with 28% share, fueled by China, India, and Japan’s expanding launch capabilities, while Europe accounted for 25%, highlighting its established infrastructure and ESA-driven projects.
 Market Insights
Market Insights
- The Satellite Launch Vehicle market size was USD 9.27 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 25.54 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 13.5%.
- Growth is driven by rising demand for small satellite launches, supported by government funding and advancements in reusable technologies that reduce launch costs and improve turnaround times.
- Key trends include expansion of mega-constellation projects for global broadband coverage and increasing private sector participation, offering flexible and rapid launch solutions.
- The market is competitive with major players focusing on innovation, partnerships, and expanding payload capacities; companies are investing in sustainable propulsion systems and reusable vehicles to strengthen their positions.
- Regionally, North America led with 40% share in 2024, followed by Asia Pacific at 28% and Europe at 25%, while the rest of the world contributed 7%; small vehicle launches dominated by holding over 55% segment share in 2024.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Vehicle
The small satellite launch vehicle segment, with a capacity of up to 350,000 kg, held the dominant market share of over 55% in 2024. Growth is fueled by rising demand for small satellite constellations supporting Earth observation, remote sensing, and communication services. Companies and governments favor smaller vehicles due to cost efficiency, quicker turnaround times, and dedicated payload deployment. Increasing adoption of CubeSats and nanosatellites further accelerates demand. Startups and private launch service providers have strengthened this segment by offering responsive, low-cost access to space for commercial and defense applications.
- For instance, Rocket Lab’s Electron vehicle completed its 70th launch on August 23, 2025. As of late September 2025, the Electron vehicle has completed 71 launches in total.
By Payload
The 500–2,500 kg payload segment accounted for the largest market share, exceeding 50% in 2024. This range balances cost-effectiveness and capability, making it suitable for communications, navigation, and Earth observation satellites. Demand is rising from commercial operators deploying small and medium-sized satellite constellations for broadband and imaging services. Flexibility to support both civil and defense missions further strengthens adoption. Expanding government space programs and private ventures are boosting investments in mid-range payload capacities, ensuring consistent demand across established players and new entrants in the SLV market.
- For instance, Arianespace’s Vega-C launcher successfully placed the 296 kg LARES-2 satellite, along with six other satellites, into orbit on its inaugural flight in July 2022. The total payload mass for the mission was approximately 474 kg.
By Object
Low Earth Orbit (LEO) dominated the market, representing more than 60% share in 2024. Its dominance is driven by rising deployment of satellite constellations for broadband internet, Earth monitoring, and defense surveillance. LEO offers reduced latency, lower launch costs, and shorter satellite replacement cycles, making it the preferred choice for commercial players such as satellite internet providers. Rapid advancements in reusable launch vehicle technology and growing support for mega-constellation projects strengthen this orbit category. Increased demand for real-time data services and global connectivity ensures sustained growth in LEO-focused launch vehicle deployments.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Demand for Small Satellites
The increasing deployment of small satellite constellations for communication, Earth observation, and remote sensing is a key growth driver in the SLV market. Organizations are launching CubeSats and nanosatellites to support applications like broadband internet and disaster management. This demand fuels the need for cost-effective and flexible small satellite launch vehicles. Growing commercial participation and defense applications are further accelerating the adoption of dedicated small satellite launches. As a result, the segment’s expansion is pushing overall market growth and creating new opportunities for private launch providers.
- For instance, SpaceX in 2023 launched a total of 96 Falcon family missions, which consisted of 91 Falcon 9 and five Falcon Heavy rockets. Most of these missions delivered payloads to Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
Government Investments in Space Programs
Rising investments from governments and space agencies remain a major growth driver. National space programs across the U.S., Europe, China, and India are expanding launch vehicle capabilities to strengthen global positioning, security, and scientific missions. Strategic funding supports both reusable technologies and next-generation heavy-lift vehicles. Countries are prioritizing sovereign space access, increasing collaboration with private companies, and driving infrastructure development. These initiatives enhance launch frequency and innovation, directly boosting demand for SLVs. Government-backed missions also offer stability to the industry, ensuring consistent growth and technological progress.
- For instance, Planet Labs operates over 200 active satellites globally in its Earth-imaging constellations.
Advancement in Reusable Launch Technology
The development of reusable launch vehicles is a key growth driver, reducing launch costs and improving turnaround times. Companies such as SpaceX and Blue Origin are demonstrating successful reusability, encouraging adoption across the industry. Reusability enhances efficiency by lowering the per-launch expense and increasing operational sustainability. This advancement is particularly beneficial for commercial satellite operators deploying large constellations. It also attracts new entrants by making launches more accessible. As reusability technology matures, it will significantly reshape the SLV market’s cost dynamics and competitiveness.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Growth of Mega-Constellation Projects
The rapid expansion of mega-constellation projects presents a major trend in the SLV market. Operators like SpaceX, OneWeb, and Amazon’s Kuiper Project are planning thousands of satellite launches for global broadband coverage. This surge drives consistent demand for frequent and cost-effective launches. It also fuels opportunities for small and medium-capacity launch vehicles. The increasing requirement for coordinated, high-volume deployment creates space for partnerships between launch providers and satellite manufacturers. Mega-constellations represent one of the most significant opportunities for long-term SLV market growth.
- For instance, ISRO’s PSLV-C58 mission launched on January 1, 2024, with the primary payload XPoSat. After placing XPoSat in orbit, the mission conducted experiments with 10 other payloads on the PSLV Orbital Experimental Module-3 (POEM-3).
Increasing Private Sector Participation
Private sector involvement is a key opportunity, shaping innovation and competition. Startups and established aerospace firms are developing dedicated launch services with faster timelines and customized solutions. Rising venture capital funding and favorable regulatory reforms further support commercialization. Private players are addressing niche markets, such as quick-response launches and micro-satellite deployments. Their agility in adopting reusable technology and digital manufacturing enhances competitiveness. This trend expands the market ecosystem and offers new growth opportunities beyond traditional government contracts, creating a more dynamic and diversified industry landscape.
- For instance, Amazon’s Project Kuiper is licensed by the FCC to launch a full constellation of 3,236 satellites, but the first deployment phase consists of 578 satellites at a 630 km altitude. Limited service may begin once this initial phase is complete, and launches for the constellation began in April 2025.
Key Challenges
High Development and Launch Costs
The significant capital required for SLV development remains a key challenge. Designing and manufacturing launch vehicles involves high material costs, rigorous testing, and advanced infrastructure. Even with reusable systems, initial investments remain steep for new entrants. Unsuccessful launches also risk financial losses and delays in satellite programs. Limited access to funding in developing countries further restricts participation. These factors create entry barriers and intensify competition among existing players. Cost pressures continue to challenge market expansion, particularly for small and emerging companies.
Stringent Regulatory and Safety Standards
The SLV market faces challenges due to strict regulatory frameworks and safety requirements. Launches must comply with international treaties, national laws, and space debris mitigation standards. Meeting these requirements increases compliance costs and lengthens approval processes. Safety concerns during launches also demand heavy investment in testing and monitoring systems. These complexities often delay missions and raise operational risks for providers. As global launch activity grows, navigating evolving regulatory landscapes and ensuring sustainable space operations remain ongoing challenges for both government and private players.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America held the largest share of the Satellite Launch Vehicle market in 2024, accounting for 40%. The region benefits from strong presence of key players, extensive government funding, and private sector initiatives. SpaceX, Blue Origin, and United Launch Alliance lead advancements in reusable technologies and heavy-lift vehicles. Growing demand for commercial satellite launches, defense applications, and communication networks further drives growth. NASA’s programs and increasing defense budgets support consistent launch activities. Strategic collaborations between government and private firms ensure technological innovation, reinforcing North America’s leadership in the global SLV market.
Europe
Europe captured 25% share of the Satellite Launch Vehicle market in 2024, supported by well-established space infrastructure and joint projects. The European Space Agency (ESA) drives advancements through programs focusing on sustainability and commercial access to space. Countries like France, Germany, and the United Kingdom play major roles with active contributions to satellite launches. Development of the Ariane and Vega series highlights regional innovation in heavy and medium vehicles. Emphasis on space autonomy, environmental responsibility, and growing partnerships with commercial operators help Europe maintain a strong position in the global SLV industry.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific accounted for 28% share of the Satellite Launch Vehicle market in 2024, emerging as a dynamic growth hub. China, India, and Japan drive regional expansion with increasing investments in space exploration and commercial launches. China’s Long March series and India’s PSLV and GSLV programs highlight capabilities in low-cost, reliable launches. Rising demand for internet connectivity, Earth observation, and defense satellites boosts activity. Government-backed missions combined with private sector participation strengthen competitiveness. The region’s growing infrastructure and innovation in reusable technologies ensure Asia Pacific remains a critical contributor to future SLV market growth.
Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa
The rest of the world represented 7% share of the Satellite Launch Vehicle market in 2024, with contributions from regions such as Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa. Countries including Brazil and the United Arab Emirates are investing in space programs to strengthen national capabilities. These markets are gradually expanding through partnerships with global launch providers and technology transfers. Infrastructure development and policy reforms are encouraging commercial space activities. Although the share remains small, growing interest in space exploration and emerging satellite applications signal steady opportunities for regional growth in the long term.
Market Segmentations:
By Vehicle:
- Small (350,000 kg)
- Medium to Heavy (>350,000 kg)
By Payload:
- 500 kg
- 500-2,500 kg
- >2,500 kg
By Object:
- Low Earth Orbit (LEO)
- Medium Earth Orbit (MEO)
- Geostationary Orbit (GEO)
By Geography:
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV) market is highly competitive, shaped by leading players such as Relativity Space, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Virgin Orbit, Rocket Lab USA, Inc., Boeing Defense, Space & Security, Firefly Aerospace, United Launch Alliance (ULA), ISRO, Arianespace, SpaceX, Lockheed Martin Corporation, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Rocket Factory Augsburg (RFA), and Blue Origin. The competitive landscape is driven by rapid advancements in reusable technology, cost-effective small satellite launches, and increasing demand for mega-constellation projects. Companies focus on developing reliable, flexible, and sustainable launch solutions to address diverse commercial, defense, and governmental needs. Strategic collaborations, joint ventures, and public-private partnerships are common approaches to enhance technological capabilities and expand market reach. Continuous investment in research and development supports innovation in payload capacity, turnaround efficiency, and eco-friendly propulsion systems. Competition remains intense, with firms striving to differentiate through specialized services, rapid response launch offerings, and integrated solutions for satellite deployment across various orbital levels.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Relativity Space
- Northrop Grumman Corporation
- Virgin Orbit
- Rocket Lab USA, Inc.
- Boeing Defense, Space & Security
- Firefly Aerospace
- United Launch Alliance (ULA)
- ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation)
- Arianespace
- SpaceX
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- Rocket Factory Augsburg (RFA)
- Blue Origin
Recent Developments
- In 2025, Ariane 6 successfully completed its first commercial mission, launching the CSO-3 military observation satellite for the French Ministry of Defense.
- In 2025, SpaceX (USA) 10th test flight of Starship, achieved key milestones, including the successful deployment of Starlink mass simulator satellites and an in-orbit engine reignition.
- In 2025, United Launch Alliance (ULA) (USA) Vulcan launched its first national security mission (USSF-106) for the U.S. Space Force, after receiving certification.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Vehicle, Payload, Object and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Demand for small satellite launches will continue to dominate due to cost efficiency.
- Reusable launch vehicle technology will gain wider adoption and reduce per-launch expenses.
- Mega-constellation projects will drive consistent demand for frequent and reliable launches.
- Government investments in national space programs will strengthen long-term market stability.
- Private companies will expand services with faster, flexible, and low-cost launch options.
- Low Earth Orbit deployments will remain the primary focus for commercial operators.
- Emerging markets will invest in space infrastructure and collaborate with global providers.
- Technological innovation will improve payload capacity and launch turnaround times.
- Regulatory frameworks will evolve to address space traffic management and debris control.
- Strategic partnerships between governments and private firms will shape global competitiveness.

 Market Insights
Market Insights

